For the purposes of organizing statistical and tax accounting, companies should determine the value of such an indicator as the number of employees on the payroll (we will discuss how to calculate it below).
The number of employees is the number of full-time employees of an organization on a certain day of the month. This indicator is used by companies and entrepreneurs when preparing tax and statistical reports, for example, form 4-FSS and “Information on underemployment and movement of workers for the quarter.”
Let us determine which categories of workers should be taken into account when calculating the size of the payroll, and which are excluded from the calculation.
Why do you need to count payroll numbers?
As stated above, the value under consideration implies the total number of employees of the enterprise. If we talk about its practical significance, then the payroll number of employees of an enterprise is a test number that helps in solving analytical problems, such as assessing labor efficiency, calculating average wages and staff turnover rates. In addition, the column of the same name is present in a number of reports submitted to regulatory authorities. For example, information on the payroll number of employees is reflected in form 4-FSS, approved by Order of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation dated September 26, 2016 No. 381. In addition, the specified coefficient is taken as the basis for another value - the average payroll composition of personnel. It, in turn, is necessary when filing tax returns electronically (clause 3 of Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), when calculating income tax at the location of a separate division (clause 2 of Article 288 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or when filling out the DAM form -1 Pension Fund.
Personnel assessment (initial data, list of generated documents)
The assessment is carried out on the basis of a working model. places, regulatory and personnel documentation, surveys, testing. It includes:
- assessment methods;
- assessing the employee’s potential and personal contribution;
- certification.
Personnel assessment methods
Assessing employee potential
Involves assessment:
- prof. knowledge, skills;
- business, moral qualities;
- prod. experience;
- human psychology;
- level of culture;
- health conditions;
- ability to work.
Assessing an employee's individual contribution
Shows the productivity of a particular employee with an emphasis on its quality and complexity. Usually done using the KTU (participation rate) and determines the (in)suitability of the position.
Personnel certification (stages)
Comprehensive assessment of special personnel commission for suitability for the position. Takes into account the employee’s potential, his individual contribution to achieving the goals of the enterprise. Based on the results of the certification, the issue of career growth, dismissal, and relocation is decided.
Career planning, career models (motivation)
There are 4 career models according to which it can be planned:
- "Springboard". Gradual career growth, changing positions to more complex and highly paid ones. Long-term work in a senior position, retirement.
- "Ladder". Each step is a specific position in which a person works for up to 5 years. The result is achievement of the highest position. After this, a smooth descent begins and less intense work is performed.
- "Crossroads". An American model that involves passing a certification, based on the results of which a decision is made on promotion, transfer or demotion of a position.
- "Snake". Horizontal movement of a person from one position to another by appointment for 1-2 years. The acquired knowledge is applied at a higher position.
Conditions and remuneration
They imply the correct organization of work and relate to:
- workplace, its technical equipment;
- formation of employee income;
- social guarantees (compensation, social benefits, etc.).
An additional source of income is social services. benefits. Depending on the category of workers, they are provided in different sizes.
Organization of personnel movement
Includes:
- Advanced training, in position (grade of worker).
- Relocation due to production necessity for other equivalent work. place.
- Demotion (grade, position) based on certification results.
- Dismissal (when changing jobs or due to inconsistency with the position held, work place).
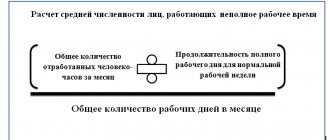
How to calculate
Calculation of the corresponding coefficient involves the question of who is included in the payroll number of employees. The answer is contained in the Instructions on statistics of the number and wages of workers and employees at enterprises, institutions and organizations, approved by the State Statistics Committee of the USSR on September 17, 1987. According to clause 2.9 of the specified document, the list of employees of the enterprise includes “all employees hired for permanent, seasonal, and also temporary work for a period of one day or more, from the day they are hired.” It should be understood that the number of employees present and on the payroll are different quantities. The latter includes not only employees present at the workplace, but also some of the personnel who did not show up for reasons such as downtime, being on a business trip, illness, annual leave, etc. The full list is determined by clause 77 of the Instructions, approved by order of Rosstat dated 22.11. .2017 No. 772.
