Separate reporting forms for LLCs and individual entrepreneurs, mandatory for submission to the tax office, extra-budgetary funds or statistical service, contain an indicator of the average headcount. For different purposes, different types of determining the number of personnel of an organization are used:
Friends, joy! We have made a calculator to calculate the average number of employees. Use it!
- actual number;
- turnout numbers;
- staffing levels;
- planned number;
- standard number;
- average number.
Various algorithms are used to determine each value; both employees on the company’s payroll and all employees, regardless of employment status (internal and external part-time workers, temporary and seasonal workers, “contractual workers”) can be counted.
Question: What are the features of calculating the average number of employees for newly created organizations? View answer
Why do we need the average headcount parameter?
Concepts such as the planned or standard number of employed workers are mostly used in economics as a regulator of the staffing level of enterprises and are defined as the optimal number of workers required for highly productive labor at a particular enterprise.
Question: What is the penalty for failure to submit (late submission) of information on the average number of employees for the previous period? View answer
The average number of personnel (ASN) is an indicator that stands apart. It is used in special cases:
- the ability of an LLC to use preferential tax schemes (STS) depends on the indicator;
- based on the SSC parameter, the need for telecommunication networks is determined when submitting reports;
- The tax authorities calculate the average salary in an LLC based on the SCH indicator.
The SSC report is a mandatory document that is provided by all organizations and individual entrepreneurs, regardless of their organizational and legal status. The document contains information for the past reporting year.
Important: for LLCs or individual entrepreneurs registered in the middle of the reporting year, the obligation to submit a report on the average headcount begins one month after the creation of the company. At the end of the calendar year, such entities submit another report on a general basis.
A special procedure for calculating the SCH is used for LLCs registered during the reorganization measures of the predecessor organization (liquidation, re-registration). Such newly created companies must calculate the average headcount taking into account information about the employees of the previous organization.
Question: What should be indicated in the information about the average headcount if the organization employs only external part-time workers? View answer
Calculation of the net financial value for the reporting period
How to calculate the average headcount for a year or another reporting period? In reporting to the tax inspectorate, the SCR is compiled at the end of the year, and for filling out the 4-FSS form, the necessary periods are a quarter, six months, nine months and a year.
If the year has been worked out in full, then the calculation rule is as follows: (NW for January + NW for February + ... + NW for December) divided by 12, the resulting total rounded to whole units. Let's give a simple example:
The list of the enterprise for 2021 changed slightly:
- January – March: 35 people;
- April – May: 33 people;
- June – December: 40 people.
Let's calculate the average salary for the year: (3 * 35 = 105) + (2 * 33 = 66) + (7 * 40 = 280) = 451/12, total - 37.58, rounded to 38 people.
If the year has not been worked in full, then the calculation is made in the same way as for an incomplete month: regardless of the number of months worked, the amount of the NFR is divided by 12. From the Rosstat Instructions: “If the organization worked for an incomplete year, then the average number of employees for the year is determined by summing the average number of employees for all months of work and dividing the resulting amount by 12.”
How to calculate the average headcount for less than a full year of work?
Let’s assume that an enterprise with a seasonal nature of activity worked only five months in a year, the monthly average was:
- April – 320;
- May – 690;
- June – 780;
- July – 820;
- August – 280.
We count: 320 + 690 + 780 + 820 + 280 = 2890/12. We find that the average is 241 people.
The calculation is carried out similarly for any other reporting period. If you need a report for a quarter, then you need to add up the cash balance for each month of real activity and divide the resulting amount by 3. To calculate for six months or nine months, the resulting amount is divided by 6 or 9, respectively.
Algorithm for calculating the average headcount
The average headcount is calculated on the basis of primary documents reflecting the daily presence of employees at their workplaces. Such primary sources are:
- time sheets T-12 and T-13;
- personnel orders (on hiring, dismissal);
- orders for business trips, vacations of all types.
Question: How to take into account the only employee - an external part-time worker - when filling out Form 4 - Social Insurance Fund in terms of wages and average headcount? View answer
To fully calculate the SCN, data on all employees who are in an employment relationship with the employer are taken into account. It does not matter what type of contract is used for execution - an employment agreement/contract, a contract for temporary/seasonal work. If business owners/founders appear on payroll records, then, regardless of their employment status, information about these individuals must be taken into account in the calculations.
