An invoice is the most important document that is required for both parties to trade transactions. Entrepreneurs who constantly issue and receive invoices know how much depends on the correct and correct completion of this document.
- Form and sample
- Free download
- Online viewing
- Expert tested
FILES
If you already know what elements are included in the invoice and what will change in the new year, as well as the basic rules for filling it out, you will find useful information on how to avoid annoying misunderstandings and problems with tax deductions.
Scope of the invoice
Invoices (hereinafter also referred to as s/f, sch-f) are issued by companies and individual entrepreneurs – VAT payers – in the following cases:
In certain cases, VAT non-payers also issue accounts and pay VAT to the budget. For example, a special regime officer is required by law to perform the functions of a tax agent.
An invoice is a document used to claim a VAT deduction. Without an invoice from your counterparty (supplier or contractor), you will not be able to reduce the VAT calculated for payment.
Since the account is used in the area related to the calculation of taxes, the use of this document is regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Article 169)
An invoice filled out in violation of the requirements cannot be accepted for accounting and used to obtain a VAT deduction (clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
On the issue of unscrupulous counterparties
From time to time, questions arise about whether a taxpayer has rights to a VAT refund on transactions made with unscrupulous counterparties. In such situations, courts sometimes take the side of the taxpayer.
One of the grounds for this is the Decree of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated October 12, 2006 No. 53, according to which the taxpayer can submit to the tax inspectorate all the documents he has in order to obtain tax benefits. In this case, the tax authority must prove any flaws in the documents, and the taxpayer enjoys the presumption of integrity until the contrary is proven.
The dishonesty of the organization's counterparty, in particular its absence from its legal address or failure to submit tax reports, does not in itself confirm the taxpayer's desire to receive an unjustified tax benefit.
If the tax service identifies circumstances confirming the dishonesty of suppliers as taxpayers, then the measures provided for by the current legislation are applied to such persons, which does not automatically entail the recognition of the buyer of their goods as an unscrupulous taxpayer.
Required invoice attributes
Let's consider the elements of the s/f, without which the document will not be considered valid (clause 5 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
If the s/f contains or lacks any details not mentioned in clause 5 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code, this cannot be an obstacle to tax deduction.
clearly on the invoice :
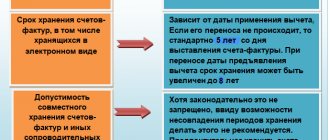
If there is an error in the invoice that does not prevent an unambiguous interpretation of the meanings of its details listed in the diagram above, then a deduction for such an invoice can . However, in some cases, claims from tax authorities may still arise, so it is better not to make .
Here are examples of minor invoice errors:
It is not enough to indicate all the required attributes of the account. It is important to enter them correctly . Rules for filling out invoices can be gleaned from two sources:
Graphs that should be in the document
Each field of the completed invoice is checked by inspectors of the Federal Tax Service during on-site or counter inspections.
ATTENTION! The details of this document must be filled out correctly, otherwise the invoice will be sent for revision or there is a risk of denial of VAT deduction to the business entity.
If there are gross errors indicating distorted facts of economic activity, the organization may be subject to penalties.
The form of each invoice consists of lines and columns with numbering and letter designation.
For sale
The sales document uses the following lines:
- 1 indicating the serial number and date of preparation of the document. The number is assigned in individual chronological order, and if the organization has a separate division that sells goods (services, property rights), the dividing line “/” is used (more information about the rules for filling out the document by separate divisions can be found here).
- 1a is used to indicate the serial number and date of amendment to the document. Before any corrections are made, a dash is placed on this line.
- 2 – indicate the name of the seller (legal entity, full name of individual entrepreneur).
- 2a – the address of the seller is indicated - a legal entity in accordance with the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or an individual entrepreneur in accordance with the entry in the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs.
- 2b – the taxpayer’s TIN, as well as the taxpayer’s checkpoint, are filled in.
- 3 – full or abbreviated name of the shipper. If the seller and the consignor coincide, the line is filled in with the words “he”; when performing work (services), a dash is added.
- 4 – full or abbreviated name of the consignee (as in the constituent documents), his address.
- 5 – details of the payment order or cash receipt are indicated if an advance payment was received from the buyer.
REFERENCE. If the invoice is issued on the day the advance payment is received, a dash is placed in line 4. - 6 – full or abbreviated name of the buyer, which is indicated in the constituent documents.
- 6a – the buyer’s address is indicated in accordance with the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs (until 01.10.2017, the address had to be indicated as in the constituent documents).
- 6b – the TIN, as well as the buyer’s checkpoint, are indicated.
- 7 – enter the name of the currency and its code in accordance with the All-Russian Classifier of Currencies (read about whether it is possible to issue an invoice in the currency of another country, where to find out and display such a code here).
- 8 – indicates the identification number of the state contract for the supply of goods, works, services or an agreement to provide subsidies to a legal entity from the federal budget in accordance with ed. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 625 of May 25, 2017. If the organization does not have such contracts, a dash is placed in line 8.
The following fields are used in the sales invoice:
- 1 with the name of the product or service supplied.
