Occupational Safety and Health
Alexey Borisov
Leading expert on labor relations
Current as of October 30, 2020
Each employee, regardless of position, specialty and workplace on the basis of Ch. 34 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer must create safe working conditions and provide information about possible risks, dangerous and harmful parameters associated with his work activities, as well as measures to minimize them. For this purpose, labor safety instructions are used - internal regulatory documents containing requirements for ensuring safety during the performance of official duties and work in production.
Normative base
Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated May 24, 2002 N 36 “On approval of intersectoral standard instructions on labor protection for workers in the public catering system”
The employer must have the following instructions:
- About first aid.
- On fire safety.
- For each position.
- In the most traumatic areas of activity (when working with electricity, at heights, on vehicles, etc.)
The obligation to develop this document is enshrined in Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Neglect on the part of the employer is punishable by a fine of up to 200 thousand rubles or imprisonment for up to 5 years. For workers, ignoring occupational safety regulations can be deadly.
How to compose
The document includes three parts:
- list of instructions for types of work;
- list of IOTs by profession (position);
- list of common IOT.
Work on the list is carried out in several stages:
- inclusion in it of all positions from the staffing table, even vacant ones;
- inclusion of rules for the types of work performed at the enterprise (for example, for the same type of work, or loading and unloading, if they are performed not by a loader, but by representatives of other professions, etc.);
- inclusion of general rules (first aid, etc.);
- assigning a clear serial number;
- establishing the person responsible for compiling the list (most often this is an OT specialist or an employee of the OT department);
- setting a review date (usually five years, but departmental documents sometimes set a different period).
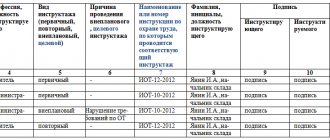
In accordance with these stages, a form is generated. It is drawn up in the form of a table, which must contain the following details:
- serial number;
- name of IOT;
- code or number;
- date of approval;
- date of inspection.
The table is divided into segments by type of IOT. The signature of the responsible person is placed below.
The document is put into effect by order of the head. The list is an appendix to it. The approved list of labor protection instructions is sent to the departments in its entirety or in the form of an extract (this is acceptable).
Development
The development of safety instructions is carried out on the basis of inter-industry or industry standard instructions. For example, a standard instruction on labor protection for a baker was approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor dated May 24, 2002 No. 36 “On approval of inter-industry standard instructions...”
In the absence of regulatory documents approving cross-industry or sectoral requirements for safe working conditions, these regulatory documents are developed on the basis of the safety requirements set out in the operational documentation that comes with the equipment.
The procedure for developing documents is determined by the employer, who can independently deal with this issue, or can entrust it to a specially appointed employee (usually a labor protection engineer, whose job description contains the corresponding responsibility).
Frequency of revision of instructions and their validity period
The instructions require revision if:
- there was a change in the technological process
- replacement of production equipment was required
- personal or collective protective equipment has changed
- the materials and (or) raw materials used in production have changed, as a result of which the level of factors specified in the instructions that affect workers has changed
When introducing new jobs, instructions should be developed no later than the new employee starts work. Therefore, if the technological process has not been carried out at the workplace before, before the work begins, employees must be trained on the new instructions.
The validity period of occupational safety instructions is not established by law. The employer has the right to do this independently. At the same time, for electrical technical personnel, the period for reviewing instructions is once every 5 years.
Professional standard Specialist in the field of labor protection
When developing regulations governing the safe work of employees, it is advisable to be guided by the provisions of the Methodological Recommendations approved by the Ministry of Labor on May 13, 2004.
Documents on safe working conditions are developed for 5 years. After this time they are subject to revision.
They must be processed ahead of schedule in the following cases:
- renegotiation of cross-industry or sectoral agreements;
- changes in employee working conditions;
- introduction of new equipment and technologies;
- occurrence of accidents;
- regulations of regulatory authorities.
If none of the above has happened within 5 years, the validity of the instruction is extended for the next 5 years.
Update
Once every five years, inspections are carried out, and, if necessary, the IOT is reviewed to determine the relevance of the requirements contained in it.
