A significant part of cargo transportation is services provided by transport companies or individual entrepreneurs. To do this, the latter buy or rent the necessary equipment. A prerequisite for such activities is the maintenance of accounting for cargo transportation in accordance with the requirements established by Russian legislation.
Our company invites transport organizations and individual entrepreneurs to cooperate, offering comprehensive accounting services. The main advantages of outsourcing accounting are the combination of affordable cost with highly qualified performers. The result is the absence of problems with fiscal authorities at reasonable costs on the part of the customer.
Features of cargo transportation accounting
The provision of services by transport organizations or entrepreneurs is a specific type of activity. It has several features that are taken into account when accounting for cargo transportation. The most important legal nuances are:
- despite the transfer of cargo, ownership remains with the owner;
- the cargo transportation route is developed by one of the parties to the transaction and agreed upon with the other;
- the payer of expenses for insurance and customs clearance of goods is established by contractual obligations;
- organization of warehousing is allowed, which is paid either by the owner or by the transport company;
- services are accompanied by the mandatory execution of a set of documents, including a consignment note, a forwarding note, etc.
Example for calculation
To understand what type of taxation is best to switch to after the abolition of UTII, let’s consider a cargo transportation company registered in St. Petersburg. Let's calculate taxes for it under different regimes. We will make the calculation based on the following parameters:
- income per year – 18,000,000 rubles;
- costs per year – 11,500,000 rubles (personnel costs, fuel, repairs, parking and others);
- number of transport units – 5;
- number of employees – 6;
- expenses for insurance premiums for employees per year - 550,000 rubles (included in costs).
Contributions for employees are indicated separately, since for the simplified tax system Income, and from 2021 for the PSN, a deduction for their amount is provided. It is equal to the amount of deductions paid, but not more than 50% of the tax amount.
If the business is run by an individual entrepreneur, his own contributions are added to the deduction. In 2021, this is 40,874 rubles + 1% of the amount of income over 300,000 rubles. For the purity of the experiment, we will assume that they were not included in the costs.
Now let’s look at the different modes and decide which one to choose when UTII is abolished for individual entrepreneurs and cargo transportation companies.
Free tax consultation
Possible tax regimes
An equally characteristic feature of cargo transportation is the choice of one of three tax regimes - OSNO, simplified tax system or UTII. Each has a set of advantages, which are easiest to understand through a comparative analysis using several criteria given in the table.
| Evaluation criterion/Tax regime | General | Simplified | Imputed income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounting in a transport enterprise: features of cargo transportation services
My native country is wide... There are many forests, fields and rivers in it, but also sellers and buyers. What if the seller is in Moscow and the buyer is in Vladivostok? However, even if we take neighboring cities, the goods between them will still not move by themselves; teleportation is not yet available to humanity.
Not every organization has its own fleet of cars to suit every taste. In such situations, motor transport companies come to the rescue, ready to deliver cargo from a given point A to point B.
Meanwhile, the accountant has his own task - to organize accounting in a transport enterprise in such a way as to comply with all legal norms. And there are a lot of them!
The content of the article:
1 . Regulatory documents for the transportation of goods
2 . Necessary documents for transporting cargo by road
3. Agreement with the carrier for the carriage of goods
4. Taxation system for a transport enterprise with cargo transportation
5. Accounting in a transport company: what is important?
6. Accounting for cargo transportation
7. Procedure for accounting for VAT in a transport organization
8. Accounting for road transport: let's look at an example
So, let's go in order.
Regulatory documents for the transportation of goods
The transport system of cargo transportation is based on the following regulatory documents of Russian legislation:
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Part 2, Section IV, Chapter 40, 41) regulates:
- general provisions on transportation;
- registration of contracts of transportation, chartering, between carriers;
- deadlines for submission and delivery of goods;
- carrier liability arising at different stages of the transportation process;
- claims and lawsuits;
- organization of the transport expedition process.
Federal Law dated November 8, 2007 No. 259-FZ “Charter of Automobile Transport and Urban Ground Electric Transport” discloses:
- cargo transportation rules;
- government oversight measures;
- types of transportation;
- determination of mass and sealing of cargo;
- storage of cargo and cleaning of vehicles by the carrier;
- features of concluding and changing the terms of transportation contracts;
- responsibility of shippers, consignees;
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 15, 2011 N 272 (as amended on December 12, 2017) “On approval of the Rules for the transportation of goods by road.” This resolution reflects the following criteria for organizing cargo transportation:
- principles of concluding a contract for the carriage of goods;
- the procedure for providing vehicles and presenting cargo for transportation;
- determination of permissible load mass;
- procedure for drawing up acts and filing claims.
