When should you draw up an act for writing off low-value items?
Any company has one or another property that it uses in its activities, but does not reflect in accounting as a fixed asset (FPE), since the cost of such property does not exceed 40,000 rubles.
These could be, for example, computers, scanners, printers, some office furniture, etc. Read more about the criteria for classification as fixed assets in the article “Guidelines for accounting for fixed assets.”
Despite the fact that such objects are not considered fixed assets, they have a certain service life, after which the company can no longer operate them. In such a situation, it becomes necessary to write off these property items.
For these purposes, a special act is drawn up.
NOTE! Currently, there is no single form of the act in question that is mandatory for all companies. At the same time, until 2013, this was the MB-8 template, approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated October 30, 1997 No. 71a.
Therefore, when writing off low-value property in 2021, a company can use the standard form of the MB-8 act or draw up a write-off act developed independently. The decision on which form will be used for this purpose is fixed in the accounting policy.
You can download the MB-8 standard form on our website.
Documentation of the fact of write-off must be preceded by a decision of a special commission that a specific low-value object is no longer advisable to use in work.
The document in question is drawn up in 1 copy. As soon as the act is drawn up and the written-off property is transferred to the storage room as scrap, such a document should be transferred to the company’s accounting department.
For information on the procedure used when writing off fixed assets, read the material “Unified Form No. OS-4 - Act on the write-off of fixed assets.”
Features of drawing up an act, sample
Today, there is no mandatory, unified form of an act for writing off low-value and wear-and-tear items, so employees of enterprises have every right to write an act in any form or, if the organization has a developed and approved sample document, according to its template. In addition, very often company representatives prefer to use the previously generally used form MB-8. This is due to the fact that it is clear and convenient in structure, contains all the necessary information, and there is no need to rack your brains over the composition of the document.
Filling out the header of the MB-8 form
The “header” of the form contains several lines for approval by its director - without his autograph the act will not acquire legal force. Then it is indicated:
- number assigned to the act;
- name of the organization and structural unit in which the write-off occurs, its OKPO code.
Filling out the front page of form MB-8
Under the “header” of the document there is the first table, where the following is entered:
- date of drawing up the act;
- transaction type code (in accordance with the classifier);
- structural unit that writes off inventory items;
- type of company activity (according to OKVED);
- information about the subaccount and analytical accounting code.
Below you enter the date of formation of the commission, the order number and the fact of write-off is recorded.
The second table includes detailed information about the property being written off:
- its name,
- quantity,
- cost,
- date of receipt,
- service life,
- reason for write-off and other characteristics.
Filling out the back page of form MB-8
On the reverse side of the act, there is first a continuation of the previous table, at the bottom of which the totals for the items being written off are summarized. Below it is indicated the total number of items, numbers and dates of their disposal. The last table of the act includes information about disposal.
The main features of the IBP for inclusion in the write-off act
Workwear wears out quickly
Due to the short service life of SBPs, they must be written off when preparing financial statements.
For this purpose, a special form MB-8 is used, an act for writing off low-value and wearable items.
How can we determine that an item belongs to the IBP and can be included in this document?
How to correctly apply the rationale for things and materials so that they truly are IBP.
From the name of such materials it can be understood that the criteria for including such production equipment in this group are low price and rapid wear.
The time limit for suitability for classifying things as IBP changed periodically. Only the service life remained constant for one year.
Based on these justifications, it can theoretically be assumed that there are 4 main options for evaluating purchased items for the group we are considering:
- The price of the item is below the monetary limit, but its useful life may be more than one year.
- The cost of the inventory is more than the limit, but it is suitable for use for up to 1 year.
- The material does not exceed the cost of purchasing it from the established upper limit, but will last more than 12 months.
- The item lasts less than 1 year and costs less than the price limit.
Quite recently, only by the fourth characteristic of an object could it be included in the IBP. As for the first, second and third groups, previously these were fixed assets. At the same time, in production they often resorted to a price limit, without taking into account the service period.
