Employees of institutions, including their managers, and individual entrepreneurs must be trained in labor safety rules, undergo safety training at the enterprise and have their acquired skills tested (Article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Rank and file personnel receive the necessary information in the form of training on the problems of ensuring safe working conditions both in the institution as a whole and at a specific place in particular. It will enable the employee to avoid various dangers in the process of activity and prevent possible problems. Instruction on labor protection and fire safety ends with a test of acquired knowledge. The best result is the correct use of work tools, compliance with labor protection requirements and organizational rules.
The list of existing occupational safety briefings, the algorithm for their implementation, and content requirements are included in Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation No. 1/29 of January 13, 2003, GOST 12.0.004-90 SSBT. Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 212 prohibits an employer from allowing employees to work who have not been trained in occupational health and safety and have not demonstrated successful knowledge of the topic.
ConsultantPlus experts discussed how to create a training program on occupational safety. Use these instructions for free.
to read.
General concepts
Occupational safety measures are carried out during work at different times, depending on the need.
What determines the technical safety measures, and the standards to be followed are determined by legislation. Attention! Accepted abbreviations: labor protection - OSH, safety precautions - TB.
In a specific sense, labor protection includes issues related to the following areas:
- workers' rights;
- social;
- hygiene and sanitation issues;
- organizational;
- treatment, prevention, rehabilitation, disease prevention;
- technical;
- and so on.
Occupational safety and health measures vary in scope depending on the state of the enterprise (for example, an office or a factory). They also depend on the presence of harmful conditions, etc.
Labor safety standards are created based on job responsibilities, depending on the position held. In addition, we must not forget about the facts of mistakes, accidents and possible risks, on the basis of which are created and tightened . Safety in the workplace is the key to life and health.
Occupational Safety Corner
Electrical safety briefing
Another mandatory type of safety training is devoted to electrical safety. It depends on whether the employee is an electrical technician, that is, whether his responsibilities include installation, adjustment, maintenance and repair of electrical installations.
To find out whether the company has such employees (from a legal point of view), study Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 328n of the Ministry of Labor dated July 24, 2013. It lists the categories of workers and the conditions for assigning different electrical safety groups.
What does health and safety include?
Occupational health and safety at work includes a set of tasks, depending on the specifics of the duties performed:
- creating conditions for working with power lines and electrical appliances;
- provision of protective equipment and protective clothing against smoke and fire;
- guarantee of safe organization of all categories of work;
- supply of serviceable equipment , as well as its inspection, repair or partial timely protection;
- maintaining all work and utility rooms in proper condition, in accordance with sanitary and hygienic requirements;
- creating conditions for working with increased noise, vibration, dust, etc.;
- ensuring conditions at high altitudes, in underground mines, as well as when working with sudden temperature changes.
The list differs in each specific case, depending on the specifics of production. General safety regulations must be followed by all employees.
Causes of accidents at work
In organizational areas, health and safety includes:
- training of management and management personnel, main and temporary workers;
- monitoring the condition of workers (annual medical examinations, briefings, training events, issuing products according to their harmfulness, sending employees for treatment or rehabilitation to sanatoriums and health institutions);
- control over compliance with health and safety rules by higher authorities of responsible persons.
All necessary information for enterprise managers, labor safety inspectors, and working personnel is contained in the labor code and local regulations.
What is labor protection
Requirements for qualifications and training of personnel
An organization operating a hazardous production facility is obliged to:
- ensure that the staff of the hazardous production facility is staffed in accordance with established requirements;
- allow persons who meet the relevant qualification requirements and do not have medical contraindications to the specified work to work at a hazardous production facility;
- conduct training and certification of workers in the field of industrial safety;
- organize and carry out production control over compliance with industrial safety requirements;
- ensure the examination of industrial safety of buildings, structures and technical devices used at a hazardous production facility, as well as carry out diagnostics, tests, inspections of structures and technical devices used at a hazardous production facility, within the prescribed time frame and in accordance with the order of the federal executive body presented in the prescribed manner authorities in the field of industrial safety, or its territorial body;
- ensure compliance with industrial safety requirements for the storage of hazardous substances;
- enter into a contract of compulsory civil liability insurance in accordance with the legislation on compulsory insurance of civil liability of the owner of a dangerous facility for damage caused as a result of an accident at a hazardous facility;
- suspend the operation of a hazardous production facility independently or by a court decision in the event of an accident or incident at a hazardous production facility, as well as in the event of the discovery of newly discovered circumstances affecting industrial safety;
- carry out measures to localize and eliminate the consequences of accidents at a hazardous production facility, assist government agencies in investigating the causes of the accident;
- take part in the technical investigation of the causes of an accident at a hazardous production facility, take measures to eliminate these causes and prevent such accidents;
- take measures to protect the life and health of workers in the event of an accident at a hazardous production facility, etc.