Order of the Ministry of Transport of Russia dated January 15, 2014 No. 7 “On approval of the Rules for ensuring the safety of transportation of passengers and goods by road transport and urban ground electric transport” sets out:
- ensuring the safety of cargo transportation.
A license is a document that provides permission for certain types of activities. This permit is issued by the Ministry of Transport and Communications through transport inspections. Certain types of transport services require licensing:
- transportation of especially dangerous goods;
- international cargo transportation.
for other shipments it is not required.
These are not all regulatory documents on the transportation of goods that an accountant of a transport organization should be familiar with. There are other regulations of a more private nature, such as traffic rules, rules for the technical operation of cars and their maintenance, etc.
Necessary documents for transporting cargo by road
Cargo transportation represents a special kind of relationship between the recipient of the cargo and the sender, which must be documented. To carry out cargo transportation on the territory of the Russian Federation, you need to have a certain list of documents that relate to both the driver and the cargo.
Driver and car documents:
- a driver's license of a certain category;
- passport;
- vehicle passport and motor vehicle technical passport;
- vehicle owner's MTPL insurance policy;
Documents for transporting cargo by road from the carrier:
- waybill, issued accordingly. It must contain data on state. vehicle number, mileage at the start of the journey, information on fuel consumption, date of issue of the form, details of the cargo registration form, medical examination mark;
- a copy of the driver’s employment contract (if he is not the owner of the vehicle);
- product quality certificate (issued by the shipper);
- power of attorney to drive a vehicle if the driver is a hired person;
- contract for the provision of transportation services;
- waybill if there is no need for a transport bill of lading.
Shipper's documents:
- a consignment note in 4 copies, which is usually prepared by the shipper, contains a commodity and transport section;
- additional documents if these are products, alcohol, animals.
One of the most important documents confirming transportation services is the consignment note (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 15, 2011 No. 272). This is the primary document on the basis of which the carrier confirms almost all of its expenses associated with transportation. This includes write-off of fuel and lubricants, driver's wages and current vehicle repairs. It must be prepared in triplicate.
Along with this document, the consignment note No. T-1 (approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated November 28, 1997 No. 78)
A consignment note is used when the shipper can act as a single carrier. When the carrier is a separate legal entity, a consignment note is used, and the shipper in this case issues a TORG-12 consignment note and an invoice if working with VAT. Both documents are not issued simultaneously for one shipment.
Agreement with the carrier for the carriage of goods
A contract for the carriage of goods is an agreement between the shipper and the carrier. It stipulates all the necessary conditions (Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Part 2, Section IV, Chapter 40, Art. 785):
- first of all, information about the cargo is written down (name, volume, total weight, etc.), the address where the cargo needs to be delivered;
- the time during which the carrier can perform the service, possibly indicating intermediate points along the route;
- financial remuneration, the amount of which is determined individually by the parties, must be specified taking into account the method of payment;
- the responsibilities and obligations of each party, spelled out specifically, will help avoid further disputes in the event of a critical situation;
- other terms of the contract, if the parties need this;
- full details of the parties and seal.
The company that sends the cargo must provide it at the appointed time, in appropriate containers, or without, if this is not required. The driver receives the necessary documents listed above from the shipper. After this, loading occurs; the shipper must control this process, if necessary and specified in the agreement. This will prevent misunderstandings if the cargo is damaged. It will also allow for financial compensation to be claimed in appropriate situations.
The contractor, in turn, must promptly provide the vehicle in a condition suitable for loading. During delivery, the carrier is responsible for the safety of the cargo and is obliged to deliver the cargo on time and to the specified address.
The cargo carrier has the right to demand the necessary markings in the accompanying documents of the cargo and to recover financial losses when the vehicle is idle due to the fault of the shipper. These situations should also be discussed in advance when concluding an agreement with the carrier for the transportation of goods.