In this way, IBEs were formed into an independent group, which was dealt with by entire departments of institutes, conducting various studies on them.
What is important to remember to fill out the form correctly
Filling out the act in form MB-8 does not present any difficulties. In particular, it is required to indicate:
- name of the object being written off;
- its nomenclature and inventory numbers;
- unit of measurement;
- cost and number of objects being written off (if they are of the same type);
- passport number of the item being written off;
- the date when operation of the facility began;
- date and reason for write-off.
After the act is completed and executed, both the chairman of the commission and all its members put their signatures at the end of the document, indicating their initials and positions.
The procedure for drawing up the act is completed by the storekeeper, who marks the date of acceptance of the written-off low-value property into the warehouse.
The composition of the information reflected in the act developed independently should be similar.
You can download a completed sample based on the MB-8 form on our website.
IMPORTANT! If it is simultaneously decided to write off several items at once, the MB-8 act must be issued separately for each such item, if they belong to different types. A general act can be for several items of the same type.
Results
An act for writing off low-value and wear-and-tear items is drawn up in cases where the company decided to write off items that were no longer suitable for use, necessary for the implementation of the work process, but due to their insignificant value were not accepted as part of the operating system.
Such an act is drawn up either according to the standard form MB-8, or according to its own template, which also contains all the necessary information about the object being retired from use. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What should be considered low-value and wearable property
For a long time, low-value and wearable items were taken into account in account 13. But now it is missing, although the MBPs themselves have not disappeared anywhere. By all criteria, this material resource should be classified as fixed assets, but its value is too small to be included in the corresponding OS account (01). Therefore, although the term IBE is not used in professional accounting language, low value is present.
It includes current assets for which:
- cost - for one unit no more than 40 thousand rubles;
- operating time - up to a year or two;
- subsequent resale is not envisaged.
They are also characterized by:
- application in the manufacture of goods directly or for the purpose of managing the production process;
- assistance in generating income.
Low-value property is included in current assets, and their value is written off as expenses:
- completely, provided that the service life is one year;
- in parts, when he is 2 years old.
Although small business enterprises are written off, they continue to be reflected in accounting (not in tax accounting) as part of industrial property. And at the enterprise, their movement must be constantly monitored to ensure safety. It is for the safety of the physical value that low value, even with zero value, is taken into account in the documentation. And this happens before it is completely worn out. The accounting policy should establish the maximum value of low-priced items.
IBP are items that are purchased by an enterprise in order to use them for a long time. But their cost is immediately written off in full to the cost of production.
Example No. 1. The organization bought a filing cabinet, paying 25 thousand rubles for it. (without VAT). This acquisition relates to furniture, that is, to fixed assets. But since its cost is less than the established limit (40 thousand rubles), the table is considered low-priced. 25 thousand rubles. written off to management expenses immediately upon commissioning.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
Attribution to otcdi from what amount in 2021
In January 2021, the organization acquired a fixed asset worth RUB 150,000. The property was registered in February and paid for in May of the same year. This means the amount is 150,000 rubles. need to be divided by 3: after all, there are three quarters left until the end of the year, taking into account the quarter when the OS is put into operation.
Fixed assets
- armored and automotive vehicles;
- production tools, household and office appliances, computing equipment.
- machine tools, power plants, lifting machines and other equipment necessary to ensure statutory purposes;
- fire fighting, special equipment;
- special equipment for key areas of activity;
Starting from 2021, the minimum value has been increased, which allows property to be classified as fixed assets in tax accounting. At the same time, in accounting, the value of this indicator remained the same. As a result, inexpensive objects are now reflected differently in NU and ACC, and this raises questions when applying PBU 18/02 (see “How to apply PBU 18/02 “Accounting for corporate income tax calculations” in practice)”). In this article we will explain how to account for temporary differences, as well as deferred tax liabilities and assets.
