Home / Labor Law / Labor Code / Work experience
Back
Published: 05/17/2016
Reading time: 7 min
0
2360
According to labor legislation, every working citizen has the right to receive twenty-eight days of rest time from his employer annually. And for some categories of employees, an additional vacation period is added to the standard vacation (Article 116 of the Labor Code).
To receive such leave, the employee must accumulate a certain length of service, which, according to the Labor Code, will allow the employer to send the employee on vacation . This period is paid for the employee. And you can count on it only after working at a specific enterprise for a certain period established by labor legislation.
- When is the vacation issued?
- What does the vacation period depend on?
- Experience accounting
- How is the calculation made?
- Accounting in enterprise documents
How is leave granted and when?
As a general rule, the duration of the main vacation is 28 calendar days for a full year worked. The employee may also be granted additional leave, for example, for special working conditions or for long work experience. That is why the duration of vacation for some employees can be up to 45 days.
The fact that the main vacation is granted for a full calendar year does not mean that the employee must work continuously for a year without the right to rest. It is established by law that annual paid leave can be granted to an employee for the first time after 6 months of his work.
Accordingly, if, as a general rule, an employee is entitled to 28 days of rest for a full calendar year, after six months he can use at least 14 days. However, by agreement with the employer, full leave can be provided in advance, that is, before the end of the calendar year; this is not prohibited by the legislator.
In this case, there is one nuance, and the employee and employer need to understand that the provision of annual paid leave is accompanied by the payment of vacation pay. And if an employee quits without working for a full year, while using the entire vacation period and receiving vacation pay in full, a difficult situation may arise between the employee and the employer regarding the return of the overpaid amount.
So, how to correctly calculate the vacation period? What day does the billing period begin?
Is rest allowed after maternity leave?
The issue of providing paid leave after the maternity period stands apart. HR and accounting departments constantly confuse when leave after maternity leave is due and whether it is allowed at all. Article 260 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a woman in labor is guaranteed paid rest. A woman can take a vacation at any time:
- before maternity leave according to BiR;
- immediately after the end of maternity leave.
IMPORTANT!
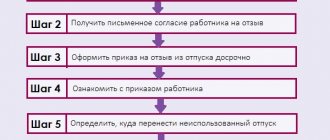
For registration you will have to meet the only condition. If the vacation has already been used before the start of the maternity period, then you cannot take out a vacation immediately after the maternity leave. Therefore, is it possible to take a vacation immediately after maternity leave? It is possible, but only if the employee has not used it completely before.
The guarantee is not subject to the minimum six-month service requirement. That is, a woman in labor will be given leave, even if she has not yet worked for six months for this employer. Moreover, the employee has the right to share the rest. For example, take only part of the paid vacation, and leave the remaining days for later.
How is the vacation period calculated?
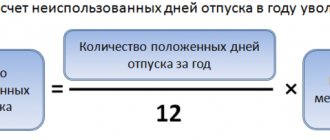
And if the situation with the billing period for a full calendar year is clear, then what to do if the year is not fully worked out, on what basis is the number of vacation days calculated?
As the legislator established, vacation is calculated according to the following principle: for each full month worked, the employee is entitled to 2.3 days of rest (main vacation).
However, a situation may arise in which an employee works for less than a full month, how to calculate in this case? If an employee works 14 or more days in a month, a rest period of 2.3 days is accrued for such a month; if the period worked in a month is less than 14 days, no vacation is assigned for such a month.
As previously established, annual paid leave is a period of legal rest for an employee; for this period, wages must be maintained and paid to the employee in the form of vacation pay. How to correctly calculate wages for a given period?
When calculating average earnings, which periods are taken into account and which are excluded?
An employee's salary may vary throughout the year and amounts may vary significantly. On what basis then should pay be calculated for the vacation period? This amount is calculated based on the employee’s average earnings.
This average salary is calculated according to the following principle: wages for twelve months are summed up, the resulting amount is divided by 12, and then divided by 28.4 (the established average duration of a working month).
If the employee worked for less than 12 months, the salary for the period worked is summed up, divided by the number of months in the period, then also divided by 28.4. Using this formula, the average salary for one day is determined; in order to calculate the full amount, the resulting figure must be multiplied by the number of vacation days.
For example, if it is known that the employee worked for six months. Salaries were: January - 10,000 rubles, February - 10,000 rubles, March - 10,000 rubles, April - 15,000 rubles, May - 15,000 rubles, June - 15,000 rubles. The total amount for the period worked was 75,000 rubles. To calculate average earnings - 75,000/6/28.4 = 440.14. The resulting amount represents the average earnings for one day.
If the employee is given 14 days of leave, then 440.14*14= 6,161.96. This amount must be paid to the employee for the period of his vacation.
