When conducting an inventory in a store, it is necessary to determine the list of persons involved in the counting and assign a role to each of them (who counts, who records, who checks the expiration date). The result of the recount is formalized through the signing of the relevant acts, then the result is entered into 1C.
When is a warehouse inventory required?
A scheduled inspection is performed once a year. Unscheduled inventory - in the presence of special circumstances. The list of these circumstances is given in Federal Law No. 402 “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011:
- Change of director, transfer of property to another person, transfer of an organization from state to unitary.
- Dismissal of more than 50% of state employees.
- Detection of theft, damage to property, and its illegal exploitation.
- Damage to property as a result of emergencies (fires, floods, hurricanes).
Inventory is also carried out before preparing annual reports. The event is regulated by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 49 “On approval of instructions for inventory” dated June 13, 1995.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Once a year is the minimum number of events. But in practice, checks are carried out more often. This is necessary for timely detection of theft.
How long can inventory take?
Taking into account the requirements and form of the inventory, the operation takes from 1 hour to several days. Let's look at the rules for the types of checks:
- when preparing balance sheets - annually (strictly from October 1 to December 31);
- when checking fixed assets - once every three years;
- settlements with counterparties - at the end of the year (December 31);
- others - in accordance with the decision of the manager.
In retail, clear standards are not provided for by the rules, but it is recommended to carry out an audit within a reasonable time.
Composition of the commission
A special commission is appointed to conduct the event. Its minimum composition is 6 employees. The commission should include these specialists:
- Chief Accountant.
- The head of the company or his deputy.
- Head of departments.
- The person responsible for ensuring compliance with the labor rights of employees.
- Logistics service representatives.
Sometimes the commission may include other professionals. Each employee must ensure the effectiveness of the event. The composition of the commission is approved by the manager of the company by issuing an order.
ATTENTION! The manager must ensure the availability of all the necessary tools: equipment for weighing, counting, transportation.
Articles on the topic (click to view)
- Commitment or document? // BC found out what a manufacturer's warranty is
- About sales receipts: filling out, issuing
- What is the fine for driving on a toll road without paying?
- Visa to Spain for Russians - 2021: how to apply for it yourself
- Difference between a loan and a credit card - how a credit card differs from a loan
- Accounting for financial guarantees
- What does judicial practice on bankruptcy of individuals indicate?
Expert opinion
Musikhin Viktor Stanislavovich
Lawyer with 10 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
IMPORTANT! The number of employees participating in the commission must be strictly observed. Otherwise, the inventory is considered invalid.
Preparation and collection of the inventory commission
The director determines the composition of the commission and the number of persons participating in its work (three or more people). These employees should not be classified as financially responsible. The requirements for staffing the commission are determined in detail by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 49 of November 8, 2010. The commission must work with its full complement, as specified in the director’s order, otherwise the results of its work can be declared invalid.
Usually such a commission is organized as a permanent one. In a small company, these responsibilities may be assigned to the audit committee. In companies that own large volumes of inventory items, several commissions can be formed to conduct an inventory of all inventory items in all departments.
The commissions can include deputy directors, accountants, managers, engineers, and employees from the internal audit department. Specialists from independent audit companies may be invited.
Preparatory work
It is recommended to clean the warehouse before the event. Representatives of the commission are provided with all documents relating to recent transactions with items in the warehouse.
For example, these could be papers about receipt, loss, damage, and expense. Previous reports were marked “before inventory”. Highlighting documents completed before the event will help identify missing objects.
Those responsible for the property are required, before starting the inventory, to sign a document stating that all papers for the products have been handed over to the commission. Another signature is affixed, which confirms that the disposed property is written off as an expense. A write-off document is attached to all inventories.
ATTENTION! There are two forms of commissions: counting and inventory. The second includes employees responsible for counting property in the warehouse.
Inventory algorithm according to MOL
The organization conducts an inventory of inventory items when changing MOL.
If the Organization conducts an inventory of goods and materials that are reported to one MOL in different warehouses, then in the Inventory of Goods only the Responsible Person from the Individuals directory . The Warehouse field does not need to be filled in.
Information in the Inventory and Inventory commission must be entered according to the algorithm specified in the paragraph above Inventory of goods and materials
Products tab is filled in automatically when you click the Fill - Fill according to stock balances .
1C analyzes the balances of inventory items in the MOL sub-report at the time of the inventory and fills in the Goods .
End of the event
Upon completion of the inventory, these documents are drawn up:
- Inventory of products in the warehouse.
- Statement of any discrepancies between inventory data and accounting data.
- Conclusion about the event.
It is also necessary to create a paper describing the property that was missing during the inspection. If the source of the shortage has not been identified, the following entries are made:
If the source of the shortage is found, the following entries are made:
If excesses are found and the culprit is found, these entries are made: DT1 KT91/1.
ATTENTION! If the scale of the shortage is within the established limits, then it relates to the costs of commodity circulation. If it is impossible to attribute the shortage to costs, it is necessary to look for the culprit. For this purpose, an investigation is ordered.
What computerization tools are used for inventory?
Obviously, it is difficult to imagine accounting in the 21st century without computer accounting systems. Every company today uses an information system focused on a complex of accounting and management operations, including inventory of goods and materials.
Large retail warehouses organize inventory using digital devices to read information from the label of each package. For this, various product scanners are used, for example, the Mindeo MD 2230AT barcode scanner. Of course, the packaging must not be damaged.
