Cash discipline implies compliance by the entrepreneur with all the rules for making cash payments established by law. In this article, we will look at how to maintain cash discipline with online cash registers, how to use it to simplify the cash register process, and what liability an entrepreneur faces in case of violations.
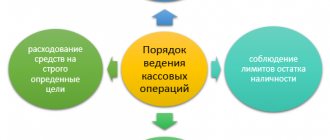
Cash discipline is compliance with the rules established by Russian legislation for cash payments, which include all types of income and expense transactions.
Basically, cash discipline at online cash desks affects the following operations:
- payment of wages;
- cash collection;
- return or issuance of borrowed funds;
- receiving or depositing money at the bank;
- settlements with accountable persons, etc.
In 2021, all LLCs and individual entrepreneurs that carry out cash payments are required to use online cash registers. Exceptions are individual entrepreneurs and LLCs on PSN, UTII (clause 2 of Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), providing services and vending. They are required to issue a document confirming the receipt of funds.
Who is covered by the procedure for conducting cash transactions?
By order of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, new rules for conducting cash transactions were introduced. At the same time, the forms for maintaining cash documents have not undergone any changes.
The changes will most affect individual entrepreneurs. And, despite the fact that individual entrepreneurs will have to change their usual mode of operation, for them this will more than pay off by simplifying cash transactions.
In addition to individual entrepreneurs, the changes will affect enterprises and organizations. In particular, innovations will affect accounting.
It is very important that individual entrepreneurs promptly familiarize themselves with the updated rules for conducting cash transactions in order to avoid penalties.
Liability and penalties
If an institution operates with funds, but does not maintain a cash book or fills it out with gross violations, then such actions are recognized as an administrative offense. Consequently, administrative responsibility will fall on the shoulders of the head (or chief accountant) of the organization. The current legislation provides for penalties:
- in relation to a legal entity - in the amount of 40,000 to 50,000 rubles;
- in relation to a senior official or chief accountant (the Federal Tax Service considers them as an individual) - in the amount of up to 5,000 rubles (Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Organization and management of cash transactions in 2018
As noted above, from June 2014 a new procedure for conducting cash transactions was introduced. This order can be divided into two parts:
- Regular (for legal entities, except banks).
- Simplified (for individual entrepreneurs and small businesses).
Cash transactions can only be carried out at the cash register. The person responsible for carrying out such operations is the cashier. If the company has several cashiers, then a senior cashier is appointed.
The head of the organization or an individual entrepreneur has the right to conduct cash transactions personally.
The accountant (chief accountant) signs cash documents. If there is no accountant at the enterprise, documents are signed by the cashier and the manager.
Cash transactions carried out personally by the head of the enterprise do not require additional signatures.
Since 2015, it is allowed to conduct cash transactions using software and hardware.
Changes have occurred in the management of cash transactions in separate divisions. A separate division should be understood as any division of the company (at the location of which there is at least one equipped workplace).
For such divisions, a cash balance limit and maintaining their own cash book have been introduced. The cash book sheets are now in one copy. They do not need to be returned the next day to the main office.
How to fix errors
Corrections of errors in KO-4 are permissible (clause 4.7 of the Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U). If the defect does not affect the cash total, then the incorrect value is carefully crossed out, and the correct inscription is indicated on top. The correction is certified by the signatures of the responsible persons.
If the error affects the final result, then the page with the error is completely canceled, and the correct data is reflected on a new sheet. Upon correction, a special certificate is drawn up indicating the changed values. Corrections are made by the cashier or other person responsible for maintenance.
Cash documents in 2021
There were no significant changes in the field of cash documents. The cash book, receipt and expenditure orders, as well as statements have not changed. All previously unified forms continue to be used. These documents should be filled out taking into account innovations.
Individual entrepreneurs, in accordance with the new procedure for conducting cash transactions, are exempt from maintaining the following list of documents:
- cash book;
- cash receipt orders;
- expense cash orders.
