Home / Taxes / What is VAT and when does it increase to 20 percent? / Book of purchases and sales
Back
Published: November 20, 2018
Reading time: 4 min
0
542
The purpose of maintaining a purchase ledger is to determine the amount of VAT that is subject to deduction. In it, buyers must register invoices issued by sellers, received on paper and electronic media.
- Transaction type code in the purchase book
- How to reflect the advance refund
- Filling out the declaration
It contains primary invoices, as well as adjustment and corrected invoices.
Transaction codes in the VAT return
In some sections of the VAT return there are columns called “Operation code”. These are sections such as:
- section 2 – to be filled out by tax agents;
- sections 4-6 - filled out by organizations and individual entrepreneurs who had export operations;
- section 7 - filled out by organizations and individual entrepreneurs for transactions that are not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation), transactions that are not recognized as an object of taxation, transactions for the sale of goods (work, services), the place of sale of which is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation, as well as for payment amounts, partial payment on account of upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), the duration of the production cycle of which is more than 6 months.
As you can see, with certain codes, the declaration reflects not ordinary transactions for the sale of goods on the territory of the Russian Federation, but “special” VAT transactions.
All VAT transaction codes are given in Appendix No. 1 to the Procedure for filling out the declaration (approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/558).
View codes for VAT returns with explanations
If you do not fill in the necessary codes in the declaration, the declaration will not pass format-logical control and will not be accepted by the tax authority.
Read also
05.10.2016
Which columns of the purchase book must be filled in when specifying code 22
If an entry is made in the purchase book for an invoice with transaction type code 22, the following columns are filled in:
Let's look at an example of how to fill out a purchase book with transaction code 22:
Elektrozavod LLC entered into an agreement with Rotor PJSC for the supply of electric motors. The cost of delivery is RUB 3,349,960. The supplier works on a 40% prepayment basis. The buyer agreed to these conditions and made an advance payment in the amount of RUB 1,339,984. (including VAT = RUB 223,330.67). Elektrozavod LLC formalized the receipt of the advance with an invoice dated July 23, 2020 No. A412 and reflected this in its sales book with code 02.
Elektrozavod LLC shipped a batch of electric motors to Rotor PJSC in August and issued an invoice dated August 29, 2020 No. 464 in the amount of RUB 3,349,960. (including VAT = RUB 558,326.67). The supplier reflected this operation in his sales book with code 01. And in the purchase book he registered an invoice for prepayment previously issued by Rotor PJSC.
Elektrozavod LLC filled out the columns in the purchase book as follows:
Below is shown how the seller Elektrozavod LLC will reflect the deduction from advance VAT using code 22 in the purchase book:
Find out about the rules for filling out field 22 in a payment order here.
When the return will be a reverse implementation
As a rule, when returning goods, no one enters into a separate purchase and sale agreement, in which the buyer becomes the seller and the seller becomes the buyer. Therefore, it is not easy to immediately imagine the situation that the Ministry of Finance is talking about.
But even if there is no such agreement, reverse implementation may occur. Look carefully at the original contract. Does it contain a condition on the repurchase of goods by the seller? For example, if the buyer was unable to sell them before a certain time. This is the reverse implementation, in which the buyer must create an invoice.
The next point is important here. To avoid claims for deduction, the contract should clearly state that the return of the goods is carried out by return delivery, in which the buyer is the seller and the seller is the buyer. Then the inspectors will have no reason to find fault with the invoice (it will not be an adjustment, but a regular one). If there is no such specificity in the contract, claims are possible against any execution of the transaction:
- You made an adjustment invoice, and the tax office says: “You have a buyback, you need an invoice from the buyer” - and removes the deduction.
- Or, on the contrary, you have issued a return delivery, and the controllers tell you: “You don’t have anything written about return delivery, it says about a return” - and you also lose your deduction and are forced to go to court.
So review your contracts and make changes if necessary.
