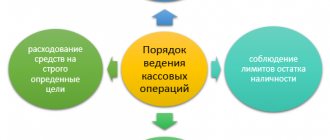
When opening a bank account, an organization must know what operations can be carried out on it and how to reflect them in accounting. The latter is handled by the accountant, who is responsible for the procedure for maintaining the current account and account transactions at the enterprise.
Any operation carried out on a bank account must have documentary justification. Papers are required confirming the operation itself through a credit institution, as well as confirming its intended purpose. The former are formalized by the bank, and the latter appear in the activities of legal entities. In this article we will examine these types of documents in more detail, as well as the features of conducting account transactions.
Select current account
What is online accounting
What the work of an accountant looked like before - a trained employee worked with piles of documents, manually filled out books and accounting registers and personally went to the tax office and funds to submit reports.
Now life is easier for an accountant. Many special programs for accounting have appeared - for example, the well-known 1C. The employee enters data into the database and monitors that the program correctly draws up reports, fills out declarations, and so on. If a company has large revenues, many employees and a common taxation system, it cannot do without accounting.
A small business with a small number of employees and not so much revenue does not always need an accountant on staff, and instead of 1-C, a small business can choose one of the online services for accounting. With their help, you can work with primary documents, submit reports to government agencies, calculate salaries and vacation pay, and so on.
Moscow State University of Printing Arts
1.
Topic 1. BASICS OF ORGANIZATION OF ACCOUNTING IN A COMMERCIAL BANK
In Russia there is a two-tier system - the Bank of Russia and commercial banks and other institutions.
The Bank of Russia performs the following functions of the Central Bank:
- pursues a unified state monetary policy aimed at protecting and ensuring the stability of the ruble;
- issues cash and organizes its circulation;
- is a lender to commercial banks and organizes a bank refinancing system;
- establishes the rules for making settlements, conducting banking operations, accounting, and reporting for the banking system;
- carries out state registration and licensing of credit organizations;
- supervises the activities of commercial banks;
- carries out currency regulation and currency control.
Commercial banks provide credit and settlement services to business entities. A commercial bank is a highly organized credit organization created to attract and place funds, precious metals, securities, funds of legal entities and individuals on the terms of repayment and payment, which meets the needs of society, reimburses expenses and makes a profit as a result of statutory activities. Statutory activity is the provision and sale of services to legal entities and individuals, who are called bank clients.
Accounting is based on economic information, the collection procedure, classification and directions of which are regulated by the laws of the Russian Federation and regulations of the government and the Bank of Russia.
The subject of accounting in banks refers to objects in the form of assets and liabilities, where assets are the funds on which the bank’s business activities are carried out, liabilities are the sources from which the funds are generated.
The bank's assets include:
- The bank's own share of the authorized capital.
- Cash and precious metals.
- Correspondent accounts of a commercial bank with the Bank of Russia and other credit institutions.
- Securities and financial investments.
- Loans provided.
- Deposits and other placed funds.
- Discounted bills.
- Bank property.
- Accounts receivable.
- Bank expenses.
The bank's liabilities include:
- Authorized capital.
- Extra capital.
- Funds.
- Correspondent accounts of commercial banks opened in the bank.
- Loans received.
- Deposits and other funds raised.
- Client funds in settlement, current and other accounts.
- Securities issued by a bank.
- Accounts payable.
- Bank income.
Assets and liabilities are involved in the business operations of a commercial bank:
- settlement;
- cash;
- on attracting and placing funds, namely credit, deposit, interbank;
- for the purchase and sale of securities and precious metals;
- with foreign currency;
- intrabank operations, namely the movement of capital, funds, property.
All operations of a commercial bank are divided into passive and active, i.e. operations to attract and place funds.
The bank's passive operations—operations to raise funds—contain three groups. The first group of passive operations is associated with the formation and development of own funds. The second group of passive operations are short-term and long-term loans provided by one bank to another. This group also includes deposits and borrowed funds from commercial banks. The third group of passive operations - deposit operations - is the main one in banking activities. It reflects the activities of commercial banks as intermediaries in the acquisition of resources on the free market for credit resources.
Active operations of a commercial bank are operations for placing client funds and own funds of a commercial bank.
