Individual entrepreneurs usually choose preferential tax regimes. This allows them to optimize costs and submit fewer reporting forms. The general taxation system for individual entrepreneurs is not the best option. As a rule, her choice is dictated by necessity. And in some cases it is not there at all, because you can end up on OSNO not of your own free will.
This will happen if you go beyond the restrictions established within the tax regime for the income of individual entrepreneurs, the number of employees or types of activities. Or if you don’t switch to a simplified tax system in time. The general taxation system for individual entrepreneurs is relevant if he works with large buyers who pay VAT. Let's figure out what the OSNO regime is and what kind of reporting needs to be submitted here.
Personal income tax on entrepreneur income
An individual entrepreneur pays personal income tax on the amount of income he receives from business activities. He has the right to reduce them by professional deductions in the amount of costs that he can confirm with documents. If there are no documents, an individual entrepreneur on OSNO has the right to deduct 20% from his income. The result is a tax base to which a personal income tax rate of 13% is applied.
The procedure for paying tax is described in Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. During the year, the entrepreneur makes 3 advance payments at the following times:
- for the 1st quarter - no later than April 25:
- for the 3rd quarter - no later than July 25;
- for the 4th quarter - no later than October 25.
At the end of the year, the individual entrepreneur must recalculate personal income tax based on how much income he actually received and paid in advances. Additional tax payment must be made before July 15 of the following year. And by April 30, an individual entrepreneur on OSNO is required to submit a 3-NDFL declaration to the Federal Tax Service.
Free tax consultation
Results
The composition of individual entrepreneurs' reporting on OSNO without employees is small. It only includes a VAT return and a 3-NDFL return. Entrepreneurs who hire employees, in addition to these two declarations, must submit a fairly wide range of reporting forms to the tax office, the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund on employees, remunerations paid in their favor, personal income tax withheld from these remunerations and accrued insurance premiums.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
VAT
OSNO is one of two taxation systems that requires payment of VAT. Tax is calculated on the cost of goods, works and services sold. The standard rate from 2021 is 20%. There are a number of preferential goods that are taxed at a rate of 10%. These are food, goods for children, printed periodicals, and some medical products. The full list is presented in paragraph 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, in some cases there is a zero VAT rate. It is used for export, international transport and cargo transportation. There are also a number of transactions that are not subject to VAT (Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Among them are the sale of certain medical goods and services, care for the disabled, activities with children in clubs and others.
The VAT allocated in the incoming invoice can be deducted by the buyer. It is because of this opportunity that entrepreneurs often choose the main tax regime. This allows their counterparties to reduce the tax payable. The individual entrepreneur himself can also take advantage of the deduction and reduce VAT by the amount of the “input” tax charged to him by suppliers.
VAT is calculated at the end of each quarter. The amount received is divided into 3 equal parts and paid before the 25th day of each month of the next quarter.
VAT returns are submitted 4 times a year - before April 25, July 25, October 25 and January 25. The peculiarity is that this report is submitted only in electronic form. You cannot fill out a paper form and bring it to the Federal Tax Service or send it by mail. In this case, it is considered that the declaration has not been filed. This rule also applies to “zero” VAT returns.
Reporting methods
Acceptance of tax returns is carried out by the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration of the individual entrepreneur (at the registration address of the person who registered the business).
There are three ways to submit reports:
- During a personal visit to the Federal Tax Service (including through a legal representative). The inspectorate employee registers the declaration on the tax authority’s website. The individual entrepreneur has the right to receive a mark of acceptance and date of acceptance on the copy of the declaration.
- Mail your tax return. In this case, the individual entrepreneur will receive a notification of acceptance (or refusal) by registered mail by Russian Post.
- Submit the declaration electronically through your Personal Account on the regulator’s information resource (website of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation). The main condition for this option is that the individual entrepreneur has an enhanced qualified electronic signature (ECES). Registration of the document and the response go through the taxpayer’s personal account.
Similar methods of providing regular reporting are in effect in the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, as well as in the Social Insurance Fund. Here you can submit forms both electronically (if you have the UKEP) and on paper.
Timely submission of reports will protect the entrepreneur from fines
Property tax for individuals
Property tax is levied on real estate that an individual entrepreneur on OSNO uses in his business. This could be an apartment, a room, a residential building, including an unfinished construction project, an outbuilding or structure, a garage, or a parking space. The tax rate varies from 0.1% to 2%.