- 1a – the code of the type of product is indicated in accordance with the unified Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity of the EEC. If the organization does not export goods outside the Russian Federation, a dash is placed in the column.
- 2 and 2a – the code and symbol of the unit of measurement are indicated in accordance with OKEI. If they are not there, a dash is added.
- 3 – quantity of goods shipped or a dash.
- 4 – price per unit of goods or tariff for services provided excluding VAT; if there is no indicator, a dash is placed.
- 5 – indicates the cost of the entire volume of services provided or quantity of goods without VAT.
- 6 – the amount of excise tax is indicated; if a non-excise product is sold, the entry “Without excise tax” is entered.
- 7 – tax rate is indicated. If goods are sold without VAT, a corresponding entry is made (clause 5 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- 8 – the amount of VAT charged to the buyer, based on the tax rate.
- 9 – the cost of the total quantity of goods shipped or services provided, including VAT, is entered.
- 10 and 10a - for goods produced outside the Russian Federation, the code and name of the country of origin of the product are indicated.
- 11 – an entry is made with the registration number of the customs declaration for goods released outside the Russian Federation.
From separate publications by our experts, you can also learn about the timing of issuing an invoice to the buyer, as well as the rules for filling out the document when returning goods to the supplier and when providing services.
Corrective
IMPORTANT! The adjustment invoice has details similar to the document for the release of goods, but the filling of some of them is different.
The form contains the following lines:
- 1 – number in general chronological order and date of the document.
- 1a – number of the correction made and its date.
- 1b – number and date of the document (or several documents) for which the adjustment invoice is drawn up, as well as the date of their correction.
- lines 2, 2a and 2b are filled out in accordance with the information entered in the same lines of the invoice for which the adjustment document is being drawn up.
- lines 3, 3a and 3b contain information about the name, location, tax identification number and checkpoint of the buyer.
- 4 – name and code of the currency.
- 5 – identifier of a government contract or agreement.
Column 1 of the adjustment document is filled out in accordance with the name of the goods, works, services indicated in the same column in the invoice for the adjustment. Column 1b is filled in with the code of the type of product according to the unified Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity of the EEC.
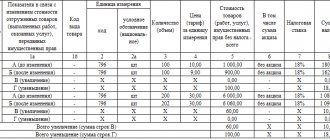
REFERENCE. The adjustment document contains information about the quantity and (or) price of goods or services, both original and changed.
The information is indicated in the lines under the letter designations:
- A – before the change.
- B – after the change.
- B – increase.
- D – decrease (cost, quantity).
The final lines (there are two of them) indicate the sum of lines B or D. In addition, the document contains information about the change in the cost of goods supplied or services performed without VAT and with VAT, as well as the difference between the amount of taxes.
Advance
When reflecting the received advance payment, the same form of invoice was developed as for sale. The preparation of an advance invoice has several differences:
- Consignor and consignee data are missing.
- The details of the payment document for the advance payment must be indicated in the appropriate line.
- With 100% prepayment, the unit of measurement, quantity and price of the goods are indicated; with partial payment, these data are missing.
An advance invoice is drawn up if there is a rate for VAT calculation of 18% or 10%. If the product is not subject to VAT or the rate is 0%, this document is not drawn up.
You will find more information about the rules for filling out an advance invoice in our special material.
Invoice form
The invoice form was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137. It can be downloaded for free from our website using the link below:
This Resolution introduced the form of not only a regular invoice, but also another type of this document - an adjustment invoice.
Later in the article we will talk about sample invoices. Here you will receive information on how to fill out an invoice, some problematic fields and special cases.
why is a cube more convenient?
Convenient online invoicing
Instantly send invoices by e-mail to your buyer
Debt control for each customer
Management reporting
Organized storage of all your documents
20% discount on accounting services from your accountant
Stop wasting time filling out templates and forms
The KUB service helps you issue invoices in 20 seconds and prepare other documents without a single error, due to the complete automation of filling out templates.
KUB is a new standard for issuing and sending invoices to customers.
Start using CUBE right now
14 days
FREE ACCESS
Need billing help or advice?
Get expert billing help from accountants
+7
[email protected] kub-24
How to fill out various invoices
The main invoice form is used in different VAT accounting situations. The filling procedure in these cases is also different:
Shipment of goods/works/services: what an invoice looks like
There should be no difficulties in entering data into the invoice. Let's note some non-obvious things in the diagram:
Received an advance: what are the features of the invoice?
Let's look at how to make an invoice for an advance payment. Let's change the situation: let's say that for the same shipment for which we showed the invoice above, we paid in advance.
Let's put on the diagram the positions for filling out the advance account, about which questions and doubts :
Adjustment rules
- Both copies are subject to changes - both those belonging to the seller and those intended for the buyer.
- Corrections must be endorsed by the head of the selling organization and certified with his seal (the signature of the chief accountant is not required). Instead of the director, an authorized person can sign, indicating his full name and position, and also mark that the signature is “for the head of the organization.”
- Be sure to date the corrections.
