Induction training is a mandatory element of labor protection in any production facility and in any organization. It is better to do everything in the employer’s power to try to prevent accidents and injuries among employees, especially since induction training is strictly prescribed by labor legislation. This is the very first procedure that every new employee must undergo before starting his glorious career in a new field.
Below we will analyze what the mandatory elements of introductory briefing on labor protection are, clarify its functions and purpose, and also provide an approximate example of this type of briefing.
- Form and sample
- Free download
- Online viewing
- Expert tested
FILES
Why are briefings needed?
Each company, in order to organize safe work, develops and approves an occupational safety standard.
It contains information about the procedure, frequency of instructions, as well as full name. and positions of responsible persons. In addition, occupational safety instructions are developed and approved for all professions and positions in the organization. These documents are basic for instructing employees. Before being allowed to work, employees must undergo:
- introductory briefing and initial on-the-job training;
- internship (from 2 to 14 shifts).
Employees can begin work after instruction, internship, testing of occupational safety knowledge and if they have proven skills in safe ways to perform work.
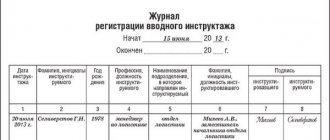
Recording those who have completed induction training
Each employee who has received an “induction” must be recorded in the appropriate journal according to the uniform form assigned to the enterprise. Typically the following information is recorded:
- date of instruction;
- Full name and position of the trainee;
- Full name and details of the instructor;
- signatures of both parties.
You can also enter additional information if the manager deems it necessary, for example, the results of checking the effectiveness of the training.
Requirements for business documentation require the pages of the magazine to be numbered, bound and sealed.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! A sample of the title and first pages of this magazine must be added to the approved induction program as appendices.
Guide: instructions and labor protection
From January 1, 2021, some acts and certain provisions of some acts of the Government of the Russian Federation are declared invalid, and acts and certain provisions of acts of federal executive authorities containing requirements, compliance with which is assessed during the implementation of federal state supervision over compliance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts, are repealed , containing labor law standards, and federal state control (supervision) in the field of social services. See Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated August 4, 2020 N 1181. Changes will be taken into account in the material when it is updated.
Continue reading in ConsultantPlus
The employee’s immediate supervisor is responsible for conducting on-the-job training. The number of classes depends on the complexity and danger of production or other non-productive activities in which the organization is engaged. An employee who has successfully completed the training can begin work.
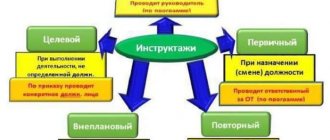
Based on the nature and timing of the briefings conducted at the workplace, they are divided into:
- introductory;
- primary;
- repeated;
- target;
- unscheduled.
Let's talk about each of them in more detail.
Who should instruct workers?
Introductory training, developed in accordance with laws and regulations, is carried out by a labor protection engineer or a specialist appointed responsible by order of the manager.
The rest of all types of briefings are carried out by the immediate supervisor of the structural unit where the employee works (head of the workshop, foreman, head nurse, head of the household and others).
The instruction itself consists of familiarizing workers with hazardous factors in the process of performing their duties and methods, work techniques in order to protect themselves and others as much as possible from accidents and injuries (occupational diseases).
An oral survey tests the acquired knowledge and understanding of the basic requirements for safe work, the use of personal and collective protective equipment, providing first aid to victims of electric shock, fire, lightning strikes (and others depending on the specifics of the work).
Initial briefing
It is carried out by the immediate supervisor, who has been trained and tested for knowledge of occupational safety requirements, as a rule, on the first working day when the employee is allowed to work independently. Required:
- to everyone entering work in the department, including employees who have entered into a contract for a period of up to 2 months. or for the period of seasonal work, as well as part-time workers;
- employees of the organization transferred from another structural unit, or employees who are entrusted with performing work that is new to them;
- seconded employees of other companies, students arriving for practical training, and other persons taking part in the production activities of the enterprise.
But for some categories of employees an exception may be made. Persons whose work is not related to the operation, maintenance, testing, adjustment and repair of equipment, the use of electrified or other tools, or the storage and use of raw materials and materials may not undergo instruction. The list of positions of employees exempt from employment is approved by the employer.