Property tax is calculated by inspection specialists. The entrepreneur receives a notification and makes payment no later than December 1 of the following year. This tax is not reported.
General tax regime for individual entrepreneurs in 2021: what taxes to pay
An individual entrepreneur under the general taxation system pays personal income tax and VAT on income received from business activities.
Income not related to business is subject to personal income tax only. If an entrepreneur uses real estate in his activities, then according to the rules established for individuals, he is also obliged to pay:
- property tax;
- land tax.
When using motor transport, according to the rules for individuals, transport tax is also paid.
Property taxes are not calculated by individual entrepreneurs independently. The calculation of transport, land taxes and property taxes for all individuals, including individual entrepreneurs, is calculated by the Federal Tax Service. They are paid by taxpayers based on notifications from tax authorities.
In addition to tax payments, the entrepreneur is obliged to pay insurance premiums for himself.
Personal income tax for employees
If an individual entrepreneur is an employer or hires individuals under civil contracts, he must transfer personal income tax to the budget from the payments he makes to them.
The tax is paid from the amounts accrued to the individual. The order is:
- income subject to personal income tax is calculated;
- the amount of tax is calculated taking into account the deductions due to the employee (Articles 218-220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the amount received is withheld from income and transferred to the budget no later than the next day.
Certain types of income have their own tax payment deadlines. For example, personal income tax on sick pay or vacation pay must be transferred by the end of the month in which they were paid. Personal income tax reporting for employees is submitted in the form of calculation 6-NDFL - at the end of each reporting quarter, no later than the last day of the next month.
Free accounting services from 1C
What is OSN
The general (standard) taxation system is the most complex taxation regime of all existing in Russia, characterized by a large number of taxes and the obligation to maintain full accounting and tax records.
By default, all entrepreneurs and organizations that have not decided on the choice of taxation system upon registration, as well as those that are no longer entitled to apply any of the special tax regimes: simplified tax system, PSN and unified agricultural tax, are transferred to OSNO by default.
The general system is not subject to any restrictions on types of activities, number of employees, income received, etc. As a rule, most large companies work on OSNO and, as VAT payers, also prefer to work with those who pay this tax.
Insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs for themselves
Every entrepreneur, regardless of the tax regime he has chosen, pays the following contributions for his insurance:
- Medical. In 2021 - 8,426 rubles.
- Pension. The contribution amount consists of two parts. The first part is fixed - 32,448 rubles for the full year 2021. If an entrepreneur’s income does not exceed 300,000 rubles, he pays only this part. If his income is greater, then he pays 1% on the excess amount. Individual entrepreneur on OSNO to calculate this amount reduces the income received for professional deductions.
Medical contributions and the first part of pensions are paid during the calendar year. The estimated portion of pension contributions must be transferred no later than July 1 of the following year. Reporting on individual entrepreneurs' own contributions is not submitted.
Accounting statements of individual entrepreneurs on OSNO
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 6 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ Individual entrepreneurs may not keep accounting records . Therefore, unlike legal entities, individual entrepreneurs are not required to send financial statements to the Federal Tax Service and Rosstat
Individual entrepreneurs must fill out books of purchases and sales, as well as a book of income and expenses. These registers, in the absence of “full-fledged” accounting, form the basis of their accounting.
However, many entrepreneurs still balance debit and credit on a voluntary basis. This allows individual entrepreneurs to assess their financial situation “in a comprehensive manner”, and it is easier to fill out tax returns when the accounting system as a whole is in place.
Sometimes an individual entrepreneur does accounting because he needs to provide financial statements to external users. These could be banks when processing loans, or counterparties if a large contract is expected to be concluded.
But even in this case, the entrepreneur is not obliged to submit a report to government agencies.
Individual entrepreneur reporting forms
In conclusion, we list what kind of reporting an individual entrepreneur submits with his employees. It does not depend on whether the entrepreneur chose the main tax system, simplified tax system, UTII, unified agricultural tax or patent. If there is at least one hired employee, the individual entrepreneur is required to take:
- Calculation of insurance premiums. Submitted to the tax office at the end of the quarter by the 30th of the next month.