The accounting method (a set of methods and techniques) is:
- documentation;
- inventory;
- ledger accounts and double entry.
Let us dwell in more detail on the accounting method in commercial banks.
Documentation is written evidence of a business transaction that gives legal force to accounting data. It provides a continuous and continuous reflection of the statutory and economic activities of the bank.
Mandatory details in the documents contain:
- Name of the bank;
- Title of the document;
- numbering;
- date;
- summary of the operation;
- quantitative and monetary expressions of the transaction;
- signatures of the persons responsible for the operation.
The main groups of documents include:
- cash documents (for processing and issuing cash in rubles and foreign currency);
- settlement documents (for payment of client obligations);
- memorial documents (when processing intra-bank transactions).
The accumulation of information on memorial documents is carried out using specialized computer programs.
Here are the main registers for maintaining the accounting records of a commercial bank:
- accounting journal (2 copies): one copy - for the daily balance, the second - for the accounting documents of the day;
- cash registers (2 copies): one copy - for cash documents, the second - for accounting documents of the day (compiled daily);
- statements of balances on first and second order accounts, personal accounts, balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts (compiled daily);
- statement of balances of placed funds;
- turnover sheet for commercial bank accounts in the context of first and second order accounts;
- balance.
The management of a commercial bank organizes internal bank control, which is divided into preliminary and subsequent (before and after drawing up the balance sheet). Preliminary control is carried out according to the control signatures of the performers affixed to the documents. Bank accounting defines a list of documents subject to additional control.
Inventory is a method of checking the availability of material assets, fixed and cash assets, precious metals, claims and obligations. Inventory either confirms accounting data or reveals unaccounted for values and funds, losses, thefts, shortages, and miscalculations. With its help, the safety of any type of property is monitored, and the completeness and accuracy of accounting data is checked. The number of inventories carried out is established by the Bank of Russia and is supplemented individually by each commercial bank independently.
Accounting accounts are registers for grouping and current reflection of information from homogeneous banking transactions. Accounts in accounting are divided into active and passive. They are named according to the parts of the balance sheet and reflect their content. The structure of accounts, regardless of their type, corresponds to the traditional form of accounts in accounting. The amount of each banking transaction is reflected in the accounts twice in accordance with the double entry principle. Reflecting the amount of a banking transaction on the debit of one account and the credit of another account is also called correspondence of accounts or accounting entry.
Information on accounts is divided into analytical and synthetic according to the method of its generalization and grouping. Analytical accounts are maintained in monetary, natural and labor dimensions. Their number and name are established by the bank independently. Analytical accounting involves opening and maintaining personal accounts by type of currency, clients, correspondent banks, types of loans and other characteristics. Each personal account is assigned a name and number, which determines its belonging to the intended purpose of the collected information and to a specific client, subdividing them by purpose and by owner. Personal accounts of analytical accounting are opened for each balance sheet and off-balance sheet account of synthetic accounting. To account for expenses and income of the federal budget, personal accounts are maintained in accordance with budget qualifications.
Personal accounts are registered at the bank in a special book, in which separate sheets are allocated for each account. This book is a classifier of personal accounts opened in banks by enterprises, organizations and institutions. The account designation must indicate:
- its name (in words);
- digital personal account number;
- for loan accounts - the purpose for which the loan was issued, the number of the loan agreement, the interest rate, the digital designation of the credit risk group for which the reserve for possible loan losses is calculated, other data as decided by the bank.
The header of the personal account indicates its number and reference data, and the headers of the personal accounts of individual borrowers indicate a reporting symbol and additional data to monitor the timely repayment of the loan. In personal accounts of analytical accounting for off-balance sheet accounts, the number of the corresponding account and the conventional digital designation of the type of transaction are not indicated. Personal accounts of analytical accounting are printed according to established standard forms, which are included in the unified system of settlement and monetary documents and are the bank's output documents. With automated accounting, personal accounts are printed on roll paper, in compliance with the forms of standard personal account forms.
The following details are common to all forms of personal accounts:
- transaction date;
- number of the document on the basis of which the entry is made;
- Number of correspondent account;
- symbol of the type of operation;
- the amount of debit and credit turnover and the balance amount.
The standard form of the main personal account is shown in Fig.