Regulatory regulation of accounting for small business enterprises
The federal law determines the requirements for accounting and execution of primary documentation
The order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia approves PBU 5/01 for accounting for inventories
The Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation approved the form of primary documentation MB-8
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation Chart of accounts
Possible ways to value low-value items
The accounting regulations provide for several options for assessing inventories. It can be carried out at cost:
- each individual unit purchased;
- weighted average;
- first in time for purchasing materials (FIFO method).
Low valuation is a special component of material reserves. The initial cost of the IBP contains all the costs that the enterprise incurred during the purchase. This is reflected in the relevant primary documentation.
Based on this, it is necessary to write in the order on accounting policies that IBP is assessed based on the actual cost of each individual unit. At the same time, you should not forget to add the amount of expenses for its purchase. A list of primary documentation is also included here. With its help, the movement of the IBP from capitalization to write-off will be traced.
IBP does not include workwear, since according to the law it should be classified as a type of property that is taken into account especially.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
Synthetic and analytical accounting of IBP
Synthetic accounting of IBP is maintained on account 10 Materials; subaccounts are allocated for IBP:
- Inventory and household supplies
- Special equipment and special clothing in stock
- Special equipment and special clothing in use
Analytical accounting is maintained for each type of IBP, for which the enterprise can create a journal that reflects the availability, issue, MOL, etc.
Include the cost of low-value property as part of material expenses. In this case, the organization has the right to independently establish the procedure for writing off such property in its accounting policy for tax purposes.
State Advisor of the Tax Service of the Russian Federation, 1st rank E. Popova
Features of using accounts in IBP accounting, depreciation and basic postings
It is most correct for an enterprise in the area of low value to use this approach:
- IBPs whose expected lifespan is more than a year should be taken into account on the account. 01 (on the corresponding sub-account).
- MBP that will be in operation for up to a year - on the account. 10 (subcount 9 or 10).
- In the first case, the corresponding subaccount will serve as a contract account. 02.
- In the second: to the account. 10 (10) → count. 10 (11).
- On the account 10 (9) takes into account inventory and household supplies, so it does not need a contract.
When a low-value asset will be used in production for more than 12 months, the accountant makes the following notes:
| Accounts | Description | |
| Debit | Credit | |
| 08 | 60 | The insignificant assessment was capitalized upon the fact of its receipt |
| 19 (1) | 60 | VAT reflection |
| 01 | 08 | Low assessment transferred to operation |
| 68 | 19 (1) | VAT credited |
| 20 or 23 | 02 | Depreciation has been accrued (you can immediately pay 100% of the value of the low-value property, or part of it for the first quarter or year) |
| 02 | 01 | The depreciation amount is written off (but not before the object is completely written off) |
When using the MBP for less than a year, the postings are as follows:
| Accounts | Description | |
| Debit | Credit | |
| 10 (10) | 60 | IBPs are capitalized according to the facts of their receipt |
| 19 (1) | 60 | VAT |
| 20 or 23 | 10 (11) | Low value is transferred for use |
| 68 | 19 | VAT credited |
| 10 (11) | 02 | Depreciation is written off at 100% of the value of the low value |
Capitalization of inventory and household supplies is carried out according to the account. 10 (9). They will be listed until they go into service. At the same time, this type of low value is written off in its entirety. The cost is included in the costs for the item for which they are used. The wiring is as follows:
| Accounts | Description | |
| Debit | Credit | |
| 10 (9) | 60 | Inventory has been capitalized |
| 20, 23 | 10 (9) | Inventory write-off |
When writing off MBP (with a service life of up to a year) for the corresponding current expenses, their cost is equal to zero. When depreciation is charged in parts, the IBP will have a certain residual value for some time.
Thus, depending on the period of operation of the low-priced asset and the corresponding method of calculating depreciation, a balance is obtained, in the active item of which is the full cost of the IBP, and in the contractual item is a similar minus cost. As a result, the value of the low price is zero.