You need to know: all calendar days of the month are taken into account in the calculations of the MSS - including weekends and holidays. The number of working people is calculated based on the working day preceding the day off.
Workers hired on home-working terms are taken into account in the list of LLCs as full-fledged units.
Let's move on to the calculations
The average number of employees per month is equal to the sum of the number of employees for each calendar day of the month, divided by the number of calendar days in the month.
Please note: the calculation takes into account holidays (non-working days) and weekends. The number of employees for these days is equal to the payroll number for the previous working day. Moreover, if weekends or holidays span several days, then the payroll number of employees for each day will be the same and equal to the payroll number for the working day preceding the weekend or holiday. This condition is contained in paragraph 87 of the Resolution.
Example 1. LLC “Kadry Plus” employs 25 people under employment contracts. The established work schedule is a 40-hour, five-day work week. The headcount as of November 30 was 25 people.
From December 3 to December 16 inclusive, employee Ivanov went on his next annual paid leave.
On December 5, accountant Petrova went on maternity leave. To fill this position, from December 10, employee Sidorov was hired on the basis of a fixed-term employment contract.
From December 10 to December 14 inclusive, student Kuznetsov was sent to the company for practical training. No employment contract was concluded with him.
On December 18, 19 and 20, 3 people (Alekseeva, Bortyakova and Vikulov) were hired under an employment contract with a probationary period of two months.
On December 24, driver Gorbachev submitted his resignation and did not return to work the next day.
It is necessary to calculate the average number of employees for December.
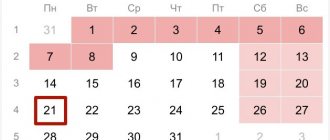
Weekends and holidays in December were the 1st, 2nd, 8th, 9th, 15th, 16th, 22nd, 23rd, 30th, 31st. Therefore, on these days the payroll number of employees will be equal to the payroll for the previous working days. That is, this figure on December 1 and 2 will be equal to the payroll number for November 30, December 8 and 9 - for December 7, and so on.
Of the workers listed above, the December payroll will include:
- Ivanov - from December 1 to December 31,
- Petrova - from December 1 to December 31,
- Sidorov - from December 10 to 31,
- Alekseeva - from December 18 to 31,
- Bortyakova - from December 19 to 31,
- Vikulov - from December 20 to 31,
- Gorbachev - from December 1 to December 24.
Petrov’s accountant is not taken into account in the average headcount (from December 5). And student Kuznetsov is not included in the payroll at all, since he does not hold any position in the company.
For clarity, let’s draw up a table that defines the payroll for December 2007:
The number of employees of LLC "Kadry Plus" in December 2007
| Day of the month | Headcount, people. | Of these, they are not included in the average headcount, people. | Included in the average headcount, people. (gr. 2 - gr. 3) |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| December 1 (day off) | 25 | 0 | 25 |
| December 2 (day off) | 25 | 0 | 25 |
| December 3 | 25 | 0 | 25 |
| December 4 | 25 | 0 | 25 |
| 5th of December | 25 | 1 | 24 |
| December 6 | 25 | 1 | 24 |
| December 7 | 25 | 1 | 24 |
| December 8 (day off) | 25 | 1 | 24 |
| December 9 (day off) | 25 | 1 | 24 |
| December 10 | 26 | 1 | 25 |
| December 11th | 26 | 1 | 25 |
| 12 December | 26 | 1 | 25 |
| December 13th | 26 | 1 | 25 |
| December 14 | 26 | 1 | 25 |
| December 15 (day off) | 26 | 1 | 25 |
| December 16 (day off) | 26 | 1 | 25 |
| December 17 | 26 | 1 | 25 |
| December 18 | 27 | 1 | 26 |
| December 19th | 28 | 1 | 27 |
| 20th of December | 29 | 1 | 28 |
| 21 December | 29 | 1 | 28 |
| December 22 (day off) | 29 | 1 | 28 |
| December 23 (day off) | 29 | 1 | 28 |
| December 24 | 29 | 1 | 28 |
| December 25 | 28 | 1 | 27 |
| September 26 | 28 | 1 | 27 |
| 27th of December | 28 | 1 | 27 |
| December 28th | 28 | 1 | 27 |
| December 29th | 28 | 1 | 27 |
| December 30 (day off) | 28 | 1 | 27 |
| December 31 (day off) | 28 | 1 | 27 |
| Total | 802 |
Let's calculate the average headcount for December:
802 person-days : 31 days = 25.87 people
In whole units it will be 26 people.