The following issues are covered during the training:
- route to the workplace;
- methods of performing job duties;
- precautionary measures;
- requirements for clothing, shoes and general appearance of the employee.
Read more: Initial briefing on labor protection in the workplace
What is induction training
Induction training is mandatory for every newly hired employee, regardless of position and rank. Those coming to work include:
- newly hired employees;
- recovered after dismissal;
- those arriving on a business trip;
- trainees;
- employees from other organizations performing any activities on the territory of the organization.
A person who comes to a new place is in a position where many circumstances are “new” to him, which should not affect the quality of his work, but mainly the safety during its performance. During induction, a new team member (alone or together with colleagues in the same position) should gain an understanding of:
- the enterprise itself;
- your personal or collective workplace;
- internal regulations;
- discipline requirements;
- other important features.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Induction training is a one-time procedure. It does not need to be repeated for internal transfers or leave. But if a person quits and then returns, induction training is necessary, as for a “newbie”.
Re-briefing
It is carried out by the immediate superior in the following cases:
- if an emergency situation arises, during which it turns out that employees lack knowledge in the field of occupational safety and workplace safety;
- after some time to update employees' knowledge.
As a rule, all workers undergo repeated training at the workplace, the frequency of which should be at least once every 6 months. It does not matter their qualifications, education, experience, or the nature of the work performed.
Workers whose work is associated with high-risk equipment must also be given repeated instructions on labor protection, the frequency of which is once every 3 months.
At the end of the training, the instructor conducts an oral debriefing to ensure that the employees have mastered the new knowledge.
How to fill out a workplace briefing log
Log form: recommended - Appendix 6 “GOST 12.0.004-90. Interstate standard. System of occupational safety standards. Organization of occupational safety training. General provisions." Highlighted in blue are those items that we suggest you include in the form proposed by GOST.
Who fills it out (conducts instructions)? Direct supervisor of the work. Assign the responsibility for conducting workplace training to specific employees by order for the organization (for example, “On conducting training on labor protection”), the order should cover all structural divisions of your company. Remember that your responsible persons must have a valid certificate of completion of special training in labor protection (at least once every 3 years). Information to fill out.
This log registers the conduct of primary, repeated, unscheduled, targeted briefings. Each person responsible for conducting the listed briefings maintains his own workplace briefing log for his department. To conduct briefings, you will also need:
- A list of labor safety instructions in force in your organization;
- Instruction programs;
- Occupational safety instructions - you may also be interested in our article.
Unscheduled briefing
It can be carried out:
- separately with each employee;
- with a group of employees with the same profession.
The volume and content of training depends on the reasons and circumstances that necessitated its implementation. It is carried out by the immediate supervisor when:
- the introduction of new and amended legislative acts relating to occupational safety, as well as instructions on occupational safety;
- changing technological processes, installing new equipment, etc.;
- violation by employees of occupational safety requirements, if this may cause an accident at work or accident;
- at the insistence of officials of state supervision and control bodies;
- during long breaks in work (for work with harmful and/or dangerous conditions - more than 30 calendar days, and for other work - more than two months);
- by the employer's decision.
The results obtained during instruction are recorded by the instructor in a special journal. The employee gets acquainted with them under his personal signature. The instructor also signs in the appropriate box.
Justification by law for the need for briefings
Today, in the main law regulating the norms of labor relations - the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - an entire X section is devoted to issues related to labor protection.
Chapter 33 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation gives the basic concepts:
- on labor protection as systemic measures to preserve the life and health of members of the workforce in the process of activity;
- safe working conditions that the employer must provide, as well as individual and collective means of protection in cases of threat of exposure of workers to harmful and dangerous production factors.
The entire occupational safety management system is a set of measures to implement work safety standards in compliance with the rules of their conduct and labor protection.
But, in order for a person not to violate the basic dogmas of security, he must know them.
One of the main responsibilities of an employer is to ensure the safety and labor protection of its subordinates, according to Art. 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is:
- train the employee in methods of safe work and providing first aid to victims of accidents;
- conducting labor safety briefings before admission to the internship in the presence of a mentor and testing the acquired knowledge.
An important condition is the prohibition on allowing persons to work independently if they have not undergone training, internship, or knowledge testing on issues related to basic labor protection rules.
