Kontur.Accounting is a web service for small businesses!
Quick establishment of primary accounts, automatic tax calculation, online reporting, electronic document management, free updates and technical support.
Try it
In accounting and tax accounting, income and expenses can be recognized in two ways.
The first one is the accrual method. It is associated with the period of actual conduct of a business transaction. The corresponding income or expense must be taken into account on the date of its occurrence according to documents or on the date of transfer of raw materials or provision of services, that is, at the moment when the income or expense was accrued.
The second option is the cash method. When using it, income or expenses should be recognized in the period when the payment occurred, that is, when money arrived or left the cash register or current account, or when the organization received or transferred other property.
In practice, most often companies keep records using the first method, following the instructions of accounting standards and the Tax Code. It is believed that the recognition of income and expenses upon shipment most accurately reflects the results of the business. However, sometimes businesses may, or are even required to, account for expenses upon payment.
The main advantage of the cash method is the reduction of cash gaps: the situation is eliminated when a company must pay tax, but the funds have not yet been received.
Who is eligible to use the cash method?
As the law states, both individual entrepreneurs and companies of other forms of ownership, whose total quarterly income during the reporting period did not exceed one million rubles, can work on the cash basis.
At the same time, the law does not unconditionally indicate that in each month the amount of profit must necessarily be less than a million, that is, in other words, the main thing is that this limit is observed in the average annual calculation. There are a number of exceptions for individual entrepreneurs and organizations entitled to the cash method of accounting.
In particular, the following are not allowed to use it:
- consumer credit cooperatives;
- organizations involved in the microfinance sector and banks;
- companies registered in other states;
- some organizations licensed in the field of subsoil use;
- enterprises operating under a property trust management agreement.
These and some other commercial companies are not allowed to use the cash method in their accounting practices.
Individual entrepreneurs and legal entities who have chosen to record income and expenses using the cash method must document this in the enterprise’s accounting policies for the upcoming tax period.
Attention! The use of the cash method in accounting and tax support is a purely voluntary right, and is by no means an obligation of the subject of taxation. You can switch to it either directly when registering an enterprise, or, if the company has been operating on the market for a long time, with the beginning of each new calendar year.
An organization that has switched to the cash method will have to control the amount of profit in the future, as well as comply with some restrictions on concluded contracts.
Accrual principle
One of the fundamental principles. All transactions in accounting should be reflected at the time of their completion, and not when the expected action from this transaction occurs. For example, you shipped goods to a buyer. This operation must be reflected in accounting at the time of shipment, and not when the expected profit arrives.
Continuity principle
Accounting can only be carried out at an enterprise that sees itself operating in the foreseeable future and does not intend to cease operations.
Principle of intelligibility
Accounting must be kept in such a way that its data is understandable to the user of the information. For this purpose, a unified procedure for recording transactions has been developed.
Materiality principle
Accounting information is of great value, so when maintaining records, care should be taken to ensure that it is presented to the point and is of interest to the user.
The principle of significance
This principle complements the previous one - all accounting information should not only be presented on its merits, but be useful and significant for the management, assessment and analysis of financial, operational, and business activities.
The principle of reliability and truthfulness
Accounting information must be presented without bias and may not contain errors.
Principle of objectivity
Without exception, all operations taking place at the enterprise must be reflected in accounting records and be documented.
Principle of prudence
The assessment in the accounting process should be carried out with caution - income and assets cannot be overstated, and expenses and liabilities cannot be understated.
The principle of completeness
The operation displayed in accounting must be logically completed and presented in full.
Comparability principle
Because accounting must be useful for the management and analysis of activities, its data must be displayed from period to period so that they can be compared. For this purpose, unified reporting forms and accounting policies at the enterprise are being developed.
The principle of consistency
Despite the fact that financial statements have established deadlines: month, quarter, decade, six months and a year, they must be consistent from year to year, from the beginning to the end of the enterprise’s activities. Thus, as when applying the principle of comparability, it is possible to monitor the dynamics of the enterprise’s development and make the necessary management decisions based on the information received.