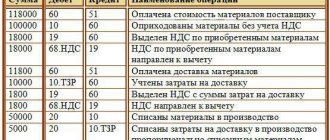
Example No. 3. The cashier-businessman bought printer paper in the amount of 1,500 rubles for cash. An advance report, supported by a cash receipt, was submitted to the accounting department. It includes VAT - 228.75. The paper has been handed over for use. Accounting entries:
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Operation |
| 60 | 71 | 1500,00 | Advance report received |
| 10 | 60 | 1271,25 | The paper has been capitalized |
| 19 | 60 | 228,75 | Input VAT accepted for deduction |
| 26 (44) | 10 | 1271,25 | The product has been sent to work |
What are the accounting entries for IBP?
In the process of forming accounting for IBP, several methods have been developed for reflecting them in transactions:
- Upon receipt, they were received and transferred for use with the cost entered into account 12 “Low-value wearable items.” At the end of each month during the year, 1/12 of the purchase price was written off. Although the period of use could exceed a calendar year, the cost of the MBP was subject to complete write-off within 12 months.
- When an item was handed over to the facility’s workflow, the amount was immediately reduced by 50% due to wear and tear. The remaining half was not touched until the final moment of its decommissioning.
Since the second write-off method was much simpler for an accountant, it was preferred by organizations.
When writing off using the first method, its shortcomings were identified. In the month when the MBP was purchased, its full cost was reflected in the entries and unjustified profits immediately increased.
And although in the future the amount gradually decreased due to wear and tear and, accordingly, contributed to a decrease in profits in the future, this was still not entirely correct.
Both methods of writing off IBP are considered imperfect from a scientific point of view. There is another significant drawback in accounting for IBP, which concerns things with very low prices.
To facilitate accounting for products, accountants ensured that low-value funds were immediately written off as operating expenses in the month they were received.
In this case, there is no need to calculate the percentage of depreciation or amortization, which is a convenient point for accounting.
Theorists were outraged by this write-off procedure, but this did not affect the outcome of the case.
Practice has shown the advantages of this method of writing off IBP, since it immediately reduced the revenue side in the month of purchase and made it easier to account for them.
Since the amount of depreciation is included in production costs, it must be taken into account when determining the tax contribution.
As we have already described, very often in practice accounting is carried out in the two most convenient ways:
- calculation of depreciation in the amount of 50% of the original cost when issuing them from the warehouse for operation, and the second half after receiving the decommissioning certificate for the IBP
- reflect 100% wear and tear when issuing MBP to workers to perform production tasks
The law does not provide for strict restrictions on this matter, therefore the enterprise has the right to independently choose the most convenient method of calculating depreciation of the IBP and apply it throughout the entire calendar year.
To enter information on the depreciation of low-value items with a short useful life, use account 13 “Depreciation of IBP”. According to its credit, in correspondence with the production cost accounts, the amount of depreciation of the IBP is shown, and the debit of account 13 from credit 12 reflects the purchase cost of inventory that has been retired.
They formalize the transfer of the IBP into operation for long-term use using an invoice.
In case of their breakdown, damage, loss of tools and devices, the head of the department must draw up a decommissioning act for the IBP. An exception in these cases concerns circumstances in which the worker’s guilt in the unsuitability of the IBP is established, since the cost of a damaged or lost item must be deducted from his salary.
Features of accounting for low value under the simplified tax system. Differences from OSNO
Since the low value property is not included in fixed assets, it can be written off as expenses according to the simplified tax system. But this can only be done after the IBP has been put into operation. The cost of only those SBPs that actually participate in the production process is subject to write-off.
For example, when purchasing a refrigerator to ensure the storage of finished products, its cost is included in expenses under the simplified tax system. When it is purchased for a household room, then the presence of its cost in expenses is unjustified. The table shows the differences in accounting for low value under the OSNO and the simplified tax system:
| Conditions for IBE | BASIC | simplified tax system |
| Accounting | On the account 10 plus off-balance sheet accounting | – |
| Time to write off expenses | Immediately upon admission | After commissioning |
| Inclusion in expenses depending on place of use | There are no restrictions. The entire cost is written off as expenses, regardless of where the low value is used - in production or in providing quality working conditions for workers | A prerequisite is direct use in the manufacturing process (reasonable costs) |
The legislation does not force simplifiers to keep accounting records. But this does not apply to fixed assets and intangible assets. Therefore, low value items, for example, stationery, are not reflected in any accounts.
