From the beginning of the new reporting period, the taxpayer was assigned the obligation to declare contributions also to the Federal Tax Service. Full responsibilities, from January 2021, control over contributions to compulsory pension insurance and compulsory medical insurance were transferred to the subordination of employees of the Russian tax service. If it is necessary to reconcile the transferred taxes and contributions, payers will have to resolve all issues regarding debt or overpayment with the tax authorities. It is now the responsibility of the Federal Tax Service to collect arrears, impose penalties and fines. In this article we will talk about benefits on insurance premiums and consider the calculation procedure.
general characteristics
The money that the employer transfers for the employees of his organization gives citizens the opportunity to count on receiving several types of payments in the future:
- Pension provision.
- Disability benefits.
- Other benefits of a social nature.
At the moment, all financial resources that are transferred in this way to the country’s budget are immediately used to provide disabled citizens with all the social benefits they are entitled to.
Reducing the cost of taxes on insurance premiums
In general, this entire process is regulated in tax legislation.
Re-registration as an individual entrepreneur and tax holidays
If an individual entrepreneur was previously engaged in entrepreneurial activities, but was deregistered with the tax office, but after some time he decided to register again with the Federal Tax Service, then he can also take advantage of the right of tax holidays .
The date of deregistration is important; it must be earlier than the date of the regional law giving the right to use the benefit. Accordingly, from the point of view of legislation, repeated registration after the date of adoption of the law is equal to the initial one.
Changing tariffs
Let's take a closer look.
Cancellation of benefits
The preferential rates for social contributions were abolished for the two largest categories of payers for whom it was most convenient to enjoy the privileges:
- Entrepreneurs.
- Companies under special regimes.
This category of beneficiaries previously had the opportunity to pay only contributions to the Pension Fund in the amount of 20% of the wages of their employees.
A large number of entrepreneurs and organizations fell under the terms of the benefit, thanks to which they had the opportunity to officially employ people for themselves, and at the same time save their money without making much effort.
So, if these organizations had officially employed persons, then the company could save up to 10% of the payroll precisely by making such contributions.
Attention! This benefit existed until 2021, when it was refused to be extended. Now this preferential category of payers does not enjoy any benefits and is obliged to pay the full amount of contributions for their employees - 30%.
Who doesn't have to pay fees?
Who is entitled to benefit?
Since 2021, new benefits have been introduced into the legislation, which will be valid until 2024. All categories except those listed above can take advantage of the benefits, although interest rates will also increase for them.
To take advantage of the benefits, the organization must meet a number of conditions:
- Have sufficient turnover.
- Business should be considered rare.
- The organization must confirm its status.
For each type of activity, the legislation provides for its own requirements. For example, this may be a requirement that the organization be in a special reserve, have a sufficient number of employees, or obtain a document indicating the existence of the status.
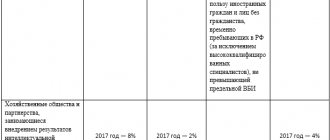
Reduced rates
| Type of payers | Rates, % | ||
| Pension insurance | Social insurance | Health insurance | |
Russian organizations that work in the field of information technology and are engaged in:
| 8,0 | 2,0 | 4,0 |
| Organizations and entrepreneurs with payments and remunerations for the performance of labor duties to crew members of ships registered in the Russian International Register of Ships (except for ships for storage and transshipment of oil and petroleum products in Russian seaports) | |||
Non-profit organizations that use the simplified approach and operate in the field of:
Exception: state and municipal institutions | 20,0 | ||
| Charitable organizations simplified | |||
| Organizations participating in the Skolkovo project | 14,0 | ||
| Organizations and individual entrepreneurs that have received the status of participant in a free economic zone in accordance with Federal Law No. 377-FZ dated November 29, 2014 “On the development of the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol and the free economic zone in the territories of the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol” | 6,0 | 1,5 | 0,1 |
| Commercial organizations and entrepreneurs with the status of residents of the territory of rapid socio-economic development in accordance with Law dated December 29, 2014 No. 473-FZ | |||
| Commercial organizations and entrepreneurs with the status of residents of the free port of Vladivostok in accordance with the Law of July 13, 2015 No. 212-FZ | |||
| Organizations with resident status of a special economic zone in the Kaliningrad region in accordance with the Law of January 10, 2006 No. -FZ | |||
| Russian organizations that produce and sell animated audiovisual products they produce | 8,0 | 2,0 | 4,0 |
Federal Law of November 29, 2014 N 377-FZ “On the development of the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol and the free economic zone in the territories of the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol”
Federal Law of December 29, 2014 N 473-FZ “On territories of rapid socio-economic development in the Russian Federation”
Federal Law of July 13, 2015 N 212-FZ “On the Free Port of Vladivostok”
Federal Law of January 10, 2006 N 16-FZ “On the Special Economic Zone in the Kaliningrad Region and on Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation”
Contribution rates for employers
Until 2021, insurance premium rates were considered temporary, since they were planned to increase from 2021. However, this decision was later revised, and all rates were transferred to the category of constant, that is, their increase is not planned.