Taxation system for a transport company with cargo transportation
Accounting in a transport company depends on the chosen taxation system. Let's take a look at the different taxation systems that can be used:
| Type of taxation | PSN | UTII | simplified tax system |
| Type of ownership | IP | Organizations and individual entrepreneurs | Organizations and individual entrepreneurs |
| Vehicle quantity limit | No | 20 | No |
| Limitations on annual revenue (in million rubles) | 60 | No | 150 |
| Number limit (persons) | 15 | 100 | 100 |
| What does the tax amount depend on? | Potential income amount | Number of cars | income or the difference between income and expenses |
| Tax rates (%) | 6 | 15 | 6 or 15 (benefits available) |
| Opportunities to reduce the tax amount | No | For the amount of insurance premiums, benefits | For the amount of insurance premiums, benefits |
| Related taxes | No VAT, personal income tax | There is no income tax, VAT, personal income tax | No income tax, VAT |
This table does not mention the general (standard) taxation system - OSNO. Its advantage is the absence of any restrictions on types of activities, number of employees, or income received. However, the tax burden here will be the highest.
OSNO is mainly used by large enterprises that are VAT payers. They cooperate with those who pay this tax. For companies involved in cargo transportation, the reason for using this system is the presence of “input” VAT.
Accounting in a transport company: what is important?
Methods of maintaining accounting and tax records in an organization providing transport services are fixed in the accounting policy. The cost of transport services depends on the composition of costs. Main types of expenses reflecting the specifics of the activity:
- Depreciation of fixed assets. This is the distribution of the cost of cars through a monthly write-off to the cost of services, depending on the established depreciation rates.
- fuels and lubricants. Fuel costs reflect the cost of purchased all types of fuel used for the needs of a motor transport enterprise. Fuel and lubricants are calculated according to standards taking into account the mileage of the vehicle.
- Spare parts and repairs. The cost of all materials consumed during the repair and maintenance of transport. This includes car tires, tools, fixtures, inventory and other low-value wearable items. It is possible to write off these costs without creating a reserve for repairs.
- Labor costs , which include the amount of accrued wages and deductions for insurance premiums. These costs can be direct if wages are paid to employees who are directly involved in providing the services. Costs can be indirect if the organization’s management personnel are paid.
- Motor transport insurance. This can be compulsory MTPL insurance, or voluntary. Insurance of the risk of loss (destruction) and damage to the car is carried out under a voluntary property insurance agreement (CASCO agreement).
- Other costs reflect the amounts of accrued taxes (transport tax), payments for maximum permissible emissions (discharges) of pollutants, business travel costs, payments to third-party organizations for fire and security guards, for training and retraining of personnel, interest on loans, etc.
Accounting for cargo transportation
Companies providing transport services have cars on their balance sheet or under a lease agreement. If you are renting a car from an individual, then read this article . The Ministry of Transport has established to keep records of normalized and current transport costs. The amount and list of company expenses depends on the brand of the car and its operating conditions.
Costs must be economically justified according to the following parameters:
| Options | Determination principle |
| Vehicle mileage | Speedometer readings |
| Consumption rates for fuels and lubricants and other consumables | Standards of the Ministry of Transport or independently developed by the enterprise. |
| Current repair costs | Actual expenses |
The enterprise must issue orders to control the consumption rates of the above costs. The orders reflect the list of persons entitled to use vehicles, fuel consumption rates, fuel and lubricants and other materials; frequency of tire replacement. The presence of orders will be taken into account when checking by the tax office in justifying costs.
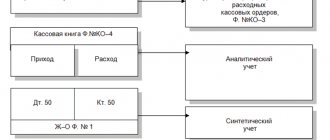
Road transportation accounting is not fundamentally different in the use of cost accounts from other industries. The cost price is formed in the following accounts:
- 20 “Main production” - those that are directly related to the production process;
- 26 “General expenses” are those incurred in the management and maintenance of the company.
| 20 / 26 | 10 | write-off of fuels and lubricants, spare parts, materials |
| 20 / 26 | 70 | payroll |
| 20 / 26 | 69 | contributions to extra-budgetary funds |
| 20 / 26 | 02,05 | depreciation of fixed assets, intangible assets |
| 20 / 26 | 76,60 | services received (rent, security, utility payments |
| 20 / 26 | 71 | travel expenses |
At the end of the reporting period, the amounts accumulated on account 20.26 must be debited to subaccount 90-2 “Cost of sales”:
| 90-2 | 20 / 26 | Expenses written off as cost of services |
Accounting for the transportation of goods also includes VAT entries if the motor transport enterprise is a VAT payer. Then the following entries will be recorded:
| 19 | 60 | VAT is allocated when accounting for goods, works, and services of third-party organizations |
| 90-3 | 68 | VAT is charged on the sale of services |
Accounting in a motor transport enterprise can also occur using accounts 23,25,29. This is typical for enterprises with a complex cost structure. For example, if there are expenses that cannot be distributed among types of services.