Using a scanner for inventory in a large warehouse greatly simplifies the inventory process
Many enterprises of different industries use the 1C:Enterprise system. It is constantly being improved and takes into account all the innovations in taxation, offering accounting and analytical systems for various sectors of economic activity, from construction, motor transport enterprises to trade and catering. It allows you to easily customize it to suit the specifics of any enterprise.
Video: using 1C when taking inventory of goods in a warehouse
The considered inventory management tool, called inventory of goods and materials, is the most important management tool for any company. Its effectiveness is manifested, however, only with a clear organization of the process and correct execution of the results in accordance with the norms of current legislation.
- Author: Natalya Kulikova
Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 0 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Inventory: identifying shortages and damage
Detection of the fact of shortage (damage) of goods is the basis for conducting an inventory (Part 3 of Article 11 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
An exception to this rule is the shortage (damage) of goods identified before the goods are registered. The fact of shortage (damage) can also be revealed during the inventory process carried out for other reasons.
Expert opinion
Musikhin Viktor Stanislavovich
Lawyer with 10 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
At its discretion, the organization can conduct an inventory of goods at any time. However, there are cases when inventory must be carried out without fail:
- before preparing annual financial statements;
- when changing materially responsible persons (for example, warehouse manager, storekeeper);
- when facts of theft, abuse or damage are revealed;
- in the event of force majeure (for example, natural disasters);
- during reorganization or liquidation of the organization;
- in other cases provided for by law (for example, when selling an enterprise as a property complex) (Article 561 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Such rules are established in paragraph 27 of the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting.
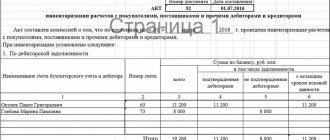
For information on what conditions must be met when conducting an inventory of goods, see table.
To document the inventory of goods, you can use the following standard forms:
- inventory list of inventory items (form No. INV-3);
- act of inventory of shipped inventory (form No. INV-4);
- inventory list of inventory items accepted for safekeeping (form No. INV-5);
- act of inventory of inventory items in transit (form No. INV-6).
When registering inventory results, the following documents must be drawn up:
- matching statement in form No. INV-19;
- statement of accounting of the results identified by the inventory, according to form No. INV-26.
This is stated in section 2 of the instructions approved by Decree of the Goskomstat of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 88, and in Decree of the Goskomstat of Russia dated March 27, 2000 No. 26.
For more information on filling out these forms, see the table.
In what cases is inventory required?
Inventory in retail trade and in the organization as a whole reveals the actual availability of property. Compares the results with those on the balance sheet. It is carried out both voluntarily and mandatory. In the first case, the audit is carried out solely on the initiative of management. In the rest - as required by law.
Table 1: Forms and differences of inventory
| Voluntary | Mandatory |
|
|
In any case, the regulations on audits (terms, forms, timing) are adopted by the manager and chief accountant. Document flow is formed taking into account the methodological recommendations of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 13, 1995 No. 49.
To document the results of the audit, the organization has the right to independently develop forms of acts and statements, but this point should be mentioned in the accounting policy. Replacing unified forms with independently developed ones should not distort information or contain errors.
Accounting: markdown
If an organization plans to discount damaged goods, then make the following entries in accounting:
Debit 94 Credit 41
– the cost of damaged goods is reflected (based on the act in form No. TORG-15);
Debit 94 Credit 42
– the trade margin attributable to damaged goods is reversed (if goods are recorded at sales prices).
For the convenience of reflecting the markdown of goods to account 41, open a separate sub-account, for example, “Goods subject to markdown”.
Debit 41 subaccount “Goods subject to markdown” Credit 94
– goods subject to discounting have been capitalized (at market value, taking into account their physical condition);
Debit 44 Credit 41 subaccount “Goods subject to markdown”
– samples of damaged goods were submitted for examination (if examination is necessary for the sale of damaged goods);
Debit 44 Credit 60
– expenses for conducting an examination are reflected (if an examination is necessary for the sale of damaged goods);
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
– revenue from the sale of goods at a discount is reflected;
Debit 90-2 Credit 41 subaccount “Goods subject to markdown”
– the cost of discounted goods is written off (the cost at which they were capitalized);
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT is charged on the sale of discounted goods (if the organization is a VAT payer);
Debit 90-2 Credit 44
– costs associated with sales are included in the cost of sales (if an examination is required to sell damaged goods).
If damaged goods cannot be used (sold) in the future, reflect their value in accounting on account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” in correspondence with property accounting accounts (account 41). Moreover, if goods are recorded at sales prices, then simultaneously with the fact of damage to goods being reflected on account 94, the trade margin attributable to damaged goods and previously recorded on account 42 must be reversed.
This is stated in the instructions for using the Chart of Accounts (account 94, 41, 42). When reflecting the fact of damage to goods in accounting, make the following entries:
Debit 94 Credit 41
Debit 94 Credit 42
– the trade margin attributable to damaged goods is reversed (if goods are recorded at sales prices).
This procedure for reflecting damage to goods in accounting is reflected in subparagraph “b” of paragraph 29 of Order No. 119n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001.
Inventory algorithm for a separate type of inventory
In 1C, for inventory inventory, a single document is provided : Inventory of Goods , which is automatically filled in with all types of inventory items: goods, materials, finished products, non-current assets.
In order to formalize inventory results separately for a specific type of inventory, you need to make the following settings for filling out the Goods of the Goods Inventory document .