1. Main personal account form
Client name__
______________________________ Name of the bank____________________________________
Date (period) for which the statement is provided
______ Extract from personal account No. ___________________________ Opening balance ________________________________________ Total turnover _________ Outgoing balance ____________
| date | Document Number | Type of operation | Number of correspondent account | Revolutions | |
| debit | credit | ||||
Total turnover___________ Closing balance_______
Rice. 1
Entries in personal accounts and statements on them are made simultaneously for all documents of the operating day with the withdrawal of the balance amount for the next day, based on the turnover for the day and the balance at the beginning of the day. The date in the personal account is printed once when the first transaction is reflected. When compiling personal accounts, a conventional digital designation of the type of transaction is used. For example, debiting funds according to a payment order or crediting payments, according to a copy of the payment order, is indicated by the number 2, cash payment by check - by the number 3, etc. Information about the movement of funds on a personal account is issued to the bank client in the form of an extract.
Statements from personal accounts issued to bank clients are compiled on electronic computers. To decipher entries in personal accounts for a loan, documents (copies of documents) are attached to the statements, according to which entries in personal accounts were made. These documents are affixed with a stamp, which is used to issue statements, and also indicates the date of their posting to the personal account. When preparing the statement, the responsible executor is obliged to ensure that it fully corresponds to the personal account, as well as the presence of the necessary applications and the correctness of their execution.
Extracts from personal accounts are issued to clients within the time limits established in agreement with the account owner. For accounts that were not valid on the last working day of the month, statements will not be issued on the first day. If there is no movement on the account during the month, clients are sent notifications about the amount of the balance as of the first day. On January 1, all personal accounts must be prepared and statements issued to clients. Based on these statements, clients must provide the bank with written confirmation of their personal account balances at the end of the reporting year.
Analytical accounting registers in credit institutions are:
- personal accounts;
- accounting journals;
- statement of balances on first- and second-order accounts, personal accounts, balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts;
- statement of balances of placed (raised) funds.
It is allowed to maintain analytical accounting of contributions from shareholders, deposits of individuals, bank employees, accounting of fixed assets, inventories, etc., operations important for the bank, according to separate programs with the total amounts reflected on the corresponding accounts in the balance sheet.
Synthetic accounts group analytical accounting data according to certain characteristics. They reflect the state and movement of bank funds and their sources in a generalized form in monetary terms. The number of synthetic accounts is regulated by the Chart of Accounts for accounting in credit institutions of the Russian Federation. Accounts are the basis for filling out reports, balance sheets and are used to analyze bank performance indicators. The main registers of synthetic accounting are daily balances and check sheets. Synthetic accounts are divided into first and second order accounts. First-order accounts have three-digit numbering, second-order accounts have five-digit numbering.
Synthetic accounting registers in credit institutions include:
- daily turnover sheet;
- daily balance.
The daily turnover sheet is compiled for balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts in the prescribed form. Within a month, turnover is shown per day. In addition, on the first day of the month, a turnover sheet for the month is compiled, for quarterly and annual dates - with increasing turnover from the beginning of the year. The daily balance is compiled according to the established form programmatically in the context of second-order balance sheet accounts. When creating reserves for possible losses, balances on active accounts are shown minus the reserve.
Balance sheets and turnover sheets are signed after their consideration by the head of the credit institution, the chief accountant.
The amounts reflected in the analytical accounting accounts must correspond to the amounts reflected in the synthetic accounting accounts. This is achieved by stable software, simultaneous reflection of transactions in interconnected accounting registers.
Before signing the balance sheet, the chief accountant or on his behalf, an accounting employee must verify:
- correspondence of the total balances reflected in the accounting journal with the turnover shown in the turnover sheet;
- correspondence of balances on second-order accounts reflected in the balance sheet with balances shown in the turnover sheet, statement of account balances;
- correspondence of balances on second-order accounts reflected in the statement of account balances with the balances shown in the statement of balances of placed (raised) funds.
A corresponding entry is made in the balance sheet about the inspection performed before the signatures of officials. If a discrepancy is identified, the reasons are determined and measures are taken to eliminate it. If necessary, correction entries are issued. The error is corrected the moment it is discovered. Reprinting of analytical and synthetic accounting materials is not permitted.