Norms Art. 225 oblige the employer to conduct instructions personally or by an authorized representative who has undergone mandatory training and knowledge testing in the Procedure approved by Resolution No. 1/29 of January 13, 2003, as amended on November 30, 2016.
Records management
All briefings carried out must be reflected in registration logs, numbered, stitched, properly signed by the person responsible for conducting the briefing (the head of the structural unit), the employer and the seal of the enterprise.
The log states:
- serial number of the record;
- date of training;
- name of the briefing;
- for unscheduled and targeted briefings - the rationale for their conduct (for example, the order number and the date of its issue);
- personal data of the person being instructed, the name of the position or profession held, specific place of work;
- information of the instructing person – position, surname, initials of first name, patronymic;
- personal signatures of the instructed and instructing workers.
When inspecting an enterprise, regulatory authorities may request:
- orders on the appointment of persons responsible for labor protection;
- orders indicating the reason for the need to conduct unscheduled and targeted briefings;
- approved programs for which instructions are provided;
- the instructions themselves.
Does the procedure for conducting occupational safety training apply to homeworkers?
Homeworkers are persons who work for the benefit of an employer at their place of actual residence. He provides them with raw materials, supplies, and necessary equipment. The conditions in which their work is organized must comply with occupational safety requirements in the same way as for “ordinary” workers. Employers are notified of the existence of this need by Art. 311 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, homeworkers also need to be trained in occupational safety in the full extent appropriate to their activities. This also applies to instruction. The employer organizes training for home-based workers and may exempt them from instructions on the same basis as employees who work on the territory of the enterprise.
To complete the tasks assigned to a home worker, he can use the help of his family. If he does this, he must remember: the employment relationship exists only between him and the employer. There is no such relationship between members of his family and his employer, therefore, they are not given occupational safety training.
Who must be instructed
The list of persons who must receive instructions from the employer is given in paragraph 1 of clause 2.1.2 of the Training Procedure. These include, in particular:
- all citizens newly hired (even if the employee quit and then got a job again at the same company, he is still included in this list);
- all persons seconded to the company from other companies;
- specialists from third-party companies performing work in a designated area;
- students of educational institutions of appropriate levels undergoing practical training;
- all other persons who participate in production activities.
The employer has no right to allow persons to work who have not completed induction training.
Prosecution
Since ignoring timely instructions can lead to irreversible consequences, including major accidents and industrial accidents with fatal consequences, for the officials responsible this is fraught with a fine of 15-20 thousand rubles in accordance with the third part of Art. 5.27.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
If a similar violation is repeatedly detected, the sanctions are tightened by increasing the amount of fines or suspending the activities of the enterprise for up to three months (the fifth part of the same article).
Who is the instructor
Clause 7.13 of the Recommendations for organizing the work of the occupational safety service in an organization, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated 02/08/2000 No. 14, indicates who conducts induction training on labor protection when hiring or transferring to another position. New employees are instructed by a special service or an occupational safety specialist, if there is one in the organization. Persons who have the right to instruct on occupational safety are established in clause 2.1.2 of the Procedure for training in labor protection and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements for employees of organizations, approved by the joint resolution of the Ministry of Labor and the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29. These are, in particular:
- Head of the organization;
- OT specialist;
- an employee who is assigned these duties by order of the employer (or a person authorized by him).
The Russian Ministry of Labor, in letter No. 15-2/OOG-2884 dated 08/09/2016, indicated that even if the organization does not have an occupational safety specialist, the employer assigns responsibilities related to instructing workers on safety precautions and other rules to any person. The main condition is that he undergo training and testing of knowledge of occupational safety requirements in training organizations accredited in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 1, 2010 No. 205n.
If the director is the sole founder of the company and an employment contract has been concluded with him, he conducts induction training for himself, provided that there is no other employee authorized for this (letter of Rostrud dated April 27, 2017 No. PG/08346-03-3).
Instruction of new employees should be carried out in a separate occupational safety room or other specially equipped room. During the event, visual aids and other modern technical teaching aids should be used (clause 7.1.3 of GOST 12.0.004-90). Let's look at step by step how to conduct an introductory briefing on labor protection in an organization for a new employee:
- Approve the program.
- Identify responsible persons.
- Set a time and place for instruction.
- Give a lecture.
- Check how employees have understood the information.
- Write down the data in the journal and certify it with the signature of the person being instructed.