- Forms of personalized accounting. SZV-M is submitted to the Pension Fund every month, the submission deadline is the 15th of the next month. At the end of the year, before March 1, the SZV-STAZH is submitted along with the EDV-1 form.
- 4-FSS. Submitted to the Social Insurance Fund every quarter. Deadlines: in paper form - until the 20th day of the month following the end of the quarter, in electronic form - until the 25th day.
Features of doing business as an individual entrepreneur
Individual entrepreneurship is a registered private business (without forming a legal entity). Any citizen of Russia who is 14 years old can become an entrepreneur.
Advantages of private commercial activity:
- Freedom to make business decisions.
- The minimum package of documents when registering your business is a passport and a receipt with payment of the state fee. When registering (unlike an LLC), an individual entrepreneur does not have to submit a package of 9 main constituent documents: the charter, certificates of registration and registration, an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, an order for the appointment of a director, and much more. No current account or authorized capital is needed.
- Fast registration. Register a private business at the place of registration. Individual entrepreneurs do not need to obtain a legal address and organize an office.
- Simple reporting system (depending on the taxation system).
- Lack of accounting.
- Profit from activities is 100% owned by the individual entrepreneur.
- Less penalties for violations.
- Prompt liquidation. To terminate the activity, it is enough to submit an application to the Federal Tax Service.
- For individual entrepreneurs, it is possible to use the PTS (patent system) - one of the most loyal tax regimes.
Disadvantages of running a business as an individual entrepreneur:
- The key disadvantage is personal financial responsibility for actions related to business activities. The individual entrepreneur is liable for all obligations with his personal property, even if he does not participate in business activities.
- All debts to the budget or contractors with whom the individual entrepreneur did business can be collected even after the closure of the individual entrepreneur (with the exception of property excluded from penalties under Article 446 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
- An individual entrepreneur is an unreliable partner from the point of view of financial institutions. Therefore, it is more difficult for a private businessman to take out a loan; it is almost impossible to sign an agreement on a line of credit. There are forms of financing that are not available to individual entrepreneurs (for example, umbrella overdraft or venture financing).
- Another difficulty when expanding a business is the impossibility of attracting outside investment.
- It is more difficult to work with counterparties in terms of obtaining a deferment or installment payment.
- There are types of activities that are closed to individual entrepreneurs (banking, alcohol sales).
- An entrepreneur is obliged to pay a fixed payment to the Pension Fund and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund, even if he does not conduct business. This obligation is removed only after the liquidation of the individual entrepreneur.
To make the right decision when choosing a tax system, you need to study the advantages and disadvantages of each of the five options
Forms, periods, reporting deadlines, percentage of deductions and amounts of payments are regulated by the taxation system that the individual entrepreneur chose to conduct his activities as an entrepreneur.
When choosing the optimal tax regime, it is worth considering several factors:
- what type of activity does the individual entrepreneur plan to engage in;
- scale of business: number of employees, turnover, estimated profit;
- main consumers of services;
- characteristics of the region where the activity is carried out;
- potential of tax benefits and preferences.
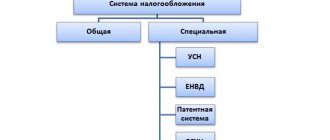
For private businesses in the Russian Federation, there are several types of taxation: the main (or general) regime (OSNO, another abbreviation is ORN), which is established by the Federal Tax Service “by default” if the entrepreneur did not declare a different regime during registration, as well as one of four taxation systems: USN, UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax or PSN.
Table: comparison of OSNO and preferential regimes for entrepreneurship
| Mode | Tax | An object | Bid | Period | Declaration provided |
| ORN (OSNO) | Personal income tax | income | 13% | calendar year | at the end of the year |
| Property tax for individuals | Types of property established by law | from 0.1% to 2% | calendar year | is not provided | |
| VAT | sale of goods and services | 0% / 10% / 18% | quarter | based on the results of the quarter | |
| simplified tax system | Simplified taxation system | income | 6% | calendar year | at the end of the year |
| income minus expenses | 15% | ||||
| UTII | A single tax on imputed income | imputed income | 15% | quarter | based on the results of the quarter |
| Unified agricultural tax | Unified agricultural tax | Income minus expenses | 6% | calendar year | at the end of the year |
| PSN | Payment of patent cost | Possible annual income | 6% | no more than a calendar year | is not provided |
You need to carefully weigh the pros and cons when choosing a tax regime
This might also be useful:
- Changes in individual entrepreneur taxation in 2021
- Increase in UTII from 2021
- Do I need to take the zero SZV-M in 2021?