Reason for using MB-8
Despite the fact that there is an approved form MB-8, from 01/01/2013 this form is not mandatory for use in work. Commercial enterprises can develop and approve at the local level their own forms for recording the movement of small and medium-sized goods.
The definition of IBP was given in PBU 5/98 (not in force today) and stated: part of the organization’s materials and equipment used as means of labor for a period of up to 12 months or during the operating cycle (if the cycle is more than 12 months), or have a cost estimate of date of purchase no more than 100 minimum wages (the limit was approved by the organization) and was taken into account on accounts 12 and 13.
Currently, MBP is also the main part of production activity, it is classified as working capital and is accounted for as part of the inventory on the basis of PBU 5/01.
Since IBPs are in constant motion, there is also a fairly large amount of documentation on them. An act for writing off the IBP (MB-8) is used when:
- loss
- damage
- expiration of service life
- breakdowns, etc.
Top five questions that are asked most often
Question No. 1. The individual entrepreneur is engaged in leasing space in the administrative building. They are furnished with furniture purchased at the expense of the individual entrepreneur. Is it possible to write them down as expenses and reflect them in accounting?
Such costs can be included in expenses. They are completely economically justified, since renting out space along with the furniture installed on it is a source of income for this individual entrepreneur.
Question No. 2. The company (OSNO) purchases about a hundred items of office supplies every quarter. They are immediately distributed to employees to ensure their work. Is it necessary to reflect the cost of office supplies in which primary documents?
To avoid claims from auditors and tax authorities, you should do this.
- Goods are accounted for. 10 with this notation: Dt 10 → Kt 71
- The receipt order is filled out.
- When distributing stationery to employees, a demand invoice is issued. On its basis, the value of the low value is written off: Dt 26 → Kt 10
Question No. 3. How to determine the amount of low-value property?
The amount depends on the characteristics of the enterprise. IBP does not include OS whose cost is more than 40 thousand rubles. These two factors should be taken into account and fixed for accounting purposes (mandatory) in the order on accounting policies.
Question No. 4. Is it possible to write off low-value property on the day it is received if payment for it has not yet been reflected in the accounts?
Is it possible. In accounting, a low value can be written off at the same time it is received. Whether the payment has been made or not is irrelevant.
Question No. 5. An individual entrepreneur bought a microwave for his employees. Will its cost be included in the expenses of the simplified tax system?
No. Expenses can only include those that are fully justified and used in production. In every enterprise, IBP accounting should not be underestimated, although it is an inexpensive asset.
Rate the quality of the article. We want to become better for you: If you have not found the answer to your question, then you can get an answer to your question by calling the numbers ⇓ Free legal advice Moscow, Moscow region call
One-click call St. Petersburg, Leningrad region call: +7 (812) 317-60-16
Call in one click From other regions of the Russian Federation, call
One-click call
When the low-valuation will be used in production for more than 12 months, the accountant makes the following notes: Accounts Description Debit Credit 08 60 The low-valuation is capitalized upon the fact of its receipt 19 (1) 60 Reflection of VAT 01 08 The low-valuation is put into operation 68 19 (1) VAT is credited 20 or 23 02 Depreciation has been accrued (all 100% of the value of the low-priced value can be applied at once, or part of it for the first quarter or year) 02 01 The depreciation amount has been written off (but not before the object is completely written off) When using IBP for less than a year, the postings are as follows: Accounts Description Debit Credit 10 (10) 60 IBP are capitalized according to the facts of their receipt 19 (1) 60 VAT 20 or 23 10 (11) Low-valuation is transferred for use 68 19 VAT is credited 10 (11) 02 Depreciation is written off in 100% of the value of low-valuation Inventory and household supplies are capitalized according to account 10 (9). They will be listed until they go into service.
