From this article you will learn:
• what types of safety and labor protection briefings exist; • how to conduct training on labor protection in the workplace; • what kind of labor safety briefings are carried out at workplaces and what ones are not; • what is the sequence and timing of labor safety briefings; • whether the occupational safety specialist must conduct all types of briefings.
All types of labor safety briefings are part of ongoing training in safety rules, starting in kindergarten and continuing in the educational sphere, and then in the workplace. Their main goal is to familiarize workers with the features of the organization’s production environment, workplaces, safe work techniques, their rights and responsibilities, and also to constantly maintain this knowledge in the “working mode”.
The obligation of employers to instruct their employees is enshrined in Art. 225 of the Labor Code. It also states their responsibility to teach safety techniques to workers who work in less-than-ideal conditions. Training in occupational safety requirements is divided into:
• primary; • periodic.
Managers of the relevant ranks organize the work of the occupational safety training system and are responsible for the results of its work, including the quality and timeliness of briefings throughout the organization and its divisions. Personal responsibility for instructing assigned employees lies with their immediate supervisors, and for organizing and conducting induction training - persons appointed by the head of the organization.
For their part, workers are required to undergo all types of safety and labor protection briefings in a timely manner and demonstrate high-quality mastery of the material upon completion. Workers who evade instructions are not allowed to perform production tasks. If this happens, their earnings are not retained. Instructed employees who showed unsatisfactory quality of knowledge (did not complete the test correctly, did not give correct answers to the instructor’s questions) are sent for retraining.
What is important to know?
In the introductory part, we have already mentioned the personal responsibility of the employer and the responsibilities assigned to him for compliance with labor protection standards (hereinafter referred to as OSH) at the enterprise. This requires the management of the enterprise to organize both general and targeted briefings for the safe performance by employees of their work duties. Instructions are carried out with all employees, without exception, in accordance with the established standards, regardless of the form of ownership of the organization and its type of activity. This provision also applies to seconded persons and anyone who enters the enterprise for the first time.
This event can be carried out individually for each employee or collectively, depending on the type of instruction and internal regulations. Responsibility for the procedure for conducting briefings rests with the occupational safety commission, which should be headed by a person who is part of the organization’s management (director, enterprise engineer, etc.). For small teams, it is possible to introduce a special staffing unit of a specialist who is responsible for the frequency of safety briefings.
In practice, management and chief engineers rarely directly carry out such activities; they delegate these responsibilities to the labor protection service or responsible persons who have undergone special training.
At enterprises, as well as in organizations and companies, appropriate local acts must be issued that regulate the procedure for labor protection measures, in accordance with the standards of current legislation.
Electrical safety instructions (ES)
According to the “Rules on labor protection during the operation of electrical installations”, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated July 24, 2013 No. 328n, it is also necessary for workers to be instructed in electrical safety.
The implementation of the event is entrusted to a specialist who belongs to electrical engineering personnel and has at least group III in electrical safety (up to 1000 V). If there is no such worker at the enterprise, the lesson can be conducted by a manager who has previously completed training and received Group III in ES.
Briefings are of the following types: introductory, primary, repeated, unscheduled, targeted.
It is known that personnel can be divided into two types:
- non-electrical;
- electrotechnical.
To understand how to carry out instruction in electronic safety, it is necessary to determine what type of specialists can be classified as. This will determine which program the training should take place and, as a result, the assigned ES group.
The list of groups and their description is contained in Appendix No. 1 to the Rules..., approved. By Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated July 24, 2013 No. 328n. You can also see Order of the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation dated January 13, 2003 No. 6.
Upon completion of the lesson, the “Registration of Electrical Safety Instruction” log is filled out. It can be conducted using the form given in Appendix No. 5 to the Rules.
Regulatory acts
Taking into account the fact that occupational safety includes many aspects (norms, standards, rules, etc.), each component must be approved by the relevant regulations of varying degrees of subordination. Currently, the occupational safety sector is regulated by the following legislative and by-laws and industry acts:
- Labor Code (Article 212, 214 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- Federal legislation, in particular, laws No. 125 (dated July 24, 1998) and No. 426 (December 28, 2013).
- Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation 13-01-2003-N-1-29, Orders, GOSTs, in particular GOST 12.0.004-90, GOST 12.0.004-2015 and GOST 12.0.230-2007, SNiPs, as well as other by-laws.
- Local acts and production instructions adopted by the enterprise and not contradicting the above standards.
Testing knowledge on OT
The main and main criterion for the mastery of labor protection requirements by those who have undergone instruction is the successful testing of their knowledge of labor protection requirements. Each briefing is considered successfully completed if the employee has proven that he has mastered the information received.
Usually this is done through an oral examination. Only after this the employee can begin to perform work duties.
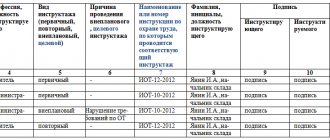
The fact of carrying out occupational safety training is recorded in a special journal indicating the date. The instructor and employee must sign.