Classification of the personnel of the enterprise
In terms of participation in the production process, personnel are:
- Industrial production.
- Non-industrial.
According to the labor functions performed, among the first group (industrial-production) personnel there are:
- Workers.
- Specialists with managers.
- Employees.
The above classification is used in accounting, in the management process, and also when conducting analysis and planning.
Industrial and production personnel
These are employees of auxiliary, transport, main workshops, auxiliary production, etc. A complete list of these employees can be found in clause 25, part 4 of the Instructions.
Workers (main and auxiliary)
Workers - workers involved in the creation of material assets, engaged in repairs, transportation, loading, provision of services, etc.
The professions of workers are presented by OKPDTR (OK 016-94), approved. Resolution of the State Standard No. 367 dated December 26, 1994 (as amended on December 19, 2012). For example: activation operator, postman, telephone operator, courier, janitor.
Specialists and managers
Workers engaged in economic, as well as engineering, technical, etc. work are classified as specialists. Examples:
- accountant;
- administrator;
- editor;
- legal advisor;
- economist;
- merchandiser
The assistants and helpers of these workers are also specialists.
Managers - persons holding positions of heads of enterprises or their divisions:
- director;
- general director;
- boss;
- manager;
- chairman;
- master.
Leaders also include deputies of the named persons, state inspectors and chief specialists. For example, chief accountant, editor-in-chief, chief engineer, etc.
Enterprise employees
This includes those workers who draw up and prepare documentation, do accounting and exercise control, household chores. service. For example:
- archivist;
- clerk;
- collector;
- accountant;
- statistician.
Non-industrial personnel
These are people who work in trade, catering, housing and communal services, workers in medical, children's, and educational and cultural institutions. We are talking about structures that appear on the balance sheet of the enterprise.
Who is excluded from the calculation
As stated above, the payroll includes employees who have entered into labor relations with the enterprise, regardless of their nature and duration. In accordance with paragraph 79 of the Rosstat Instructions mentioned above, the following employees are not included in the payroll:
- hired externally;
- working under civil contracts;
- enterprises working under special agreements with government services to attract labor (military personnel and persons serving sentences);
- transferred to work in another organization;
- aimed at training without work and without pay;
- those who submitted a letter of resignation and stopped working before the expiration of the warning period or stopped working without warning;
- lawyers;
- military personnel in the performance of military service duties.
Concepts of profession, specialty, qualification
Profession is a type of work activity (occupation) of a person that requires special training and education. Information professions: scientist, programmer. Creative: writer, actor, musician.
The concept of “specialty” implies the presence of a whole complex of knowledge, skills and abilities in one area within one profession. The specialty is confirmed by a diploma. For example: therapist, cultural specialist, manager, hairdresser.
Qualification - the degree of training, compliance with a specific level of professional requirements. For specialists serving in the workforce, its level (category 1, 2, 3) is determined by education and certification. For workers, the level (category) depends on professional training.
What are the differences from the average
As we previously found out, the number of employees on the payroll is the number of people who have entered into an employment relationship with the organization in the form of an employment contract. This value is calculated for each day in whole units and corresponds to the number of people declared on the working time sheet. The resulting indicator is taken as the basis for calculating the average headcount, a significant value for statistics and taxation. Its calculation for a month is carried out as a calculation of the average value: the average value for each calendar day is summed up, the resulting amount is divided by the number of calendar days. The quarterly coefficient is calculated in a similar way. However, in order to obtain correct data when calculating both quantities, it is necessary to take into account a number of nuances.
Personnel efficiency indicators
The key indicator characterizing the degree of efficiency in the use of labor resources is labor productivity (LP). Increased productivity is reflected in increased production volumes with a constant number of personnel and the least amount of labor expended per unit of production.
Labor productivity
In the classical sense, PT is the number of products that one employee can produce per unit of time. It is characterized by:
- output (products produced by 1 employee per week, month, quarter, year);
- labor intensity (working time spent on producing 1 unit of product).