The rules for calculating the average number of employees for a quarter, year or other period are as follows: it is necessary to add up the average number of employees for each month of the period and divide by the number of months. For example, if you want to know the indicator for a quarter, then you need to divide by 3, if for a year - by 12. In this case, the indicator obtained for the month should not be rounded to whole units. Only the final result of the average headcount for the billing period is subject to rounding.
Categories of employees not taken into account in the calculation of the SCH
Each LLC employee who shows up for work or is absent for a valid reason is to be included in the calculation of the average headcount. Only employees classified in the following categories are not taken into account:
- employees permanently employed in another company, working in an LLC on an external part-time basis;
- founders or managers who do not have income in the form of wages;
- young mothers on maternity leave (including child care);
- lawyers and military personnel;
- employees sent on a foreign business trip;
- students signed up for a student agreement with a scholarship;
- students and applicants on leave without pay to take the examination session;
- persons working under GPC agreements;
- employees who have announced their resignation and do not perform their job duties before the expiration of the contract.
It should be remembered: in the calculations of the SCH intended for the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund, both external part-time workers and people working under civil contracts must be taken into account.
Who is not included in the list?
The calculation does not include specialists named in Rosstat Order No. 498. These include:
- external part-time workers – their records are kept separately;
- individuals who performed one-time functions under a civil contract (for example, consulting a doctor, performing artists, repairing equipment, conducting an examination, etc.);
- employees sent to serve abroad;
- persons hired under special contracts (military personnel, convicts);
- lawyers - never increase the number of workers;
- persons sent to another employer without salary;
- employees sent to study at an educational institution and receiving a scholarship;
- founders of the company who are not paid a salary;
- persons who voluntarily stopped going to work from the first day of absence.
The number of employees on the payroll is the number of specialists for whom this employer is the main one and who receive wages from him. If salary payment is suspended, the person is not counted for a specific period.
Formula for calculating MSS
To calculate the monthly average headcount, you need to know the initial data:
- duration of the calendar month (in days);
- the amount of all employees subject to accounting for a calendar month (in man-days).
The quotient of dividing the sum of man-days by the number of calendar days will be an indicator of the average headcount for the current month.
You need to know: the average headcount for a quarter, half-year or year is determined by the arithmetic average method. To do this, the monthly indicators of the SCH are summed up and divided by the number of months in the required period.
When calculating the SCH for the year for new organizations, the following rule is applied: regardless of the actual number of calendar months in which the newly created organization operated, the total number of months in the denominator of the formula is taken to be 12.
How to count part-time workers
It all depends on the basis on which part-time employment is applied.
If part-time work is an initiative of the employer or a legal requirement, such workers are considered a full-time employee. And if part-time work is established by an employment contract, staffing schedule or with the written consent of the employee, then in proportion to the time worked in the following order (clause 79.3 of Rosstat instructions No. 711):
- Calculate the total number of man-days worked. To do this, divide the man-hours worked by the length of the working day, based on the length of the working week:
- with a 40-hour work week - by 8 hours (with a 5-day work week) or by 6.67 hours (with a 6-day work week);
- at 36-hour - by 7.2 hours (with a 5-day work week) or by 6 hours (with a 6-day work week);
- at 24-hour - by 4.8 hours (with a 5-day work week) or by 4 hours (with a 6-day work week).
An example of calculating the “man-days” indicator to determine the average number of part-time workers from ConsultantPlus There are two employees at Alfa LLC - Sidorov A.D. and Samokhin N.I. work on a part-time basis. One - 6 hours a day, the other - 5 hours a day. Both employees have part-time working hours by agreement of the parties. In July 2020, Sidorov A.D. worked 23 days, Samokhin N.I. - 22 days. The organization operates on a five-day workweek schedule, so the working day is 8 hours (40/5). You can view the entire example in K+ by getting free trial access.