The procedure for accounting for VAT in a transport organization
Transport services are subject to value added tax depending on the place of their provision and the category of the carrier. Based on the terms of the contract, the percentage of VAT charged may vary.
When applying the general taxation system, the provision of transportation services (transportation), as well as services directly related to transportation on the territory of the Russian Federation, is recognized as an object of VAT taxation (clause 1, clause 1, article 146, clause 4.1, clause 1, article 148 Tax Code of the Russian Federation). A general rate of 18% applies . more about how the VAT tax base is determined in a separate article .
There are conditions when it is possible to charge VAT at a rate of 10% , this preferential tax regime (clauses 1 and 6 of Article 3 of the Federal Law “On Amendments to Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” dated 04/06/2015 No. 83-FZ was introduced) for air carriers.
In these cases, taxpayers have the right to reduce the VAT tax base by the amount of tax presented by suppliers. The tax is reflected in account 19 with further direction for reimbursement (posting Debit 68 - Credit 19). A prerequisite for using VAT deduction is:
- availability and correct completion of invoices;
- received goods and materials (services, works) are involved in those operations that are subject to VAT;
- goods, works, services are capitalized by the buyer.
, a rate of 0% can sometimes be applied . This rate is used in the cases listed in paragraph 1 of Art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, this is the transportation of natural resources (oil, gas) in Russia and abroad and international transportation of goods.
Preferential VAT conditions also apply to carriers under simplified tax regimes. So, in Art. 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that there is no obligation for payers of the simplified tax system to calculate and pay VAT.
The UTII regime exempts you from obligations to pay VAT. Complying with the requirements of sub. 5 p. 2 art. 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, namely the ownership of no more than 20 units of equipment, allows you to calculate and pay only a single tax on imputed income.
Accounting for road transport: let's look at an example
On January 15, 2021, Mebel LLC entered into an agreement with Avtomobil LLC for the transportation of goods. The cost of the contract was 77,000 rubles with the cost of expenses being 62,000 rubles. (fuels and lubricants, wages, spare parts). Under the terms of the contract, he is obliged to ensure delivery of the goods on time (until January 20, 2021) and records are made at the address specified in the contract for the provision of services:
Debit 51 - Credit 62 - in the amount of 90,860 rubles - the client paid for the cost of services
Debit 62 - Credit 90-1 - in the amount of 90,860 rubles - revenue from the provision of services is reflected
Debit 90-3 – Credit 68 – in the amount of 13,860 rubles. – VAT charged
Debit 20 - Credit 10, 70, 69 - in the amount of 62,000 rubles - expenses incurred during transportation were collected
Debit 90-2 - Credit 20 - in the amount of 62,000 rubles - the cost of transportation was written off
Debit 90-9 – Credit 99 – in the amount of 15,000 rubles – the financial result of transportation is written off
Author of the article: Evgenia Strelova, accounting specialist in the field of cargo transportation, especially for our website.
Unfortunately, all the nuances of accounting in motor transport enterprises that transport goods cannot be covered in one article. We invite you to watch the recording of the master class “Accounting in a transport enterprise ,” which took place on February 14, 2021.
Read the full description and purchase the recording here.
In it, using a practical example, all the intricacies of accounting in a motor transport enterprise were analyzed, in particular:
- — purchase and rental of vehicles;
- — services of fuel companies and car services;
- - fuel and lubricants standards;
- — preparation for the driver’s flight, medical examinations;
- — examples of transportation documents;
- — transport and waybills;
- — transport tax and pollution charges;
- — reporting of a motor transport enterprise, etc.
Accounting in a transport enterprise: features of cargo transportation services
Advantages of outsourcing accounting for a transport company
Selecting a favorable tax regime is a difficult task, the solution of which greatly depends on the efficiency of a transport individual entrepreneur or company. Experts will make the right choice. Additional advantages of accounting outsourcing:
- no expenses for creating your own accounting department and equipping work places for full-time accountants;
- confidentiality guarantee;
- professional consultations with specialists;
- financial responsibility for the quality of consulting services provided;
- low cost of accounting combined with the qualifications of the employees involved.