Before the expiration of the specified period, the occupational safety manual is changed if:
- changes were made to inter-industry and sectoral occupational safety rules and standard guidelines;
- working conditions have changed;
- new technologies and equipment were introduced;
- such a need is confirmed by the results of an analysis of industrial accidents, accidents, and occupational diseases;
- a request from a government agency has been received.
If during the period of validity of the occupational safety manual the employee’s working conditions have not changed, then the validity of the document is extended for the next period.
Preparation of work safety documents
The regulatory act on occupational safety must contain sections with safety requirements:
- general section;
- before starting work;
- during work;
- in emergency situations;
- upon completion of work.
If necessary, additional sections can be included.
It is recommended to format the first sheet as follows:
For new capacities being commissioned, it is allowed to develop and apply temporary regulations for employees who must ensure the safe conduct of production processes and the safe operation of equipment.
Procedure for keeping a TB journal and sample filling
According to federal legislation, each individual enterprise must maintain a specialized safety journal.
The registration procedure is standard, but you need to know some features. Among them it is customary to highlight:
- the registration log of briefings is a stationery book in A4 format, which was developed in accordance with the requirements of GOST and is in the public domain;
- all sheets, without exception, must be numbered and certified by the signature of the enterprise management, if present with a seal;
- The title page must include the following important data: full name of the organization, name of the instructed structural unit, start and end dates of maintenance.
For convenient systematization, it is strongly recommended to create a registration log separately for each specific type of instruction. At a minimum, this will greatly simplify the work.
For your information! Instructing and filling out a specially designed log is assigned to the immediate supervisor or safety engineer. The authorized responsible person must have a certificate confirming his authority. Training for this takes place every five years.
The sample and form of keeping a TB journal are established by federal legislation.
List of labor safety instructions
All developed and approved regulations governing work safety are subject to recording and issuance.
The first journal (accounting) is kept in accordance with Appendix No. 2 to the Methodological Recommendation dated May 13, 2004, its form is as follows:
| № | date | Name of instructions | Approval date | Designation or number | Planned inspection period | Full name and position of the employee performing accounting | Employee signature |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
Types of occupational safety briefings
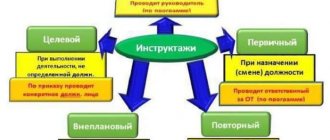
In practice, safety instructions alone are not enough to inform workers about all the rules of behavior and handling of equipment. Therefore, there are different types of instructions. from each other in time, repetition and content.
All such subtleties are understood either by the head of the organization (if we are talking about a small organization) or by an OT engineer. This employee is familiar with all legislative acts, necessary rules, and complies with the procedure and timing of mandatory events. Developing briefings in terms of content is also his responsibility.
In addition to educating the state about TB, knowledge testing is a good solution. That is, the engineer first gives a lecture to employees about safety precautions, teaches how to operate the equipment, and then tests whether the material has been mastered. The employee confirms knowledge by signing the logs.
Introductory
The very first briefing given to employees is called induction. It is organized on the very first working day, during the signing of the employment contract. Mandatory for all people applying for work. The introductory training session is conducted by a manager, engineer or HR specialist. The new employee is introduced to the basic safety rules of the organization. Their list depends on the specifics of the enterprise’s activities. Approximate content:
- legislative acts and local regulations on labor protection;
- rules of behavior at work and during emergency situations;
- information on personal protective equipment (PPE).
For example, in “safe” organizations, instruction is limited to studying the evacuation plan and the rules for using electrical equipment. In industrial production, induction training is more complex, but still not too voluminous. Its task is to introduce the basic rules of behavior on ordinary days and in emergency situations, without delving into the specifics of the work. Special subtleties and details are contained in the initial instructions.
Types of briefings vary in timing, content and frequency
Primary
Primary instruction in content is related to the profession and the specifics of the enterprise. It is passed by everyone whose work poses a risk of injury or harm to health during the performance of work duties. Accordingly, the content of the training will vary. Approximate content:
- familiarization with the technological process at the work site;
- rules for using equipment;
- workplace preparation rules;
- requirements for condition, appearance, use of PPE;
- first aid;
- liability for violation of safety rules.