In addition to accounting, bank institutions maintain operational records. The latter, as a rule, is not checked by the balance sheet and is maintained directly by operational employees. In an operational manner, first of all, changes in balances in personal accounts that occur in connection with receipts and payments of money are taken into account. Such accounting, maintained during operating hours, allows payments to be made from settlement, current, budget and other accounts only within the limits of available funds. Operational accounting is carried out by counting the amounts of money received and paid, balancing them and displaying the balance for each account. The new account balance received promptly is recorded on documents: in the personal account or in the verification sheet for the previous day.
The chart of accounts for commercial banks and the accounting rules were developed by the Bank of Russia. The rules for its application are based on the following accounting principles:
- Continuity of activity of the credit institution in the future.
- Consistency of accounting rules, ensuring comparability with reports of the previous period.
- Prudence involves a reasonable assessment of assets and liabilities, income and expenses, which allows not to transfer risks that potentially threaten the financial position of the organization to subsequent periods.
- Reflection of income and expenses using the “cash” method, after receipt of income and expenses, except for cases established by the Rules.
- The day of reflection of the transaction provides for the reflection of transactions (receipt of documents) on the day they are performed, unless otherwise provided by regulations of the Bank of Russia.
- Separate and detailed reflection in the accounting of assets and liabilities.
- Continuity of the opening balance according to the balances of balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts at the end of the previous and beginning of the current period.
- The priority of content over form provides for the reflection of transactions in accordance with their economic essence, and not their legal form.
- The unit of measurement provides that assets and liabilities are recorded at their historical cost at the time of acquisition or occurrence.
- Openness provides for a reliable reflection of business transactions that avoids ambiguity in the position of a credit institution.
- Consolidation provides for a consolidated balance sheet and reporting for the credit institution as a whole and daily balance sheets for secondary accounts.
- Non-repetition of data on the balance sheet and off the balance sheet (on off-balance sheet accounts), except in cases provided for by the Rules and regulations of the Bank of Russia.
A chart of accounts is a list of synthetic accounts of the first and second order, sufficient for organizing accounting. It is presented in the form of the following table:
| No. of balance accounts | Name of sections and accounts of the balance sheet | Account attribute | |
| I order | II order | ||
The chart of accounts includes five sections, which look like this:
| Section number | Section name | Account number 1st order |
| A. Balance sheet accounts | ||
| 1 | Capital and funds | 102-107 |
| 2 | Cash and precious metals | 202-204 |
| 3 | Interbank transactions | 301-328 |
| 4 | Customer Transactions | 401-476 |
| 5 | Transactions with securities | 501-525 |
| 6 | Funds and property | 601-614 |
| 7 | Performance results | 701-705 |
| B. Trust Accounts | ||
| These accounts record transactions stipulated by the trust management agreement for resources not owned by the bank. A separate balance sheet is drawn up for these accounts. Active accounts Passive accounts | 801-810 851-855 | |
| B. Off-balance sheet accounts | ||
| 2 3 4 5 6 7 | They take into account valuables and documents accepted for storage, collection, commissions, sources of financing for capital investments, strict reporting forms, and shares. A separate balance sheet is drawn up for these accounts. Unpaid authorized capital of credit institutions Securities Payment transactions and documents Credit and leasing operations Debt written off and taken off balance sheet due to impossibility of collection Corresponding accounts: — for correspondence with passive accounts with double entry — for correspondence with active accounts with double entry | 906 907, 908 909-912 913-915 916-918 99998 99999 |
| D. Urgent operations | ||
| Accounts for recording transactions for purchase/sale transactions of funds in foreign currency, precious metals and securities for which the transaction dates do not coincide with the settlement date. These are memorial accounts that take into account the volume of transactions concluded before the payment is due. When this period occurs, the data will move to balance sheet accounts. A separate balance sheet is drawn up for them. They consist of accounts: - for cash transactions; — forward transactions; — unrealized exchange rate differences Active accounts Passive accounts | 930-940 960-970 | |
| D. Securities accounts | ||
| They are used to record transactions with issue-grade securities accepted from clients for storage or for the implementation of trust management of them. Operations on securities accounts are called depository. A separate balance sheet is drawn up for them: Active accounts Passive accounts | 98000-98035 98040-98090 | |
The chart of accounts contains only active and passive accounts; there are no active-passive accounts. To organize accounting, paired accounts have been introduced: one is active, the other is passive. At the beginning of the operating day, transactions are reflected in the paired account that has a balance. At the end of the operating day, if the account balance changes place, it is transferred to the matching account.