- The average number of part-time workers for the reporting month is determined in terms of full employment. To do this, divide the person-days worked by the number of working days according to the calendar in the reporting month. At the same time, for days of illness, vacation, absences, the hours of the previous working day are conditionally included in the number of man-hours worked.
Let's explain with an example (for a regular 40-hour 5-day work week).
The organization had 7 employees working part-time in October:
- four worked 23 days for 4 hours, we count them as 0.5 people (4.0: 8 hours);
- three - 3.2 hours a day for 23, 15 and 10 working days, respectively - this is 0.4 people (3.2: 8 hours).
Then the average number will be 2.8 people:
(0.5 × 23 × 4 + 0.4 × 23 + 0.4 × 15 + 0.4 × 10) / 22 working days in October.
For information on how long working hours can be, read the material “Normal working hours cannot exceed?” .
Human Resources Information
How is personnel assessment performed? Using generally accepted indicators, specialists analyze compliance with all requirements. If changes occur, then not only quantitative characteristics are assessed, but also qualitative ones. When analyzing indicators, deviations from the norms that were determined for previous periods are established.
Management can verify that workers comply with all standards. An increase in the company's staff, changes in the structure of work, and the emergence of means to increase efficiency must be taken into account.
Everything in the specialty Management
The state of personnel is characterized by the following indicators: 1. The number of employees (over the entire total, by position, etc.), including the calculation of attendance, payroll and average number of employees. The calculation is made on the basis of Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated December 15, 2003 No. 112 “On approval of the Procedure for filling out and submitting the federal state statistical observation form.” Attendance number is the number of employees on the payroll who showed up for work, according to the time sheet. I h = number of conditional jobs * hours of work per week / hours of work of an employee per week Hours of work of an employee per week - the full fund of working time plus time for carrying out preparatory and final operations for opening and closing the organization (15 minutes per day). The payroll number is the number of employees of an enterprise performing permanent, seasonal or temporary work for one day or more, both actually working and absent from work for any reason. Employees who are welcome to work on a part-time or part-time basis, as well as those hired on the floor. rates in accordance with the staffing schedule are taken into account in the payroll for each calendar day as whole units, including non-working days of the week. The number of employees on a weekend or holiday (non-working) day is taken to be equal to the number of employees on the previous working day. The following employees are not included in the payroll: - those performing part-time work from other organizations; - sent to work in other organizations if their wages are not maintained; — sent by organizations to study at educational institutions outside of work, receiving a scholarship at the expense of the organization; - those who submitted a letter of resignation (are excluded from the payroll from the 1st day of absence from work); — its owners who do not work in this organization; — hired to work under special agreements with government organizations to represent the workforce (military personnel). Headcount is a momentary indicator. The average headcount is the number of personnel determined on average for the corresponding period of time (month, quarter, year). The average payroll number is determined by summing the number of payroll employees for each calendar day of the month, including holidays and weekends, and dividing the resulting amount by the number of calendar days of the month. The number of employees on a weekend or holiday (non-working) day is taken to be equal to the number of employees on the previous working day. Ss. h. = (I h. * working days per year): (days of work of the seller per year) When determining the average number of employees, some payroll employees are not taken into account: - women who were on maternity leave, child care; — employees studying in educational institutions and on additional leave without pay. 2. Specific gravity (characterizes the structure of personnel).
The success of any work activity is characterized by its effectiveness. Labor efficiency is determined by the quantity and quality of services provided, the degree of satisfaction of demand and customer service, the speed of their service and is expressed by the following indicators: 1. labor productivity; 2. savings in consumption costs (customers’ time spent); 3. level of trade service (quality of service). Labor productivity as the amount of turnover per average employee in general, as well as for individual categories per unit of time. Consequently, labor productivity in trade is understood as the ability of a worker to sell a certain volume of goods per unit of working time, and the amount of time spent on selling a unit of goods is called labor intensity .