Before preparing annual reports, the Organization conducts an inventory of materials in the Main Warehouse . Financially responsible person - Ivanov A.P.
The results of the inventory of materials must be included in a separate inventory.
Step 1. Open the document Inventory of goods , section Warehouse - Inventory - Inventory of goods.
Step 2. Open the document form settings window ( MORE - Change form ).
Step 3. Add the item type to the Products . To do this, in the Products , move the cursor to the Nomenclature and click the Add fields . In the selection window, check the box next to the item Type of item .
As a result, the new details will be reflected in the form settings window.
Step 4. Fill out the document, Fill - Fill in according to stock balances .
Step 5. To leave only materials in the document, you need to mark an unnecessary type of item for deletion using 1C hotkeys.
To delete rows on the Products in our example, simply mark with the cursor the first position in the Products and the last one - the SHIFT + left mouse button combination. Products product type will be highlighted in yellow.
Step 6. Delete selected positions using the right-click context menu command Delete .
Thus, in the Goods Inventory only items with the required type of inventory items should remain - Materials .
See also:
- Inventory procedure
- Reconciliation of settlements with tax authorities
- Subconto Analysis report
- How to make a reconciliation report with a counterparty
- Surplus of goods as a result of inventory
- Shortage of goods and materials. The culprit has been identified
- Shortage of goods and materials. The culprit was not found, confirmed by a document from a government agency
- Universal report on materially responsible persons for OS
- Purchasing goods from a separate division with delivery costs included in their price
- Processing of printed forms for off-balance inventory of goods and materials
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Accounting: losses from damage
The procedure for writing off in accounting losses from damage to goods that cannot be used (sold) depends on the cause of damage:
- natural decline;
- the fault of the financially responsible person (other persons found guilty of damage);
- force majeure circumstances.
Write off losses from damage to valuables within the limits of natural loss by posting:
Debit 44 Credit 94
– the cost of damaged goods is written off within the limits of natural loss.
The current norms of natural loss are presented in the table.
This procedure follows from paragraph 5.1 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49, and the Instructions for the chart of accounts.
Attribute damage to goods in excess of the norms of natural loss to the perpetrators (clause 30 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n). At the same time, make the following entry in accounting:
Debit 73 (76, 60. ) Credit 94
– the amount of losses from damage to goods in excess of the norms of natural loss is attributed to the perpetrators.
For more information on how to recover damages if an employee of the organization is found guilty of damage, see:
This procedure follows from paragraph 5.1 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49, and the Instructions for the chart of accounts.
Situation: is it possible to recover the cost of compensation for damage to goods from a dismissed employee? A financial liability agreement was concluded with the employee. The inventory was carried out after dismissal.
Article 232 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that termination of an employment contract does not exempt an employee from compensation for damage. But in order to prove that damage to goods occurred due to the fault of the employee, it was necessary to conduct an inventory upon his dismissal (clause
27 Regulations on accounting and reporting). After the passage of time, it is impossible to prove the guilt of the dismissed employee.
This means that it is also impossible to recover the cost of damage from damage.
If the perpetrators have not been identified or the court has refused to recover the amount of damage caused from them, write off the damage to goods to the financial results of the organization. Refer the amount of damage to other expenses.
A document that can confirm the absence of guilty persons can be, for example, a court acquittal, a decision to suspend a criminal case, etc.
(Clause 5.2 of the Methodological Instructions approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49). Determine the amount of loss based on the cost of the damaged goods according to accounting data.
In this case, do the wiring:
Debit 91-2 Credit 94
– loss from damage to goods is written off due to the absence of the person at fault (refusal to recover damages).
This procedure follows from paragraph 11 of PBU 10/99 and the Instructions for the chart of accounts (account 94).
If the cause of damage to goods was force majeure, take into account the cost of damaged goods as part of the losses of the reporting year at the balance sheet (accounting) value. Do the following wiring:
Debit 91-2 Credit 94
– loss from damage to goods resulting from force majeure is written off.
This procedure follows from paragraph 13 of PBU 10/99 and the Instructions for the chart of accounts.
What is an inventory of inventory items (materials and materials)
A businessman’s property brings him income, so every entrepreneur wants to be sure of its integrity. Control over the safety of business property is carried out, in particular, through periodic inventories.
The essence of the inventory process is to check the availability of each specific object, which is reflected in the accounting department as the property of the company, as well as the real state of affairs regarding the fulfillment of financial obligations. Simply put, the enterprise carries out control measures, the results of which make it clear whether everything is in place and whether the paper (accounting) list of property corresponds to the actual one.
Inventory includes several stages:
- Preparatory work, which in particular includes:
- issuance of an order by the head on the composition of the commission, the timing and objects of inspection;
- actions of storekeepers, who usually check inventory cards for all inventory items (in paper form or in a computer program);
- the activities of materially responsible persons (MRP), who confirm in writing that they have submitted to the accounting department all documentation for the receipt and release of inventory items;
- the work of accountants who post all the information on the movement of inventory items to accounting accounts and display results for these accounts (it’s good that modern computer management systems perform all posting operations automatically at the time of entering information about the receipt of inventory items according to supplier documents and expense invoices).
- Carrying out physical and documentary verification of inventoried goods and materials: all valuables are counted, measured, weighed and assessed while simultaneously being reflected in the inventory list.
- Object-by-object comparison with accounting and filling out the reconciliation sheet.
- Writing a commission report based on the results of the reconciliation.
- Preparation of a commission protocol containing a conclusion on the results of the inventory.