The content is developed and approved on site, taking into account its own specifics. For example, in medical organizations, a new employee will be introduced not only to the general rules of conduct, but also to the procedure for storing medicines and potent medications. The safety instructions for a pharmacist in a pharmacy will be similar, since this specialist’s responsibilities include the sale and storage of substances whose circulation is restricted by law.
An engineer or a specially appointed employee has the right to organize initial training. For example, the head of a department or a workshop foreman. The authority of an official must be confirmed by a special order or regulation.
Repeated
Repeated instruction is carried out to refresh and consolidate information. His task is to re-inform employees about safety rules, and also to make sure that employees remember all the rules and comply with them. Usually carried out every 6 months, that is, twice a year. But for workers servicing dangerous equipment, more often - every 3 months.
The regularity of repeated briefings and the list of employees required to participate in it must be approved by a separate order.
This is an optional procedure. For example, if a person's activity does not involve hazards, re-instruction is not carried out. Its content also does not need to be worked out separately; it duplicates the primary one.
Unscheduled
Sometimes unforeseen situations happen in enterprises. For example, the production order changes or new equipment arrives. To ensure labor safety in the updated conditions, unscheduled instruction is required. Its task is to introduce employees to the changes and teach them how to work safely in a new environment.
Situations when unscheduled instruction is necessary:
- new equipment, the operating technology of which differs from that previously used;
- when new legislation comes into force;
- after an accident or a requirement from regulatory authorities;
- after a break in work of 1 month;
- by decision of the manager.
Target
The meaning of targeted instruction is clear from its name. It is carried out when it is necessary to inform about the rules of behavior in a specific situation or at a specific point in time. It differs from unscheduled in that, as a rule, it is known in advance or its content covers only a specific issue and does not duplicate the primary and repeated procedures. For example, safety training in the winter - its necessity is known in advance, and the content is subordinated to informing about the procedure for working in cold and icy conditions.
Situations when targeted instruction is carried out:
- one-time atypical work for employees;
- elimination of accidents, fires, floods and other natural disasters;
- before public events;
- briefing before the route;
- before being allowed to work with a special permit.
Employees who have completed the training must sign in a special journal
Logbook form
Employees must be familiarized with the requirements of documents regulating work safety upon signature. This does not mean that every employee needs to study all the regulations in this area. This means that the employee must be familiar with those provisions of regulatory documents that relate directly to his professional activities. However, there are documents with which all employees must be familiar - these are regulations on first aid and fire safety.
Employees' familiarization with documents on work safety must be recorded; for this purpose, a second log form is provided (Appendix No. 3 to the Methodological Recommendations dated May 13, 2004)
| № | date of issue | Instruction number | Name | Number of copies issued | Full name, profession, position of the recipient | Signature |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
Results
Timely and complete training of employees is designed to minimize the number of traumatic situations and accidents.
This is especially true in the presence of complex technological processes. Following safety instructions ensures the completion of production tasks and the safety of equipment, avoiding threats to health and sometimes even the lives of people. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Contents of the safety magazine:
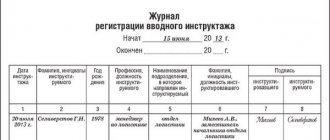
The log contains the following data in rows in order:
- record number;
- date of;
- FULL NAME. the employee who is being instructed;
- date and year of birth of the instructee;
- indication of profession and position. In some cases, instruction may be given to an employee of another organization. In this case, it is necessary to enter data regarding the details of the official ID or order, which is the basis for the employee’s presence at the briefing;
- type of training provided. If the purpose is repeated or extraordinary, the reason for the purpose should be indicated;
- FULL NAME. the one who conducts the training;
- signature of the person for whom the training was conducted and the person who carried it out. It is very important that the autograph of both one and the other be affixed with an indelible pen;
- If necessary, data on the number of shifts and the date of internship is entered.
Important! Based on the specifics of the enterprise’s activities, the structure of the journal may differ slightly. One general rule is that it requires filling out.
Types of standards
The regulatory system for the safety of the physical health of personnel is a set of legal norms aimed at creating safe working conditions.
These standards are recorded in:
- domestic legislation;
- technical safety rules;
- collective agreements;
- departmental guidelines and orders.
They contain:
- Standards governing the preparation of plans and the actual organization of work processes in companies.
- Norms and rules for technical safety and industrial sanitation.