Labor productivity is calculated by 3 methods: in natural, value and labor terms. The choice of method for measuring labor productivity depends on accounting at a particular enterprise, its specialization, and the range of goods sold. 1. When using the natural method, this indicator has major disadvantages, because does not allow measuring labor due to the wide range of goods and the variety of units of measurement of these goods. It can be used when selling simple assortment goods (bread, milk, vegetables, etc.). Measuring PT by the number of customers is not used due to the fact that in trade it is very difficult and not always advisable to set a standard time for servicing customers, because this may be due to a deterioration in the quality of trade services; 2. The cost method is the most common, because allows you to measure labor productivity over time, but is also not without its drawback, because changes in the range of goods sold and in the level of prices for goods are not taken into account. Therefore, in order to determine the real dynamics of labor productivity, it is necessary in the analysis process to exclude the influence of changes in the structure of trade turnover and in the price level using labor intensity and price indices. 3. The labor method is the least common and consists of calculating the cost of working time to sell a unit of product. Consequently, its use depends on the state of labor regulation at the enterprise. It has its drawbacks. Thus, the use of standard hours does not take into account the complexity and quality of work. Necessary conditions for the application of this method are the same intensity of standards, the coverage of workers who are paid on a time basis. At the same time, in production practice, in analytical calculations when calculating the growth of labor productivity, the labor intensity indicator is widely used, i.e. labor time costs per unit of production in physical terms. Depending on the degree of coverage of labor costs, labor intensity can be full, technological and production. The full factory labor intensity of products takes into account the labor costs of all industrial production personnel, while the technological labor intensity takes into account the labor costs of only the main production workers. Accordingly, the labor intensity of products can be determined for all other more detailed categories and professional groups of enterprise employees. Labor intensity differs between normative, planned and actual. Standard labor intensity is determined on the basis of technical time standards, service standards, numbers, etc.; planned - based on standard labor intensity, taking into account measures aimed at increasing production efficiency and increasing labor productivity provided for in the planning period. Actual labor intensity indicates the real labor costs per unit of production in a certain period of time and is a mirror image of the labor productivity indicator. The task of constantly increasing labor productivity, and therefore reducing costs per unit of production, requires the search and use of all types of reserves. In this case, reserves are understood as opportunities to increase productivity both through the fullest use of growth factors and by eliminating various types of losses in the enterprise. The reserves for growth in labor productivity are diverse and possible at all levels of management and at all levels of production. All reserves can be classified as follows: 1. According to the source of labor productivity growth: - improvement in the use of means of production; — improving the use of labor. 2. By level of identification and use: - factory; - workshops; — brigade; - at work. 3. According to functional significance: - reserves of main production; — auxiliary production reserves; — control reserves. 4. By terms of possible use: - current; - promising. The problem of identifying and implementing reserves for increasing labor productivity, along with technical and organizational factors, is closely related to the social aspects of labor - a more complete account of the socio-economic and psychophysiological conditions of the production activities of workers, which include the creation of working and rest conditions, reducing staff turnover, reducing unproductive costs of the worker time, increasing the level of labor discipline, developing initiative and creative potential of employees. The labor productivity indicator performs the following functions: 1. Planned - is the most important, because Using productivity indicators, the planned number of employees is justified, the volume of labor costs is compared with their required quantity, and wage costs are calculated. 2. Accounting - manifests itself in measurement and evaluation, searching for possible reserves for productivity growth, assessing the efficiency of labor functioning in an enterprise by comparing the growth rate of labor productivity and average wages. 3. Stimulating - is implemented through the correspondence of the employee’s wage level to the level of his qualifications, as well as the growth of labor productivity. 4. Labor productivity is of great importance in the economy of an enterprise: - PT predetermines the volume of logistics, number of employees, material and technical base; — PT is an assessment indicator of the level of labor organization and use of personnel; — PT is used to assess the relationship between the growth rate of PT and the growth rate of average wages. Labor efficiency is achieving the final result at minimal cost. The goal setting must be related to the mission - to satisfy the increased needs for goods. Factors influencing labor efficiency: 1. External. 2. Internal: - general economic (volume and structure of trade turnover); - Labour Organization; — material incentives for labor; — social and psychological factors. An increase in labor productivity is of great importance: - economic effect (increase in trade turnover): EE = (P/t plan - P/t fact) * CR plan = +/- changes in turnover. — social effect (reduction of distribution costs).