How to issue an order on a commission for writing off an IBP
In order to regulate issues related to the write-off of IBP at the enterprise, a permanent commission is appointed by order of the manager. Who needs to be appointed in such cases and what are the nuances of its design?
The commission must include any persons from the administration of the enterprise who are competent in matters of wear and tear and accounting of small-scale equipment. These can be persons from the engineering and technical staff of the enterprise, accounting department, quality control department, laboratory, if there is one in production. The main thing is that people can competently assess and justify the deterioration of the MBP.
The order indicates the positions and individual details of each member of the commission. Then they enter the reason for issuing the decree: “In order to organize work to establish storage periods for documents, carry out their selection for archival storage and use, I order: Create an expert commission.” Next comes a list of the members of the commission, starting with the chairman.
The issue is not regulated by legislative acts. If one of the commission members is absent at the time of decommissioning, a temporary order is issued to appoint another commission member in his place for the duration of his illness or other reason for not going to work.
How to correctly write off a low value
The only condition that must be met: the act must be signed by all responsible persons included in the commission (autographs of employees involved in writing off low-value and wear-out items must be “live”). But it is necessary to certify the form using a seal or stamp only if the norm for the use of stamp products is enshrined in the internal regulatory documents of the organization. The act is drawn up in one copy, but if necessary, additional copies can be made. What to do after drawing up the act After drawing up the act, written-off low-value and high-wear items are sent to scrap (to the closet or warehouse), and the act itself is transferred to the company’s accounting department for the final completion of the write-off procedure. That is, upon commissioning, it is necessary to draw up an acceptance certificate in Form N OS-1, and also create an inventory card in Form N OS-6. Accounting Unfortunately, the authors of the Letter did not touch upon accounting. But here, too, options are possible. Many people charge 100% depreciation on the cost of “cheap” fixed assets, which is then written off as expenses. Example 1. In December 2004, Aktiv CJSC purchased a printer worth RUB 10,620. (including VAT - 1620 rubles). The accountant made the following entries: Debit 60 Credit 51 - 10,620 rubles. — the supplier’s invoice has been paid; Debit 08 Credit 60 - 9000 rub. (10 620 - 1620) - the printer has been capitalized; Debit 19 Credit 60 - 1620 rub. - VAT reflected. In January 2005, the fixed asset was put into operation: Debit 01 Credit 08 - 9000 rubles. — the printer is put into operation; Debit 68 Credit 19 - 1620 rub. - VAT included. In February 2005. At the same time, this type of low value is written off in its entirety. The cost is included in the costs for the item for which they are used. The postings are as follows: Accounts Description Debit Credit 10 (9) 60 Inventory capitalized 20, 23 10 (9) Write-off of inventory When writing off small business equipment (with a service life of up to a year) for the corresponding current expenses, their cost is equal to zero. When depreciation is charged in parts, the IBP will have a certain residual value for some time. Thus, depending on the period of operation of the low-priced asset and the corresponding method of calculating depreciation, a balance is obtained, in the active item of which is the full cost of the IBP, and in the contractual item is a similar minus cost. As a result, the value of the low price is zero. Example No. 3. The cashier-businessman bought printer paper in the amount of 1,500 rubles for cash. An advance report, supported by a cash receipt, was submitted to the accounting department.
The procedure for filling out the MB-8 form
Federal Law 3 for the preparation of documents (regardless of whether a unified or independently developed document form is used) identifies the following mandatory details:
- full title of the document
- date when the document was drawn up
- organization that compiled the document
- content of the operation performed (recognition of unsuitability and scrapping of the MBP)
- quantity and units of measurement
- positions of persons who completed the operation
- signatures of persons and their decoding
Directly in MB-8 there are design features:
- the corresponding account is indicated
- name of the IBP, its nomenclature and inventory numbers (for each IBP separately)
- date of receipt and service life
- basis, reason for write-off
- sums up the written-off small business enterprises
- registration of scrap or scrap, its destruction indicating the delivery invoice number
- signatures of all commission members are placed in accordance with the order
How to correctly write off low value in an enterprise
At the same time, in production they often resorted to a price limit, without taking into account the service period. In this way, IBEs were formed into an independent group, which was dealt with by entire departments of institutes, conducting various studies on them. How to draw up an act To draw up an act, a special type of entering information is provided.