- The rate for pension insurance is 22% - the maximum value and 10 percent if it is exceeded.
- Insurance premiums for temporary disability - 2.9%.
- Health insurance is 5.1%.
- Personal injury premiums range from 0.2% to 8.5%.
Distribution of insurance premiums
Features of insurance coverage in 2021
From January 1, 2017, the procedure for calculating and paying insurance coverage for individuals in Russia has been changed. The new order is established:
- Tax Code, namely chapters 2.1 and, regarding insurance premiums administered by the Federal Tax Service;
- Federal Law No. 125-FZ dated July 24, 1998 regarding the FSS NS and PZ. Federal Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009 lost its force on December 31, 2016.
Based on current legislation, some policyholders may qualify for a significant reduction in the amount of mandatory payments for insurance coverage. The procedure for applying reduced insurance premium rates (benefits) for policyholders in 2021 is determined by:
- Art. 427 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- Art. 21 No. 125-FZ (in 2017-2020, clause 2 of Federal Law No. 419-FZ dated December 19, 2016 was defined).
From 2021, preferential categories of legal entities specified in Art. 427 of the Tax Code, there is no need to specifically notify the tax authorities about the application of reduced tariffs and wait for an official response (permission or refusal). Information on the application of the benefit will be determined from a single calculation of insurance premiums at a reduced tariff, but documentary evidence will exclude requests and clarifications from regulatory authorities.
Conditions under which preferential rates apply
Individual business entities have the right to expect to receive certain concessions when determining the amount of payments transferred to the funds.
In particular, companies that are engaged in activities aimed at introducing the results of intellectual work and their partners have the right to take advantage of such privileges. The amount of preferential rates for such organizations in 2021 is:
- Pension insurance - 20%.
- Disability contributions are 2.9% for foreign employees and 1.8% for stateless persons.
- Medical insurance - 5.1%.
In order for a company to benefit from preferential tariffs, it must fulfill several conditions:
- Carrying out development and design activities.
- All activities should be carried out in a simplified manner.
- The register must contain information about the creation of this company.
Companies and individual entrepreneurs who are engaged in:
- Technology and innovation activities.
- Tourist and recreational activities.
Preferential rates for this category of organizations are similar.
Resident organizations that develop information systems and software have the right to use other preferential tariff rates:
- 8% of wages is transferred to the Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund.
- Health insurance premiums are 4%.
But you can take advantage of such benefits only if a number of conditions are met:
- There is a document confirming accreditation.
- The income received from the main activities of the company is 90% for the reporting period.
- The average number of employees is more than 7 people.
Legal entities and entrepreneurs who have one of the following statuses can take advantage of benefits when paying contributions:
- Member of the free economic zone.
- Resident of a zone with advanced socio-economic development.
- Resident of the port of Vladivostok.
The lowest contribution rates apply to this category of payers:
- Pension insurance is only 6%.
- In case of temporary disability - 1.5%.
- For health insurance - 0.1%.
Benefits are provided for ten years from the date of registration of the corresponding status.
Reporting on insurance premiums
The sliders below list all the reporting that needs to be submitted for insurance premiums in 2021:
Reporting to the Federal Tax Service
Starting from 2021, insurance premiums must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service every quarter. The calculation is submitted no later than the 30th day of the first month of the next quarter. Thus, in 2021 it must be passed:
- for 2021 – no later than February 1, 2021;
- for the 1st quarter of 2021 – no later than April 30, 2021;
- for the first half of 2021 – no later than July 30, 2021;
- for 9 months of 2021 – no later than November 1, 2021;
- for 2021 – no later than January 31, 2022.
Starting with reporting for 2021, the DAM must be submitted in a new form, approved by Order No. ED-7-11 / [email protected] dated 10/15/2020.
Reporting to the Pension Fund
Every month you need to submit a report to the Pension Fund in the SZV-M form, which contains information about working pensioners. The deadline for submitting the report is no later than the 15th of the next month.
Once a year, it is necessary to submit the SZV-STAGE form to the Pension Fund of Russia, which reflects information about the insurance length of the insured workers. This report must be submitted no later than March 1 of the following year.