Tasks of analyzing the number of resources: 1. Assessing the staffing level in the reporting year (ChR pl., ChR f., Specific weight pl., Specific weight ph.). - very rarely performed; — +/- change in PD = PD f. – CR pl. — +/- change ud. weight = beat. weight f. — Ud. weight pl. – assessment of qualitative changes in the personnel structure. — frame movement coefficients are calculated. 2. Identification of factors that influenced the state of personnel and quantitative measurement of this influence. Method of chain substitutions: CR = function (volume of salary; payroll) CR = sum of payroll / payroll (labor productivity) Sum of payroll = amount of full wages / level of the salary fund. CR = amount of the wage fund / level of the salary fund / payroll CR = amount of the wage fund / average salary per employee Amount t/o = (Output per hour * hours of work per day) * number of days per year CR = (Output hour * hours of work per day) * number of days in a year / p/t. 3. Analysis of the dynamics of the Czech Republic (in total by composition) for 2-3 years - +/- change in the Czech Republic over several years. Efficiency of personnel use: - labor productivity - Ef = sum t/o / CR = quality of trade service, = savings in consumption costs. — Price CR = total productivity / CR. 4. Proposals for improving personnel: - increasing material incentives, - improving the organization of work, - organizing team forms of work, - organizing work with long breaks, - improving the solution of social issues, - developing social packages. The initial data when planning HR at an enterprise are: - materials from HR analysis for the reporting year, - data on the development of the material and technical base of the enterprise, - measures to increase the quality of trade services. Methods of planning the CR: 1. Experimental economic: CR plan = CR fact. current +/- change in average CR 2. Economic-statistical: CR plan = CR fact * time t/o CR plan = amount t/o / p/t plan (through the elasticity coefficient of the dependence of CR on the volume of t/o). +/- change in PR = +/- change in t/o * elasticity coefficient. Elasticity coefficient t/o = +/- change in CR / CR: +/- change in t/o / amount t/o 3. Service standards: Area per seller for food products - 20 sq. m., for non-food products - 21 .5 sq. m. K urm – workplace staffing ratio K urm = sales floor area/area per employee Final number = Ss. h - replacement person (number) Ch.z. = manager's working hours department per week per week behind the counter / 40 hours (if the manager works at least 2 hours) If up to 0.5 hours - discarded, if more than 0.5 - equals one. Distribution of sellers by categories: senior and junior. By decision of the manager, taking into account working conditions, cashiers are calculated in a similar way (1 workplace - 1 cash register). Planning of administrative and managerial personnel (on approximate standard staffing levels) - taking into account economic feasibility (using controllability standards and a map of work performed). Support staff (approximate standard staffing levels, service standards),
Staff list of employees: sample
Information about the number of company employees is reflected in a special document - the staff list. This is a list of full-time specialists, regardless of the fact that they are currently in service, who retain their jobs.
The standard form contains the following information:
- name of the compiling organization;
- the date on which the information provided is current;
- job title;
- Full name of the employee;
- bid;
- an indication of whether the specialist’s work is the main one or whether he is hired as a part-time worker.
The frequency of filling out the document is not determined by law; the company decides how often to update the data. This can be done on the first day of every month. A special folder is allocated for finished documents. The shelf life of the papers is 75 years.
What does the list of employees mean? This is the number of hired specialists for a specific date, calculated in accordance with the explanations of Rosstat. The indicator is necessary for internal analytics at the enterprise and reporting to the fiscal authorities. This is the reference point for determining the average headcount.
Methods for filing SCR in 2021
The average number of employees can be submitted:
- In paper form (in 2 copies). One copy will remain with the tax office, and the second (with the necessary marking) will be returned. It will serve as confirmation that you have submitted the declaration.
- By mail as a registered item with a description of the contents. In this case, there should be an inventory of the investment and a receipt, the number in which will be considered the date of delivery of the number.
- In electronic form via the Internet (under an agreement through an EDF operator or a service on the Federal Tax Service website).
note
, when submitting SCR information in paper form, some Federal Tax Service Inspectors may additionally require you to attach a file with an electronic version of the report on a floppy disk or flash drive.
Categories
All employees are divided into 2 groups according to employment option. This must be taken into account to perform headcount calculations. One category includes workers, and the other includes employees. There are much more of the former than the latter.
The employees are the leaders. These include accountants, engineers, economists, editors, and researchers. It is important to correctly categorize everyone so that the documentation is compiled correctly.