- UST in 2021
- Income codes in certificate 2-NDFL in 2021
- What reporting must an individual entrepreneur submit?
Is the information useful? Tell your friends and colleagues
Dear readers! The materials on the TBis.ru website are devoted to typical ways to resolve tax and legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your specific issue, please contact the online consultant form. It's fast and free!
In what cases is the use of OSNO beneficial?
It is beneficial to use a general taxation system:
- if most of the counterparties are on OSNO and are thus interested in “input” VAT;
- when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation (VAT paid when importing goods can be deducted);
- the main part of the activity is related to wholesale trade;
- the organization is exempt from income tax (for example, educational institutions).
Free tax consultation
Individual entrepreneur reporting under special tax regimes
Special regimes are tax regimes with a preferential tax burden for entrepreneurship.
The simplified tax system is the optimal mode for doing business
The tax rate under the simplified tax system depends on the object of taxation chosen during registration of an individual entrepreneur:
- “income” with a rate of 6%, when the tax is calculated on the amount of income;
- “income minus expenses”, rate - 15%. For the calculation, income is taken, which is reduced by the amount of expenses.
For private entrepreneurs there are “tax holidays”, which are valid for individual entrepreneurs registered before 2021. During this period, a zero tax rate can be confirmed for starting individual entrepreneurs. This applies to businessmen who have received their status for the first time and are conducting their activities in production, consumer services, as well as in the social or scientific sphere. The vacation period is 2 years.
At the regional level of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, the rate for certain types of activities can be reduced to 1% for the object “income 6%”. And for the object “income minus expenses”, regional legislation may apply differentiated tax rates for individual entrepreneurs - from 5 to 15 percent. The rate can be applied to all taxpayers of a federal subject (territory, republic) or to certain categories.
Advantages of doing business using the simplified tax system:
- A wide range of permitted types of business activities (unlike the Unified Agricultural Tax, PNS, UTII).
- Exemption from income tax, corporate property tax, VAT (with some exceptions).
- Individual entrepreneurs using the “simplified” system do not pay tax on personal income. persons, only income from business activities is taken into account.
- An individual entrepreneur does not make payments for property tax for an individual that is used for business.
- According to the simplified tax system, the simplest form of reporting is a tax return submitted only once a year.
- If an individual entrepreneur does not have hired employees, he is not required to keep accounting records and submit financial statements to the Federal Tax Service (it is enough to keep an accounting book).
A simplified tax regime is often chosen by entrepreneurs engaged in retail trade in industrial or food products.
Restrictions and responsibilities when doing business under the simplified tax system:
- The number of employees in an individual entrepreneur should not exceed 100 people.
- The annual income and residual value of the enterprise is no more than 150 million rubles.
- An individual entrepreneur does not have the right to switch to another regime until the end of the tax period - the calendar year. The notification in this case is submitted to the Federal Tax Service before January 15 of the year in which the individual entrepreneur wants to apply a different regime; this must be done in writing (electronic or paper). If the notification is not delivered to the tax office, then the taxpayer is required to report according to the simplified tax system by the end of the year.
- There is a limitation when switching to the simplified tax system from other tax regimes: if the organization’s income exceeded 112.5 million rubles. for 9 months of the calendar year, it will be impossible to make the transition (Article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- You can go to the simplified tax system from a single tax on imputed income only from the beginning of the month in which the obligation to pay UTII was terminated. In this case, you need to notify the tax office at least 30 days in advance (in writing).
Table: reporting under the simplified tax system
| Regularity | View | Deadline | Where |
| Annually | Declaration of the simplified tax system | until April 30 next year | Inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration |
Taxes and reporting under the Unified Agricultural Tax
The unified agricultural regime is a preferential tax system for participants in the agricultural production market. In this mode, the individual entrepreneur contributes a minimum percentage to the budget - 6% of the difference between income and expenses.
Advantages, features and benefits under the Unified Agricultural Tax:
- The main condition for determining this regime is that the share of individual entrepreneurs’ income from the sale of agricultural products must be at least 70% of the income received.
