The balance sheet is a statement that is mandatory for almost every enterprise. This document is necessary to fully reflect the processes that take place within the company, but not everyone has an idea of how to draw it up correctly. This issue is especially relevant for people who have just registered an enterprise and are faced with such a procedure for the first time. Let's look at this question in our article using an example for dummies and try to formulate a number of recommendations that can help in drawing up a balance sheet.
What is a balance sheet and why is it prepared?
Most Russian companies compile and present various accounting reports.
The main set of such reporting includes five forms:
- Form No. 1 - “Balance Sheet;
- Form No. 2 - “Report on financial results”;
- Form No. 3 - “Report on changes in capital”;
- Form No. 4 - “Cash Flow Statement”;
- Form No. 5 - “Appendix to the Balance Sheet”.
I propose to take a closer look at form No. 1 – balance sheet.
The balance sheet is information about the company’s property (assets) and the sources of its acquisition (liabilities), grouped as of the reporting date in the form of a table. An asset is always equal to a liability!
Let's get acquainted with the principles of drawing up a balance using the example of the budget of one Russian family.
Example
A large, friendly Pugovkin family lives in the city of N. The family is wealthy by city standards. They have: an apartment, a car, household appliances, furniture, clothes, food, a summer house. In addition, there is money in the wallets and bank accounts of family members.
In general, the Pugovkins have everything they need for a comfortable active life. These will be the assets of the Pugovkin family.
Take a sheet of blank paper and write all of the above in 2 columns.
Assets of the Pugovkin family:
| Article | Name | Cost, thousand rubles |
| 1 | Apartment | 4 000 |
| 2 | Country house | 1 000 |
| 3 | Car | 1 100 |
| 4 | Appliances | 300 |
| 5 | Products | 50 |
| 6 | Money in wallets | 30 |
| 7 | Money in the bank | 450 |
| 8 | Furniture | 610 |
| 9 | Cloth | 40 |
| 10 | Total | 7 580 |
To acquire all this, the family needed funds. Therefore, the Pugovkins took out a bank loan and borrowed part of the money from friends. In addition, the Pugovkin family currently has unpaid utilities and property taxes.
A bank loan, debt to friends, unpaid utility bills and taxes are the liabilities of the Pugovkin family.
Liabilities of the Pugovkin family:
| № | Name of liability | Cost, thousand rubles. |
| 1 | Bank loan | 6 184 |
| 2 | Debt to friends | 1 200 |
| 3 | Debt to utilities | 11 |
| 4 | Tax debt | 25 |
| 5 | Salary of family members | 160 |
| 6 | Total | 7 580 |
The assets and liabilities of the balance sheet are divided into several parts.
Asset sections:
- non-current assets;
- working capital.
Passive sections:
- capital and reserves;
- long term duties;
- Short-term liabilities.
The balance sheet is in demand by various users.
External users:
- tax authorities;
- banks;
- investors;
- partners (counterparties).
Internal users:
- shareholders of the company;
- planning and analytical department.
What is the document for?
The indicators reflected in the balance sheet indicate the financial position of the company.
They are necessary for the enterprise itself to have an accurate idea of the results of its activities obtained for a specific period: month, quarter, year. All companies are required to maintain and annually submit a balance sheet to various persons:
- tax office;
- statistical government agencies;
- shareholders.
The document shows the financial stability of the company. Therefore, it is used by counterparties: existing and potential partners, clients, banking institutions, government agencies.
The balance sheet determines not only the current state of the company, but also predicts the results of its future activities. Banks use it to calculate the creditworthiness of a legal entity in the course of assessing it as a potential client for servicing and lending.
How to draw up a balance sheet - step-by-step instructions for beginners
The process of preparing a balance sheet is very complicated, not only for beginners. Some aspects of its preparation may cause difficulties for professional accountants.
I propose to consider with me step by step its main points.
Step 1. Specify the details
As a rule, filling out any reporting form begins with the title page. The balance sheet is no exception. To fill it out, a unified form approved by the Ministry of Finance is used.
The first sheet contains the details of the company making up the balance sheet:
- the date on which the form is drawn up;
- Date of preparation;
- Company name;
- an identification number;
- type of economic activity;
- type of ownership;
- unit of measurement;
- location of the company.
Step 2. Fill in the rows of the asset table
The next step is to fill out the asset balance sheet. We take all the information from the balances of the company’s accounts (we use the balance sheet (SAS)).
Example
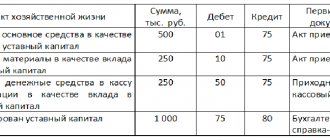
For Pomidorka LLC, 2021 is the first period when the company needs to report, because it was in this year that the company was created. Let's present the balances according to accounting data in the form of a table.
