Home / Taxes / What is VAT and when does it increase to 20 percent? / Declaration
Back
Published: 07/28/2017
Reading time: 7 min
0
324
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation taxes the sale of goods for export at a rate of 0%. The application of the zero rate must be confirmed by the availability of a package of documentation. There are 180 calendar days for its collection. The start of the 180-day period coincides with the date of shipment for export operations to the EAEU countries, and to other countries - with the date of placing the goods under the customs procedure.
The conditions for confirming the application of the 0% rate are the presence of:
- a taxpayer’s contract with a company or authorized person for sales abroad;
- customs declaration, which notes that the goods were released for export with inspection, with a mark on crossing the border at the control point (airport, etc.);
- copies of transport and accompanying documents for the goods with marks from the customs authority;
- a contract drawn up for an intermediary person if the sale of goods is carried out through an agent or by proxy.
A 0% rate is applied when exporting when the contract is signed by both parties. In particular, from 2021 it is necessary to present papers and certificates confirming the mutual agreement of the parties regarding issues of price, sales, and other factors. It is also necessary to indicate the details of all persons involved in the transaction, clearly describe the products, nuances of quantity or weight, dimensions, etc.
The company may exercise the right to claim tax deductions for export transactions.
- Filling rules
- Section 4
- Section 5
- Section 6
Subtleties in accounting for VAT on an unconfirmed export transaction
VAT information is included in Section 6 of the declaration if there are export sales during the reporting period. The tax rate at the time of sale is 0%. You can use the bet if:
- goods sold and exported abroad of the Russian Federation;
- the accountant provided the Federal Tax Service with a special package of documents within 180 days that confirm the right to apply the preferential rate;
- sales for export are reflected in the declaration.
The list of documents with a zero VAT rate that prove the existence of an export transaction includes:
- the purchase and sale agreement and any attachments or specifications;
- statement of transactions from the bank on received export proceeds;
- accompanying package of documents for the goods: shipping and delivery note, invoice, waybill, power of attorney from the buyer (if necessary);
- quality certificate for the product, including sanitary and veterinary;
- application for payment of indirect tax and import of products;
- VAT declaration.
The organization must submit a list of documents simultaneously with the declaration, which indicates the amount of VAT on exports. If the organization does not meet the 180 days allotted for collecting documents, then VAT will have to be charged and the transactions reflected in section 6 of the declaration.
Setting up accounting policies and accounting parameters in “1C: Accounting 8”
In accordance with clause 3 of the Protocol on the procedure for collecting indirect taxes and the mechanism for monitoring their payment when exporting and importing goods, performing work, providing services (Appendix No. 18 to the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union), when exporting goods from the territory of one member state EAEU to the territory of another EAEU member state:
- a zero VAT rate is applied when submitting to the tax authority the documents provided for in paragraph 4 of the Protocol;
- the right to tax deductions is exercised in a manner similar to that provided for by the legislation of a member state of the Eurasian Economic Union in relation to goods exported outside the EAEU.
A taxpayer carrying out transactions taxed at a 0 percent rate must make the appropriate program settings.
On the VAT tab of the Accounting Policy form (menu Main -> Settings -> Accounting Policy), set the checkbox Separate accounting of incoming VAT and Separate accounting of VAT on account 19 “VAT on purchased values”.
In the accounting parameters settings (menu Administration -> Program Settings -> Accounting Parameters) by following the hyperlinks Setting up a chart of accounts and By counterparties, invoices received and accounting methods, set the parameter Accounting for VAT amounts on purchased assets to: flag in the line with the value By methods accounting.
After making the settings, in the tabular part of the documents of the accounting system Receipt (act, invoice) with the transaction type Goods (invoice), the column VAT accounting method will appear. This column displays information about the selected VAT accounting method, which can take the following values:
- Accepted for deduction;
- Included in the price;
- Blocked until confirmation 0% (until 07/01/2016 - For transactions at 0%);
- Distributed.
Please note that for all goods received by exporters before 07/01/2016, for which the VAT accounting method was set to For transactions at 0%, the accounting method will be automatically changed to Blocked until 0% is confirmed.
In order for the VAT Accounting Method value to be filled in automatically in the Receipt document (act, invoice), you need to use the settings for the information register of the Item Accounting Account (menu Directories -> Goods and Services -> Items).