Individual entrepreneurs keep tax records of income and physical indicators that characterize their type of activity.
To maintain cash documentation, you can now choose electronic or paper media.
An incoming accountant (an individual who works under a service agreement) has the right to draw up cash documents.
Separate divisions of the enterprise now transfer cash book sheets in a new way. A copy of the book sheet (which is certified by the head of the unit) is transferred in the manner established by the legal entity itself. That is, cash book sheets can be submitted once a year - when preparing financial or accounting statements.
Errors in cash documents (on paper) can now be corrected, with the exception of incoming and outgoing cash orders.
The main innovations are as follows:
- It is allowed to maintain cash documentation in electronic form using an electronic signature;
- paper copies of the cash book and orders (receipt and expense) are not required if electronic documents are available;
- It is impossible to correct errors in electronic documents (a signed document with an error is deleted and a new one is filled out in its place);
- the second sheet of the cash book is no longer relevant;
- a single receipt order can now be issued on a strict reporting form;
- The manager’s own record of terms and amounts is not required;
- there is no register of deposited amounts (but this column is retained in salary slips);
- the recipient can enter the amount in words on the expense order;
- the cash book is not filled out if no cash payments were made on any day.
The cashier puts a stamp and his signature on the receipt for the cash receipt order. Cashiers can now transfer money without a debit order based on the cash ledger.
Cash book structure (rules for filling out fields)
The cash book corresponding to form No. KO-4 contains 3 types of pages:
- front (sample cover or title);
- internal (pages 3 to 10);
- final (located at the end of the document).
The front pages contain information about the company, as well as the year for which the cash book reflects cash transactions. The internal pages of the document contain the following columns:
- “Cash for” (it records the dates of certain transactions with funds);
- “Sheet” (the serial number of a specific sheet of the cash book is indicated here);
- “Document number” (this column records the order number - incoming or outgoing);
- “From whom received or issued to” (initials of the person or company that deposits or receives cash);
- “Number of the corresponding account, sub-account” (this column records the account that corresponds in the prescribed manner with account 50, individual entrepreneurs do not fill out this area of the cash book);
- “Receipt” (the amount of funds on receipt orders is recorded);
- “Expenses” (indicate the amount of funds for settlement orders);
- “Total for the day” (receipts are summed up, as well as cash payments for the cashier’s work shift);
- “Cash balance at the end of the day” (the amount of the cash balance is indicated).
In the “Transfer” column of the cash book, the total amount of funds for orders of both types can be recorded, reflected in a specific table, so that the cashier has the opportunity to continue entering information on the next page.
The following signatures must appear at the end of each internal page of the cash book:
- the cashier of the organization, who fills out basic information in the cash book;
- an accountant (who simultaneously indicates the number of PKOs and RKOs, and also certifies the fact that he received and checked the orders).
On the last (final) page of the document, it is indicated how many sheets are stitched and numbered, the date of compilation of the cash book, and also the signatures are affixed:
- chief accountant;
- head of the company.
Cash balance limit in 2021
In 2015, the cash balance limit was changed. The new formula for calculating the cash limit is not tied to cash receipts. The organization has the right to make calculations based on the amount of expenses or revenue.
The cash limit is mandatory, except for small and micro enterprises. It establishes the amount of funds that can be freely stored in the cash register. Enterprises and organizations have the right to personally introduce a certain limit. If the limit has not been entered, it is considered zero. The entire remaining amount is deposited into the bank account at the end of the day.
The formula for calculating the cash limit is regulated by the new regulation. An enterprise can choose one of two proposed calculation formulas:
- The calculation is made based on cash proceeds (receipts from goods, services, etc.).
- The calculation is made based on the amount of funds issued.
If there are separate divisions, the total cash limit is determined taking into account the limit established for the division.
That is, the amount of the limit can be distributed among separate divisions.
The cash limit of a separate division is established by a responsible administrative document.