An important factor in the safe operation of a hazardous production facility is the human factor, i.e. professionalism of operating personnel capable of quickly and correctly acting in extreme conditions. Timely response of maintenance personnel to pre-emergency and force majeure situations can be the key to trouble-free operation of a hazardous production facility.
The basic conditions for safe operation include the following requirements:
- correct selection of specialists responsible for ensuring safe operation of high-risk facilities that meets relevant requirements;
- good theoretical and practical training, high professional skills, solid knowledge of production, equipment being serviced, technological processes and the requirements of labor protection standards, ensuring highly productive and safe work. The fulfillment of this condition must be ensured by the system of instruction, training and appointment of personnel provided for by the relevant provisions;
- determination by special regulations (taking into account local conditions) of a specific list of main responsibilities in the field of labor protection: the manager and chief engineer of the enterprise, their deputies, chief specialists, heads of workshops and departments, all other specialists and their compliance;
- full compliance of buildings, structures, workplaces, equipment, machines, fixtures, tools, all other means of production and technological processes with the requirements of relevant labor protection standards, state standards and technical conditions. The most important measure in solving this issue is planned, persistent work on the constant development of technical progress based on the achievements of science and technology, best practices, improvement of culture and aesthetics, which are crucial for creating comfortable and safe working conditions, preventing accidents and incidents;
Of course, the most important determining condition for safe work is a high level of labor protection.
The organization is obliged to strictly comply with all requirements for the operation of hazardous production facilities by the relevant regulatory legal acts and technical documents, which is the key to safe work.
comments powered by HyperComments
Share news:
The entry was published on November 11, 2014 by Oleg Petrovich Frolov in the Industrial Safety section.
TB awareness activities
The responsibilities of the Health and Safety Service include:
- development of internal standards;
- training and knowledge testing;
- control over execution.
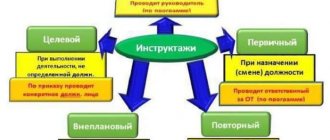
There are two types of training :
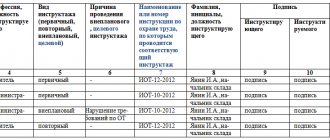
- Instructions (the employer instructs the employee, after which he begins to work). Briefings can be introductory, primary at a specific workplace, repeated, unscheduled, targeted. Introductory safety training at any production or enterprise is carried out by a labor protection specialist or person in charge. It is mandatory for both newly arrived employees and trainees, regardless of their planned time of stay at the enterprise. Initial briefings are optional for employees not involved with equipment and production materials. The same ones who pass the primary ones pass the repeated ones. Unscheduled briefing is carried out in emergency cases (as prescribed, introduction of new equipment, accident). Targets are carried out according to the admission order.
- Direct training and testing of knowledge. To do this, it is necessary to have a program at the enterprise, which should include as much as possible the goals prescribed in GOSTs (for example, personal protective equipment, if necessary). A program is developed for each type of instruction.
If an employee does not pass the health and safety exam, he is not allowed to enter the workplace and is sent for re-training.
Example of an induction training log
How to draw up a Regulation on briefings
Instruction rules, types and tasks of occupational safety briefings and methods of training workers in safe work practices are enshrined in the Regulations on the procedure for conducting occupational safety briefings.
A draft of this Regulation is being developed by the heads of the enterprise departments together with labor protection engineers. The finished project is agreed upon with the employer. After approval, it is put into effect by order of the chief. All employees of the organization must be familiarized with the completed Regulations.
Employer Responsibilities
The employer must fulfill his responsibilities directly in terms of occupational safety, which include:
- provide employees with Codes, legal acts, laws;
- select and approve the staff of the labor protection service;
- create and approve a system for the functioning and management of the labor protection service;
- together with the responsible persons, he must develop safety instructions for each staff unit and develop programs;
- safety instructions are created for each full-time position available at the enterprise;
- create a workplace and a thematic office for the labor protection service, ensure the availability of visual aids and safety materials if necessary.
In addition, the employer is obliged to provide employees not only with training material, visual aids, illustrations, etc., but also to organize workplaces according to requirements, provide them with special clothing, and organize a rest room if necessary. The employer is obliged to personally monitor the health status of employees and take measures for treatment, prevention and recovery.
OT office
What regulations govern
The main issues of safe operation of the enterprise are regulated by regulations at the federal and municipal levels.
Federal acts include:
- Constitution of the Russian Federation;
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation (section 10, articles 209 – 231);
- Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ;
- Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ;
- Federal Law of July 21, 1997 No. 116-FZ;
- GOST R 12.0.006.2002;
- industry and inter-industry agreements containing requirements on labor protection issues.
Acts at the municipal level are documents containing requirements regarding compliance with safety regulations in a separate municipality.
