Goals and objectives of cash accounting
Accounting for amounts in the form of cash or non-cash assets is necessary to obtain information about the availability of the necessary funds at the moment in the organization. This makes it possible to conduct economic activity and redistribute finances to the necessary areas of use. Process objectives:
- the presence of documented records indicating the movement of finances of an economic entity, that is, an enterprise;
- compliance with all legal regulations and maintaining the necessary records, which indicate the absence of various violations;
- redistribution of funds for specified purposes that are most important at the moment;
- inventory and control;
- settlements with various individuals and organizations.
When receiving information about the availability of the required amounts through reporting, the organization makes settlements with various legal entities and individuals, including employees or creditors.
PBU 23/2011 includes the entire theoretical basis. The document used for this procedure has Form 4 (Cash Flow Statement). Among the main features is the need for an organization to maintain separate reporting when there are several taxation options.
Sample Cash Flow Statement
Another important task is the analysis of information regarding taxation, since the report makes it possible to obtain data on actual costs for a specified period.
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 02.02.2011 N 11n “On approval of the Accounting Regulations “Cash Flow Statement” (PBU 23/2011)
Forecasting
Cash forecasting comes down to calculating possible sources of inflow and outflow (expenditure) of funds. You can forecast for a year, quarter, month.
To calculate possible cash receipts, it is important to know the terms and procedure for payment for goods, how sold goods are paid for (cash/non-cash payment), whether advance payments or trade credit are provided for in the supply agreement. The terms of payment for goods are specified in supply contracts, so it is possible to calculate what part of the proceeds for sold products will be received in a particular period (month, quarter).
Cash receipts can be increased through the sale of fixed assets, intangible assets, material assets not used in production, dividends from contributions to the authorized capital of other enterprises. The financial well-being of an organization largely depends on the receipt (inflow) of funds to cover its obligations.
To calculate possible expenses, take into account the terms of supply contracts, wage and bonus systems, deadlines for payments of taxes and fees established by law, annuity payments for repaying debt on loans, etc.
By comparing the inflow and outflow of funds, you can identify their shortage or surplus in the current account. Analysis of the situation will make it possible to determine the cause of the excess or deficiency.
Accounting for an organization's funds
Accounting is considered to be control over the fact of receipt or use of funds. This highly liquid asset includes:
- money in the bank;
- cash on hand;
- money issued on account;
- other assets that have a high level of liquidity.
Reporting is generated by the financially responsible person.
Attention! Any non-cash movement must be recorded using a special record.
If cash payments are used, then such an operation is performed using cash rules. It is possible to maintain cash reporting using a simplified form that is available to small entrepreneurs or individual entrepreneurs.
The formation of the process and reporting itself is carried out using a number of options:
- Cash desk - 50.
- Estimated - 51.
- Foreign exchange - 52.
- Bank special accounts - 55.
- Transfers on the way - 57.
It turns out that when receiving or sending money it is necessary to use the established reporting form indicating the option.
Read also: Inventory shortage
Postings on retail revenue and preparation of cash documents
Receiving cash revenue from retail sales imposes certain responsibilities on the organization. If settlements between organizations for the sale of goods, works, and services occur mainly in a non-cash manner, then settlements with individuals usually occur in cash, less often using electronic means of payment.
In this article we will examine in detail the preparation of cash documents, accounting, tax accounting and postings for retail revenue that comes in the form of cash from individuals. Let's touch a little on the need to use cash register equipment.
The content of the article
1. Selling for cash with a cash register
2. How to register retail sales
3. How to fill out the cashier-operator log
4. Retail sales report
5. PKO for retail revenue
6. Entering PKO data into the cash book
7. Postings for retail revenue - example
8. Retail invoice and sales ledger
9. Retail accounting using the simplified tax system
10. Report on retail sales in 1C: Accounting
So, let's go in order. If you don't have time to read a long article, watch the short video below, from which you will learn all the most important things about the topic of the article.
(if the video is not clear, there is a gear at the bottom of the video, click it and select 720p Quality)
We will discuss the topic further in the article in more detail than in the video.
Selling for cash with cash register
A legal entity or individual entrepreneur planning to accept cash as payment for his goods, work or services or make payments using payment cards, first of all decides whether he is obliged to use cash register equipment, or whether he can use other forms of confirmation of payment acceptance .
The scope of application of cash register equipment (CCT) is regulated by Federal Law dated May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ “On the use of cash register equipment when making cash payments and (or) settlements using electronic means of payment.” In 2021, global changes have been made to it.
Despite the fact that the topic of this article is not directly devoted to the use of cash registers in calculations, we will touch upon this issue. Because Further paperwork directly depends on this.