The chart of accounts does not provide for separate reflection of transactions in foreign currency. All transactions are reflected in national currency. Currency codes and ruble equivalent are maintained on personal accounts. Active and passive accounts take into account the time factor for completing settlement transactions and are divided by type of client, taking into account the form of ownership, type of activity and country of origin.
In analytical accounting, the construction of a personal account code is interconnected with the numbering of second-order synthetic accounts in the chart of accounts and is built according to the following principle.
Personal accounts opened for clients in a commercial bank are designated by a twenty-digit code. The first digit is the section number of the chart of accounts. The next two are the account number of the first order (always starting from zero). The fourth and fifth digits are the second-order account number, namely its numbering. For each first-order account, this numbering begins with “01”. The next three digits are the code of the currency or precious metal. The ninth digit is the security key. The next four digits are the branch or division number. The last seven digits for bank clients represent the serial number of the personal account. Similar numbering is used for credit accounts. For income and expense accounts, the first five of the last seven digits are the income statement symbol. The last two are the serial number of the personal account. Free positions when assigning personal account numbers are filled with zeros, which are located in the positions on the left, i.e. numbering is from right to left.
The numbering of trust accounts, off-balance sheet accounts, urgent transaction accounts, and custody accounts is established by the bank independently, taking into account the instructions of the Bank of Russia. In accordance with the plan, the first five digits of the numbering accounts contain the account number of the second order.
The elements of accounting are:
- balance;
- reporting.
The balance sheet as an element of the accounting method is a grouping of information about the resources and funds of the bank, which are distributed in it according to the degree of liquidity. The balance sheet of a commercial bank is compiled daily and reflects the state of the bank's borrowed and own funds, as well as their placement in credit and other operations. According to the balance sheet, the formation and placement of monetary resources is controlled; the state of credit, settlement, cash and other banking operations; correct reflection of transactions in accounting. The balance is drawn up monthly according to Form No. 101.
The reporting covers the statutory activities of the bank, satisfies the information requirements of internal and external users (founders, clients, tax authorities, Bank of Russia) and is divided into reporting at the end of the month and reporting at the end of the quarter. The procedure for compiling, content, and deadlines for submitting current financial statements by commercial banks is determined by the Bank of Russia. Current reporting at the end of the month is submitted to the Main Directorate of the Bank of Russia and contains:
- balance;
- consolidated balance sheet (including balance sheets of branches);
- deciphering the balances of loan debt and non-payments on loans from banks of organizations by industry;
- decoding of individual balance sheet accounts according to the timing of raising and distributing funds;
- decoding of individual balance sheet accounts for economic standards for the activities of a commercial bank;
- list of major creditors;
- decoding of balance sheet accounts;
- calculation of economic standards;
- calculation of the required reserve fund;
- decryption of balance sheet account 30102;
- decoding of balance sheet accounts for correspondent accounts 30109, 30110.
Commercial banks carrying out transactions in foreign currency additionally submit to the Main Directorate of the Bank of Russia a report on the movement of foreign assets and liabilities in freely convertible currencies, as well as in other types of currencies for transactions with non-residents, highlighting countries far and near abroad. In addition to the above forms, banks performing operations in foreign currency submit to the Bank of Russia branch a special report on maintaining an open currency position and a report on the movement of cash foreign currency and payment documents in foreign currency.
To prepare an annual accounting report, banks at the end of the reporting year conduct an inventory of all cash and valuables, fixed assets, household and other materials, and settlements recorded on balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts. Accounts receivable and payable are analyzed, and active measures are taken to repay them. Unrealistic amounts must be written off from the balance sheet and recognized as losses. The loan portfolio is analyzed, and measures are taken to identify unrealistic loan debt, as well as accrued interest on such loans and write them off in the prescribed manner. Similar work is carried out for all other types of assets in order to reflect real and reliable data on assets and liabilities in the annual balance sheet.