The document indicates information about the departure and arrival of workers. The “arrival” indicates where the new employee came from. And in “departure” the type of dismissal is indicated. This distribution allows you to quickly navigate through the compiled documentation.
Report requirements
The document is drawn up in the prescribed form. There are many types, but there is one suitable for every occasion. Only then will it be possible to accurately determine the number of employees. This is necessary for proper document management. In this case, all notes are made based on the originals. For example, if an employee is sick, then it is prohibited to make changes without a sick leave.
Another important point is the transfer of departments or employees between companies. In this case, you can delete a person from the document only in the next period. Data entry is also carried out. If an error is noticed, changes must be made to the report in which the problem appeared.
The average headcount is used to identify labor productivity, average wages, and turnover. A calculation for a specific period is required. To determine the average headcount, it is necessary to divide the number of employees by the number of days in a month (including workdays and holidays).
Where to take the SChR in 2021
A report on the average number of employees is submitted to the tax authority:
- Individual entrepreneur - at the place of residence;
- LLC - at its location (legal address).
The address and contact details of your tax office can be found using this service.
Note
: the average number of employees by location of separate units does not need to be submitted. Data on department employees is indicated in a general report for the entire organization, which is submitted to the Federal Tax Service of the head office.
Indicators of changes in the number of personnel on payroll
To assess personnel turnover, its importance for the enterprise and its features, indicators of changes in the number of employees are used. These include the following:
- Hiring turnover ratio is calculated by dividing the number of specialists hired over a certain period of time by the average number of personnel (ASN) of personnel for the same period.
- Attrition turnover ratio is obtained by dividing the number of employees who have left (regardless of the reasons for leaving the organization) by the personnel average.
- Replacement rate - you need to find the difference between newly hired and fired employees, and then divide the result by the average.
- Personnel constancy coefficient is obtained by dividing the number of employees who worked the entire time interval by the total number of employees for the same period.
To assess staffing levels, it is not enough for management to know how to determine the number of employees on the payroll; they need to be able to evaluate the indicator over time. For example, if the replacement rate is positive, the company is expanding its workforce and developing new capabilities. The larger it is, the faster the recruitment rate.
A negative coefficient value indicates a reduction in staff. Possible reasons for this are a reduction in production, crisis phenomena at the enterprise.
The staff retention rate shows what the payroll means in terms of loyalty to the employer. If this indicator grows, the company’s personnel policy is improving; if it falls, the turnover of employees is high, and this is an “alarm bell” for management.
Nuances and difficulties
In addition to persons on maternity leave, there are other categories of employees that cause controversy when calculating staff numbers. For example, the question often arises whether the owners of the enterprise are included in the SC. According to paragraph 77 of the Rosstat Instructions (approved by Rosstat Order No. 772 dated November 22, 2017), the answer to this question is affirmative, provided that the owners worked and received wages. Paragraph 78 of the document also contains commentary regarding internal part-time workers. Each of them is counted as one person in the account balance. As for persons who have an employment contract and a work contract with the organization at the same time, they, in accordance with paragraph 78 of the Instructions, are taken into account in the SCH and SSC once at their main place of work.
Labor resource assessment
Thanks to the workforce, the specifics of the enterprise's activities are reflected. The main goal of management is to ensure maximum productivity. To do this, management evaluates the staff structure in order to:
- the company had the necessary labor resources;
- there was an improvement in labor efficiency;
- there was rational use of the wage fund.
Data sources through which these tasks are solved include reporting documents. They are compiled by personnel department employees.
Changes in the company's roster
What is the list of employees of the enterprise? This is not a static value, but an indicator subject to constant change. In a truly functioning enterprise, staff departures and the hiring of new specialists under labor contracts regularly occur. The need for employees changes depending on what stage the company is going through: rapid growth or crisis.
The number of payrolls increases due to the selection of personnel carried out from two sources:
- External
Searching for workers from the outside: through newspaper advertisements, specialized websites, recruitment agencies.
- Internal
Development of employees within the company, promotion through the “career ladder”. This option is cheaper than the first and strengthens the attachment of specialists to the company. Its disadvantage is the lack of new employees with fresh views.
The departure and recruitment of new specialists, regardless of the methods and reasons, is called personnel turnover.