Expert opinion
Mikhailov Vladislav Ivanovich
Lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specializes in family law. Knows everything about the law.
All data related to the briefings and testing of occupational safety knowledge must be taken into account during the external audit of occupational safety and health.
If, when checking the State Labor Inspectorate, it is discovered that there are no documents confirming that briefings and inspections were actually carried out, the employer, on the basis of Art. 5.27.1. The Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation faces a fine of 15 to 130 thousand rubles.
Candidate of Economic Sciences, specialist in the field of labor protection with more than 8 years of experience. I write, read, practice, teach.
Occupational safety instructions must be available at every workplace. This is a prerequisite for ensuring safe work for workers. In the article we will tell you what instructions need to be developed, how to approve them, for how long they are valid, and provide a sample instruction.
Labor safety briefings: procedure and timing
These activities, according to current standards, are usually divided into the following types: introductory, primary, repeated, unscheduled and targeted. Let us consider in detail the procedure for carrying out the listed activities.
Types, procedure and timing of briefings
Introductory
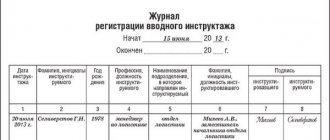
Conducting induction training is mandatory for persons entering work, business travelers, as well as employees of third-party organizations performing various types of work on the territory of the enterprise. This requirement also applies to those undergoing internship or industrial training (practice). They must be given prior instructions.
Procedure for conducting induction training
In other words, introductory training in HSE (safety) and fire safety (fire safety) must be given to everyone who has gained access to the territory of the enterprise, regardless of whether they are directly related to production activities or not. The event is carried out by a specialist approved by the relevant order of the employer.
Primary
Conducting initial briefing is the responsibility of immediate supervisors. This event is carried out at the workplace and is mandatory in the following cases:
- Before a new employee hired by the enterprise performs his duties.
- With an employee of an enterprise transferred from another workshop, site or division.
- When performing a new type of work.
- If an employee of another enterprise is sent to the site or a temporary worker is hired.
- Before carrying out work by construction crews working on the territory of the production site.
- Upon admission of interns, students and students for practical training.
The procedure for conducting initial briefings
The programs and texts of initial briefings must contain information on labor protection and safety, taking into account professional specifics, as well as the basics of fire safety.
Repeated (periodic)
According to the established procedure, this event should be carried out every six months. All employees who have previously listened to primary instructions at production sites and divisions of the enterprise must take it.
Procedure for repeated briefings
The head of the unit, section or other immediate superior is appointed responsible for conducting repeated briefings. At the end of the event, an oral test of knowledge of occupational safety, health and safety requirements is carried out, after which a corresponding entry is made in the registration log and certified with the obligatory signatures of the person being instructed and the instructor.
They undergo repeated instruction both individually and collectively, if the event is intended for employees of the same professional field. At the event, it is recommended to consider cases of violation of labor protection standards and basic safety regulations, if any.
Unscheduled
To carry out this event, regulatory documents provide for the following cases:
- Changes in current norms, rules or requirements for labor protection, safety or industrial safety, which must be immediately notified to employees of the enterprise.
- Modernization of equipment or changes in production technology.
- An incident caused by a violation of safety standards and requirements, labor protection or labor discipline. As a rule, after this, employees undergo an extraordinary knowledge test.
- Obtaining an order from supervisory authorities or other regulatory organizations on the need to carry out an unscheduled event.
- A forced break from work for a period of more than two months for ordinary activities or more than a month if the specialization involves increased danger.
The procedure for conducting unscheduled (extraordinary) briefings
These activities are similar in their main aspects to periodic ones, but attention is focused on the reason for the unscheduled conduct. The content of unscheduled briefing is determined by the purpose of its conduct.
Please note that receipt of unscheduled instructions is not reflected in the schedule of regular (periodic) events, but must be recorded in the journal. The content of unscheduled briefing directly depends on the purpose of its implementation.
Target
Such an event is envisaged to be carried out in cases where one-time work is planned, for which a special permit, order or other permits are required. The most typical example is the elimination of the consequences of a natural disaster or man-made emergency.
When is targeted training carried out?
There are also less tragic reasons for receiving new introductions. This may be work that is not directly related to the main professional activity, for example, loading and unloading equipment. A person designated as the responsible manager is responsible for completing training in safe techniques and methods of performing work at a new location. Upon completion of the briefing, an oral test of the acquired knowledge is carried out, about which a corresponding entry is made in the accounting journal and, if required, in the work permit. Signatures of the instructor and those being instructed are required [ ].
On-the-job training
On-the-job training is called that because it talks about the rules for safe work performance directly at the employee’s workplace.