Responsibilities of the OT service
The OT service can be represented by one employee or constitute a group of individuals. Their responsibilities:
- develop and submit to the manager for approval an action plan for organizing safe work at the enterprise;
- develop and submit safety instructions to the manager for approval, ensure that employees of the enterprise are familiar with them, store copies signed by employees, provide visual aids, video tutorials, thematic information cards during training;
- conduct investigations of injuries, mutilations, and accidents; organize a special investigation group in agreement with the manager;
- carry out periodic testing of the knowledge of industrial safety among employees of the enterprise;
- participate in the preparation of all internal documents at the enterprise related to the field of labor protection;
- control the passage of medical examinations by employees: remind, post lists;
- control the receipt of products for hazardous working conditions;
- control the receipt of required benefits for certain categories of employees;
- order, purchase, issue protective clothing;
- organize training events on occupational safety.
In addition, the OT service is responsible for properly completing all documentation. Responsible persons have the right to send orders to departments to suspend the work process due to the discovery of a violation of safety regulations at work.
Why do you need to follow safety precautions in the workplace?
The answer is obvious: “So as not to get injured.” But there are other reasons.
So, 5 reasons why you need to observe safety precautions in the workplace:
1. So that the employee remains alive, healthy and does not become disabled. Think about it, about 2,000 people die a year at Russian enterprises and about 4,000 people become disabled per year!
2. Causing damage to the health of other employees. For causing harm to the health of citizens, both administrative liability is provided (Article 5.27 of the Administrative Code) and criminal liability (Article 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
3. Failure to provide various benefits and guarantees not provided for by the collective agreement. Thus, many enterprises do not pay the 13th salary to violators of labor discipline.
4. Decrease in the quality of products and services.
5. Dismissal at the initiative of the employer. The administration of the enterprise has every right to terminate an employment contract for repeated violations of safety regulations or for a single gross violation of safety regulations (Articles 81 and 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
TB training
Safety training and knowledge testing at the enterprise are provided primarily for management personnel and workers who are responsible for safety. In addition, it is provided for persons employed in hazardous conditions. Training involves studying the basic principles of behavior in dangerous situations, general safety rules for operating equipment, completing an on-the-job internship and passing an exam to obtain an official permit to work.
Training is carried out both upon hiring and at intervals of once a year or three years.
TB training
Fire safety briefings
A separate type of instruction—fire instruction—is devoted to the rules for preventing fires, as well as behavior during such an emergency. Fire safety training is mandatory for all organizations. The procedures are recorded in a fire safety log.
Fire safety briefings are similarly divided into:
- introductory;
- primary;
- repeated;
- unscheduled (when preventing a fire threat or an incident at another enterprise);
- targeted (when eliminating the consequences of a tragedy or before a mass event).
Approximate contents of fire safety instructions:
- rules for handling equipment that poses a fire risk, including open flames during hot work;
- signs of a starting fire;
- evacuation plan, PPE storage locations and fire safety system operating procedures;
- rules for handling a fire extinguisher, calling the fire department and other duties and recommendations in case of an emergency.
Responsibility for violation of safety rules
Responsibility for violation of safety rules can be assigned to the manager, the safety service, or employees. Appointed officials are primarily responsible. Employees are directly responsible for violation of safety rules, as for violation of labor discipline (with the exception of criminal liability).
Responsibility may be:
- administrative and criminal , depending on the severity of the consequences and the intentionality of failure to comply with the instructions;
- disciplinary;
- material.
The resulting administrative liability provides for fines in various monetary amounts.
Disciplinary liability includes demotion , reprimand, reprimand, removal from a position for a certain period or temporary or complete removal from duties in whole or in part.
Financial liability is expressed in compensation for damage caused by careless handling of entrusted property, resulting in its damage or in the event of theft of property. Issues that arise can be resolved on the spot between the employee and management or through the court. Recovery can be carried out in whole or in part by deducting small amounts from wages.
Criminal liability arises in situations where, through the fault of an employee, another person is injured, as a result of which he becomes disabled or dies.
Responsibility for violation of labor protection rules - Article 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation
Who is responsible for worker safety?
First of all, the employee himself is responsible for fulfilling all requirements. If the accident occurred through the fault of a co-worker himself and the fact of non-compliance with the requirements is proven, then during the investigation the percentage of blame will be assigned to him. However, in most cases, even if the worker is proven completely wrong, only 25% is allocated to him, and the rest to management.
For the rest, responsibility lies with the immediate supervisor, who is obliged to monitor the equipment of the workplace, provide instructions, and also monitor the implementation of orders.
Control over the OT service
The OT service itself, regardless of the number of representatives, reports to the head , who, as a responsible person, controls the work of this service.
In addition to the internal control of a senior manager, there are control services:
- at the state level (executive authorities at the federal and local levels), they have the right to check the work of the occupational safety service at any stage and in any area, at any time;
- departmental (implies control of a responsible superior enterprise over a subsidiary or subordinate);
- non-departmental (from the pension fund, policyholders, etc.);
- public (verification by individual citizens on existing grounds, work collectives, thematic movements, the media).
Attention! An inspection of the work of the labor protection service can be sudden or planned.