Inventory has a certain algorithm of actions.
After the inspection is completed, a set of measures is necessarily carried out aimed at eliminating the detected problems.
Thus, the accounting department enters into the accounting registers the identified differences in the real quantity of inventory items of the company from what was previously reflected in the accounting:
- makes entries for the netting of assets if a so-called misgrading has been identified;
- reflects the income of surpluses, attributing them to the company’s income;
- carries out accounting operations based on the results of identifying deficiencies (for example, collection from the MOL or attribution to the company’s losses).
If significant deviations in the actual availability of inventory items from the accounting ones are detected, it is the turn of the company management to record conclusions about the quality of work of personnel at all levels and about the financial responsibility of the employees who are guilty of this (from collecting the shortfall from wages to drawing up a statement to law enforcement agencies).
The shortage was identified before the goods were registered
If the organization reveals a shortfall in delivery (damage) when accepting goods (i.e. before registering the goods), then there is no need to conduct an inventory. To document the fact of such shortage (damage) by trade organizations, Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated December 25, 1998 No. 132 provides standard forms:
- No. TORG-2 (if goods of Russian origin are received);
- No. TORG-3 (if imported goods are received).
Expert opinion
Musikhin Viktor Stanislavovich
Lawyer with 10 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
In some industries, instead of form No. TORG-2 (No. TORG-3), other acts may be used. For example, in relation to medical goods in pharmacies - an act in form No. A-1.2 (Section 4 of the Methodological Recommendations approved by the Ministry of Health of Russia on May 14, 1998 No. 98/124).
Documents that record the fact of shortage or damage are the basis for filing a claim with the supplier (Articles 518, 519 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
If the goods were transported by a specialized transport organization, to submit claims to the carrier you need to use the report form valid for transport. Such rules are established in the instructions approved by the Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated December 25, 1998.
No. 132. For example, when transporting by rail, a commercial act is drawn up (clause
2.1 of the Rules approved by order of the Ministry of Railways of Russia dated June 18, 2003 No. 45).
Its form was approved by order of the Ministry of Railways of Russia dated June 18, 2003 No. 45.
However, if a standard document form for reflecting losses during transportation by appropriate transport has not been established, acts in forms No. TORG-2 and No. TORG-3 can be used to present claims to the carrier. In the absence of standard forms to reflect the fact of shortage (damage to goods) identified during acceptance of goods, the organization can draw up a document in any form, reflecting all the necessary details (Part.
2 tbsp. 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). For more information, see
How to formalize and record a claim against a counterparty.
Compensation for damage by the responsible person
The employee assumes responsibility at the time of signing the relevant agreement. If a shortage is detected, full responsibility rests with the staff if:
- an administrative or other crime has been committed;
- the fact of intentional harm has been proven;
- the employee was found to be intoxicated.
In any case, damage is compensated only for direct costs (full cost of inventory items, reduction in total cost). The responsible person provides a written explanation for the shortage or damage to the goods. The results are transmitted to the manager. He issues an order for damages.
The accounting department withholds no more than 20% per month from the employee’s earnings and repays the debt to the organization. The employee must be familiarized with the results of the inspection against signature. If you do not comply with the regulations, the employee can challenge the results of the audit in court.
Store inventory and its goals
- Identification of the actual availability of inventory items.
- Store inventory allows you to control the correct balances in the program. Incorrect balances lead to incorrect operation of the auto order. Which will lead to overpacking and write-offs or empty shelves and decreased sales.
- Allows you to control the percentage of losses - expiration, shrinkage, shaking, loss of original quality, theft.
- Identification of misgrading.
- Identification of surpluses.
- Checking compliance with storage rules.
How to take inventory
When preparing for an assigned scheduled inventory, they usually check the existing inventory items and the order of their location in storage areas.
You should compile in advance all the documentation that records the movement of inventory items:
- receipt (for example, invoices),
- consumption of inventory items when released for production or sales,
- write-off for various reasons (for example, marriage).
During the inventory, it is necessary to restrict access to the territory of unauthorized persons.
At the time of the inventory, management must ensure the following conditions:
- the presence of a minimum number of clients and other unauthorized persons in the inspected territories;
- availability of a sufficient number of properly trained personnel to provide technical assistance at the time of the commission's work.
During the period from the beginning to the end of the inventory, it is prohibited to adjust the database reflecting the availability of inventory items of the enterprise.
When preparing for inventory, you should take into account the territorial location of the inventory items to be checked. This applies both to large fixed assets and to working capital or goods for a trading enterprise located in various warehouse areas. For small companies (atelier, canteen, small store), where there are no warehouses that have the status of a structural unit with a separate distribution center, inventory of goods and materials is carried out simultaneously throughout the entire enterprise.
If there is a significant range of materials or goods, one should proceed from the structure of the warehouse organization. Specific warehouses can be either independent divisions of an enterprise, or as part of larger accounting units.
The commission examines and records in the inventory the actual availability of inventory items and the prices of their receipt, checks the integrity of the packaging and product labels. During the work of the commission, a specific MOL is always present.
The inventory is carried out by an appointed commission in its entirety
Drawing up an inventory list
The main stage of inventory is drawing up an inventory list. It is recommended to use the standard INV-3 form.
Such a document is filled out in the process of recalculation, weighing, and remeasurement of values. All these operations are carried out separately for each stock storage location. Two copies of the inventory must be filled out - one for the MOL, and the second must be kept in the company’s accounting department for at least 5 years.