By the way, buyback is possible not only for unsold quality goods, but also for defective ones (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated May 15, 2019 No. 03-07-09/34582, No. 03-07-09/34591).
Results
Code 22 in the purchase book in 2020-2021 is indicated in the case when the VAT calculated for payment from a previously received advance is accepted for deduction when the terms of the contract are changed or terminated. The same code is reflected in the purchase book when deducting advance VAT at the time of shipment for which such an advance was previously received.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/136
- Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 23, 2018 No. SD-4-3/ [email protected]
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What an exporter of goods to Belarus needs to know: legal acts and VAT rate
Belarus is a member of the Customs Union (CU) and is subject to the rules in force on the territory of the CU member countries. When exporting goods by Russian suppliers to the territory of this republic, it is necessary to comply with the norms of the relevant legal regulations:
- Clause 1 Art. 72 of the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union (signed on May 29, 2014) - this clause determines that in mutual trade between the member countries of the Customs Union, indirect taxes are collected according to the principle of the country of destination, which provides for the application of a zero VAT rate and (or) exemption from excise taxes when exporting goods .
- Appendix No. 18 to the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) - it describes the procedure for collecting indirect taxes when exporting goods and the mechanism for monitoring their payment.
The following figure will help you become more familiar with this procedure in relation to the export of goods from Russia to Belarus:
Document movement report
Let's carry out the adjustment document and check what postings we have as a result.
Fig. 10 Document movements
We see that, having reflected the adjustment in the document, the program generated the necessary transactions. The document also made entries in the “Purchase VAT” accumulation register.
Fig. 11 VAT purchases
If the “Generate transactions” checkbox is not checked by the user, then when posting, entries will be made only in the “Purchase VAT” accumulation register.
Fig. 12 Generate transactions
Fig. 13 Changing VAT amounts manually
Thus, the program allows the user to make changes to VAT amounts manually. In this case, all changes are reflected in the reporting.
Contractual insurance against unscrupulous buyers
In order to somehow protect yourself from careless buyers from the EAEU, provide special conditions in your contracts with them. For example:
- The buyer's obligation to pay a fine (compensating for the seller's losses from paying VAT and penalties on it) if the import application is not received from him within the agreed period (for example, no later than 160 days from the date of shipment).
- An indication of the judicial authority (Russian or Belarusian) in which the dispute will be heard if the buyer refuses to pay penalties. It is no secret that it is better to protect your interests on your own territory with the participation of competent lawyers.
The “penalty” element of the contract may look like this:
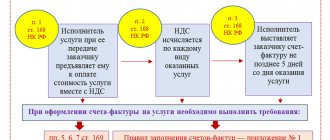
Features of filling out an amended invoice
In both forms of the corrected invoice, under the main heading of the document containing its number and date, a line (or lines) is provided for entering the number and date of the correction:
- there is only one line in the invoice, and it is located directly under the heading;
- in the adjustment invoice—2: one is intended for information about the correction of the adjustment invoice itself, and the second is for indicating the details of the original invoice for which the adjustment invoice was drawn up.
There are no other features in the design of the corrected invoice. It is formatted in the same way as a regular one, only incorrect data in it is replaced with correct ones.
Features of registering an amended invoice
If the correction invoice is issued in the same quarter as the original invoice (adjustment invoice), then in the same quarter:
- The seller must register the corrected invoice in the sales book and re-register the erroneous invoice, but reflect all its numerical indicators with a minus sign.
ConsultantPlus experts have prepared an example of registering a corrected invoice in the sales book. Go ahead and get trial access to K+ for free.
- The buyer, if he has reflected an erroneous invoice in the purchase book, must register a corrected invoice in the purchase book and re-register the erroneous invoice, but reflect all its numerical indicators with a minus sign. If the buyer has not shown an erroneous invoice in the purchase ledger, he only records the corrective invoice.
An example of registering a corrected invoice in the purchase book is available in the ConsultantPlus system. Get trial access to the system for free.