The form was developed according to the MB-8 form, approved at the legislative level of the Russian Federation. The document code is indicated in the OKUD classifier with the value 0320004. But, despite the same requirements for the execution of this act, organizations can edit it and make their own changes for ease of filling out.
Before you begin to draw up documentation for the write-off of an IBP, a decision must be made about this by the management of the organization. It can also be accepted by representatives of the commission, which includes experts. The order to appoint competent members of the commission is issued by the head of the organization.
Any enterprise is required to keep records not only of non-current assets and inventories, but also of low-value goods available. Without furniture, office equipment and other similar goods, the full functioning of any production activity is impossible class=”aligncenter” width=”1000″ height=”667″[/img]
Moreover, all operations that are carried out with small and inexpensive items at the enterprise are always subject to accounting and tax accounting.
Therefore, it is important to know what is considered low value, as well as the procedure for accounting for its receipt and write-off.
Creation of a commission
Any property of an enterprise is written off, as a rule, by a specially created commission. It may include both company employees and third-party experts.
The appointment of commission members occurs by drawing up an appropriate order, which also approves the need to write off low-value items and which is issued on behalf of the director of the organization.
Members of the commission perform the following actions:
- study technical documentation (if any),
- certify the fact that the property has fallen into disrepair, is outdated or worn out,
- looking for reasons for this
- record that repair and further use of these inventory items is impossible.
Is this underrated?
Very often, to ensure uninterrupted operation of production, an enterprise purchases office equipment and similar goods for personal use for a long time.
New objects are characterized by the fact that:
- used in the direct production of products or for management purposes;
- have been in use for more than one calendar year;
- are not purchased for the purpose of resale;
- contributes to profit generation.
The listed characteristics allow these objects to be classified as fixed assets in accordance with PBU 6/01.
But, at the same time, this same provision makes it possible to take into account funds whose cost does not exceed 40 thousand rubles as part of the inventory. It is only important to fix the upper limit of cost in the accounting policy.
As a result, low-value or low-value items are items purchased by a company for personal use over a long period of time, but are immediately written off in full to the cost of production.
Only special clothing cannot be included in this category of objects, since in accordance with legislative norms it belongs to a specially taken into account type of property.
Write-off of low value
The receipt of low-value property established by the accounting policy is accounted for as inventories in an additional sub-account opened to account 10 “Materials” at actual cost.
The transaction is credited with a score of 60.
Next, the cost of the received objects is written off to production in full as part of the costs of core activities.
Accordingly, the actual value of the low-priced property is transferred to the debit of expense accounts 20, 26, 44. For accounting purposes, the cost of low-priced property recognized as inventory can be written off on the same date together with capitalization, regardless of the fact of payment.
Finally, the number of low-value items is recorded on an off-balance sheet account or by maintaining a unified card for each item.
Act of low value
In the case of low-value and wearable items that last less than a year, the unified form of the MB-8 act is used when writing off. Most often, such an act is issued at the moment when the property becomes unsuitable for further use in the production process.
Each company has the right to develop its own easy-to-write form for writing off low-value inventories, using the approved form as a sample.
The decision to write off low-value items from production can be made by:
- responsible persons, approved by personnel documents for the enterprise;
- a special liquidation commission appointed by resolution of the head of the company.
Rapidly worn out inventory is displayed in the act at actual cost, taking into account all expenses directly related to them.
Sales of low value items are most often carried out at the same cost. If the sales price exceeds the actual price, the amount of the difference is included in the income book.
The act is drawn up in one copy, signed by the commission, the responsible person and goes to the accounting department.
Based on his data, the accountant writes off these materials from accounting.