When making these calculations, it is necessary to understand that the calculation of average earnings includes all amounts received by the employee, with the exception of amounts of financial assistance that were not assigned for labor merit, for example, upon the birth of a child or on anniversaries.
Part-timer's leave
In addition to his main job, an employee may have a part-time job. How to combine vacations in this case? For such categories of workers, the legislator has established a certain guarantee. It lies in the fact that leave from a part-time job is necessarily granted to the employee simultaneously with leave from the main place of work, regardless of the period worked by the part-time worker.
That is, in the case of external part-time work, the employee applying for leave must, along with the application, provide a certificate from his main place of work stating that he is granted annual paid leave for a certain period. If the question concerns internal part-time work, in this case everything is a little simpler; the employee writes two applications for leave (for each position) addressed to the employer. Refusal to grant leave to a part-time worker in this situation is unacceptable.
This kind of measure is provided so that the employee can get proper rest, because it is impossible to be on vacation half-time.
Working hours
Today, regulatory documents regulating labor issues separate two concepts, namely working time and working time. It seems to many that these concepts have the same meaning, the words are simply rearranged. In practice this is not the case. And the final decision during the calculation and provision of a specific type of paid time off will depend on the application of each specific term.
Work time . This term includes the time period when the worker directly performed actions useful for the company (for example, worked at a machine, was engaged in intellectual activity).
Working hours . This takes into account the entire time period of the employee’s presence at the workplace, taking into account the preparatory process (preparation of tools, equipment, workplace), technological breaks, waiting for work, as well as direct labor functions.
It is important to note that in the process of calculating the period, determining the main period of legal absence is guided by the total time of work. At the same time, if it is necessary to determine the duration and legality of an employee receiving additional leave for harm, periods of working time are applied.
Other special cases
In addition to annual paid leave, some categories of employees may be granted additional leave, as well as study leave:
- Additional vacation. This type of leave is provided in accordance with current legislation. For some categories of employees, this provision of this leave is mandatory, as evidenced by regulatory legal acts. However, the employer is not prohibited from independently establishing this type of leave for those positions that are not provided for by law. During the period of additional leave, as in the case of the main leave, wages are maintained.
- Study leave. This type of leave is provided to those persons who, along with performing their work functions, receive education at any educational institution. The employer is obliged to provide leave to this category of employees; this leave is not related to the main and additional annual leave. That is, if an employee has the right to these types of leaves, he can receive them in full for a certain period. However, there is a limitation with higher education. An employee has the right to receive paid study leave only after receiving his first higher education.
- Unused vacation. A situation often arises when an employee, having worked for a certain period of time, quits without using his right to leave. In this situation, upon dismissal, compensation for unused vacation must be transferred to the employee along with the payment. The period is calculated according to the general rule.
Previously, there were frequent cases when employees did not use the right to leave and continued to work, receiving compensation in monetary terms. Today, this practice is prohibited by law in relation to primary leave. Only days of additional leave may be subject to monetary compensation.
This rule was introduced primarily to protect workers from unscrupulous employers who do not want to provide annual paid leave.
So, the main points for calculating vacations have been considered. Having an understanding of the intricacies of granting vacations, both the employee and the employer will be able to protect themselves in labor relations.
Legislative regulation
The main regulatory document regulating the provision of compulsory rest to employees from work is the Labor Code. It sets the minimum duration of rest periods. It is worth noting that vacations can be paid, and without pay.
Additional documents on the basis of which vacations are established are:
- special laws (for example, regulating issues of military service, police, other law enforcement agencies, education);
- government regulations (they mostly apply to civil service employees);
- orders of relevant ministries;
- collective agreements of specific enterprises.
It should be noted that issues of determining the amount of rest for employees should be based on the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and then simply take into account the peculiarities of work in a particular area. In most cases, these regulatory documents increase the number of days of rest or clarify the procedure for providing it.
All types of vacations are divided into two main groups:
| View | Description |
| Basic | They are provided to all workers of the enterprise without exception. This is the minimum guarantee that the employer must comply with. |
| Additional | To obtain them, you will need to fulfill certain conditions stipulated by law or local regulations. For example, for working in harmful (dangerous) conditions, for irregular work, in the Far North. Employers are empowered to independently determine additional conditions for their provision (for example, for loyalty to the company). |
| Social | Occurs under certain circumstances and is usually compensated by the government. As an example, maternity leave is due to a young mother after the birth of her baby. This also includes rest intervals of varying lengths for disabled people. |
Remember, all regulatory documents issued on the basis of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation can only improve the conditions for granting leave, or specify these issues, taking into account the characteristics of the work activity of a particular category of employees.