CCT is used by all organizations and individual entrepreneurs when they make cash payments or payments using payment cards in the case of the sale of goods, performance of work or provision of services. This is the default condition.
Terms of mandatory use of cash register systems for cash and card payments with customers:
- - from February 1, 2021 - for those who are already using CCP
- - from July 1, 2021 - for organizations and individual entrepreneurs providing services to the population (now they issue BSO), for taxpayers on UTII and patent (now they can issue sales receipts at the request of the buyer), owners of vending machines.
Cash registers used in calculations must allow online transfer of calculation data to the tax office via the Internet via a fiscal data operator (FDO). The buyer can receive both a paper check and a check by email (this will be implemented through a special application on the buyers’ phones).
There are a number of exceptions when CCP may not be used. Among them, for example, the sale of newspapers and magazines, travel documents, trade at markets and fairs, peddling trade, sale of kvass and milk from tanks, hawking vegetables, etc. Also, cash register systems are not used for settlements in remote and hard-to-reach areas.
Therefore, in the near future, when selling for cash, it will be mandatory to use a cash register, with very limited exceptions.
How to register retail sales
So, from now on we will assume that you are using a cash register. But simply running a check on a cash register and handing it over to the buyer (send it to him by email) is not all. Or rather, everything is just beginning, since you need to know how to document retail sales.
You should clearly understand the differences between the operating cash desk and the main cash desk of the organization. The operating cash desk is a box with cash at the cash register (the accounting document here is the journal of the cashier-operator). The main (main) cash register is the money for which the cash register limit is set (the accounting document is already different - the cash book).
First, we will discuss the responsibilities of the cashier-operator for accepting funds and processing documents. Then we will analyze the procedure for transferring cash from the operating cash desk to the main one.
So, during the sale, each buyer is punched and given a cash receipt. All movements on the operating cash desk are reflected in the Cashier-Operator's Journal . In connection with the transition to online cash registers, it is not yet clear whether this journal will need to be maintained in the future or not. But while it is in use, it has not been cancelled, so we will discuss the procedure for maintaining and filling it out.
Regulations:
- “Standard rules for the operation of cash registers when making cash settlements with the population” (approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation on August 30, 1993 No. 104, applied to the extent that does not contradict Law No. 54-FZ)
- “Album of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for recording cash settlements with the population when carrying out trade operations using cash registers” (forms approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 1998 No. 132) - this document approved the form of the Cashier-Operator Journal KM-4.
Despite the dates, these documents are current.
The cashier-operator's journal is used to record transactions regarding the receipt and expenditure of cash (revenue) for each cash register machine of the organization, and is also a control and registration document of meter readings. The cashier-operator's journal KM-4 is the main document reflecting the movement of cash in the store's cash register. It is set up for each cash register separately.
How to fill out a cashier-operator log
The journal must be laced, numbered and sealed with the signatures of the head and chief accountant of the organization.
All entries in the “Journal of the cashier-operator” KM-4 are kept by the cashier-operator in chronological order, line by line, without spaces, in ink or a ballpoint pen.
Entries are made on the basis of z-reports (report with cancellation), which are taken at the end of the working day (shift). We will not give examples of z-reports, because... their appearance depends on the cash register used.
Each new report must be formatted on a new line. You can see an example of filling in the screenshots below.
If three shifts and different cashiers work on one cash register, then three separate lines from the same date must be entered.
Pay attention to column 11 “Deposited in cash” - this column indicates only the amount of cash received from customers (card payments and returns are not included).
An entry in the journal should be made every time a shift at the cash register was opened, even if no cash was received at the cash register for the day.
Retail sales report
After the z-report is taken and the next line in the cashier-operator’s journal is filled in, the cashier-operator’s certificate-report is filled out in form No. KM-6 . The certificate report reflects the readings of the cash register counters at the beginning and end of the shift, revenue for the day (shift), and the amount returned by customers. These data are identical to those entered in the cashier-operator’s journal.
The Z-report is attached to the cashier-operator's certificate (retail sales report) and, together with cash proceeds, is submitted to the main cash register.
PKO for retail revenue
So, we found out that at the end of the working day, retail revenue is transferred from the operating cash desk to the main cash register. In this case, the cashier of the main cash register receives (from the cashier or senior cashier) cash proceeds, a certificate from the cashier-operator (retail sales report) and a z-report attached to it.
The cashier must issue a PKO in the name of the person depositing cash proceeds to the main cash desk (cashier, senior cashier) - for the entire amount of proceeds received from him. If several cashiers hand over the proceeds, then the PCO is issued for each one.