Principle of unity of measurement
Despite the fact that in the process of conducting business, information is received in monetary, natural and labor measures, its comparison and analysis can only be carried out using monetary indicators. This is how other principles important for decision-making are implemented - the principles of comparability and consistency.
Principle of confidentiality
Accounting data is a trade secret. If exceptions are possible, they are discussed with the accountant in advance. Violation of this principle in the Russian Federation provides for administrative and criminal liability.
The regulatory and legislative framework of the Russian Federation in this area is built on the above principles of accounting.
5.The subject of accounting and the scope of its application.
The subject of accounting is the reproduction of the social product, which includes production, distribution, exchange and partial consumption of the social product. Accounting is characterized by the generalization of information into cost indicators, which are complemented by detailed analytical indicators expressed in natural and labor measures. Thus, the subject of accounting is the reproduction process in that part that can be represented by information in a single monetary measure, that is, the state and use of funds in the course of economic activity, as well as business transactions as the primary elements of this process. The subject of accounting is the property of the enterprise , in the form of funds and liabilities; movement of this property through business transactions occurring in the sphere of supply, production and sales of products; as well as the result of the enterprise’s activities, expressed in monetary value, that is, the enterprise’s funds used by it in carrying out economic activities.
The property of an enterprise, its obligations, sources of formation of this property (own and borrowed), economic processes are the object of economic accounting.
Important accounting objects at an enterprise include: intangible assets (patents, trademarks, licenses), fixed assets (buildings, machines), materials, inventory, monetary assets that the enterprise has, its legal relations with the state (taxes), with other enterprises , finished products and their sales, credit and settlement operations, financial results, as well as business transactions, as a result of which these values and relationships change.
At the same time, accounting objects represent economic assets used by the enterprise to carry out business activities.
The composition of the enterprise's property is quite diverse. It is determined by the content, industry specifics and volume of economic activity of the enterprise. The company's assets have a value and are called economic assets.
What is a revenue limit: example
The limit on the amount of revenue is the already mentioned limit on the quarterly profit of the enterprise. Let us remind you that it is exactly one million rubles. Moreover, it is calculated not quarterly, but on an average annual (but not calendar!) period.
Let's give an example
Limited Liability Company "Sibiryak" has been wanting to switch to the cash method of accounting for income and expenses for some time now. To determine the possibility of its application in the second quarter of 2015, the company needs to calculate whether the revenue from the work performed and services provided for the previous period corresponds to the limit established by law (excluding VAT). So, for just 4 quarters the revenue table looks like this
- 0.8 million rub. – in the second quarter of 2014
- 1.0 million rub. – in the third quarter of 2014
- 1.3 million rubles. – in the fourth quarter of 2014
- 0.6 million rub. – in the first quarter of 2015
If you add everything up, it turns out that for four consecutive quarters, before the second quarter of 2015, the amount of revenue is equal to 3.7 million rubles, excluding VAT. At the same time, its average quarterly value will be 0.925 million rubles. Thus, from this simple calculation it is clear that the limit of one million rubles was not exceeded, which means Sibiryak LLC has every right to use the cash method of accounting for income and expenses, starting from the second quarter of 2015.
The concept of revenue in accounting
Based on PBU 9/99 “Income of the organization”, revenue in accounting can be recognized only if: (click to expand)
- the enterprise has the right to receive this revenue, that is, this right must be confirmed either by a concluded agreement or in another way;
- the amount of revenue can be determined;
- after receiving the proceeds, the organization will receive economic benefits;
- the goods have been transferred to the buyer, or the service has been provided (work accepted);
- It is possible to determine the expenses that an organization incurred to obtain specific revenue.
Reflection of income using the cash method
When choosing the cash method, the management and accounting department of the enterprise must remember that the law provides for the need to reflect income. How should they be taken into account?
The main requirement for this part is that all income received by the organization must be taken into account strictly on the date of its receipt.