What are the advantages of online accounting
The main advantage is budget savings. An accountant's salary is only one cost item. For successful work you will also need:
- license for accounting software;
- server where the accounting database will be located;
- system administrator who will maintain the server;
- The accountant's workplace is a computer, a desk, and so on.
It's easier with online accounting. All of the above costs disappear; you only need to pay monthly for access to the service.
You don’t even always need an accountant to work with online accounting. In a small company, the director himself or a specialist can handle the accounting remotely. And some services try to make your participation minimal and submit reports and declarations for you independently.
In addition to saving money, online accounting has several other important advantages:
- access to the accounting database from anywhere in the world via phone or tablet;
- there is no connection to a workplace - you work on a computer, and then you can switch to a tablet or phone without losing data;
- no need to bother with updates - the service does it automatically;
- you can integrate online accounting with online banking to download bank statements;
- information is reliably protected.
General rules for maintaining bank records
Maintaining bank records of a credit organization must be carried out continuously from the date of its state registration until the moment of reorganization or liquidation in the manner prescribed by law. When maintaining banking records, a credit institution must apply the same rules, with the exception of significant changes in activities or legislation. If these rules are violated for one reason or another, then in the explanations to bank statements it is necessary to ensure the comparability of accounting data.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Course work Bank accounting and its postings 410 rub.
- Abstract Bank accounting and its postings 270 rub.
- Test work Bank accounting and its postings 200 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
In general, banking accounting does not differ from accounting in other business entities. Property, banking and other business transactions are recorded in accounting accounts using the double entry method. The main difference is that a chart of accounts developed specifically for credit institutions is used for accounting. Credit organizations also form a working chart of accounts based on a legally approved plan.
Entry into banking registers is carried out on the basis of primary accounting documents recording the fact of commission or the fact of permission to carry out business transactions. Primary banking documents are drawn up at the time of or immediately after a business transaction.
Note 1
All entries in primary banking documents and accounting registers are made in Russian. If any banking document is drawn up in a foreign language, it is subject to mandatory translation into Russian.
Need advice on your academic work? Ask a question to the teacher and get an answer in 15 minutes! Ask a Question
How to choose online accounting in a bank
The first requirement of the bank is to have an open current account. Therefore, in fact, you cannot choose online banking accounting; you will open it only in the bank where the current account is opened.
The presence of online accounting and its functionality is an important criterion when choosing a bank where you intend to receive services. Therefore, when searching for a bank, pay attention to this.
The service will help you choose a bank. It contains information about all bank tariffs. Select the number of payments per month, your region, and the site will show which bank will suit you best. All you have to do is find out if the bank has online accounting
In addition, you can read our article “Where is the best place to open a current account for individual entrepreneurs.”
Organizational aspects of bank accounting
Definition 1
Banking accounting refers to the flow of information about the availability, condition, movement of property, cash and credit funds, funds and securities, reserves, income and expenses, results of financial and economic activities of banks, formed for the purposes of management, analysis, planning and control activities of a commercial bank.
Banking accounting is aimed at ensuring a common understanding of information about the resources available to the bank and their use (allocation).
Why do you need a statement if you can already see any information on your account every day?
It is needed to control your money . Everyone makes mistakes, even banking programs. It happens, for example, that a commission for bank services is written off twice, but on different days, and you won’t notice. Or accidentally pay the same bill twice. You may miss an important payment, although you will be sure that you definitely made it. In general, all this can be tracked by looking with fresh eyes at the list of receipts and debits of money over a longer period than one day. For a week or a month, for a quarter.
Accounting policy of a credit institution
In accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, credit institutions are required to develop and approve accounting policies that include:
- working chart of accounts developed in accordance with the standard Chart of Accounts;
- forms of primary accounting documentation for which there are no mandatory standard forms;
- procedures for settling intrabank settlements between bank divisions and conducting accounting operations;
- methodology for assessing the property and liabilities of a credit institution;
- selected methods of accounting for assets, liabilities and business transactions;
- principles of document management and information processing technology;
- features of inventory;
- other decisions requiring approval in the accounting policies of the credit institution.
It is advisable to present the accounting policy of a credit organization in the context of the following sections: general provisions; formation of accounting policies, organizational and technical principles of accounting; methodological foundations of accounting, as well as the tax aspect of accounting.
Note 2
The accounting policy is subject to approval by the head of the credit institution.