- Incorrect data must be crossed out, the correct data must be written in the free field, and “corrected” must be indicated next to it, and which indicators should be added to which and in which column.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION! If there are too many errors and correction is difficult, it is easier to reissue the damaged document. This does not contradict the law, since the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not directly prohibit replacing a defective invoice with a new document. But sometimes such a right will have to be defended in court.
Shipping conditions have changed: what invoice to make?
It is necessary to distinguish when to write out a corrective account and when to write a corrected one. Adjustment and correction are different facts of economic activity. Therefore, they require reflection in different documents.
A corrected invoice is used if an error - technical or arithmetic. The algorithm for selecting a form for a corrected account is simple:
But when we take the form of the adjustment account (clause 1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
Check out the option for filling out the account when adjusting a shipment:
And here is a diagram with the nuances of entering data into the account, which is written out when revising the terms of shipment:
What types of invoices for services are established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation?
Invoices issued for services, as well as those drawn up for the sale of goods or work, are divided into 3 types:
- regular, issued upon shipment;
- advance payment, issued upon receipt of advance payment for the provision of services;
- adjustment, created in cases of agreement on a change in the price or volume of services performed, for which shipping documents have already been issued.
The execution of each of these types of documents has its own specifics.
Required details
An invoice is subject to accounting and registration with the tax department if the payment document contains the following details:
- Serial numbering and date of document generation. The seller numbers the forms in any way convenient for him. The only requirement: the numbering must be in ascending order and continuous. If an individual entrepreneur makes an error in assigning numbers (for example, after generating invoices with numbers 16, 17, a businessman issued an invoice with number 9), the deduction is processed according to the standard procedure. But such a situation can create accounting confusion.
- The names of the parties to the transaction (seller, buyer), their address details, numbers obtained from government agencies, allowing the identification of counterparties. The name can be indicated either in full or in abbreviated form. It must comply with the constituent documentation. Address data must comply with the Charter and be indicated in full (together with the index).
- The name of the sender and recipient of the cargo, their address details. This information is only necessary when selling products. If the goods are sent by the seller himself, then the sender’s address details are not indicated in full. The phrase “He is” is written in the corresponding line. In some cases, sellers enter their details in full, including name and address. This is acceptable, the document will not be considered erroneous. Information about the recipient of the product is specified in detail. In this case, it does not matter whether the recipient of the goods and the buyer are separate entities or represented by the same person. The name and address data are indicated based on the statutory documentation.
- List of products sold, services provided, their measurement units.
- Quantitative characteristics of products sold and services provided.
- Monetary units used in calculations. Based on the All-Russian Classifier of Currencies, the currency code is indicated in the invoice. The most commonly used monetary units are:
- if the cost of products (services) is indicated in Russian rubles, then code 643;
- when paying in American currency (US dollar), code 840;
- if the transaction value in the invoice is indicated in euros, then the code is 978.
- Cost of a unit of product (service), excluding taxes.
- The total cost of goods (services) sold.
- Tax rate. It can be zero or 10%, 20%.
- Amount of tax.
- The total cost of products sold and services provided (including taxes).
- For imported products, the state where it was produced and the registration number of the customs declaration are indicated.
From January 1, UPD and invoices can only be issued in the new format
The Federal Tax Service has approved a new format for primary documents, invoices and UPD. All organizations that exchange electronic documents should switch to it.
What's changing
Until January 1, 2021, electronic primary documents, UPD forms and invoices can be created in two formats:
- in the old one, which is enshrined in the order of the Federal Tax Service dated March 24, 2016 No. ММВ-7–15/ (hereinafter referred to as order 155),
- and the new one, which was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service dated December 19, 2018 No. ММВ-7–15/ (hereinafter referred to as order 820).
On January 1, 2021, Order 155 will no longer be in force; it will be possible to create invoices and UPD only in a new format. In the old format, they will not comply with the requirements of the law (clause 1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The Federal Tax Service will accept documents in the old format that you submitted before January 1, 2020 until the end of 2022. In 2023, receiving complexes will no longer process electronic invoices and UPD with invoices in the old format. You will only be able to submit a printed form of the document.
Labeling changes
Product codes can be recorded in electronic UPD forms using the new format. For traceable imported products, fields are allocated for the registration number of the product batch and its quantity.
One document can contain either traceable or tagged goods, since the corresponding prefix is indicated in the file name.
Changes related to procurement
The Federal Treasury authorizes all expenses of recipients of budget funds. To track payment for purchases, the documents indicate, in particular, contract information.
In the format according to order 155, this was only the identifier of the government contract (Table 5.9). In the new UPD format, a new block has appeared (Table 5.10), where the date and number of the government contract, the seller’s personal account number, the name of the territorial body of the Federal Treasury and other details are entered.
Changes affecting document processing
It is easier for EDI users and regulatory authorities to work with primary documents in the new format. Transaction participants can agree on the structure of information fields and fill out documents according to this structure. It has become more convenient to reflect the date of provision of services, completion of work or delivery of goods. The characteristics, grade, article and code of the product were placed in separate fields - now the EDI system can automatically process this data.
All format changes and completion requirements are reflected in Order 820.