- The state provides individual entrepreneurs with the opportunity to reduce the tax base by the amount of losses that were incurred in previous years while running a farming business.
- If an individual entrepreneur chose the ORN or a simplified taxation system during registration, you can switch to the Unified Agricultural Tax only from the next calendar year. If the types of activities of an individual entrepreneur meet all the conditions of the Unified Agricultural Tax, it is enough to submit an application to the Federal Tax Service before December 31 of the current year.
- If an individual entrepreneur wants to close his business, he must submit a declaration no later than the 25th day of the month following the month in which the activity was terminated.
Individual entrepreneurs who do not produce agricultural products, but only carry out their primary or subsequent (industrial) processing, are not entitled to apply the unified agricultural tax.
Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation
https://www.nalog.ru/
Entrepreneurs who have the right to apply the unified agricultural tax:
- agricultural producers;
- fishing cooperatives engaged in fishing (other river and sea biological resources);
- private entrepreneurs who provide support services to rural producers (sowing, harvesting, mulching, etc.).
Farms in the country can work under the Unified Agricultural Tax
If you sell the fruits of your labor from your personal garden or dacha, this is not a business.
Running a personal subsidiary plot is not an entrepreneurial activity - the farmer produces and processes agricultural products for his own needs, and sells the surplus.
Public services
https://www.gosuslugi.ru/
Table: tax reporting under the Unified Agricultural Tax
| Regularity | View | Deadline | Where |
| Annually | until March 31 next year | Declaration of Unified Agricultural Tax | Federal Tax Service |
How an individual entrepreneur should report on UTII
In the case of using the Unified Tax on Imputed Income for Certain Types of Activities (UTII), the amount of income of the entrepreneur is not taken into account for tax purposes. The tax rate is fixed - 15% of imputed income, which is set by local authorities and applies only to certain types of services.
Starting from 2021, single tax rates may be established in municipal territories ranging from 7.5 to 15%, depending on the categories of taxpayers and types of activities falling under UTII.
Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation
https://www.nalog.ru/create_business/
Advantages and features of the UTII mode:
- With this taxation system, a person does not pay personal income tax, property tax for individual entrepreneurs (if it is used to conduct business) and VAT.
- An individual entrepreneur has no obligation to maintain accounting records.
- The list of enterprises entitled to operate under UTII is limited by type of business activity. Individual entrepreneurs who carry out:
- retail trade;
- catering points;
- car repair, maintenance and washing services;
- hotels;
- cargo transportation and passenger transportation;
- veterinary services;
- leasing of land plots and places of trade;
- advertising and so on.
- Separate accounting of indicators for each area of UTII activity is necessary.
- The individual entrepreneur's staff must consist of less than one hundred people.
- Individual entrepreneurs are required to regularly submit data on the number of their employees to the Pension Fund.
- To be removed from the “imputed” registration, an individual entrepreneur must submit an application to the tax office within 5 working days from the date of termination of activities under UTII.
- As soon as the individual entrepreneur left the UTII, he has the right to switch to the simplified tax system (from the month when the obligation to pay UTII ended).
Entrepreneurs providing various services to the population, subject to compliance with the norms established by law, can apply the UTII regime
UTII taxpayers have the right to reduce the amount of tax calculated for the tax period by the amounts of payments and benefits paid in favor of employees employed in those areas of the taxpayer’s activity for which a single tax is paid. However, the amount of such reduction cannot be more than 50% of the calculated tax.
Individual entrepreneurs who do not have employees - that is, they do not make payments and other remuneration to individuals - can reduce the amount of the single tax on imputed income by the amount of insurance contributions paid (for themselves) in a fixed amount to compulsory health insurance and compulsory medical insurance without applying the 50% limit .
Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation
https://www.nalog.ru/
Table: tax reporting for UTII
| Regularity | View | Deadline | Where |
| Quarterly | before the 20th day of the 1st month of the next quarter | Declaration of UTII | Federal Tax Service |
Patent regime
The patent price (PSN) is determined by the type of activity of the individual entrepreneur. The standard calculation of the tax base is based on a rate of 6% and the possible annual income of an individual entrepreneur.
