By the way, in older versions of 1C 8.2, inventory takes place according to the same principles, only the appearance of the interface differs.
The general inventory scheme in the 1C program is as follows:
- Creating and filling out an inventory document. It is used to fill in actual data on the presence or absence of items in the warehouse. The document does not make any entries.
- If a shortage of goods is detected, it must be written off using the document “Write-off of goods” (less often ““).
- If there is an excess, it is accounted for using “ “.
Let's look at these documents in detail.
In the 1C Accounting 8.3 interface, the inventory document log can be found in the “Warehouse” section:
To create a new inventory in the journal that opens, click the “Create” button. Let’s fill in the header of the document with the details “Organization”, “Warehouse”:
The next stage is filling in the accounting quantity of goods in the warehouse. To do this, click above the tabular part “Fill” - “Fill according to stock balances”:
Please note: The accounting quantity is filled in on the date of the document, and not at the current moment
!
A list of all available goods will appear in the table (according to credentials in the 1C program):
We see two columns:
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
- Quantity fact - this data must be filled in based on the actual balances in the warehouse. By default, 1C fills in these quantities from the credentials.
- Quantity accounting - how much product is in stock according to the program data.
Now the most interesting thing is that we count how many goods are actually in stock and enter them in the “Factual quantity” column:
Once all the data is entered, write down the document. Now you can print the necessary primary documentation by clicking on the “Print” button:
- Inventory list of goods - INV-3
- Order to conduct an inventory - INV-22
- Matching sheet INV-19
If you noticed, the inventory itself does not make any entries into accounting. Now you need to write off or capitalize the goods that need it.
Our video on filling out inventory in 1C 8.3:
The need to maintain off-balance sheet accounts
Data on property, which is kept on the balance sheet, makes it possible to correctly evaluate all the assets of the enterprise. Without this information, no audit firm will be able to provide a positive opinion. Complete accounting of property will come to the aid not only of the enterprise, but also of the tax authorities inspecting its activities. For example, by recording data on leased fixed assets on account 001, you can always justify the costs of their repair.
If an enterprise transfers its property to other companies as collateral or for rent, then information about this reflected in off-balance sheet accounts (AB) will come in handy for drawing up a financial plan and maintaining management accounting. Off-balance sheet data is increasingly being used in the development of financial statements. Therefore, it is so important to maintain APs and periodically conduct their inventory.
Why are off-balance sheet accounts of MC needed (MC.01, MC.02, MC.03, MC.04)
In the chart of accounts of the 1C: Accounting program there is a number of additional off-balance sheet accounts in addition to the 11 generally accepted ones. This is done for more thorough and convenient accounting.
Account MC.04 is a subaccount of the MC account “Material assets in operation” along with three more subaccounts:
- MC.01 “Fixed assets in operation”,
- MC.02 “Workwear in operation”,
- MTs.03 “Special equipment in operation.”
МЦ.02—an off-balance sheet account used to account for special clothing issued to an employee to perform his official duties. Account MTs.03 accumulates information on special tools and equipment transferred into operation. Account MTs.01 is often used if the fixed asset is reflected differently in tax and accounting.
The introduction of these accounts into accounting is due to the need to control property written off from the organization’s balance sheet, included in costs, but used in the organization’s economic activities. Their debit reflects the values to be accounted for, broken down by item items, financially responsible persons and storage locations. The loan reflects the write-off of assets. In this case, transactions are recorded only in debit or only in credit of such accounts - correspondence is not typical for off-balance sheet accounts.
You can familiarize yourself with the features of using off-balance sheet accounts in accounting in the article
.
Information reflected in off-balance sheet accounts
An enterprise has the right to use eleven legal provisions provided for by law. Their totality is conditionally divided into the following blocks (groups):
| Groups | AP taking into account |
| 1 | property that does not belong to the company |
| 2 | obligations and security |
| 3 | other property |
Purpose of the ZS:
- recording values that the company does not own, but temporarily uses or stores;
- control over the conduct of business transactions of a certain type.
If explicit APs do not provide for any objects specific to a particular enterprise, then it is possible to supplement their composition. Another solution is to introduce subaccounts to those already in use. All such actions must be recorded in the accounting policies.