From 07/01/2016, in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (as amended by Law No. 150-FZ), the procedure for deducting input VAT on the acquisition of goods (work, services), property rights for operations involving the sale of goods for export using a tax rate of 0%, including to the member states of the EAEU, depends on whether or not the exported goods are raw materials (clause 10 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by Law No. 150-FZ).
So, if a taxpayer exports non-commodity goods:
- deduction of the presented amount of VAT in relation to purchased goods (work, services), property rights registered on July 1, 2016 (clause 2 of Article 2 of Law No. 150-FZ) is carried out in the generally established manner, i.e., similar to the deduction for goods (works, services), property rights acquired for carrying out transactions subject to VAT at rates of 18% and 10% (clause 3 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- The taxpayer does not have the obligation to determine the amount of VAT relating to goods (work, services), property rights acquired from 07/01/2016 for the production and (or) sale of goods using a 0% rate, i.e. there is no obligation to maintain separate accounting (para. 2 clause 10 of article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by Law No. 150-FZ).
Please note that if the taxpayer carries out only VAT-taxable transactions in the domestic market and ships only non-raw materials for export (moreover, the goods (works, services, property rights) used in export operations were acquired after 07/01/2016), then he does not have the obligation to maintain separate accounting. However, for the program to work, in particular, to be able to automatically generate accounting system documents when confirming/not confirming the validity of applying the 0% rate, it is still necessary to make the settings of the accounting policies and accounting parameters described above.
Codes of types of goods related to raw materials are determined by the Government of the Russian Federation in accordance with the unified Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity of the Eurasian Economic Union (paragraph 3 of clause 10 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended by Law No. 150-FZ).
In the absence of a Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation, you can preliminarily indicate whether or not goods sold for export belong to the group of raw materials by placing the appropriate flag for each specific HS code (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Flag "Commodity"
By default, the Commodity flag is cleared, i.e. all goods sold are classified as non-commodity products.
In addition, from 07/01/2016, in accordance with subparagraph 15 of paragraph 5 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (as amended by Law No. 150-FZ), invoices issued in respect of goods exported outside the territory of the Russian Federation to the territory of the EAEU member states must indicate code of types of goods in accordance with the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity.
In the absence of appropriate changes in the form and Rules for filling out the invoice, approved. By Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 (hereinafter referred to as Decree No. 1137), the HS code is automatically displayed in column 1 of the invoice, separated by a comma after the name of goods (work, services), property rights in all cases where a 0% rate is applied. and when such a code is indicated for a given product item in the Nomenclature directory.
Tax consequences of export VAT
Tax on proceeds from export transactions is calculated in the usual manner. The organization includes it in the tax base and reduces it by the amount of input VAT, using the right of paragraph 1 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When determining the tax base for export transactions, it is necessary to follow the regulations established by Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Namely, the moment of revenue recognition no later than the last day of the quarter in which documents were collected to confirm the preferential VAT rate.
If the organization is late, you will need:
- calculate tax and penalties;
- pay the arrears to the budget;
- draw up a declaration and include Section 6 in it.
In this case, the date of shipment of the products serves as the moment for determining the tax base.
Note! For organizations that operate on a simplified system, there is no requirement to confirm a zero rate. The exemption from the obligation to declare an export transaction is confirmed by the letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-11-11/2021 dated January 19, 2017.
Submission of the Register of customs declarations to the Federal Tax Service via email. form
When confirming the VAT rate of 0% for export transactions, the taxpayer has the right to submit to the Federal Tax Service in electronic form registers of customs declarations (full customs declarations) indicating in them (clause 15 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- registration numbers of the relevant declarations (clause 3, clause 1, article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- transport, shipping and (or) other documents (clause 3 and clause 4, clause 1, article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The register replaces all documents specified in it confirming the 0% VAT rate, except for the contract.
The forms and electronic formats of the registers are approved by the Federal Tax Service (Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated September 30, 2015 N ММВ-7-15/427). The order contains 14 registers intended for various operations. To confirm export, the register according to Appendix No. 5 is used.
See also Registration of customs declarations for export operations
In our example, the Register of customs declarations (full customs declarations), as well as transport, shipping and (or) other documents according to Appendix No. 5 is provided.