Calculation of values:
VR=OPR/TRP (4)
Abbreviations: VR - output, OPR - production volume, TRP - labor intensity.
TRP=ZT/OPR (5)
Abbreviations: LT - labor costs.
Methods for determining labor productivity
The use of a particular method depends on the unit of measurement of production volume.
Natural method
According to this method, PT is defined as the ratio of the physical volume of work to the SFC of the relevant personnel. It allows you to determine the output of workers by profession, i.e. find out, compare the PT of some workers, teams, and plan their composition.
Labor method
It is used in an enterprise where a strong regulatory framework has been formed and the level of regulation is quite high. Necessary to determine the PT of the main workers, whose work is always standardized. Defined as the ratio of labor costs in man-hours to the number of products (in physical terms).
Cost method
Calculation by this method is carried out by dividing the products produced (by cost) by the number of working employees. It is characterized by simplicity, generalization of different products, and the use of summary indicators. Minus: the influence of the price level on the value of PT.
Factors for increasing labor productivity
These include factors that:
- create conditions for increasing PT (increasing qualifications, strengthening labor discipline);
- contribute to the growth of PT (rational organization of labor, stimulation of workers);
- directly determine the level of industrial processes (new technologies, automation of the production process).
Where do maternity leave belong?
It was demonstrated above that the procedure for calculating the quantitative characteristics of personnel is quite simple. Confusion arises, as a rule, due to the existence among the staff of those who are included in the number of employees on the payroll, but are not included in the average payroll. This applies, for example, to such a category as women (in some cases men) on parental leave. Are maternity leavers included in the payroll? An affirmative answer to this question is given by clause 77 of the Rosstat Instructions (approved by Rosstat Order No. 772 dated November 22, 2017). However, clause 79.1 of the same document states that this category of workers is not included in the average. The rule also applies to persons studying or entering an educational institution while on leave without pay.
Maintaining staffing
The law does not oblige employers to maintain staffing levels. They can do this solely at their own discretion. In this case, this document can be maintained both in electronic form (for example, in Excel or Word) and in paper form.
Maintaining staffing and keeping it up to date is quite simple (even if such work is not automated). It is enough for the personnel officer to enter all information about the employees (for example, the date of return from long-term vacations or the presence of disability, etc.) in the staffing form. The more detailed the staffing arrangement is, the more useful it will be. For example, based on staffing, you can generate reports for management on various issues. For example, the director can periodically clarify which employees are currently on vacation. Using the standard layout, preparing a report with this information will not be difficult.
Nuances and difficulties
In addition to persons on maternity leave, there are other categories of employees that cause controversy when calculating staff numbers. For example, the question often arises whether the owners of the enterprise are included in the SC. According to paragraph 77 of the Rosstat Instructions (approved by Rosstat Order No. 772 dated November 22, 2017), the answer to this question is affirmative, provided that the owners worked and received wages. Paragraph 78 of the document also contains commentary regarding internal part-time workers. Each of them is counted as one person in the account balance. As for persons who have an employment contract and a work contract with the organization at the same time, they, in accordance with paragraph 78 of the Instructions, are taken into account in the SCH and SSC once at their main place of work.
HR system
We are talking about the principles and methods of personnel management within the enterprise. Working with it is considered as a system that includes 6 interconnected subsystems: frame. policy, selection, assessment, placement, adaptation, training of personnel.
The focus is on building an organizational structure for personnel management, including their retraining and advanced training.
Human resource management concept
The concept of human resources management affects the labor market, includes the interconnection of management subsystems, and also contains:
- classification of personnel by categories of workers;
- formation of a management system for it (development of appropriate technology, management methodology).
Personnel policy (concept, components)
It is a system of principles and goals that determine the direction and content of work with personnel. The main components of the frame. politicians:
- philosophy of the enterprise (intra-company rules for relationships between employees and workers);
- labor rules regulations (regulations for employees, employers);
- collective agreement (legal act regulating social and labor relations);
- leadership style (authoritarian, democratic, liberal, mixed).
