If you are at the very beginning of your professional journey, it will be convenient for you to follow the “Occupational Safety and Health from Scratch” plan, which tells you step by step what needs to be done first and progressively. Indeed, in the direction of “Occupational Safety and Health,” as in any other matter, experience does not appear immediately; it needs to be accumulated and multiplied.
There is a lot to learn and do, and we should not forget that the rules and regulations in legislation often undergo changes, more and more requirements are added to ensure safe working conditions for workers - and all this needs to be monitored, trying not to get confused.
And to simplify your task, I will continue to talk in small steps about the basics of labor protection. And if you have something to add, tell or want to ask a question, write comments and we’ll discuss.
- Certificate for workwear
What influences the way a company organizes labor protection
The method of organizing OT depends on:
- level of mechanization and automation of the technical process;
- ergonomic indicators (work and rest schedule, emotional and physical stress of workers);
- aesthetic requirements for the working environment;
Occupational Safety and Health
- sanitary factors (air quality, water quality, gas pollution, noise, lighting);
- organizational abilities of management (work regime, form of its organization, discipline);
- the severity of work, emotional and physical stress of employees;
- social factors;
- natural and climatic factors;
- economic factors.
The operating conditions of an enterprise directly affect how labor protection is organized.
Organization of labor protection in production
What is the mandatory minimum of labor protection in every organization?
Labor protection and fire safety at the enterprise
A newly formed enterprise is required to have at its disposal the following minimum list of documents on occupational safety. You will need papers regarding labor protection. Personnel documents will also be required. An enterprise cannot start operating without:
- staffing table;
- internal regulations;
- orders for granting vacations and their schedule;
- work books and employment contracts;
- instructions that all employees are required to study;
- personal cards of workers (the individual entrepreneur may not have them);
- documents on the procedure for issuing wages.
It is necessary to have documents related to electrical safety:
- a journal for recording the knowledge and standards acquired by the employee in the field of working with electrical installations;
- a list of professions and positions, as well as jobs to which the electrical safety group is assigned.
Documentation regarding fire safety will also be required.
Most of the documents are available in finished form; the management of the enterprise can only interpret them for their own production.
Documentation
Can a Health and Safety Engineer work part-time?
The Labor Code obliges the employer to create the position of safety engineer or an entire service if his enterprise has 50 or more employees. If there are fewer of them, the employer is allowed:
• introduce the position of occupational safety and health engineer or create a corresponding service; • do this work independently; • assign these responsibilities to another employee (the employee must have education in labor protection in accordance with the professional standard); • involve a third-party specialist.
At the same time, the employer determines the amount of time allotted to the safety engineer to perform his work independently and records this in the staffing table. Therefore, it is not prohibited for a health and safety engineer to work part-time, part-week, or part-time. To optimize calculations of the load that is planned to be assigned to one person, it is advisable to use inter-industry standards for the number of workers in the occupational safety service developed by the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation. This is a document of a recommendatory nature.
Features of labor protection at manufacturing enterprises
Occupational safety and health at catering establishments
Labor protection at manufacturing enterprises has the following features:
- this issue is under the jurisdiction of the organization’s management (Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- if a company has more than 50 employees, a separate division responsible for labor protection is created on its basis (Article 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
Important! One person appointed by the manager may be responsible for labor safety measures developed from scratch according to the step-by-step instructions of 2021.
How to organize
Absolutely all managers and specialists of the organization are involved in the process of organizing and managing occupational safety. But the obligation to have an entire structure on staff is provided only for large enterprises. In accordance with Art. 217 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, its own division or labor protection service is formed when the number of personnel exceeds 50 people. Productions with a smaller number of employees implement it with the help of one specialist hired part-time.
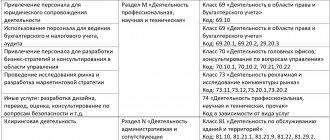
If a specialized labor and industrial safety service is created at an enterprise, regulations must be developed for its normal operation. It is usually specified in the Regulations and contains information about the organizational structure, subordination, responsibility, types of activities, and controlling units. We list the main documents that an organization must have:
- orders to create a unit whose purpose is to ensure occupational health and safety at work;
- orders on the appointment of responsible persons, the creation of a commission to test knowledge of safety precautions;
- instructions, schedules of briefings, logs of their registration;
- introductory and initial training programs;
- job descriptions that specify the responsibilities of managers in labor protection and industrial safety;
- lists of professions and positions exempt from instruction;
- other documents (regulations, rules, job descriptions, training programs, examination reports, certificates, etc.).