See also Which register to submit to the Federal Tax Service in 2021?
The register of customs declarations is drawn up using the regulated report VAT Register: Appendix 05 in the Reports section – 1C: Reporting – Regulated reports – Create button – All tab – Tax reporting – VAT Register: Appendix 05 folder.
the VAT Register: Appendix 05 report is carried out after generating the regulated VAT Declaration .
On the title page, select VAT Declaration , to which the VAT Register is filled out: Appendix 05 . In our example, the VAT return for the 3rd quarter is selected.
Click the Fill out the VAT Register report to automatically fill in the data from the documents Customs Declaration (export) and Confirmation of the zero VAT rate .
How to post unconfirmed VAT in accounting
In accounting, to reflect the export on the date of actual shipment, if the documents have not been collected, you need to make the following entries:
| Debit | Credit | Comments on the operation |
| 90.3 | 68.2 | VAT payable has been calculated (rate 18 or 10%) |
| 99.1.1 | 68.2 | Penalties charged for overdue VAT |
Postings that will reflect the export in accounting, with a full package of necessary documents:
| Debit | Credit | Comments on the operation |
| 41.1 | 60.1 | Items for sale have arrived |
| 19.3 | 60.1 | The amount of input tax is reflected |
| 52 | 62.1 | Received money from buyer |
| 62.1 | 90.1.1 | Shipment of export products has been formed |
| 90.3 | 68.2 | Tax reflected at 0% rate |
| 90.2.1 | 41.1 | The cost of goods sold has been generated |
| 68.2 | 19.3 | The amount of input VAT accepted for deduction |
Note that in Russian accounting, export transactions are reflected in rubles at the current exchange rate of the currency used by the buyer. Recalculation is carried out on the payment date. Currency balances should be revalued at the reporting date. The results of the operation are reflected in account 91 (positive or negative).
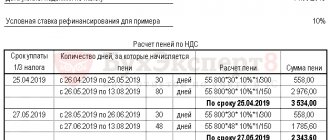
An exporter who prepared documents at the zero rate late, namely 181 days, must do the following:
- an invoice for unconfirmed exports is recorded in an additional sheet of the purchase ledger;
- reflect the restored VAT by posting: Dt 68.2 Kt 68.Export;
- include the deduction amount in section 6 of the declaration on line 040.
It should be remembered that after filing the report, there will be an overpayment of tax. Her organization has the right to reimburse from the budget.
Customs clearance of goods for export to Belarus
Belarus is a member of the Eurasian Economic Union (formerly the Customs Union). The EAEU also includes Russia, Armenia, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan. This education was created to develop the national economy and improve the living standards of the population of the participating countries. The Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union provides for the freedom of movement of goods, services, capital and labor, as well as the implementation of a common economic policy.
During customs clearance of goods of the EAEU member states, filling out declarations has been abolished - registration of foreign economic transactions takes place through the submission of statistical forms. To do this you need:
- fill out all fields of the statistical form on the department’s website;
- ensure the accuracy and completeness of the entered data;
- find out the system number and download the form;
- endorse the document;
- send the form on paper by registered mail with return receipt requested to the customs authority at the place of registration (or through the account of a foreign trade participant on the department’s website).
Having received the statistical form, the customs officer loads it into the register using the system number, checks the data and registers it, assigning an identification number. When sending a document electronically, it must be signed using an electronic signature.
Among other documents required to complete the customs clearance procedure between the borders of the Russian Federation and the Republic of Belarus:
- foreign economic agreement, including details and legal addresses of the parties;
- transaction passport for contracts worth over 50 thousand USD);
- currency control documents;
- certificates and licenses for certain types of goods (for example, food products);
- documents on the origin of the goods;
- transport documentation, cargo specifications;
- export permits (optional).
Another feature of exports from the Russian Federation to Belarus is the possibility of applying a zero VAT rate. You can learn about all the intricacies of this rule by ordering services from M&J Logistic.