The first formula for calculating the cash limit looks like this:
L = V / P x Nc , where: L - limit in rubles; V is the volume of revenue in cash; P - billing period, the number of working days for which the volume of cash receipts is recorded (but not more than 92 working days for legal entities). Nc - the period of time between depositing proceeds to the bank: 1–7 working days (if there is no bank nearby, up to 14 days).
The second formula for calculating the cash limit is L = R / P x Nc , where:
R is the volume of cash disbursement (excluding the amounts of salaries, stipends or other payments to employees).
What you should not spend cash on
Quite often, store owners or accountants have a question about what expense items can be spent on cash proceeds from the cash register.
First, let's look at what an entrepreneur has the right to spend cash proceeds on:
- Payment of wages to employees;
- Expenses for scholarships;
- Issuance of travel expenses to accountable persons;
- Any other payments to persons who are accountable;
- Expenses on goods or services (except for payment for securities);
- Insurance payments;
- Payment for returned goods;
- Issuance of funds for services/work not provided;
- Issuance of funds for the consumer needs of the owner of the organization, if these needs are classified as personal;
- Payments to the paying agent when carrying out banking transactions.
The list of expense items on which an entrepreneur cannot spend cash from the enterprise’s cash desk includes much fewer items, but their compliance is strictly mandatory:
- Rent;
- Interest on loans, as well as the issuance or repayment of the loans themselves;
- Any manipulation with securities;
- Costs of organizing games from the gambling category.
If an entrepreneur needs to make one of the above payments, the funds will need to be withdrawn from the organization’s current account.
Cash limit for small and micro enterprises
The instruction of the Bank of the Russian Federation No. 320-U dated March 11, 2014 states that all small and micro enterprises are exempt from the mandatory establishment of a cash limit. This means that these types of enterprises have the right to keep any amounts in the cash register.
The criteria for classification as micro and small enterprises are as follows:
For micro-enterprises:
- income limits on the tax return for the previous year - 120 million;
- The average number of employees for the previous year was 15 people.
For small businesses:
- income limits on the tax return for the previous year - 800 million;
- the average number of employees for the previous year was 100 people.
According to these criteria, individual entrepreneurs are classified as micro or small enterprises, therefore, it is not necessary for individual entrepreneurs to introduce a cash limit.
Application of cash register equipment
Individual entrepreneurs providing services to individuals can make calculations without using cash register systems. A detailed list of activities is presented in paragraph 2 of Art. 2 of the Federal Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ. Let's note some of them:
- sale of ice cream and soft drinks on tap at kiosks;
- acceptance of glassware and waste materials from the population, with the exception of scrap metal, precious metals and precious stones;
- shoe repair and painting;
- production and repair of metal haberdashery and keys;
- and others.
CCPs are not used by entrepreneurs working in remote or inaccessible areas. The specified areas do not include cities, regional centers and urban-type settlements (Clause 3, Article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ). The list of remote or hard-to-reach areas is approved by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
In all other cases, IP uses CCT.
From July 1, 2017, entrepreneurs are required to use a new type of cash register (online cash register).
From 07/01/2018, in the case of providing services to individuals, individual entrepreneurs will be required to issue BSOs printed on a special device - an “automated system for BSOs”. The device is a prototype of a cash register, with a fiscal recorder for transmitting data to the Federal Tax Service (Federal Law of July 3, 2016 N 290-FZ).
Issuing money from the cash register for reporting
Accountable persons are employees who are given money from the company's cash register to pay for any production services or purchase goods for internal needs. Since August 19, 2017, money against the report is issued to the employee on the basis of an internal document. Moreover, the form and name of this document are not regulated in any way by the Central Bank. Those. it must be drawn up in any form, indicating in it, in accordance with clause 6.3 of the Bank of Russia Directives dated March 11, 2014, as amended, the following data:
- Full name of the person to whom the cash is issued;
- amount of cash;
- the period for which cash is issued;
- manager's signature and date.
Until August 19, 2017, money should have been issued only on the basis of an employee’s application.