If you are faced with issues of ensuring technospheric safety for the first time, then use the step-by-step instructions “occupational safety from scratch” as a diagram.
Step 1. Determine the need
Here we are talking about the staffing level at a specific enterprise. If it is more than 50 units, then a separate service is created. If finances allow and there is a need, then a service is organized provided that the staff is less than 50 workers. This structure must report directly to the manager, because the employees of this unit have the right to issue instructions to eliminate identified deficiencies. The recipients of the instructions are deputy heads of the enterprise and heads of structural divisions. In addition, the order of a service specialist can only be canceled by the official to whom he is subordinate, and only in writing. The occupational health and safety management system has its own hierarchy, which is not related to staffing. For this reason, occupational safety workers report to the first person of the enterprise.
The OT service must solve the following tasks:
- directly ensuring the safety of all stages of the production process;
- professional training and advanced training, propaganda and visual agitation;
- participation in the selection of optimal work and rest regimes;
- professional selection of performers for dangerous and harmful production areas.
Step 2. Assigning responsibility
Occupational safety specialists are required to comply with the professional standard approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor dated August 4, 2014 No. 524n. This requirement is necessary to ensure the safety of technological processes and production. A specialist must have specialized education and experience; it will not be possible to assign “your” person to this job. If there is no specialist, he is invited to work part-time.
Those responsible locally are not required to have special education in technospheric safety, but are required to undergo training within the framework of the program provided for by the Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of January 13, 2003 No. 1/29. All local responsible persons are appointed by the employer’s local regulations, because industrial safety and labor protection require a clear delineation and delegation of authority.
Step 3. Preparation of regulatory documentation
After selecting and approving those responsible, it is necessary to develop a regulatory framework, which includes:
- instructions and regulations, for example, instructions on labor protection and industrial safety when working with pressure equipment;
- interaction schemes between services and departments;
- regulation (standard regulation on OSMS approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor dated August 19, 2016 No. 438n).
Why is labor protection needed in a manufacturing enterprise?
Labor protection at the enterprise: rules, organization
Labor protection at an enterprise is necessary:
- to reduce the risk of occupational injuries, including those incompatible with life;
- improving working conditions, which automatically reduces the number of paid sick leaves and the amount of compensation for harm;
- to reduce plant downtime due to the absence of injured employees.
For this purpose, every enterprise implements an occupational safety management system.
Sample list of documents
What is safety precautions in an enterprise?
These are rules whose compliance guarantees the life and health of workers at a specific production facility. Occupational safety and health is the responsibility of the employer, which is imposed on him by a number of regulations, including:
- Labor Code;
- Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ;
- Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ;
- Order of the Ministry of Labor dated December 29, 2014 No. 1197;
- Government Decree No. 1160 dated December 27, 2010 and a number of others.
Occupational safety (OSH) is associated with the prevention and prevention of injuries and occupational diseases. At the end of 2021, 4,479 serious accidents were recorded in Russia, 1,158 people died. The Ministry of Labor in its message did not specify who is to blame for the deaths of workers, but, as a rule, the main cause of death is the human factor. Occupational safety is ignored by individual workers, which ultimately leads to tragic consequences. Compliance with industrial safety norms and rules and unconditional compliance with workplace regulations allow you to:
- save the lives of yourself and other workers;
- not to violate the law and not to cause harm to people’s health with subsequent administrative (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses) or criminal liability (Article 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation);
- do not violate labor discipline and maintain all benefits and additional payments at the workplace;
- keep your job, since violation of safety regulations by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for termination of the employment contract (Article 81 and Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Occupational safety management system in the organization
The OT management system means:
- organizing training classes and allocating appropriate training hours to train employees in occupational safety standards and regulations;
- equipment of the workplace in accordance with legal norms;
- creating working conditions that would not have a negative impact on the employee’s body;
- organizing the supply of PPE to all employees;
- working on plans to deal with emergency situations that result in employee injury;
- measures to provide workers with necessary treatment.
The list of measures to improve occupational health is being introduced gradually.
Sample order on labor protection at an enterprise
When choosing a person responsible for labor safety, the head of the enterprise is obliged to sign the corresponding order. It is compiled according to a generally accepted model by any competent employee of the company and contains:
- information about the enterprise;
- information about the responsible person;
- list of responsibilities of the responsible person.