Balances of Pomidorka LLC as of 01/01/2017:
| № | Name | Check | Debit | Credit |
| 1 | Fixed Assets (Fixed Assets) | 01 | 500 | |
| 2 | Depreciation of fixed assets | 02 | 26 | |
| 3 | Intangible assets (IMA) | 04 | 100 | |
| 4 | Depreciation of intangible assets | 05 | 4 | |
| 5 | Reserves | 10 | 460 | |
| 6 | VAT | 19 | 16 | |
| 7 | Money in the cash register | 50 | 40 | |
| 8 | Funds in bank account | 51 | 120 | |
| 9 | Authorized capital | 80 | 30 | |
| 10 | Reserve capital | 82 | 10 | |
| 11 | retained earnings | 84 | 150 | |
| 12 | Settlements with suppliers and contractors | 60 | 275 | |
| 13 | Settlements with buyers and customers | 62 | 85 | |
| 14 | Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings | 67 | 300 | |
| 15 | Calculations for taxes and fees | 68 | 16 | |
| 16 | Social insurance calculations | 69 | 90 | |
| 17 | Payroll calculations | 70 | 250 | |
| 18 | Total | 1236 | 1236 |
When drawing up a balance sheet, remember that:
- debit and credit balances in the balance sheet are not collapsed;
- Fixed assets and intangible assets are shown at residual value;
- assets in the balance sheet are reflected at book value.
Information in the balance sheet is divided item by item (approved by the Ministry of Finance). Opposite each item is the amount taken from the SALT on the reporting date; in 2 adjacent columns the itemized value of the property for the two previous reporting dates is indicated.
Continuation of the example
Based on the accounting data of Pomidorka LLC, we will compile a part of the balance sheet called “Asset”.
Active:
| Index | Calculation | Code | as of 12/31/2016 | as of 12/31/2015 |
| ASSETS | ||||
| I. Non-current assets | ||||
| NMA | sch04-05 | 1110 | 96 | — |
| OS | sch01-02 | 1150 | 474 | — |
| Summary of Section I | 1110+1150 | 1100 | 570 | — |
| II. Current assets | ||||
| Reserves | sch10 | 1210 | 460 | — |
| VAT on purchased material assets | sch19 | 1220 | 16 | — |
| Cash and cash equivalents | sch50+51 | 1250 | 160 | — |
| Summary of Section II | 1210+1220+1250 | 1200 | 636 | |
| BALANCE | 1100+1200 | 1600 | 1206 | |
Information is indicated in whole thousands or millions of rubles. Blank rows are not included in the table. In a real balance sheet, all lines must be present; they are simply marked with a dash.
Step 3. Fill in the rows of the liability table
We do the same when filling out the “Passive” section. Let's take a closer look at the example of Pomidorka LLC.
Example
Filling out the “Passive” section:
| Index | Calculation | Code | as of 12/31/2016 | as of 12/31/2015 |
| PASSIVE | ||||
| III. Capital and reserves | ||||
| Authorized capital | count 80 | 1310 | 30 | — |
| Reserve capital | count 82 | 1360 | 10 | — |
| retained earnings | count 84 | 1370 | 150 | — |
| Summary of Section III | 1310+1360+1370 | 1300 | 190 | |
| IV. long term duties | ||||
| Borrowed funds | count 67 | 1410 | 300 | — |
| Summary of Section IV | 1410 | 1400 | 300 | — |
| V. Current liabilities | ||||
| Accounts payable | count 60+62+68+69+70 | 1520 | 716 | — |
| Summary of Section V | 1520 | 1500 | 716 | — |
| BALANCE | 1300+1400+1500 | 1700 | 1206 | — |
Step 4. Compare table values
Do you remember that asset = liability? In the balance sheet, line 1600 and line 1700 have the same figure of 1206 thousand rubles. This indicates that the form is drawn up correctly.
If there are discrepancies in these lines, it means that an error has crept into the accounting, which must be found.
Let me tell you right away, this is not an easy task. First, I recommend checking the arithmetic calculations. If there are no problems with arithmetic, proceed to checking the accounting entries in OSV.
Step 5. We analyze the balance sheet according to its indicators
Analysis of the balance sheet and its indicators is a complex, multi-stage process. I told you how to do it above. The results of the analysis help optimize the financial policy of the company. A high-quality analysis allows you to make competent management decisions.
Forms for formation
The balance sheet must be prepared in a specific form to be presented in a convenient manner to users. Usually it is drawn up according to Form No. 1, which was approved by the Ministry of Finance in 2010. The form is not mandatory, so it can be modified depending on the specifics of business activity and the needs of the company.
For internal use, various forms are created, classified on various grounds:
- By frequency: balance (for a specific date) and turnover (turnover for a specific period).
- Based on initial data: inventory or accounting balance.
- On accounting of regulatory articles.
- Depending on the volume: full and short (simplified) report.
- The document can be preliminary, interim, final, forecast.
- Regarding the event: introductory, unification, separation, liquidation.
This list is not closed. There are other classifications of report forms used by enterprises depending on their needs, interests, and characteristics.
Who provides balance sheet services - review of the TOP 3 companies
Accounting services, including services for preparing balance sheets, are offered by many companies.
By tradition, I have prepared for you, my readers, a selection of reliable, highly professional accounting firms.
1) My business
Internet accounting “My Business”, despite its young age (founded in 2009), has earned well-deserved respect from more than 50,000 users in all Russian regions.