Page 1 - title page of INV-3
Filling out the first sheet begins with the design of the header of the form. First, write down the name of the company (the division is indicated if the inventory will not be carried out throughout the entire organization). The form reflects the OKPO code and the type of activity of the company (OKONH code). The header must indicate the number and date of the order.
It is not necessary to indicate some codes on the first sheet, for example, the type of operation and the code of the structural unit.
The title includes the date of compilation of the inventory and its number, and also indicates (in accordance with the order) the type of inventory items subject to inventory and the ownership of the assets being checked, i.e. whether they are the property of the company or were received for processing.
On the first sheet of the inventory there is also a receipt from the MOL stating that by the beginning of the audit, the responsible person had completed the transfer to the accounting department of all primary documents, receipts, disposals and write-offs of all inventory items.
During inventory, an inventory of inventory items is compiled
Main part of the inventory (pages 2 and 3)
The main part of the INV-3 form (pages 2 and 3) is intended to contain a list of inventory items used for inventory. Each inventory is compiled only for a specific type of inventory. Separate inventories are made for different species.
The columns record the names of the inspection objects, their quantity and units of measurement in the same way as they were reflected upon arrival at the enterprise. The inventory indicates the article, grade, item number (if it is applied to the object of inspection).
Column No. 9 is filled in only for goods that have a passport (for example, complex technical products).
It is important that the values indicated in columns 10 and 11 may not coincide with the values in columns 12 and 13. If the actual balances differ from those indicated in columns 12 and 13 or other discrepancies with the accounting data are identified, then these differences are subsequently entered into the matching statements .
The bottom line of the pages in question indicates the total values, i.e., the quantitative indicators in the units of measurement used are summed up, and the total cost of all inventory items is also indicated. For a large warehouse, several pages may be filled. In this case, the results must be summarized twice - both for each page and for the inventory as a whole.
On each page, two total values are indicated (not in numbers, but in words):
- number of scan object numbers on the page;
- number of units of recalculated objects (in physical terms). The unit of measurement does not matter.
Pages 2 and 3 of the inventory list contain a list of inventory items.
Empty lines cannot be left in the inventory sheets, and they must be crossed out at the end of the last sheet.
If an error was made when compiling the inventory, you need to cross out the erroneous entry and enter the correct value at the top. The correction is certified by the signatures of the commission members and the MOL.
Page 4 - conclusion
After filling out the main part of the statement, move on to its final part (page 4).
The correctness of the entered prices of the objects being checked, the taxation of the cost of the goods being checked and the calculation of the total are reflected by a mark at the end of the last sheet.
The last page of the inventory reflects evidence of the audit results. All members of the commission and the MOL, who are noted on the first sheet of the document, must put their signatures here, which confirms the fact of their presence during the inspection. If the inventory is carried out when changing the MOL, then the employee who accepts the goods and materials must sign for receipt, and the one who handed them over must sign for delivery.
Page 4 of the INV 3.1 form is filled out according to the sample
A complete inventory includes a recalculation of not only those goods and materials that are the property of the company, but also those accepted for safekeeping (goods received by delivery error, defective products from suppliers, awaiting examination, etc.). For such inventory items, the INV-5 form is used.
Filling out such an inventory list is carried out according to the same rules as INV-3.
Photo gallery: sample of filling out the inventory sheet INV-5
Page 1 of the INV 5 form is filled out according to the sample
Pages 2 and 3 of the INV 5 form are filled out according to the sample
Page 4 of the INV 5 form is filled out according to the sample
Guidelines for inventory in the warehouse and on the sales floor
- Each rack is counted by 2 employees. First, one employee goes through and scans the barcodes of all the units on the rack. After this, the second employee goes through again and also counts the goods. It turns out: each product is counted in two passes.
- All positions are counted from left to right and top to bottom. The product can be placed in different places - on the top and bottom shelf. Jumping from one row to another is not allowed.
For example, on the top shelf there is Milk “House in the Village” and on the bottom shelf there is the same milk. Milk is not transferred from the bottom shelf to the top, but is counted where it is. - Weighted goods are counted once, since there is an error in weighing.
- The results for two independent passes are entered into the program, and a matching sheet is generated. It checks errors and inconsistencies of the first and second passes. If the calculations diverge, then recalculate according to the discrepancies. It is not allowed to move on to the next rack until the results of the two passes are determined to be the same.
- It’s very easy to forget and miss a certain rack in a large supermarket. Therefore, after confirming the same data on the rack on the store diagram, the rack is marked “calculated”. The marks on the diagram allow you to clearly see which zones have been calculated.
- Local inventory of goods is carried out in the same way as complete inventory, but at the product group level.
Retail arrival
In the configuration, retail receipts are reflected as receipts to a warehouse with the “Retail” type. The following business operations are automated in the program:
- Receipts from a retail supplier are reflected in the “Receipt of Goods” document if the warehouse specified in the document is of the “Retail” type;
- Retail receipts from a wholesale warehouse are reflected in the “Transfer of Goods” document if the receiving warehouse specified in the document is of the “Retail” type;
- The receipt of retail products from production is reflected in the document “Transfer of finished products to the warehouse” if the warehouse specified in the document is of the “Retail” type.
Please note that the methodology used does not involve keeping records in sales prices and using account 42 “Trade margin”.
The first results of the inventory must be double-checked
After calculating the entire store, a general comparison sheet is generated with calculation errors - how much the information in the program differs from the actual one. This control check represents about 5% of the store's inventory.