Order
The document ends with the number and date of its preparation.
Important! The order can be printed or issued by hand; it does not have to be certified with a seal (an individual entrepreneur may not have a seal).
Drawing up an order for the appointment of responsible persons
A responsible person for labor protection is appointed in organizations with a staff of over 50 people. The design of this document on labor protection is not strictly regulated; it is written in free form. Indicated:
- Full name, position of the responsible person;
- responsibilities that are assigned to him.
The document makes reference to the legislative act or order in pursuance of which it is drawn up.
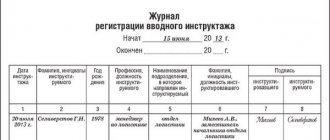
The employee must be familiar with the order against signature. The order is approved by the head of the organization. The document is drawn up on company letterhead and recorded in a special journal.
Compiling a list of harmful and dangerous production factors
When taking into account harmful and dangerous factors, they study:
- features of equipment, materials and raw materials with which workers come into contact;
- the results of the checks performed;
- results of tests and studies for the presence of harmful or dangerous factors;
- information about previous accidents associated with the harmful effects of production factors on workers;
- suggestions received from employees.
Important! A correctly compiled list of factors harmful to employees of an enterprise does not exclude the need to measure the time of their impact on individuals in a particular profession.
After taking into account all the factors, they take a list of the organization’s employees and, based on information about the profession and position of each employee, make a list of what can be considered harmful to health and life, including, for example, radiation from a computer monitor, lack or excess of light, loud sounds.
Action plan for organizing labor protection
An action plan for organizing occupational safety usually consists of the following points:
- event numbers;
- names;
- implementation deadlines;
- columns to indicate the responsible person;
- lines to indicate the cost of the work performed.
The plan may be part of an employment contract concluded between the employer and employee or an independent document. The list of measures necessary to improve the quality of occupational safety is contained in Order of the Ministry of Labor No. 181n. To implement it you will need:
- Create an OT management system at the enterprise.
- Appoint a person responsible for occupational safety.
- Issue an OT Order.
- Adopt an Order on the appointment of persons responsible for occupational safety.
- Approve OT instructions.
Important! Responsible persons are required to implement activities in accordance with the plan.
Organization of personnel training
All individuals working in the organization are required to periodically pass an occupational safety exam. To this end:
- general briefings are conducted for all employees who have just joined the company (one time);
- special briefings (once a year) for certain categories of employees (regularly).
In total you need to go through 5 types of instructions:
- introductory (when applying for a job);
- primary (conducted by the head of the structural unit);
- repeated (once every 3 months);
- target (if the technician needs to perform a specific job);
- unscheduled (if required by the inspector).
If necessary, employees of the organization are sent to OT training. After conducting the briefing and passing the safety knowledge (HS) exam, employees sign in the logbook for registering the briefing.
Important! 40 hours are allocated for training a manager, and at least 20 hours for training ordinary workers.
Employer Responsibilities
The requirements for what the working environment, labor protection and safety precautions should be for each specific employer are established in Art. 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, among them:
- ensuring the protection of workers when performing their job duties;
- organization of OT system management;
- acquisition and provision of employees at the expense of the employer with the necessary means of protecting health and life (PPE);
- development and implementation of instructions on labor protection and industrial safety for each profession, taking into account the specifics of the enterprise;
- training, briefings and testing of personnel knowledge in the field of production processes;
- control of correct use, this function is sometimes transferred to the industrial safety and labor protection department;
- accident prevention;
- participation in compulsory insurance programs against accidents and occupational diseases, etc.
In addition to these responsibilities, the employer is required to organize and conduct special assessments of the workplace of its personnel. The need for this event is established by Federal Law No. 426-FZ dated December 28, 2013 and is designed to ensure labor safety in industry. During the assessment of workplaces, control measurements will be carried out in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Labor dated January 24, 2014 No. 33n. The result of the measurements is the establishment of a hazard class for each specific workplace.
Read more: What the enterprise administration needs to do to carry out SOUT
Preparation of training programs
The educational process is impossible without properly developed instructions and training programs relating to each profession and type of work performed. Ready-made programs can be purchased from companies that compile them.
Ready-made training programs on labor protection
Employees’ knowledge is tested using ready-made training programs, after which an inspection protocol is drawn up. Employees must undergo training annually or every time there is a change in profession, position, after a transfer or break in work. Management is retrained once every 3 years.