In the line “Accepted from” the full name of the person who is donating the proceeds is indicated, in the line “Base” - retail proceeds (you can also indicate the name of the store or the number of the operating cash register).
The receipt from the PKO is stamped and given to the depositor (cashier).
Data on receipt of cash proceeds is entered into the cash book.
Entering PKO data into the cash book
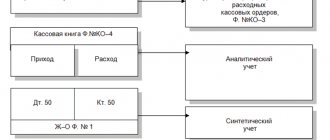
A cash book is a special form (journal) for recording cash transactions, which contains information on all receipts and withdrawals of cash at the organization’s cash desk.
Maintaining a cash book is based on the following regulatory documents :
- — Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88 “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for recording cash transactions and recording inventory results”
- — Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U.
The first contains a standard cash book form (No. KO-4), the second contains some rules for filling it out. A legal entity carrying out transactions with cash, regardless of the taxation system applied, is required to maintain a cash book (clause 1, clause 4.6, clause 4 of Directive N 3210-U). Individual entrepreneurs may not keep a cash book.
The cash book can be maintained on paper or electronically :
- - on paper, the book is drawn up by hand or using a computer (other equipment) and signed with handwritten signatures.
- — in electronic form, the book is prepared using a computer (other equipment) ensuring its protection from unauthorized access and signed with electronic signatures.
There are two ways to maintain a cash book on paper:
- — filled out by hand (the book is printed in advance or purchased, bound and pages numbered);
- - filled out using software and hardware (the book is filled out on a computer and then printed).
It is convenient to fill out the cash book using technical means, for example, in an accounting program. Typically, the program generates a cash book automatically, based on the entered incoming and outgoing cash orders.
At the end of each working day, the cashier prints out and signs a sheet of the cash book, and hands over the PKO and RKO issued for the day to the accountant. If no cash transactions were carried out during a working day, no entries are made in the cash book for that day.
During the calendar year (or other period determined by the organization), the printed sheets of the cash book are numbered (usually numbering occurs automatically when printed from an accounting program), collected in a folder, and at least once a year stitched into a single book, sealed in the same way as the cash book, filled out by hand, certified by the signatures of the chief accountant and the head of the organization and the seal of the organization (if you use one).
See below for an example of filling out a cash book.
Postings for retail revenue - example
Now that we have dealt with the preparation of primary documents, let's look at the postings for retail revenue using an example.
Ogorodnik LLC is engaged in the retail sale of vegetables to individuals. On September 14, vegetables worth 22,000 rubles were sold, incl. VAT 10%. Individuals pay in cash in the store. The cost of goods sold was 8,000 rubles. Let's make entries for retail revenue:
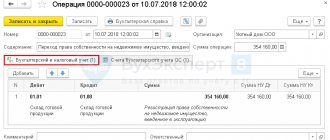
Debit 50-2 – Credit 90-1 – in the amount of 22,000 rubles. – revenue is reflected
Debit 90-3 – Credit 68 – in the amount of 2000 rubles. – VAT charged
Debit 50-1 – Credit 50-2 – in the amount of 22,000 rubles. – cash proceeds are deposited into the main cash register
Debit 90-2 - Credit 41 - in the amount of 8,000 rubles. — the cost of goods sold is written off.
You can also use account 62, in which case the transactions for retail revenue will be as follows:
Debit 62-1 – Credit 90-1 – in the amount of 22,000 rubles. – revenue is reflected
Debit 50-2 – Credit 62-1 - in the amount of 22,000 rubles. – the buyer’s debt is repaid.
The rest is all the same.
A few words about the recognition of income for the purpose of calculating income tax. Income is recognized:
- With the accrual method: on the date of sale of goods, works, services.
- With the cash method: on the day money is received in bank accounts or at the cash desk.
In retail sales, if we do not consider prepayment, the moment of receipt of payment for goods, work, services and the transfer of goods, performance of work, provision of services coincides in time. Therefore, the date of recognition of income in tax accounting under the accrual method and the cash method will coincide.
Income will be recognized on the date of sale of goods, work, or services. Those. in our example, Ogorodnik LLC will reflect the receipt of income on September 14.
Retail Invoice and Sales Book
If the seller organization is located on OSNO, then it is a VAT payer. Consequently, when selling goods, there is an obligation to charge VAT and issue an invoice. However, a retail buyer who purchases goods for his own consumption does not need an invoice.
For this situation, the Tax Code provides a separate rule. According to clause 7 of Article 168 of the Tax Code, when selling goods for cash by organizations and individual entrepreneurs in retail trade, public catering and when performing work or providing services to the population, it is not necessary to issue invoices. It is enough to issue the buyer a cash receipt or other document in the established form.