We are ready to develop a personal commercial offer for you. To receive it, just contact a company employee and answer a few questions about the specifics of your business.
Use modern accounting software
Many companies today still rely on old accounting software that cannot fully meet the needs of modern businesses. Companies are dealing with an increasing amount of data that must be processed and recorded accurately in order to provide meaningful information to all stakeholders who may use the information. Legacy accounting systems cannot cope with large volumes of data and this can lead to ineffective decision making.
New cloud-based accounting software offers a wide range of useful features, including artificial intelligence and business analytics. These more advanced systems can automate manual tasks, promote collaboration, and integrate with other business systems to improve efficiency. Cloud-based systems can be especially useful for firms in the logistics industry that deal with a diverse range and high volume of transactions.
Purchase of a patent (PSN)
After the UTII is abolished in 2021, individual entrepreneurs will be able to purchase a patent for the provision of cargo transportation services. Organizations are prohibited from using this regime.
There are certain restrictions on the use of the patent system. Thus, from the beginning of the year, an individual entrepreneur must earn no more than 60 million rubles in income from all purchased patents. Another rule is that the number of persons working for him within the framework of patent activities cannot be more than 15.
The tax for PSN is its cost. It is considered as 6% of the amount of potential income of an individual entrepreneur for the type of specific patent activity. Insurance premiums can be deducted from the amount received in 2021.
It is worth adding that PSN will soon receive other improvements. For example, it will be possible to use this system in retail and public catering with a hall area of up to 150 square meters. meters (previously - only up to 50 sq. meters). But the main thing is that the list of types of patent activities will be significantly expanded.
But it was not without difficulties. While there is a federal limit on the potential income of an individual entrepreneur, from which the tax is calculated. However, in 2021 it will be canceled, that is, regions will be able to set the income limit at their own discretion. They will also be able to set additional restrictions on the use of PSN.
Let's calculate the cost of a patent for a business from the example - this can be done on the Federal Tax Service website. For now, however, you will have to rely on data from 2021, since the tax service has not updated its service. For St. Petersburg, with a number of vehicles of 5 units, the cost of a patent for the transportation of goods for a full year will be 240,000 rubles.
Now let’s calculate the individual entrepreneur’s contributions for ourselves. The base is the amount of potential income reduced by 300,000 rubles. The meaning we need is contained in the law of St. Petersburg dated October 30, 2013 No. 551-98. The potential income per vehicle for individual entrepreneurs (cargo transportation) is 800,000 rubles. This means that he will pay contributions for himself in the following amount: (800,000 * 5 – 300,000) * 1% + 40,874 = 77,874 rubles.
The total amount of contributions for employees and entrepreneurs will be: 550,000 + 77,874 = 627,874 rubles. Due to this amount, you can reduce the cost of the patent by 50%. That is, you will have to pay 240,000 / 2 = 120,000 rubles for it. In total, the fiscal burden on individual entrepreneurs will be equal to 627,874 + 120,000 = 747,874 rubles.
Is cargo transportation possible when self-employed?
When running a business, an entrepreneur strives not only to make it reliable and profitable, but also does everything possible to ensure that its scale grows. Until the beginning of 2021, it was profitable for a small business to open as an individual entrepreneur. Of course, there was still the opportunity to create a limited liability company, but in this case the costs of registration and operating activities were much higher.
Note! Starting from January 1, 2021, it became possible to engage in entrepreneurial activities by registering as a self-employed person. This opportunity is new and still raises various questions about how to properly register and start doing business in this status.
The activities of self-employed persons are regulated by Law No. FZ-422. It sets out restrictions for those who want to use such a tax system, including for cargo transportation and chartering. Here are some of them:
- While engaged in business, such a person does not have the right to hire employees.
- Self-employed people are not required to pay contributions to social funds. They do not have a fixed payment to the Pension Fund.
- When providing cargo taxi services (carrying out transportation for a fee in the interests of third parties), the driver is required to receive an electronic receipt for payment online using the appropriate application (the “My Tax” program) on a smartphone.
- This status may include persons whose annual income does not exceed 2.4 million rubles. Here we consider the amount that is calculated for the calendar year.
Self-employed people have the right to carry out cargo transportation, but must not use hired labor.
Self-employed people who transport goods are required to open and carry a waybill. It must be completed by the customer. Such persons pay a small tax, it varies depending on who the customer is:
- If transport is used for a legal entity, then the tax amount is 6% of the payment amount.