First, the largest discrepancies from 5,000 rubles are checked, then from 1,000 rubles. For example, in the program there are 24 bottles of cognac on hand, but according to the inventory results, 36 bottles were counted: the discrepancy amount is more than 5,000 rubles. Let's count the cognac again.
The store is not opened until discrepancies based on inventory results of up to 1,000 rubles are checked. It is better to check the results with a new shift of employees.
Large stores are counted all night, and by the morning the employees are already very tired and make a lot of mistakes. The arrival of two or three new employees on the morning shift will allow us to complete the inventory with renewed vigor.
If during the inventory period a low-quality product was found - expired, broken, damaged goods - it is included in the inventory and written off after it is closed.
How does inventory work in a store?
As a general rule, inventory begins with:
- an order is issued (form INV-22) to begin the inspection, where the deadlines and members of the commission are established;
- materially responsible persons submit a receipt to the accounting department stating that the turnover has been completed, all inventory items have been capitalized, written off, and reports about this have been transferred to the accounting department;
- access to the hall where the audit is being carried out is limited to outsiders;
- If it is necessary to interrupt the procedure, the room is closed and sealed.
Actual data about the product: weight, quantity, volume are entered into the inventory act (INV-3) by the commission members. The document is drawn up in two copies. No blots, errors or corrections in entries are allowed.
At the time of the audit, all members of the commission must be present in the store along with sellers, merchandise experts and other financially responsible persons. This provides a guarantee that goods and materials will not be replaced, surplus will be taken away, or a quality item will be written off as scrap.
It is difficult to exclude the arrival of new goods during the inventory process. If a delivery is made during this period, it is entered into a special sheet “Inventory received during inventory” and is received upon completion.
If it is necessary to remove something, you need to coordinate this step with the manager and accountant, and enter what is being written off in the inventory “Inventory items disposed of during inventory.” It should be remembered that each action must be carried out in the presence of witnesses: members of the commission, persons responsible for the goods.
Loss rate based on inventory results
Each retail outlet has its own percentage of losses, which is acceptable based on the results of the store inventory. The percentage varies depending on the store format, 1.7 – 2.3% of total turnover.
The percentage of losses depends on the specifics of the outlet, but the first signal that there are problems in the store is a sharp increase in the percentage. For example, year after year a supermarket reported an inventory loss of 2.4%, and a sharp increase to 3% indicates that the supermarket has problems.
Often the main reason for a sharp increase in losses based on store inventory results is improper organization of work.
Revaluation
Since retail outlet inventory is carried out at sales prices, it is very important to correctly reflect the revaluation. Incorrect reflection of this operation can significantly distort the inventory results.
Before changing the price, it is necessary to conduct an inventory of all retail outlets for which this price is used (or rather, the type of prices to which the changed price belongs).
Carrying out an inventory before changing the price is necessary in order to correctly reflect sales from the time of the last inventory until the moment the price changes (at the old price). If an inventory is not carried out before changing the price, then during the next inventory it will be considered that all inventory items sold since the last inventory were sold at the new price.
Note that during revaluation, inventory is allowed only for those item items for which the price changes.
How is inventory carried out?
Only responsible specialists are allowed to carry out inventory at an enterprise or at a retail outlet. She is responsible for the duties of an accountant . If such a specialist is not on staff, the inventory is carried out by employees of a third-party organization (outsourcer).
Expert opinion
Musikhin Viktor Stanislavovich
Lawyer with 10 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
Methods and technologies for performing work may be different. With an automated accounting system in trade and production, inventory is reduced to:
- to reading barcodes on products and goods using special equipment,
- analysis of data accumulated in the database.
Practice shows that in small enterprises inventory activities are carried out the old fashioned way. In such cases, a manual or semi-automatic method is used.
Where does inventory begin in a store?
Carrying out an inventory in a store begins with preparing the premises, sorting retail goods by type, section, department, and storage location. A voluminous list of items requires a lot of time to check. It is possible to achieve accuracy and save time if you follow the following sequence:
- stop trading: receipt, write-off and transfer of inventory items to other departments;
- group products by type to count them sequentially;
- sort goods with a barcode: if there is a code on part of the product, it will be easier to count it separately;
- determine the actions of each member of the commission: one monitors the list, another keeps count, the third checks the expiration dates of goods.
Reference! From July 1, 2021, in the field of trade, the entire assortment must be entered into the online cash register database, even in small stores. This allows you to determine what exactly the buyer purchased.
How is a product written off?
During the inventory, individual goods and groups of goods are often identified that are subject to write-off . The latter must be formatted accordingly.
With automated accounting, write-offs are carried out, like inventory, using a special form. It is automatically filled with missing items.
A write-off operation is carried out without special conditions. But when filling out, checking and posting a document in the accounting program, it is worth considering that not every product can be written off.
Some products are written off using a special form. Violation of the rules for conducting inventory and writing off goods is fraught with serious penalties for a legal entity.
Inventory work with damaged/expired goods has its own characteristics. A uniform procedure for writing off such inventory items is not established by current legislation.
In relation to damaged/expired goods, a general scheme for reflecting reporting results is applied. For such commodity items, a corresponding act must be drawn up, which is signed by the inventory commission.
Write-off of detected shortages is also carried out according to a certain scheme. Most often, inventory items are classified as costs associated with production or circulation according to natural loss. In addition, the shortage can be attributed to:
- at the expense of those guilty of embezzlement with their subsequent bringing to financial responsibility;
- for other expenses of the enterprise, if the culprits of the shortage are not identified.