The article was edited in accordance with current legislation 06/04/2018
How is cash discipline checked?
Cash discipline is checked as part of on-site activities of the tax service.
The main aspects that the Federal Tax Service pays attention to:
- Algorithm for posting revenue, availability of uncapitalized funds;
- Compliance with the cash limit;
- Condition, serviceability and availability in the state. online cash register register;
- Compliance of cash documents with actual amounts;
- The fact of issuance/non-issuance of cash receipts to customers;
- The presence of large amounts issued on account for unreasonably long periods, etc.
This might also be useful:
- Online cash registers in 2021
- Taxpayer personal account Nalog.ru
- Chart of Accounts 2019
- What an individual entrepreneur needs to know about auditing cash transactions
- Cash discipline for individual entrepreneurs in 2021
- How can an individual entrepreneur keep accounting records?
Is the information useful? Tell your friends and colleagues
Dear readers! The materials on the TBis.ru website are devoted to typical ways to resolve tax and legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your specific issue, please contact the online consultant form. It's fast and free!
What rules must an individual entrepreneur follow?
What can you spend money on from the cash register?
You can spend cash from the cash register only for certain needs. Their list is given in paragraph 2 of the instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated October 7, 2013 No. 3073-U “On cash payments.” In particular, these are:
- payments to employees included in the wage fund and social payments;
- payment of insurance compensation (insurance amounts) under insurance contracts to individuals who previously paid insurance premiums in cash;
- issuance of cash for personal (consumer) needs of an individual entrepreneur;
- payment for goods (except for securities), works, services;
- issuing cash to employees on account;
- refund for previously paid in cash and returned goods, uncompleted work, unrendered services;
- issuance of cash when carrying out transactions by a bank payment agent (subagent).
As you can see, an individual entrepreneur can take cash from the cash register for personal needs without any restrictions. At the same time, an entrepreneur does not have the right to repay loans and credits in cash from the cash register (see “For what violations of cash discipline do tax authorities fine entrepreneurs and organizations”).
Restrictions on cash payments
Let's say you entered into a deal for the supply of office furniture. The client - an individual entrepreneur or organization - wants to pay in cash. The invoice amount is 150,000 rubles. Don't rush to take money from him.
The fact is that Directive No. 3073-U sets a limit on cash payments within the framework of one agreement - no more than 100 thousand rubles. This restriction does not apply to the following cases:
- making customs payments;
- issuance of salaries;
- issuing money on account;
- settlements with ordinary individuals (not individual entrepreneurs).
Violation of the individual entrepreneur's payment limit is subject to a fine under Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation - from 4,000 to 5,000 rubles. Some entrepreneurs, wanting to circumvent the ban, resort to cunning. They divide the amount exceeding 100,000 rubles into several payments, and for each they conclude their own separate agreement. As a result, cash payments for each such agreement are within the limit, which makes it possible to formally comply with the requirements of the Central Bank. However, during inspections, inspectors expose the ruse and declare that all “small” contracts with the same counterparty should be considered as a single transaction (see “What violations of cash discipline do tax authorities fine entrepreneurs and organizations for”).
Issuance of money on account
The rules for issuing cash to an employee (for example, to fulfill any business needs - purchasing office supplies, cleaning supplies, etc.) are determined by clause 6.3 of the Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U. These rules also apply to individual entrepreneurs
Money can be given to an accountable person upon his written application. But if an individual entrepreneur himself takes money from the cash register, whether for personal needs or to carry out activities, he does not write any statement.
Please note: newly registered entrepreneurs (or their accountants) can use a special accounting program for individual entrepreneurs for free for a year. This is a web service “Kontur.Elba”, which allows you to keep track of income and expenses, calculate the amount of fixed contributions and taxes under the simplified tax system and UTII, prepare reports and submit them via the Internet. Those individual entrepreneurs can work in the program for free if less than three months have passed from the date of registration as an entrepreneur to registration in Kontur.Elbe.