- Standards defining social benefits and compensation for working in conditions detrimental to health.
- Regulations regulating the powers of supervisory structures and monitoring the preservation of favorable working conditions.
- Regulations fixing the legal liability of officials for violation of established legal requirements.
Who develops the instructions
It is the employer’s responsibility to develop and approve labor safety guidelines (Article 212 of the Labor Code).
The staff, in turn, must familiarize themselves with their instructions in a timely manner. This must be done before signing an individual employment contract or at the same time (Article 68 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Attention! An employee can begin his direct work only after instructions have been given to him.
There must be a corresponding entry in the employer’s register or journal about the briefing. Usually, a separate register/journal is created for these purposes. Or it is permissible to create an introductory sheet directly in the rules (instructions) themselves on paper.
In addition, it is allowed to receive receipts from each employee, which indicates: who, when, and what they were familiar with. This is confirmed by the personal signature of the familiar employee. Such receipts are attached to the rules (personal, collective instructions).
The manual is developed for each position on the staff, profession involved in the company or type of work performed.
Attention! The employer develops and approves rules and instructions on labor protection for personnel, taking into account the opinion of the trade union or other authorized representative body on the part of workers (Part 22 of Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Download for viewing and printing:
Labor Code of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 2001 N 197-FZ (as amended on June 18, 2017)
Registration of labor protection acts
According to Art. 211 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, state labor protection standards are mandatory for legal entities and individuals when they perform any kind of business, including:
- design, construction (reconstruction) and use of objects;
- design of units;
- technical equipment;
- development of production and labor processes.
State labor protection standards are contained in:
- occupational safety standards,
- rules and standard manuals on labor protection,
- state sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations (SNiPs, sanitary norms, rules and hygienic standards that establish requirements for factors in the industrial environment and the labor process).
Kinds
There are several types of instruction:
- Introductory. It is carried out with everyone who comes to work. The safety engineer or the manager directly is responsible for this if the company is small. Its essence is to conduct an explanatory conversation with a newcomer and familiarize himself with the instructions. It is carried out exclusively individually. The results of its implementation are entered into the journal.
- Repeated. The need for its implementation is prescribed by law. It is required to be carried out every 6 months, regardless of the company’s activity. This need arises to update the initial briefing data. It can be carried out unscheduled if it is necessary to familiarize employees with new data. This type of training is group in nature and is carried out only by an authorized person.
- Target. Such a study of instructions is narrowly focused. The main goal is to educate the employee about the specifics of implementing a particular task. They are carried out at construction sites, factories or when transferring to a new site. This instruction is required to avoid harm to health and life; it is individual.
- Unscheduled. Does not apply to the training plan that is recorded at the enterprise. It is practiced when introducing a new work scheme, introducing other equipment and when launching an additional technological process.
Important! In some cases, unscheduled training is associated with systematic violations of safety regulations or emergency situations at the enterprise. Sometimes it is carried out at the request of higher authorities.
First aid
The employer’s obligation to train its employees to provide first aid to victims is established by Article 225 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Training must be carried out with the invitation of a medical professional.
The training procedure and deadlines are specified in the Appendix to the Resolution of the Ministry of Labor dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29 (clause 2.2.4).
To do this, the employer needs to develop instructions and include them in the initial training program.
Training of workers in how to provide first aid to victims should be carried out periodically and at least once a year.
All newly hired employees must undergo training within the period determined by the employer in its regulatory document on training. This period does not exceed one month from the date of hiring.
Regulations on training at the enterprise
The Labor Code obliges employers to provide safety training. To streamline this work, it is recommended to issue a regulation setting out the order of briefings, their content, and the responsible persons. This document may be drawn up in free form in accordance with the procedure adopted by the enterprise.
Approximate contents of the Regulation:
- General characteristics of the document, its purpose and scope of action.
- Information about induction training - who conducts it, who is taking it, where it is conducted and what will be included.
- Similar points about initial, repeated, targeted and unscheduled briefings.
- Responsible employees, requirements for their qualifications, procedures for retraining and incentives.
- Final information - when it comes into force and how changes are made.
Regulations on safety briefings at enterprises: Regulations on the procedure for conducting occupational safety briefings