- When working with individuals, the rate will be lower - now it will be 4%.
Individual entrepreneurs are allowed to register self-employment in order to transport goods without refusing to register as an individual entrepreneur.
When registering, the individual entrepreneur must correctly indicate OKVED
Taxation of intermediary contract services
Revenue from the provision of services is the remuneration paid by the client. Expenses paid during the implementation of the contract to third parties in the amount of fees, warehousing fees, and insurance are not expenses of the enterprise and are covered by the client. Costs do not reduce the tax base when calculating profit or single tax.
The tax base for calculating VAT is the revenue received by the forwarder. Tax amounts issued by suppliers of fuel and other consumables and spare parts used for the operation of vehicles are subject to deduction.
Transport expedition: accounting and taxation
Road transportation accounting is not fundamentally different in the use of cost accounts from other industries. The cost price is formed in the following accounts:
- 20 “Main production” - those that are directly related to the production process;
- 26 “General expenses” are those incurred in the management and maintenance of the company.
In order to avoid the rise in price of the service due to taxation, often owners who have only one truck at their disposal do not want to legalize their type of activity.
Attention! There is a restriction on the use of UTII and a patent at the same time. It is not allowed to use systems at the same time; the entrepreneur must choose one form of taxation according to which he will pay tax.
Further, if the place of sale is Kazakhstan (according to the table above), then one more fact must be taken into account: if the contractor (counterparty from the Russian Federation) is not registered with the tax authorities of Kazakhstan, then the VAT is paid by the customer.
Sometimes, for cooperation between two parties, it is enough to conclude an agreement; this document specifies the volume of supplies, terms and amount to be paid. If the client orders goods from time to time and in different quantities, an invoice is issued for each individual transaction, which indicates the cost of a one-time purchase.
To switch to the OSNO with the simplified tax system, you must, before January 15 of the year from which the transition to the general regime is planned, submit to the tax office at the place of registration a notice of refusal to use the simplified tax system in form No. 26.2-3.
The decision on this tax system, as a rule, is made by municipal authorities of city districts or districts. If the region in which this type of activity is registered has not adopted such a taxation system, then it will not be possible to use it.
The transfer to the OSN from the PSN is carried out after 5 days from the date of submission to the tax authority of the application for termination of activities on the patent. If the right to use a patent is lost, the entrepreneur is transferred to the general system from the beginning of the period for which the patent was received.
If one of the presented conditions or several is registered, the businessman should make a transfer at the applicable value added tax rates.
In other words, you need to understand the nature of the relationship (type of transaction) between the sender and the recipient of the cargo.
Let's consider the features of taxation, and also find out whether it is profitable to use the patent taxation system in Moscow or is it better to remain on the simplified taxation system? Let us say right away that in order to carry out private entrepreneurial activities, it is necessary to register an individual entrepreneur. The next point that an accountant needs to understand in order to organize correct document flow is the transfer of ownership of the cargo. Obviously, the carrier or forwarder has the cargo listed in off-balance sheet accounting - in account 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping.”
Organization of transportation accounting from the point of view of business processes
For managers, the most important thing in transportation is the speed of fulfillment of requests and travel safety. To do this, it is necessary that the work of drivers be transparent.
The manager must know:
- does the driver follow the trip route,
- how many times the driver stopped and refueled the vehicle,
- where is he now,
- at what speed does it travel?
It is not easy to keep track of these items. Not all employees are conscientious and responsible: some may provide false information or not communicate at all, drive carelessly and waste gasoline.
Therefore, driver control should be automated. This will allow you to find out the location, status and workload of the driver at the moment.
Mandatory orders of the enterprise
To ensure the standards of indicators, the enterprise must issue orders of a one-time nature or when operating conditions change. Standard list of orders establishing:
- List of persons receiving the vehicle for storage.
- Consumption standards for fuel, fuel and other liquids, indicating the indicator for each vehicle.
- Fuel consumption standards established for seasonal operation.
- Norms and frequency of tire replacements.
- The composition of the commission responsible for assessing the condition of the transport, the need for repairs, and the list of components to be replaced. The commission calculates the frequency of medium and major repairs.
The presence of orders establishing spending standards is checked by the Federal Tax Service as documents that allow determining the validity of taxation. Cost rationing is applied by enterprises that provide transport services or have vehicles for their own transportation of goods or employees.