Summing up the inventory
The results of the inventory must be reviewed by the commission no later than 10 days after the formation and execution of matching statements.
The company's management draws conclusions on the safety of property and the level of organization of its storage. They are reflected in the protocol, and if there is a shortage for a specific MOL, the manager makes a decision.
Also, the head of the enterprise can draw conclusions about the quality of the accounting work of personnel both at the level of warehouse accounting and in the accounting department.
Surplus or shortage
An ideal option for the results of checking the availability of inventory items can be considered the case when the inventory items reflected in the inventory sheets fully correspond to the accounting data for the same inventory items (in terms of quantity and price). But usually deviations are still detected.
Based on the results of the inventory, surpluses may be discovered, i.e., the amount of property according to the inventory list exceeds the amount of the same type of property according to accounting data. Such inventory items are recognized as income of the company. Any excess property discovered should be recorded according to an act indicating the specific storage location and specific MOL. The price of inventory items is set, as a rule, according to similar assets available at the enterprise, or according to the price lists of suppliers.
Shortages identified during inventory are considered an expense for the company. This is where the rules for accounting for shortages of inventory items provided for by law come into effect.
There is a concept of “natural loss rate” for inventory items. It is used in any type of activity. In the workshop, when processing metal, some of it goes into chips. In a store, when weighing goods (especially bulk goods, such as cereals, sugar, etc.), a small part spills out - these are technical features of working with goods and materials. At these moments, norms for the loss of material resources are established.
The shortage, in which the size of inventory items is within the limits of natural loss norms, is attributed to the expenses of the enterprise. Any shortage of property exceeding this figure must be recovered from the guilty parties. The price is set in accordance with the market price. Such an employee must also be immediately removed from the management of material assets, and the inventory and materials, according to the act, are transferred to another person appointed to this position. If the amount turns out to be large, the head of the company can contact law enforcement agencies with a statement to bring MOL to criminal liability for theft of the organization’s property.
An agreement on full liability serves as the basis for applying sanctions to the perpetrator
When calculating the amount of recovery, the amount of VAT on missing materials, which was reimbursed from the budget when posting such inventory items, is also calculated. This amount is subject to restoration and must be added to the company’s current VAT debt, reflected in the credit of balance sheet account 68.
If the perpetrators could not be identified or the court refused to recover from the guilty person, the shortfall is attributed to the company’s losses. But this, as a rule, does not happen. This is the meaning of regular inventory of goods and materials.
The presence of small deviations cannot be considered a significant drawback in working with inventory materials. When identifying surpluses or shortages, you should pay attention to their volume and try to find the line between minor carelessness and deliberate abuse.
Table: calculation of the amount of recovery from the MOL for shortage of goods and materials and restoration of the amount of VAT
| No. | Name | Amount (rub.) | Calculation algorithm |
| 1 | Shortage amount (book value) | 2600 | X |
| 2 | Shortage amount (at market prices) | 9000 | X |
| 3 | VAT on missing materials | 468 | 2600 rub. * 18% = 468 rub. |
| 4 | VAT restored based on missing materials | 468 | 2600 rub. * 18% = 468 rub. |
Business Solutions
- Order (form INV-22) – a decision by the manager on all the steps that need to be taken regarding the event. At large enterprises, several copies of the form are allowed for different types of warehouse inventory. Most often, a large number of orders are created when it is necessary to conduct an audit of several premises within one company.
- Inventory list of goods and materials (form INV-3) - required in 2 copies to record the total upon counting of products. The documents are kept by the employee being inspected and in the accounting department.
- Inventory report of goods and materials (INV-4 form) issued earlier (INV-4 form) - filled out for items received for which there is no payment. For such positions there are special conditions for the transfer of ownership rights. The form classifies them into two categories: revenue not received due to delays and due to non-arrival of the payment date.
- Inventory of inventory items, which is kept by the employee responsible for savings (INV-5 form) - all inventories are taken into account. The receipt for the form indicates which items need to be capitalized or written off. Facts of disagreement with accounting data in the accounting department are recorded in the statement (form INV-19).
- Inspection report of valuables that have not arrived at the warehouse (INV-6) - is appropriate for accounting for products that are not delivered due to long-term transportation, are delivered, they are declared with the appropriate notes during the inventory of goods in the warehouse, we will consider in more detail how to properly carry out such an inspection below.
Reflection in 1C of surplus and shortage
If accounting is automated, then it is much easier to process and analyze the results of inventory inventory in 1C. For example, we suggest using the version “Trade Management 10.3”.
In the “Warehouse and Inventory Management” section, the “Recalculation of Goods” operation is created, which reflects:
- actual and accounting quantities of goods;
- deviations between actual and accounting quantities.
First of all, create a document:
Figure 2: analysis of inventory results
The form is filled out automatically, sampling data based on daily transactions. After execution, transactions are generated in the program and conditions for inventory items are registered, changing the actual balances in warehouses: excess is credited, shortage is written off.
For convenience, the program generates a report that clearly shows the name, article number of the item, number of units and deviations.
Figure 3: Balance Sheet
The unified forms that are required for the audit can be edited. The total number of participants in the inventory commission changes (by law there must be at least 3 people).
The accounting program service makes it possible to revaluate obsolete goods. Or carry out an additional valuation taking into account changed market prices for similar products. Find out more in the video:
In addition, it is possible to connect cash register equipment and a scanner for recalculating inventory items to the program. This allows you to eliminate errors, taking into account the workload of personnel and the volume of items in the trade sector.