How to fill out the VAT return section 6
Information on exports is entered in the manner established by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
| Line code | Operation |
| 010 | Specify operation code |
| 020 | Reflect the tax base for the transaction |
| 030 | Calculate the amount of VAT that needs to be paid (rate 18 or 10%) |
| 040 | Specify tax deduction amounts: · input VAT; · tax paid when importing products into the Russian Federation; · VAT paid by the tax agent when purchasing products. |
| 050 | Indicate the total tax amount calculated for payment |
| 060 | Indicate the amount of deductions by which the tax amount is reduced |
| 160 | Show the amount of tax to be paid |
| 170 | Reflect the amount of VAT that will need to be reimbursed at the end of the reporting period |
Reference! If within 3 years the organization does not collect the necessary export documents, then the amount of tax can be reflected in expenses when calculating income tax.
Section 5
Section 5 is completed in the declaration in the period when the right to deduct VAT arose for transactions for which the minimum rate was or was not confirmed:
- Line 010 – year of submission of the declaration for goods sales operations.
- Line 020 - tax period code.
- Line 030 is the operation code.
- Line 040 is the tax base that relates to justified export transactions.
- Line 050 – VAT amount from line 040.
- Line 060 is the tax base, which relates to unjustified export transactions.
- Line 070 – the amount of input VAT on unjustified exports.
- Line 080 - amount to be reimbursed from the state budget.
The provision of land plots to disabled people is carried out on preferential terms. How to properly privatize a plot of land with a house? We have described all the details here. How to order a cadastral plan of the territory correctly? Detailed information is provided in our article.
When is section 6 of the declaration submitted?
Until 180 days have elapsed, export transactions are not declared. How to determine whether this period has expired or not?
Let's look at an example:
- the export transaction was carried out in the 1st quarter of 2021;
- The 180th day begins on September 25, 2021;
- export documents were prepared by September 30, 2021;
- The last day for submitting the declaration is October 25, 2021.
The exporter is required to declare the transaction if he prepares documents with the Federal Tax Service by September 25. therefore, the point at which the export sale is determined will be recorded in Section 4 of the VAT return in the 3rd quarter.
But, if the deadline is missed, then the fact of sale is reflected in the 1st quarter of 2021. The tax is calculated and indicated in Section 6 of the report. After paying VAT, recalculate penalties and pay them additionally.
If we assume that the organization prepared export documents before September 25, then the sale will be reflected in the 3rd quarter, and Section 6 of the declaration does not need to be filled out.
Step-by-step instruction
Attention! The VAT rate has been changed from 01/01/2019 from 18% to 20% and from 18/118 to 20/120.
The organization entered into an export contract with a foreign buyer Hotseasonsp. zoo (Poland) for the supply of non-commodity goods in the amount of 10,000 USD.
March 15 to the buyer Hotseasonsp. zoo goods were shipped for export: Fans (1,000 pcs.) worth 10,000 USD.
September 05 The Organization collected a package of documents (within 180 days) to confirm the 0% VAT rate on export shipments.
Based on the results of the 3rd quarter, the Organization submitted to the Federal Tax Service a set of documents and a VAT return for the 3rd quarter to confirm the VAT rate of 0%.
Conditional courses for example design:
- September 05, the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation is 62.00 rubles/USD.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Export of non-commodity goods confirmed within 180 days | |||||||
| Registration of customs declarations for export operations | |||||||
| 05 September | — | — | — | Registration of customs declaration for export | Customs declaration (export) | ||
| Confirmation of VAT rate 0% for 180 days | |||||||
| 05 September | — | — | 620 000 | Confirmation of VAT rate 0% | Confirmation of zero VAT rate - Confirmed 0% rate | ||
| — | — | 620 000 | Reflection of export SF in the Sales Book | Sales book report | |||
| Submission of the VAT return for the 3rd quarter. to the Federal Tax Service | |||||||
| September 30th | — | — | 620 000 | Reflection of the amount of export sales | Regulated report VAT Declaration - Section 4 p.020 | ||
| Submission of the Register of customs declarations to the Federal Tax Service in electronic form | |||||||
| September 30th | — | — | — | Filling out the Register of Customs Declarations to confirm the 0% rate | Regulated report VAT Register: Appendix 05 | ||
Flowchart of Export of non-commodity goods to non-CIS countries for goods purchased from 07/01/2016
The diagram shows the procedure for exporters to reflect data in:
- sales book;
- VAT declarations regarding shipment and deduction;
- 1C.
Let's consider the procedure for the event. Documents (Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) are collected on time (180 standard days) .