Recruitment (definition, stages)
This is the process of selecting suitable applicants to fill vacant positions. places from those listed at the enterprise or labor exchange. The main task is to find people capable of working for new jobs. places (positions), perhaps even change occupation.
Calculation of personnel requirements
Such calculations are made for the future based on the projected demand for labor resources. It is determined by the requirements of the production program and possible changes in personnel.
Chrs=Def*NORchis/Kpo (6)
Abbreviations: Chrs - number of workers, employees,
ODA - production volume (million Russian rubles),
NORchis - standard number (million Russian rubles),
Kpo (=20) is an adjustment factor for ruble inflation and in relation to the non-technical sector.
Job models
Provides selection, placement, assessment of labor resources on a unified basis. Includes about 15 elements characterizing the workplace, namely:
Professional recruitment
It means assessing the professional suitability of an employee, determining whether his capabilities correspond to the specific conditions and characteristics of work in a certain position. There are 4 components in professional selection:
- medical;
- physiological;
- psychological;
- pedagogical.
Job interview
In practice, 4 interview techniques are used:
- British: personal conversation with the applicant.
- German: preparation and presentation of “employment” documents along with recommendations.
- American: testing the candidate’s abilities (intellectual, creative), psychological testing, observing him in a private setting.
- Chinese: written exams.
Formation of a personnel reserve (development reserve, functioning reserve)
Personnel reserve is a group of employees capable of managerial work, who correspond to a particular position, have been selected and qualified, but have not yet been appointed to the position.
The development reserve consists of specialists and managers who are preparing to work in new areas. Functioning reserve - those of them who must ensure the efficient functioning of the enterprise in the near future.
Statistical reporting
Every Russian enterprise that has employees is required to annually submit information on the average number of workers to Rosstat. The report form, timing and method of presentation depend on the average composition of the workforce at the enterprise.
There are 3 forms of statistical reporting for enterprises that are not small entities, where the staff number is more than 15 people.
Table. Statistical reporting for enterprises that are not small entities.
| Form | Submission deadline |
| P-1 “Information on production and shipment” | It must be completed and submitted no later than the 4th day of the month following the reporting period. |
| P-3 “Information on financial condition” | No later than the 28th day of the month following the reporting period. If the form is submitted based on the results of the quarter, the due date is set before the 30th day of the month following the quarter. |
| P-4 “Information on the number and wages of hired workers” | Submitted to Rosstat monthly by the 15th day of the month, which follows the reporting month. |
In form P-4, the average number of employees is rounded to a whole number, with the exception of calculating the indicator separately for external part-time workers. This calculation option is allowed due to the fact that there may be a small number of workers in this category; accordingly, the size of the number may also be quite small.
If personnel officers are faced with the question of how to calculate the indicator for a quarter, then in this case all three values of the monthly calculation are summed up and divided by 3 (months in the quarter). The average number for 6 months, 9 months or a year is calculated accordingly.
Seasonal workers
In fact, enterprise managers are often faced with a situation where the number of employees on the staffing table is significantly less than originally planned. This is due to the fact that it is much more profitable for companies to hire seasonal or temporary employees than to enter into formal contracts and include the employee on the staff.
In the latter case, it is necessary to pay all relevant taxes and insurance payments for it - to the compulsory medical insurance fund, the Russian pension fund. If the employee works on a temporary basis, then you can save on all this. This is often what managers of usually small firms and companies do.
In addition, when the structure and number of employees is low, it is easier to keep records of them. And if the needs for the services of a particular employee arise irregularly, then he does not need to pay a monthly salary, but can limit himself to actual payments for the amount of work directly performed.
By the way, a convenient system of hiring for temporary or seasonal work is common in many countries around the world. This is done by specialized agencies that find you the necessary employees for a pre-agreed time period.
Often such agencies recruit employees who then move from one company to another through leasing operations. This way you can carry out the full functioning of the company without changing the average number of full-time employees. As a rule, this applies to production and economic specialties. For example, employees of cleaning companies, security guards, maintenance workers.