Features of the patent tax system:
- a narrow list of types of activities (similar to types of services under UTII);
- there are “tax holidays” with a rate of up to 0% for certain types of services;
- the simplest accounting and reporting procedure has been defined for PSN (you don’t even have to submit a tax return);
- PSN is available only to entrepreneurs whose number of employees does not exceed 15 people;
- a patent is granted to an individual entrepreneur for any period (from 1 to 12 months), but only within 1 calendar year;
- if an individual entrepreneur runs several types of business in parallel, a patent is purchased for each type separately;
- Each region of the Russian Federation has its own list of areas and types of activities for PSN. Tax rates are determined by municipalities.
Is it possible to get a tax deferment?
There are times in life when an individual entrepreneur does not have the opportunity to pay taxes and fees in full. In this case, a private entrepreneur has the opportunity to send an application to the regulatory body for a deferment or gradual payment of debt for the enterprise.
Deferment (or installment payments) can be approved by the Federal Tax Service for a period of up to one year. But for this, the individual entrepreneur must have compelling reasons to suspend payments to the budget. It will be necessary to prepare and submit to the Federal Tax Service the necessary package of evidentiary documents.
The Federal Tax Service must make a decision on deferment (or refusal thereof) within 30 working days after registration of the application from the entrepreneur.
Obtaining a tax deferment allows you to use the released funds for business development
Who has the right not to pay taxes and insurance premiums and when?
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains a list of taxpayers who have the right not to pay taxes and contributions during periods when they did not conduct their activities, but were listed as individual entrepreneurs.
Individual entrepreneurs are temporarily exempt from paying taxes and insurance payments:
- for the period when a woman (or one of the family members) is caring for a child up to one and a half years old;
- for the period of caring for a disabled person of group I, a disabled child, as well as for an elderly person (over the age of eighty);
- military service is taken into account;
- for a period of up to 5 years, individual entrepreneurs who live with their family in places where the individual entrepreneur does not have the opportunity to work are exempt from payments to the budget. This category includes family members of military personnel, contract soldiers, diplomats, etc.
If until 2021 the main condition for such a concession on the part of controllers was mandatory documentary confirmation of the fact of absence of activity during such periods, now there are no such instructions in the Tax Code.
If in the billing period there were months during which these persons carried out business activities, then they must pay contributions in proportion to the number of calendar months when such activities were carried out.
Individual entrepreneurs’ reporting on employees is the same for different taxation regimes
Paying taxes is serious business
It is the duty of every entrepreneur operating on the territory of the Russian Federation to pay the state all established taxes and fees in a timely manner and in full. This responsibility should not be neglected. The risks for individual entrepreneurs are too great to ignore.
Violations of legal requirements can lead to both administrative and criminal liability.
A short list of actions of an individual entrepreneur that may entail sanctions from regulatory authorities:
- conducts its activities without registration in the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs;
- operates without licenses required to conduct certain types of activities;
- hides his income when submitting a tax return to the Federal Tax Service;
- shows inflated costs for organizing its activities, thereby reducing the tax base.
The current legislation of the Russian Federation in these cases defines different types of punishments - from a fine to imprisonment.
Of course, individual entrepreneurship has a number of advantages over other forms of business:
- simplified reporting;
- lower fines for violations (than for legal entities);
- full disposal of your profits;
- quick and simple liquidation procedure (an application to terminate the activities of an individual entrepreneur is sufficient).
Considering the benefits and preferences for individual entrepreneurs, it is necessary to focus on the main thing: for all financial obligations to the state and counterparties, a private entrepreneur is responsible with his personal property.
And even if the property is not involved in business activities, regulatory authorities may consider it when collecting it. Another important point for private businesses is that if there are debts, then even after the closure of the individual entrepreneur these debts may be subject to collection by regulators.
The most common sanction for defaulters today is the blocking of all bank accounts of an individual with individual entrepreneur status. Moreover, if income is declared incorrectly and business is conducted illegally, an entrepreneur may lose part of his property or real estate.
Arrest and confiscation of an entrepreneur’s property for debts are common measures to combat tax evasion
Property that cannot be recovered from an entrepreneur (Article 446 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation):
- Housing (part of it), if this is the only premises suitable for living at an individual. persons (with the exception of real estate purchased with a mortgage).
- A plot of land, if there is a house on it. But again - if this is the only place of residence for the individual entrepreneur and his family.