But the question arises, if an invoice is not issued for retail sales, what then should be recorded in the sales ledger? The Rules for Maintaining the Sales Book (approved by Government Decree No. 1137 dated December 26, 2011) stipulate that in such a situation, the details of the cash register control tape (z-report) generated per day are registered in the sales book.
When filling out the sales book, you will also be faced with the question of what to indicate in columns 7 and 8. This is the name and TIN/KPP of the buyer, you do not have them. You need to put dashes in these columns. In column 2 “Operation type code” you will indicate code 26. This is the code for VAT evaders, including individuals.
Retail accounting using the simplified tax system
In tax accounting using the simplified tax system, the date of recognition of income is the date of receipt of funds from the buyer (cash method). Those. for our example, if Ogorodnik LLC works on the simplified tax system, income will be recognized on the same day - September 14, when the sale took place and the funds arrived at the cash desk.
Postings for retail revenue on the simplified tax system will be similar to the previous example, only postings for VAT calculation will be absent.
Retail tax accounting using the simplified tax system is maintained in the Income and Expense Accounting Book. The basis for making an entry in the book will be a cash receipt order, because it is the primary accounting document confirming the deposit of funds into the cash register.
The entry in the book will be something like this:
100
PKO No. 54 dated 09.14.16
Received from sales to retail customers
22000
Retail sales report in 1C: Accounting
For those who keep records in the 1C: Accounting program - see how to create a report on retail sales in 1C: Accounting in video format.
What problematic issues did you encounter regarding the accounting and processing of retail revenue? Ask them in the comments!
Postings on retail revenue and preparation of cash documents
How to keep accounting records of cash in the cash register?
Working with cash is subject to a number of conditions that are specified in the special instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U. Important details:
- the presence of a maximum and minimum limit on amounts at the cash desk;
- the person in charge is selected from among the employees by the employer. Most often, this person is appointed as a cashier;
- any cash transaction is recorded in a cash book;
- The receipt of finance means the use of PKO (cash receipt order), and the departure - RKO (cash expenditure order).
Accounting for cash transactions
Cash transactions using a cash register are accompanied by the use of an account. 50 (checkout). Receipt of money means making an entry with Dt50, and issuing Kt 50, where Dt is a debit and Kt is a credit.
Additionally, corresponding numbers can be used. For example, 60 is used when receiving payment from a supplier, and 70 is used to pay employees.
An example of posting funds through a cash register. For a month of work, employees receive a salary totaling 400,000 rubles. For this purpose, a statement is drawn up, to which the RKO is attached indicating the amount and posting Dt 70 Kt 50.
Directive of the Bank of Russia dated March 11, 2014 N 3210-U “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions by legal entities and the simplified procedure for conducting cash transactions by individual entrepreneurs and small businesses”
Accounting for refunds to the buyer for goods
Reflection in accounting for a refund for goods returned by the buyer depends on when this event occurred:
- in the same tax period with the sale (and it does not matter whether the day of sale coincides with the day of return) - in this case, reversing entries are used;
- different tax periods - here the return during the period of its implementation will have to be reflected through non-operating income and expenses.
Separately from the receipt of revenue, the return transaction will be shown even if the day of return coincides with the day of sale, since Law No. 54-FZ (clauses 1 and 4 of article 4.1, clause 3 of article 4.3, clause 1 of article 4.7) requires separate registration, storage and transfer to the Federal Tax Service of each document generated by the cash desk.
Accounting transactions using reversing entries will look like this:
- goods received from buyer:
Dt 41 Kt 76 (62);
- refund made:
Dt 76 (62) Kt 50 (51);
- adjusted revenue:
Dt 76 (62) Kt 90.1 reversal;
- Corrections have been made to write off the cost of goods sold:
Dt 90.2 Kt 76 (62) reversal.
If retail accounting is kept at sales prices, then upon return there will be an entry to restore the amount of the trade margin:
Dt 90.2 Kt 42.
If the tax periods of the sale and return do not coincide, then in the last 3 transactions, instead of subaccounts 90, account 91 with similar subaccount numbers will be used.
With regard to adjusting the amount of VAT on sales (if the seller works with this tax), it should be taken into account that here, in accordance with the requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 5 of Article 171), it will be necessary to make a deduction for the amount of tax corresponding to the amount of the refund. In this case, the purchase book must contain the details of either an adjustment invoice or an expense cash order that formalized the issuance of money to the buyer (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 19, 2013 No. 03-07-15/8473).