Export from Russia to Belarus
Business is the art of selling goods, services or ideas profitably. The Republic of Belarus is an attractive destination for Russian business, and this fact is not greatly affected by the current economic situation and the ruble exchange rate. There are no customs barriers between countries, which makes trade turnover simple, fast and profitable. According to statistics, exports from Russia to Belarus for 9 months of 2015 amounted to 12,724.6 million US dollars, and the balance of foreign trade transactions turned out to be positive for Russia and amounted to 4,929.2 million US dollars during this period. Which suggests that Russian companies sold more than they bought. The detailed picture of exports to the Republic of Belarus for 9 months of 2015 looks like this:
- Fuel, oil and products of their distillation” (HS 27) – the volume of supplies is 53.4% (6,788.1 million US dollars);
- Vehicles, machinery and equipment (HS 84-90) - 13.5% (USD 1,720.8 million);
- Metals and metal products (HS 72-83) – 9.3% (USD 1,184.4 million);
- Chemical products (HS 28-40) – 9.0% (USD 1,150.2 million);
- Food and agricultural products (HS 01-24) – 5.3% (671.98 million US dollars);
- Textiles and footwear (HS 50-67) – 2% (USD 254.9 million).
It is obvious that many Russian companies work with Belarusian partners, and it is also clear which products are in greatest demand in the Republic. This is something that Belarusians themselves do not produce or produce little of - fuel and cars. Clothing and food are those goods that, on the contrary, are imported into Russia. But even among them you can find your sought-after position. However, finding the right product for export and concluding a supply agreement is half the battle. The main thing, as usual, lies in the design.
Export of goods is their removal from the customs territory of the Russian Federation without obligations for re-import. It is regulated by the norms of the Customs Code. When carrying out export operations with EAEU countries, organizations do not need to fill out a customs declaration or make marks on transport documents. In order to be able to apply for a VAT deduction, you must obtain an application for the import of goods from the organization purchasing the goods. This document will confirm the fact of payment of VAT in his country.
VAT on export of goods
According to the legislation of the Russian Federation, when sending goods for export, a 0% VAT rate is applied. What needs to be done in order to receive this rate when exporting:
- When exporting goods, it is necessary to comply with the customs export procedure;
- Export goods provided that they are moved to a special economic zone;
- Carrying out international transportation.
By customs procedure it should be understood that when exporting goods outside the country, it is necessary to pay customs duties, comply with all movement rules, namely not export prohibited goods outside the Russian Federation, provide documents and certificates for exported goods, which contain information about the origin of the goods that are going to export.
Goods transported to the FEZ are allowed to be warehoused, stored, processed for production, sent for repair, and other loading/unloading activities are carried out for further transportation to their destination.
Results
The indication of codes for transactions is provided both in the VAT return and in the accounting registers of documents drawn up in connection with this tax.
However, the ciphers of such codes for declarations and accounting registers have a different number of digits in them and are approved by different documents. For use in 2021, the basic code registries have been supplemented with a number of cipher values recommended by the Federal Tax Service of Russia. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Operation code selection
The transaction code is a mandatory element of section 4; without it, reports will not be accepted. The list of transaction codes declared in Section 4 of the VAT report is given in Section 3 of Appendix 1 to the Procedure. The codes are differentiated by type of activity, country of the counterparty, affiliation with it and other characteristics.
Special codes have been introduced to reflect information about transactions with related parties, as well as for adjustments due to changes in the cost of goods (work, services) or returns.
Separate codes for re-export have not yet been established. The Federal Tax Service, in letter No. SD-4-3/532 dated January 16, 2018, recommends using codes for similar export transactions before making changes to the Procedure.
Since each type of activity may correspond to several transaction codes, when filling out reports, you must carefully study their list and select the correct code. In case of an error, you will have to submit a correction.
Who should pay VAT
Value added tax is levied on buyers of goods or services. They are charged an amount equal to the difference between the final sale price and the purchase price (production cost). Payers of this indirect tax are:
- organizations (legal entities);
- Individual entrepreneurs conducting commercial activities within the country;
- all economic entities moving goods across the state border.
There are more VAT payers conducting international trade than enterprises operating within the Russian Federation, because not all taxpayers within their country apply the SST. When moving goods through customs checkpoints, the participant in foreign economic activity is obliged to pay VAT, regardless of the taxation system applied.