Accounting policy
An accounting policy is a regulatory document that regulates the combination of legislative norms and independent convenient decisions of the organization on the issue of maintaining financial records.
It is developed by the chief accountant, who is obliged to take into account all the nuances of accounting and tax accounting intended for use by his employees.
One of the significant and mandatory sections of the document is the rules and regulations established by the company for accounting and assessing the flow of funds, including low-value property.
Accounting for low value
With regard to low value, the accounting policy should contain the following constructive norms and rules:
- The amount of the limit on the value of objects, within which they can be classified as low-value inventories. The maximum legal limit for the limit is 40 thousand rubles. Otherwise, the enterprise will not have a low value and any item whose service life is more than a year will have to be taken into account as part of fixed assets. The value limit of less than 40 thousand rubles will lead to a difference between accounting for accounting and tax purposes.
- Option for assessing the write-off of low-value property, including its use in the production cycle. For any MPP, there are three assessment methods:
- at unit cost;
- according to the average cost value;
- FIFO.
- List and forms of documentation used to secure data on the movement of low-value objects.
- Accounting accounts of low value:
- subcount to count 10;
- off-balance sheet account to control actual availability.
Off-balance sheet accounting
For off-balance sheet accounting of low-value property, account 012 “Low-valued property” is recommended. As a result, it keeps a quantitative record of all inexpensive and written-off items that remain effective in the company's business activities.
The use of off-balance sheet accounting for inventories classified as low-value allows you to:
- control their movements after debiting account 10;
- keep records of employees responsible for the rational use of these facilities;
- confirm the feasibility of additional expenses tied to the low price.
All accounting information for low-value items after write-off is recorded in a special journal. The name, inventory number, dates of receipt and disposal and responsible persons are noted on the sheets of the book.
Low value up to what amount?
Acquired objects whose value is in the range of up to 40 thousand rubles can be considered low-value property.
At the same time, the maximum amount for classifying small items in accounting as low-value, in other words, as materials, is established by the internal documents of the enterprise, first of all, by the accounting policy.
It is important for any financial specialist dealing with low-value goods to distinguish between:
- for accounting, the cost limit is set by the company independently in the range from 0 to 40 thousand rubles;
- For tax accounting, property purchased for less than 40 thousand rubles is always not depreciated.
It is more profitable to set matching limits for the convenience of maintaining both accounts. In addition, it will be possible to remove property of this category from property taxation.
How to write off a low value?
Write-offs of low value are carried out in compliance with a number of recommendations:
- Accounting provides for the reflection of the receipt of these funds in the debit of account 10 “Materials”, and the disposal or write-off of the loan in correspondence with expenditure and production accounts. Low-value objects are written off in parallel with their release into the production process.
- The write-off operation is subject to documentation by filling out the appropriate unified forms. Just like other types of MPZ, low-value items are written off in the form of an act, which indicates the name and number of items. The act must necessarily contain information about the reason for the write-off and contain the signatures of the manager, chief accountant, accountant for goods and materials and MOL.
What is low value in accounting?
Financial consultant for tax optimization. I work for a company that outsources accounting and legal issues. We help our clients save on accountants and lawyers. I like to optimize everything, including my expenses.
Accounting for low-value and wear-and-tear property (IBP) at an enterprise in 2021
The enterprise keeps records of capital, current and non-current assets. It is also important to correctly register the movement of less expensive property, which is classified as low-value and wearable items. In the article we will talk about accounting for low-value items (LBP), and give examples of postings.
Drawing up an act for writing off low-value property
In order to write off MBPs whose service life is up to a year, the standard MB-8 form is used. It is advisable to draw it up when inexpensive property has completely worn out and has become unsuitable for further use for its intended purpose.
The decision to write off low-value assets is made by the liquidation commission. She is appointed as a manager and collaborates with the accounting staff. Low-value property must be recorded at its actual cost when written off. The document is signed by each member of the commission, approved by the head and sent to the accounting department. Based on it, the accounting employee writes off the low value from the account.