Program objects used in warehouse inventory
Automated inventory accounting of goods and materials involves the use of several documents available through the menu section Warehouse - Inventory:
- main warehouse recount data document “Inventory of goods”:
- document “Receipt of goods”:
- document “Write-off of goods”:
It is recommended to draw up the last two documents on the basis of the “Inventory” document - this significantly reduces the time spent on summarizing inventory results and adjusting accounting records.
Document “Warehouse Inventory”
The main document contains three bookmarks:
- Products – item items, quantity according to fact and program accounting, accounting value are entered, the quantitative deviation, actual and accounting amounts of the position are automatically calculated. Please note: when filling out the tabular lines of a document, it is very convenient to use the “Fill” - “Fill according to warehouse balances” block: the configuration itself will pull up all the inventory items present in the warehouse accounting, indicate their quantity and the posting price:
The second line of the “Fill” block refills accounting quantities and amounts in the event of adjustments being made to the original posting documents, transfers to warehouses, or write-offs. The actual amount is the product of the columns “Quantity fact” and “Price”. If, based on the results of the inventory, a discrepancy between the actual and accounting values is established, then when the actual indicator changes, the price per unit is recalculated (as the quotient of dividing the actual amount by the actual quantity).
If the product/material is not available or is less than the accounting quantity, the “Deviation” column will be automatically filled in - the indicator is displayed with a negative sign, this is a shortage. A surplus (the actual quantity is greater than the accounting quantity) is indicated by a positive deviation figure.
- The document tab “Carrying out an inventory” is intended for entering the data of the procedure itself: the period, information about the basis document, the reason for the inventory recalculation is filled in manually in the text field:
The document tab “Inventory Commission” determines the members of the commission responsible for the inventory; the flag platoon “sets” the chairman:
It is important to understand that the document “Inventory of Goods” does not make any accounting movements at all - it does not write off shortages and does not capitalize surpluses. This is just a statement of actual availability and software, with the output of quantitative and total deviations. But it is this statement that is the basis for further adjustments to accounting. After recording the document, the necessary printed forms are available for printing - inventories, statements, inventory orders:
If an organization has a single warehouse in its accounting, then documentary operations will be carried out on it by default - it will not even appear in the header of a specific form. If there are several items in the warehouse directory, then a field for selecting the required warehouse will appear in the header of the inventory document:
Using the basic data of the recount document, the documents “Receipt of goods” and “Write-off of goods” are drawn up - most of the columns are filled in automatically. These documents, of course, can be created on their own.
Document “retail sales report”
If the company conducts retail trade (the program has the appropriate settings for accounting policies and program functionality), based on the document “Inventory of goods”, it is necessary to draw up the document “Report on retail sales”:
The ability to create a retail sales document will appear only in a situation where the inventory has detected an excess of actual availability over accounting. Otherwise, the program will generate an error - and this is understandable: if there is no surplus, then there is no indication for registering retail sales.
If the inventory reveals that in fact there is less product/material than is displayed in the program, and it is known for sure that the difference is sold (and not stolen or damaged), a retail sales document is drawn up for the amount of the deviation:
The “Quantity” column will contain the data of the positive deviation from the inventory document (surplus), the price and amount can be specified manually with recalculation. When conducting the “Retail Sales Report”, it makes movements in the inventory account (in this case 10.01 “Raw Materials and Supplies”), the income account with analytics and the expenses account, the cash account is indicated in the header.
To avoid manually entering an accounting account for each material/product, it is recommended to set up accounting accounts for the corresponding item items. This option is available through the hyperlink “Item Accounting Accounts” in the header of the “Nomenclature” directory, after which the required accounting account for a certain product or material item will be pulled up in all documents. A minimum of manual work means a minimum of random errors in accounting.
Based on the completed document, if necessary, you should issue a return from the buyer or capitalize the cash amounts:
Document “Receipt of goods”
The formation of this document is intuitive. The need for its registration arises only when an inventory count reveals surplus goods/materials that should be placed on the organization’s balance sheet.
It is convenient to draw up this document on the basis of the “Inventory of goods in the warehouse”. The “Quantity” column is filled in according to the positive inventory deviation; in the header you should define the income item (by default “Capitalization of surplus”):
The accounting accounts entered for item items will be included in all documents compiled - this is convenient, the accountant will not additionally have to control this point. Capitalization generates the corresponding transactions:
Document “Write-off of goods”
Compiled when inventory reveals a shortage of inventory items that are subject to write-off from the organization’s balance sheet. Almost identical to the capitalization document, taking into account the opposite of the operation. Below is an example of an inventory document with a shortage of two item items and a write-off document generated on its basis:
In the “based on” document creation mode, the tabular parts are automatically filled with items that are in short supply according to the indicators of the basis document. From the table rows you should exclude items whose shortage is due to their actual location in another warehouse (if the enterprise has several warehouses and is accounting for them). To change the actual location of inventory items, it is necessary to draw up and post the “Movement of Goods” document.
The posted write-off document generates the following movements in accounting:
From its form, acts of write-off of goods (TORG-16) are printed - printed forms are standard and unified; if necessary, connect your own printed forms.
Most often, according to inventory results, both types of documents are in demand: surpluses are credited, shortages are written off. The same nomenclature item of an inventory document is not possible in a write-off document and a capitalization document.