- Personal belongings (shoes, clothes) and household items (furniture, dishes, etc.) vital for existence (household appliances, luxury items, jewelry can be confiscated).
- Property for running a business (if the individual entrepreneur proves that it is impossible to work without it, and the value of the property does not exceed 10,000 rubles).
- Animals that are not associated with business activities (this list includes bees), as well as food and outbuildings for their maintenance.
- Food and money for the minimum subsistence level (the amount for food for the debtor and his dependents is taken into account).
- Fuel for cooking, heating homes and utility rooms.
- Disabled people do not have the right to confiscate their means of transportation, including personal transport.
- Bailiffs also do not have the right to take away prizes, awards, memorable signs, cups, etc.
Therefore, it is worth weighing all the risks and opportunities before trying to win by hiding income or delaying submitting a declaration to the Federal Tax Service.
It is important to choose the correct and beneficial tax system for individual entrepreneurs. The choice depends on the type of activity of the individual entrepreneur, the amount of income, the number of employees, the regional specifics of preferential treatment, consumers of individual entrepreneur services and other factors.
The forms and deadlines for reporting when doing business depend on the chosen tax regime for individual entrepreneurs. The procedure for changing the regime and switching to another form is strictly regulated. This must be taken into account when registering a business.
If an individual entrepreneur did not choose one of the special (preferential) tax regimes during registration, the Federal Tax Service will by default impose a general tax regime on the entrepreneur. In this case, the entrepreneur must, in addition to paying personal income tax (personal income tax), pay property tax and VAT (value added tax).
It will be possible to change the tax regime only from the beginning of the next calendar year.
Timely payment of taxes is the responsibility of every businessman
“Non-entrepreneurial” ways to reduce personal income tax
In addition to the professional deduction, an individual entrepreneur can reduce his expenses that arise in the course of business activities through social, standard and property deductions.
Take a concrete example of training costs:
Individual entrepreneur Sokolova T.O. two children.
One child attends a preschool institution, which costs 30,000.00 rubles per year. He also attends an art school - tuition fees are 25,000.00 rubles.
The second child goes to a sports school - tuition fees per year are 54,000.00 rubles.
In connection with production costs, individual entrepreneur Sokolov T.O. wants to claim a deduction for training expenses in the amount of 100,000.00 rubles (50,000.00*2), which will allow him to reduce the tax paid for the year by 13,000.00 rubles (100,000*13)
Note!!! The total amount of expenses for which an entrepreneur can be provided with a social deduction, with the exception of expenses incurred for expensive treatment and education of children, cannot exceed 120,000 rubles.
What is provided for failure to submit a report to the tax office?
An individual entrepreneur must submit the main report to the tax service at the place of registration of his business within the time limits established by the current tax legislation. Penalties are provided for failure to comply with the deadlines for submitting tax reports under the OSN regime. In this case, reports must also be submitted retroactively. The amount of penalties is specified in Art. 119 and 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as in Art. 15.5 and 15.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. Persons who do not pay taxes on their economic activities are subject to administrative prosecution.
Important! In cases where an individual entrepreneur does not conduct economic activity and has no movement of money in his current account, instead of zero interim reports, he can provide a single simplified declaration, reducing the number of penalties and saving his time.
Using the basic tax system when conducting individual entrepreneurial activities can expand the opportunities of a small business owner and provide him with convenient conditions for developing his business.
Four main advantages of a common tax system for individual entrepreneurs
Unlike simplified taxation systems, in OSNO individuals do not have to keep full accounting records, which allows them to save on hiring a professional accountant. Keeping primary records of expenses and income is necessary to understand how things are going in the company. Based on such information, two main reports are compiled in the form of personal income tax and VAT declarations. This is more convenient and profitable than doing monthly reporting under the simplified tax regime.
Comparison with other modes
Individual entrepreneur on a patent - what reports must be submitted and within what time frame
Owners of small companies often try to immediately switch to alternative accounting modes:
- simplified tax system;
- UTII;
- ESNH.
Comparison of DOS with other reporting modes
At the same time, many people forget that there are a number of areas of economic activity in which only the general tax accounting system can be used. Unlike other OSNO systems, it requires filling out more reporting documentation. An entrepreneur should always accurately indicate his expenses and income in the primary account in order to pay all taxes.