Since for the correct implementation of the deduction (indicating the details of the document giving the right to it), the VAT amount must be reflected on account 19, the logical entry for reflecting the amount intended for deduction would be:
Dt 90.3 Kt 19 reversal.
It will essentially replace 2 entries: for adjusting VAT on revenue (Dt 90.3 Kt 68 reversal) and for calculating the same amount of tax for deduction (Dt 19 Kt 68 or Dt 68 Kt 19 reversal).
The deduction for the amount reflected in account 19 on the date of its accrual will be made by the usual posting for it:
Dt 68 Kt 19.
Read more about creating a purchase book in the article “What are the basic rules for filling out and maintaining a purchase book?” .
How does accounting for individual funds differ from accounting for an enterprise?
For special modes of activity, for example, individual entrepreneurs or small entrepreneurs, the procedure has a number of nuances.
According to Federal Law No. 402-FZ, such persons are allowed not to use the standard version of the accounting type. It turns out that a small entrepreneur or individual entrepreneur may not keep a cash book and not use PKO and RKO.
Additionally, the exemption from financial reporting allows you not to prepare Form 4.
An important point is the activity that is included in the exceptions, since if there is an obligation to maintain and there is no reporting, the entrepreneur may be subject to fines and liability.
Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ “On Accounting”
Cash accounting
The accountant reflects information about the receipt of cash in the organization as a debit to account 50, and expenditures as a credit. Under one agreement, a commercial organization has the right to accept from the counterparty no more than 100,000 rubles. In this case, it is necessary to use cash register equipment (CCT) with an online data transfer function that issues fiscal receipts. Failure to use CCP may result in serious fines.
For synthetic accounting, a journal order for account 50 and a general ledger are used; the accountant maintains analytics for each division separately in special registers. The balance (remainder) must be displayed at least once a month. Accounting data must correspond with other accounts.
Home accounting online
There are many programs on the Internet that offer home accounting in virtual mode. To do this, you don’t need to download or master anything, just go online and find a suitable site.
Important! As a rule, such resources offer only a set of basic functions for free - you will have to pay extra for the rest.
A good option is to create a budget online using Google. To start using the program, you will need to register an account. Security is considered a disadvantage of online accounting, because no one can guarantee complete confidentiality of data posted on the Internet. In addition, if there are technical problems with the service, the information may simply disappear.
Home accounting in Excel
Microsoft has a convenient office program that is familiar to all accountants - Excel. It is free and can be used even if the Internet is down.
Screenshot 1. Sample of accounting in Excel.
To keep track of the family budget, you can create a table yourself, or you can download a ready-made template from the Internet. Thanks to this, as well as the automation of all calculations, the question of how to correctly fill out Excel tables will not arise.
Each chapter must be filled out correctly, and then the calculations will be carried out automatically according to the given formula. All you need to do is enter the expense values daily and systematically summarize the results. The convenience of this method lies in automatic calculations and quick filling of tables. However, the downside may be the need to master this program and compile the correct formulas in it.
Automated management of individual entrepreneurs' activities
In a private enterprise, accounting can be organized by introducing special software.
There are several types of such software.
Enterprise Resource Planning System (ERP) is software designed to manage the business processes of an enterprise, regardless of its size, including company projects, supplies, procurement and finance.
It can adapt to changes in current business processes and allows for centralized document flow in one program instead of several previously used ones. Representatives of such software are: SAP Business Suite, SAP NetWeaver, Microsoft Dynamics AX, PDM/PLM systems, 1C:Enterprise.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is software designed to maintain a common database of customers and partners in one place and has a unified business logic. The system is equipped with a specialized set of tools, applications and functions that are located in a single environment.
Representatives of such software are: Supasoft CRM, APEK CRM Lite, Galloper CRM, ASoft CRM and other free and paid analogues.
Warehouse Management System (WMS) – software designed to manage labor resources, warehouse operations, product operations and document flow.
Allows you to identify goods in the system and build an accounting hierarchy in accordance with the selected level of complexity. Representatives of such software are: Solvo.WMS, RadioBeacon WMS, Exceed WMS 1000, Distribution Center Solution, Avalon system vision and other analogues.
Software products aimed at business automation are equipped with levels of protection against unauthorized access, theft and damage to the database, allowing each user of the implemented system to be assigned certain access rights to the existing database.
Thus, the likelihood of duplicating existing information by other departments of the enterprise or making changes to the database without coordination with all departments included in the unified system is reduced to zero.
Most often, software products of the 1C line of various versions are introduced to manage the accounting department of an enterprise, for example, “1C: Enterprise” or “1C: Accounting”.