Payments not subject to contributions
First of all, income that is not subject to insurance premiums includes amounts that are not subject to taxation.
For example, payments and rewards that were received by a person under a gift, lease, loan and sale agreement. Contributions do not accrue for dividends either, since taxes are not paid on them.
The legislation also lists several other payments for which insurance premiums are not calculated:
- Benefits for temporary disability, BIR, child care.
- Daily payments.
- Material assistance, the amount of which does not exceed 4,000 rubles per employee.
Who applies the benefits?
By law, the person who pays the premiums is the insurer for all of his employees. Among such payers are:
- Organizations where employees work under an employment contract or a GPC agreement.
- Individual entrepreneur.
- Individuals, if they are sources of income for other citizens, even if they do not have the status of an entrepreneur.
- Individuals engaged in the practice of law or providing notarial services.
Attention! Individual entrepreneurs, lawyers and notaries must additionally pay insurance premiums for themselves.
Receiving benefits
The moment of accrual of a person’s income and all payments due to him is determined by the date of such accrual.
Most often this is the last day of the billing period. Accordingly, until this moment the organization does not have any arrears in contributions. But not everyone can take advantage of such conditions. For example, individual entrepreneurs, lawyers and notaries are required to pay contributions from the date of their insurance. That is, the absence of hired workers on the staff cannot be a reason for non-payment of contributions, since this category of citizens is obliged to contribute funds for themselves.
All payers independently determine the size of their contribution rates. The main indicators take into account the Tax Code article and several conditions:
- The period of time during which the payer carries out its activities.
- Number of employed workers.
- Revenue volumes
- Type of preferential activity.
Attention! If an organization uses two taxation systems at once, then all preferential income should be taken into account separately. If this condition is not met, the payer loses his right to receive benefits.
Recipients and validity period of individual entrepreneur tax holidays
Tax holidays for individual entrepreneurs were introduced in 2015. Initially, it was assumed that this measure of support for Russian entrepreneurs would be temporary, but it proved to be quite effective, so officials decided to extend the duration of the benefit. It is currently known that tax holidays for individual entrepreneurs will be valid until 2023 .
Newly registered individual entrepreneurs who have chosen the USN or PSN as their taxation system can take advantage of the right. The following tax holiday periods are provided:
- under the simplified tax system - the maximum period is set at 2 calendar years (when registering in the middle of the year, the rest of the current year and the next one are taken into account)
- with PSN – the validity period of 2 patents (if the first patent is issued for 12 months, and the second for 6, then the tax holiday will last 18 months)
Insurance contributions from the self-employed population
Self-employed citizens are individuals who are engaged in private practice and individual entrepreneurs who are required to make contributions to the fund, regardless of whether they have employees or whether they have received any income.
For this category of payers, several types of tariffs are provided:
- With incomes of less than 300,000 rubles, you will have to pay for pension insurance according to the formula 12 months * equal to the minimum wage * 26%.
- If a person’s income exceeds 300,000 rubles, then in addition to the basic payment for pension insurance, the payer must transfer 1% of the amount exceeding the minimum threshold.
- Contributions for compulsory medical insurance are fixed and do not depend on the amount of income received: 12 months * by the minimum wage * by 5.1%.
The law provides for several situations in which a person may be exempt from paying contributions:
- Completion of emergency service.
- BIR leave.
- Holiday to care for the child.
Write-off of contributions for the 2nd quarter. 2021
Federal Law No. 172-FZ dated 06/08/2020 for individual entrepreneurs affected by coronavirus reduced the monthly fixed contributions to compulsory pension insurance (for themselves) by 1 minimum wage for the entire 2021 - from 32,448 rubles. up to 20,318 rubles.
Also, Federal Law No. 172-FZ dated 06/08/2020 for organizations and individual entrepreneurs affected by coronavirus canceled (reset to zero) insurance premiums for the 2nd quarter of 2021 - from payments to individuals accrued for April, May and June 2021.
For more information, see “Features of payment of insurance premiums by organizations and individual entrepreneurs for the 2nd quarter of 2020.”
Responsibility for individual entrepreneurs
If an individual entrepreneur does not make payments within the time limits specified by law or does not transfer them in full, he may be held liable in the form of a fine.
The penalty is 20% of the amount not transferred to the funds. If such non-payment was made intentionally, the fine increases to 40%. Most often, territorial authorities apply only penalties to such a violator, but only if the payment was made within a short period of time and the amount of the debt turned out to be small.
Penalties are accrued regardless of what exact penalties were applied to the debtor. The accrual is made in the amount of 1/300 of the refinancing rate.