Important! Although the general taxation system has a complex structure of the reporting component, unlike other simplified regimes, it does not limit a businessman in economic activity with the prohibitions provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The complexity of maintaining reports in OSNO is compensated by the absence of restrictions that exist in simplified taxation systems, which are imposed by current legislation on:
- number of employees;
- volumes of annual income;
- number of types of commercial activities.
In some cases, you can use the general system in combination with one of the simplified modes for accounting for expenses and income. Organizations can combine the general accounting system with the UTII regime, and individuals with a patent and a single tax. This combined option will help expand the scope of activity and increase profits.
Since the development of an enterprise may involve various areas of activity, in some cases OSNO can be combined with various options for simplified systems. For organizations, the general system can be combined with UTII. For individual entrepreneurs, you can use OSNO in combination with a patent and a single tax.
It is beneficial to use the OSNO system if:
- most partners pay VAT and work under the general taxation system;
- large-scale production or wholesale trade is carried out;
- acceptable conditions are exceeded when using a simplified system;
- trade in imported goods is carried out;
- income tax has been replaced by personal income tax.
In this case, the entrepreneur reduces the amount of deductions from the profit received from 20% to 13%. In the absence of documentary evidence of expenses, an individual entrepreneur can take them into account when filling out personal income tax in the amount of up to 20% of income received.
The system allows you to receive tax deductions for property involved in business. If there are no employees in the company, the individual entrepreneur pays fixed amounts to pension and extra-budgetary funds.
Statistical reports of individual entrepreneurs
Sometimes entrepreneurs must report to statistical authorities. But this duty is irregular. An entrepreneur can work for years and know nothing about statistical reports. These reports may not concern small entrepreneurs at all, with the exception of continuous statistical observation, which is carried out once every five years.
Rosstat decides independently every year who should report and on what forms; for this they draw up a sample. If an individual entrepreneur is not included in this sample, you can forget about statistical reports for the current year.
To find out whether you need to report this year, contact your local statistics office or use the Rosstat service.
Accounting for income and expenses for tax purposes
Accounting book forms (KUDIR) are approved for the following systems (each type of taxation has its own):
- general (OSNO);
- simplified (USN);
- patent (PSN);
- unified agricultural tax (USAT).
In any of these books, entries must be arranged in chronological order, amounts are calculated in ascending order, and the resulting data serves as the basis for filling out tax returns (the exception is the patent system: accounting of amounts is needed here to check whether the income compliance threshold has been exceeded).
What about UTII? After all, there is no form for it. Yes, there is no book - but it is important to take into account characterizing physical indicators, these could be:
- the number of retail spaces or the size of sales areas;
- number of vehicles or seats for passengers;
- number of staff;
- other objects (areas).
That is, the numerical volume on the basis of which the “imputed” tax is paid. You can record the available data in a separate document, compiled independently - this will be the accounting register for UTII.
Comments
Alexey 02/26/2016 at 04:08 # Reply
Hello! I registered as an individual entrepreneur on 12/28/15 and unknowingly ended up on OSNO. What reports and when do I need to submit them now?
ostapx1 09.24.2016 at 14:33 # Reply
Hello! This is the information contained in the article.
Alla 04/28/2016 at 04:43 pm # Reply
Thanks for the article, everything is simple and clear
12/13/2017 at 07:05 pm # Reply
Is it possible to keep all records in VLSI if we are an individual entrepreneur on OSNO? Is this not a violation of the BU?
ostapx1 12/13/2017 at 10:37 pm # Reply
Hello. Any third-party accounting department is not prohibited by law if it conducts its activities in accordance with the law and accounting rules.
01/29/2018 at 09:11 # Reply
I submitted the documents on December 12, they arrived on January 20, I can’t switch to the simplified system, what should I do? After all, this is not my fault!
01/29/2018 at 15:41 # Reply
Good afternoon. You had to submit documents for the simplified system within 30 years from the date of registration of the individual entrepreneur. The registration date is indicated in the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs. If the documents came to you so late by mail, then it is possible to apply for the simplified tax system and attach documents that confirm that you received them late.
Olga 10/12/2019 at 10:40 pm # Reply
Tell. We're back to basics. But we are not working yet. What reports should we submit?