What local documents regulate
State regulations set out the requirements that must be observed by legal entities and individuals in the process of carrying out production and other activities:
- in construction - during the design, construction of buildings, reconstruction;
- during operation of objects;
- designing equipment, various mechanisms, machines;
- development of technological processes;
- labor organization.
At the level of local regulations (LNA), the employer approves documents that further determine:
- how the occupational safety and health management system (OSMS) will function;
- the procedure for the safe performance of all types of work - it is prescribed in detail how this or that operation is performed;
- procedure for equipment operation and maintenance.
Office work on labor protection is included in the general document flow of the enterprise.
Documents on labor protection at the enterprise
The enterprise must have the following documents on occupational safety:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- Orders of the Ministry of Labor;
- safety instructions, both general and specific (for each type of work);
- an order for the enterprise regarding the appointment of persons responsible for organizing labor protection;
- a list of employees who are required to undergo regular medical examinations;
- a list of professions and types of work that are particularly dangerous (there may not be any);
- occupational safety action plan;
- briefing log;
- journal for issuing personal protective equipment.
The presented list of documents can be supplemented in accordance with the order of the organization’s management or at the request of the inspection person.
Plan
Step 8 | Dermatological personal protective equipment
Many people miss the fact that when implementing and building their “occupational safety and health from scratch” plan step by step in an organization, they must not forget, in addition to workwear, to include the issuance of dermatological personal protective equipment.
For example, creams are necessary as a protective shell for the skin, because exposure to harmful factors can lead to serious occupational diseases for employees. The employer is obliged to purchase them at his own expense and issue them free of charge.
It is necessary to approve a list of professions that should receive rinsing and disinfecting agents. To do this, you need to use the order of the Ministry of Health No. 1122n.
Let me remind you that Order No. 805n abolished the employer’s obligation to record the provision of soap in personal cards if employees work in jobs with easily washed off contaminants.
All others are issued in accordance with the rules. By the way, in addition to soap, employees should be given additional protective, regenerating and restorative creams, cleansing creams, gels and hand pastes free of charge.
All others are issued in accordance with the rules.
By the way, in addition to soap, employees should be given additional protective, regenerating, restoring and cleansing creams, gels and hand pastes free of charge.
This is for those employees who come into contact with oils, lubricants, petroleum products, adhesives, bitumen, irritating chemicals and other things.
The quantity, period of use and what exactly needs to be given out are found in the order of the Ministry of Health No. 1122n. We develop standards for issuing PPE, after which they are approved by the employer, also without worsening the conditions for workers.
You can read more about the distribution of cleaning agents and disinfectants here. There are also sample documents 
We record the issue in personal cards signed by employees. Unreasonable omissions in the provision of creams will lead to fines, because the inspector will consider this a gross violation and issue a fine.
The law provides for the following punishment (Part 1 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses):
- for officials and individual entrepreneurs – from 2,000 to 5,000 rubles;
- for legal entities – from 50,000 to 80,000 rubles.
Why is it beneficial to seek help from specialized companies?
It is possible to involve third-party organizations in assessing working conditions and drawing up programs for training workers in occupational safety standards and conducting such training; this is beneficial. To the employer:
- there is no need to keep a specialist on staff who could train the rest of the staff;
- there is no need to allocate a special place where lessons could take place.
Important! A specialized company usually guarantees that the employee undergoes all necessary training. Upon completion of the SOUT or training process, the customer is issued a corresponding report.
What is the responsibility for violations in labor protection organizations?
If the head of an enterprise has not taken measures to train employees in occupational safety standards, he is responsible for this before the law.
Criminal liability
This type of liability occurs if an accident occurs at the enterprise due to non-compliance with safety regulations, and the person responsible is caught in it. They are held accountable under Art. 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. The culprit of the incident is punished depending on the degree of guilt and the harm caused. The court has the right to fine the guilty person in the amount of up to 400 thousand rubles*, send him to forced, compulsory or correctional labor, and restrict freedom for up to 1 year (possible loss of license for the same period).
If people died, the term of imprisonment is increased to 4 years, and the period of disqualification to 3 years.
Administrative responsibility
They are brought to administrative responsibility under Art. 2.4 and art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Responsible persons are fined or forced to cease activities until all labor safety problems discovered by the inspector are eliminated.
The legislative framework