In the diagram, we showed the procedure for the seller and buyer when the data in the invoice changes or if there are errors in it.
If the corrective invoice was drawn up in another (next) quarter:
- The seller must record the corrected invoice on an additional sheet of the sales ledger for the quarter in which the erroneous invoice was recorded. In the same additional sheet of the sales book, register the erroneous invoice, indicating all its numerical indicators with a minus sign.
- The buyer must draw up an additional sheet to the purchase book for the quarter in which he registered the erroneous invoice and, in the same additional sheet to the sales book, register the erroneous invoice, indicating all its numerical indicators with a minus sign. If the buyer initially did not reflect the invoice issued with errors in the purchase book, then the corrected one must register the corrected invoice only in the purchase book of the quarter in which this document was received.
What can prevent you from confirming your export on time?
Even if the exporter conscientiously approaches the procedure for collecting documents, there is no complete confidence that he will meet the deadline allotted by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation to confirm the validity of applying the zero VAT rate. This is due to the fact that the set of supporting documents includes an application for the import of goods, which the buyer must hand over to the supplier. And it is difficult to influence the actions of a buyer (especially one located abroad). At the same time, the absence of an application for the import of goods deprives the seller of a tax preference in the form of a zero VAT rate (if the buyer has not paid the tax).
The main difficulty in obtaining such a document is that the Belarusian buyer must pay the tax, put a stamp on the application with his tax authorities about payment and, with such a mark, transfer the application to the supplier.
It happens that the export seller was unable to receive an application because the buyer:
- for some reason I did not send the application, although I paid the tax;
- did not pay the tax and did not send anything to the seller;
- I sent the application, but without a tax payment mark.
There are two possible scenarios here:
- If the Belarusian buyer has paid the tax, the situation is not hopeless - Russian tax authorities can check the fact of tax payment in their database (within the framework of electronic information exchange), and the supplier himself can check in a special electronic service on the Federal Tax Service website.
- If the tax is still not paid, the Russian export seller will not be able to confirm the zero rate.
We will tell you in the next section what a supplier can do to protect itself from possible material losses due to unscrupulous buyers.
Nuances of calculating advance VAT during the transition period 2018-2019
From January 1, 2019, the VAT rate increased from 18% to 20%, and the estimated tax rate also changed from 18/118 to 20/120 and from 15.25 to 16.67% (Law No. 303-FZ dated August 3, 2018). Business operations were not interrupted in connection with such innovations: in 2021, suppliers received advances from buyers for shipments that occurred or were yet to occur in 2021. But this did not in any way affect the design of purchase and sales books and the codes of transaction types in them. The codes must be the same as in 2021.
How to cope with the nuances of the transition period was explained by the Federal Tax Service of Russia in a letter dated October 23, 2018 No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] The procedure for the buyer and seller according to the tax service’s methodology is presented in the figure below:
Let us explain the procedure proposed by the Federal Tax Service using an example.
In November 2021, the office furniture supplier Mebelshchik LLC received an advance payment in the amount of RUB 276,000 from the buyer Service Center PJSC. From this amount, Mebelshchik LLC calculated VAT:
276,000 × 18/118 = 42,101.69 rubles.
In January 2021, furniture was shipped to PJSC Service Center in the amount of RUB 233,898.31. The supplier charged VAT on this transaction at a rate of 20%:
233,898.31 × 20% = 46,779.66 rubles.
VAT accrued on prepayment in November 2021 was accepted for deduction in the amount of RUB 42,101.69.
Transactions with VAT from the buyer PJSC "Service Center":
- after the prepayment is transferred, VAT in the amount of RUB 42,101.69 is accepted for deduction;
- after receiving the furniture, tax in the amount of RUB 46,779.66. accepted for deduction with the simultaneous restoration of VAT in the amount of 42,101.69 rubles. with prepayment.
Find out what a taxpayer should do if an additional 2% VAT is paid due to an increase in the tax rate from this publication.