Features of inventory of assets on off-balance sheet accounts
Inventory is a form of monitoring the state of the property and liabilities of an enterprise and their actual availability. It is necessary to compare the data contained in the accounting with the actual data. There is no way to do without the results of inventory work when the time comes to compile the annual report.
The need to carry out an inventory of property recorded on the balance sheet is enshrined in the Federal Law and the Regulations on Accounting. Behind the specified documents, this method of actual control covers all obligations of the enterprise and its assets. Inventory in full concerns property that is registered but does not belong to the enterprise.
Filling out an inventory document in 1C: Accounting
For this operation, a separate item is provided in the program interface in the “Warehouse” section:
When you go to the section, a list of previously completed inventories opens, but we need to create a new document. This is done as standard by clicking the “Create” button:
Please pay attention to filling out the fields in the document header:
- a date must be set. The balances will be filled exactly on this date;
You can generate a document by warehouse or by responsible person. When choosing the first method, the balances of the specified warehouse will be filled. In the second option, balances will be generated for all warehouses that are assigned to this responsible person.
Let's analyze the inventory of the warehouse. The document needs to be filled out; this is done automatically when you select a filling method from the drop-down menu of the “Fill” button:
A table will be generated with all the goods that are listed in the specified warehouse in 1C:
The table shows the item, its actual and accounting quantities. The document can be recorded and printed to be sent to the warehouse for direct inventory. A printable form is provided for this:
The form is filled out by warehouse employees, after which the actual data is entered into the corresponding column of the table:
The program itself calculates the deviation: shortages are indicated in red with a “-” sign, and surpluses are indicated in black. After filling out the column, the document is recorded and posted. Based on it, you can print out the necessary paper forms:
Inventory in 1C:Accounting itself does not write off or capitalize; separate documents are provided for these operations.
Postings reflecting the results of the inventory
At the end of the inventory work, the final acts are signed:
- Each member of the commission.
- Employees who are entrusted with financial responsibility.
The inspection may go smoothly and not reveal any discrepancies. But the discovery of excess property or a shortage of assets listed on the property owner is a completely possible phenomenon. Such facts are reflected in the corresponding accounting notes:
| Debit | Credit | Description |
| 003 | Writing off shortages of materials accepted for processing | |
| 91.2 | 76 | Losses are included in other expenses. They were obtained due to the lack of materials previously taken for processing |
When excess off-balance sheet assets are discovered, they are allowed to be taken into account in the balance sheet as other income:
| Debit | Credit | Description |
| 003 | Capitalization of surplus | |
| 10.1 | 91.1 | Excess materials taken for processing are included in the assets of the enterprise |
The inventory process of off-balance sheet accounts: step-by-step instructions
An inventory is carried out before preparing annual reports. By the beginning of such serious work, all information about the actual state of assets at the AP should be at the disposal of the accountant. It is quite acceptable:
- do not take inventory of property when it has already been checked in a similar way two to three months before the end of the year (October-December);
- an inventory of library collections should be carried out every five years, and fixed assets – once every 3 years;
- enterprises located in the Far North should take inventory of current assets when they have the least amount in their balances.
Sequence of the inventory process:
| Stages | Content | Explanation |
| First | Creation of an inventory commission | Formed by order of the head, has powers throughout the year. If there is a lot of work, you can create a working commission |
| Second | Issuing an order to conduct an inventory | Specific timing and reasons for control are indicated. Members of the commission are determined |
| Third | Fixation of asset balances with accounting data | Provided by the accountant on the start date of the inventory |
| Fourth | Direct inventory | It takes place in the presence of persons bearing financial responsibility. The actual amount of assets and how real the recorded financial liabilities are are revealed. Information is recorded in documents: acts and inventories |
| Fifth | Registration of results | The summary is made in the Statement of Results |
Order of conduct
Inventory is carried out in accordance with this order:
- Appointment of a commission that will conduct the inventory. She is appointed on the basis of an order from the manager and receives powers that will be valid for the entire year.
- Issuing an order on the procedure. The order specifies the timing of the procedure and its reasons. The members of the commission are indicated.
- Carrying out inventory. The event is carried out in the presence of commission members and financially responsible persons.