This responsibility rests with the immediate supervisor of the work. If, for example, several teams work in a workshop, then the task of conducting on-the-job briefings lies with the foremen, and not with the workshop manager.
download the order appointing those responsible for conducting workplace training |
The procedure for conducting briefings is determined by the relevant regulations.
provisions on conducting briefings with employees |
Inadmissibility to perform work
During an oral inspection, it may be discovered that the employee did not understand the information received about labor protection and safety standards. Such a person cannot be allowed to perform his duties until he undergoes repeated instructions. According to standard production instructions, an order is issued for the enterprise, which indicates the reasons why a certain person cannot be allowed to work independently.
No payroll will be processed until clearance is obtained. A detailed description of this provision can be found in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Chief's responsibility
What is the liability for failure to instruct workers or for allowing an untrained employee to work:
- for officials and individual entrepreneurs - an administrative fine in the amount of 15,000 to 25,000 rubles;
- the legal entity will have to pay a fine of 110,000 rubles. up to 130,000 rub. (Part 3 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Criminal liability arises if failure to instruct and allow an untrained employee to work negligently resulted in serious harm to health or the death of a person or several people. More details in Art. 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Sample list of introductory briefing questions
The program for introductory instructions is developed by enterprise managers or a designated service, in particular, the labor protection department. The list of issues under consideration can be found in Appendix 3 to GOST 12-0-004-90. The text of the introductory briefing is approved by the employer (manager) and the chief engineer of the enterprise, after which it is registered. As a rule, the questions under consideration contain the following information:
- Data about the organization and main activity (production features).
- Basic provisions on labor protection, safety, as well as part of the introductory fire safety briefing.
- Excerpt from the employment contract, which stipulates working hours, break schedules, social security, requirements for the employee, etc.
- Inner order rules.
- Data on the locations of various services and production facilities.
Registration of completion of induction training must be recorded in a log. The content of introductory briefings necessarily includes consideration of various hazards inherent in this production, which can lead to serious consequences, including a threat to life. It is recommended to have information posters on occupational safety, health and safety in the room where the training is carried out.
Unscheduled briefing
Unscheduled briefing is carried out by:
- upon the introduction of new or revised standards, rules, instructions on labor protection, as well as amendments to them;
- when changing the technological process, replacing or upgrading equipment, devices and tools, raw materials, materials and other factors affecting labor safety;
- in case of violation by workers and students of labor safety requirements, which can lead or have led to injury, accident, explosion or fire, poisoning;
- at the request of supervisory authorities;
- during breaks in work - for work for which additional (increased) labor safety requirements are imposed for more than 30 calendar days, and for other work - 60 days.
Sample list of questions for initial training
The information contained in the program of primary instructions for employees of a certain section or workshop is processed at the first stage by the immediate manager of the department. After this, the compiled text is reviewed by the labor protection service or the employer or an authorized person.
A correctly composed text should not only reflect current norms and requirements, but also take into account the specifics of a given production unit, as well as the characteristics of the employee’s profession. First of all, it is necessary to proceed from the occupational safety requirements, taking into account operational standards and technical documentation. You can familiarize yourself with the recommended list of questions in Appendix 5 to GOST 12-0-004-90. The text should reflect the following information:
- Data on the specifics of the equipment used on the site and the technological cycle.
- Information on how to properly organize a dedicated workplace, taking into account occupational safety, health and safety requirements.
- If there are dangerous zones in the mechanism of a machine or other equipment, pay attention to them.
- Consider the possibility of blocking equipment, operation of alarm systems, etc.
A complete list of questions for certain professions is given in regulatory documents. After workers have completed the initial training, an oral survey can be conducted to determine their knowledge of basic production instructions. If the test result is positive, a registration is made in the logbook, which indicates that special training in safety standards was carried out in accordance with the requirements of current norms and standards. After this, permission to independently perform their duties is issued by order, after which you can begin to use the skills of safe working methods.
Related articles:
- The damaging effect of electric current on the human body
- Safe exit from the step voltage zone
Re-briefing
All workers undergo repeated training at least once every six months. Drivers are given briefings every quarter.
Repeated instruction is carried out according to the initial instruction program at the workplace in full.
Initial training program
This is a document issued for each profession. It indicates the topics of the briefing and the time required to study them. And most importantly, the numbers of instructions according to which workers of a particular profession are instructed.
initial training programs |
If an enterprise treats training formally, then sometimes you can see in a magazine how on the same day a dozen people in one department were trained, and according to different instructions. If at least one hour is allotted for each person in the program, then the instructor would have to have a ten-hour working day. This can only mean that in fact people were given to sign in a pre-filled journal.
At the same time, you can conduct briefings with employees who have the same training programs.
On the basis of what documents are instructions developed?
Safety instructions are developed on the basis of labor protection rules, operating instructions, taking into account the job responsibilities of a particular employee . If an employee performs part-time work, then he needs to be familiarized with the instructions both at the main and at the combined workplace.
But if both electric forklifts and forklifts are used in the same workshop, it is necessary to develop instructions for each type of fuel, even though the worker has the same profession - forklift driver. Therefore, instructions are developed in strict accordance with the type of equipment or machines being serviced.
In one case, the fuel system is gasoline, and in the other, it is powered by electric energy. Accordingly, security measures will differ.