Users note a number of advantages that they have and which predetermined the choice of this company.
Advantages of online accounting “My Business”:
- affordable prices (subscription fee from 366 to 2083 rubles per month);
- friendly, fast and professional support;
- wide range of services and opportunities;
- clear educational materials that can turn a beginner into a professional;
- the ability to register your business online;
- a large database of ready-made document templates for most business processes;
- accountant's bureau, consisting of 17 sections with answers to more than 10 thousand user questions.
If you are still hesitating, then visit the “My Business” website, read reviews from real users, and learn more about the functionality of this service.
A pleasant bonus for new users will be the opportunity to use online accounting services for free for a month.
2) Project-KM
The Moscow company Project-KM has been providing professional accounting services to legal entities, individual entrepreneurs and individuals for more than 9 years.
For the company's staff of highly qualified specialists, it will not be difficult to:
- formulate an Accounting Policy;
- organize accounting of any complexity;
- carry out full or partial restoration of accounting;
- carry out tax accounting;
- organize effective management accounting.
A potential client can receive an initial consultation by visiting the Project-KM office, calling the company, or consulting online on the website.
In addition, on the Project-KM website you can fill out an online form for a preliminary calculation of the cost of services, order services and pay for them.
3) Abacus BC
Abak BC is an accounting company that employs professional accountants with more than 16 years of experience. The company has successfully passed more than 500 tax audits.
Company Services:
- calculation of financial results, taxes and fees of the customer’s company;
- conducting banking and cash transactions;
- preparation and submission of reports;
- personnel records management and organization of settlements with personnel.
Abak BC clients receive a number of benefits from cooperation:
- savings on paying for a full-time accountant;
- 24-hour consulting professional support;
- complete confidentiality.
If you transfer the accounting of your company to the specialists of Abak BK, the savings on accounting costs will be about 32%. This result is achieved due to the fact that the customer pays only for the work actually performed.
Where to submit and when?
First of all, the annual balance must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service.
Suppliers or founders may also request a balance sheet to assess the financial position of the company.
The deadline for submitting the balance sheet for 2021 is March 31, 2020 inclusive.
Previously, one copy of the balance sheet as part of the financial statements had to be sent to the territorial statistics body (Article 18 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). This obligation has been canceled for reporting for 2019. The exception is organizations whose reporting contains state secrets, and those obliged by the Government of the Russian Federation.
All organizations are required to submit reports for 2021 electronically through an EDI operator. Small businesses could also submit reports for 2021 on paper, but this is now prohibited.
What is reflected in the “Inventories” line
All inventories and expenses in balance line 1210 must be entered correctly. To do this, you need to consider:
- Debit balance of account 10 “Materials”, add to it the balance of account 11, which reflects information about animals that are fed and fattened;
- Then the balance of account 14 is subtracted, where reserves are registered that go towards reducing the value of material assets, and the debit balance of account 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets” is added;
- Next, you need to calculate the resulting amount plus/minus the balance of account 16, which reflects information about deviations in the cost of material assets;
- Then add the debit balance of such accounts as 20, 21, 23, 28, 29, 41;
- We subtract from the resulting amount the balance of account 42, namely the data on the trade margin, and add all this to the balance of accounts 44 in the balance sheet, 45, 97.
It is worth noting that the data on accounts 15 and 16 relate only to part of the stocks of raw materials and supplies, and in account 97 only those costs of the enterprise are taken into account, the write-off period of which is no more than a year.
There is a legally accepted form for filling out this line. As experts note, the new form, unlike the previous one, is simplified. It only requires the presentation of basic data without detailed analysis. Despite this, they recommend carrying out this procedure only for those inventories whose original cost is more than 5% of the total size. Thus, all information will be fully disclosed, and such detailed reporting indicates the company’s competent attitude to the preparation of such documents.
As inventories, which are subject to registration in line 1210, we accept tangible and intangible assets that:
- Are used and exploited in the form of raw materials or production materials for the creation, development or production of a labor product;
- The manufacturer plans to send it for sale. It includes finished products in the balance sheet as the final result. Moreover, it must go through all stages before release, namely: high-quality processing, quality testing, checking for compliance with all necessary technical parameters, standards and documentation regulations;
- Management purchased them to apply them to the control system.
There are also actual material costs in the balance sheet for the purchase of inventories, which include:
- The total amount of funds that were paid by the organization to the seller of inventory. All this data is written down in the corresponding document;
- Financial resources that were sent to companies providing information transfer, as well as for consultations. This information is entered in line 1210 only if the organization’s activities directly related to the sale or purchase of inventory;
- The cost of gross output in the balance sheet, distribution costs;
- Expenses for payment of customs duties;
- Payments of taxes that are not refundable. Moreover, they must be related to the purchase of inventories by the company;
- Costs for the transfer of rewards that were paid by the intermediary company after the acquisition;
- Expenses of the organization that were allocated to procurement processes, as well as transportation of inventories. Economists include the costs of maintaining an organization’s warehouse as this type; transport services that were necessary for the delivery of goods, costs of the procedure for selling inventory on the retail market, and so on.