- Results of the event. The results are confirmed by inventories, which are signed by those present during the inventory. The information is summarized in the Statement of Results.
Inventory INV-1 is compiled in two copies. If discrepancies are found between reality and recorded data, comparison sheets are drawn up. They are created according to the forms INV-18 and INV-19. Form INV-5 is used in relation to property accepted for safekeeping.
Statement of results identified by inventory
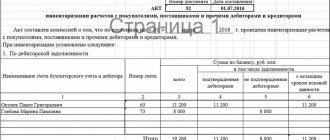
Below is an example of a Statement of Results:
| No. | Name sch. | Account number | The result revealed during the inventory. | Established asset damage | From the total ∑ shortages and losses | ||||
| shortage | surplus | Credited for regrading. | List in previous attrition rates | Attributed to the culprits | List for production costs | ||||
| 1. | OS | 01, 03 | |||||||
| : : | |||||||||
| Off-balance sheet accounts | |||||||||
| 1 | Rented OS | 001 | – | – | – | ||||
| 2 | Materials accepted for recycling A B IN | 003 | 10 000 | 4000 | – | 4000 | 6 000 | ||
Director Molotov R. Yu.
Main accountant Pronina A. O.
Chairman of the commission Malin N.D.
The identified surplus of material A is offset by misgrading, and the shortage of material B is written off as expenses (taking into account misgrading).
Important! If there is misgrading, you can count surpluses and shortages among themselves. Employees responsible for the safety of assets are required to provide explanations written in their own handwriting.
When there is a need for inventory on off-balance sheet accounts
An inventory of property should be carried out:
- Subleasing assets, selling them or buying them back.
- Before you start writing your annual report.
- When theft or damage to assets is established.
- In emergency situations caused by extreme conditions, natural disasters.
- When a company is liquidated or reorganized.
- If there is a change in responsible persons. An example would be hiring a new cashier. The previous employee must transfer the cases, and the commission takes an inventory of the cash register on the same day. The cashier is responsible not only for the movement of cash, but also for the storage of strict reporting forms. They are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 006.
An example of the main part of the required inventory is given below:
Inventory list of the Central Bank and BSO No. ________
| Organization _LLC August | ||
| Structural unit Cash register | ||
| Basis for inventory: order Number Date | 25 | |
| 19.04.16 | ||
| Inventory start date. | 20.04.16 | |
| Inventory end date. | 20.04.16 | |
| Accounting account number | 006 | |
| No. | Central Bank,BSO | Unit change | Fact. Availability | According to accounting data | Result | |||||||||||||||||
| name | code | name | COEI code | № | series | denomination, rub. | quantity | amount, rub. | № | series | denomination, Rub. | quantity | amount, rub. | surplus | shortage | |||||||
| № | series | quantity | amount, rub. | № | series | quantity | amount, rub. | |||||||||||||||
| 1. | BSO | 012 | PC. | 012 | 12-22 | CA | 100,0 | 12 | 1200 | 12-22 | CA | 100,0 | 12 | 1200 | ||||||||
Write-off of goods in 1C from the warehouse
In order to write off goods based on inventory, you need to create a new write-off document.
In “Inventory”, click the “Create based on” - “Write-off of goods” button:
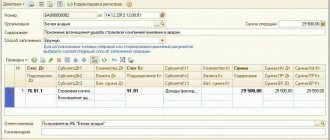
The 1C Accounting 8.3 program will automatically generate a write-off for items that had a shortage:
If everything is correct, just click the “Pass” button. Let's check the postings for writing off goods:
Features of inventory of off-balance sheet accounts in budgetary organizations
There are many more APs in budget accounting - 30. In addition, institutions can additionally enter more if this will help collect the necessary data for maintaining objective management accounting. It is carried out according to the so-called “simple system”, which provides for reflection:
By debit:
- values received;
- guarantees received or issued.
By loan:
- removal of valuables;
- repayment of those obligations that were secured by guarantees.
There is no correspondence from the AP. Transactions are reflected on them depending on what happened to the accounting object. Records are made reflecting its increase (admission) or decrease (departure). The inventory of off-balance sheet accounts is carried out in the manner described above.
Important! Only the commission can decide, for example, to write off the debt of insolvent debtors from account 04.