Income can be either cash for goods or services, or some other types of financial receipts and transfer of property, including, for example, offsets.
Let's give an example
From the very beginning of its activities, IP Chainikov has been using the cash method of accounting for income and expenses. On January 27, 2021, he delivered goods to the customer for a total amount of 236 thousand rubles. (including VAT 36 thousand rubles). March 18, 2021 Individual entrepreneur Chaynikov agrees with his customer on a mutual settlement in the amount of 118 thousand rubles. (including VAT 18 thousand rubles). This means that on the date of signing this agreement there was a balance of debt on the part of the customer. What income in this situation should be reflected for individual entrepreneur Chainikov? In short, on the date of the offset agreement with the customer, that is, March 1, 2021, he is obliged to take into account income equal to the amount of the repaid debt (excluding VAT), that is, 100 thousand rubles. (118 thousand rubles – 18 thousand rubles).
Which method should be used in restaurants?
In restaurants, of course, profits should be considered on an accrual basis. Because a catering company answers positively to both questions from the previous paragraph - the restaurant has a direct connection between the catering services provided during the selected period (dishes sold) and the expenses incurred (cost, wages, rent, services, etc. ).
You can use the cash method if you are a “grandma with pies”, or if you are not interested in your profit and efficiency, but only the cash balance is important (also a very real option).
Write-off of expenses using the cash method
The main point that accountants and management of commercial organizations should not forget about: reflecting the write-off of expenses when using the cash accounting method for income and expenses at an enterprise is possible only after the actual payment of a particular operation.
However, there are a number of subtleties. For example, wage costs, material costs, as well as interest on the use of credit funds are taken into account immediately after payment. But for example, an enterprise has the right to reflect the price of materials and raw materials in tax accounting not only after payment, but also after they are written off for production.
Let's give another example
Veresk LLC uses the cash method for tax accounting. On March 14, 2014, the above-mentioned company purchased materials for their further use in production. The total purchase amount was 118 thousand rubles. (including VAT 18 thousand rubles), and full and one-time payment was made on the same day. On March 20, 2014, materials worth 50 thousand rubles, excluding VAT, were partially released into production. The question arises: how can all the above actions be reflected in the income tax base? It’s simple: if the cash method is used, then the price of materials can be taken into account in expenses after they have been paid for and written off for production. That is, if on March 14, 2014, all purchased materials were paid in full, and only materials worth 50 thousand rubles were written off for production on March 20, 2014, then it is precisely this figure that must be reflected in expenses for tax purposes.
Reflection of revenue in accounting
In order to reflect revenue in accounting, you need to rely on supporting documents. That is, on such documents that can confirm that the right to the goods has transferred to the buyer, for example, a deed or invoice, as well as other primary documents. There are a certain number of requirements for these primary documents. They, for example, must be drawn up either according to standard forms of accounting documentation, or according to a form approved by the organization.
The procedure for determining revenue, according to PBU 9/99, revenue is taken to be those amounts that are equal to receipts of money and property in monetary terms, as well as accounts receivable. At the same time, revenue is recognized in accounting taking into account VAT and excise duties, but they are not revenue.
In cases where the buyer does not fully pay his debt to the company, revenue should be recognized in the accounting of the supplier organization as the amount of payment received, as well as receivables from this buyer.
Loss of the right to work on a cash basis
If certain circumstances arise, including non-compliance with the statutory requirements for the right to use the cash method, the enterprise, regardless of its desire, will have to waive the right to use it. In this case, it is obliged to switch to the accrual method, and this will not have to be done immediately, but from the beginning of the new calendar tax period. The right to use the cash method is limited:
- if the enterprise has entered into a simple partnership agreement or a property trust management agreement;
- if the amount of income from transactions and operations carried out by the enterprise is higher than the legal limit.
The facts presented in this material indicate that the use of the method of cash control over income and expenses, like any other method of tax accounting in commercial companies, has its own nuances, features and subtleties.
Before making a decision on the final transition to it, the company management or individual entrepreneur needs to make sure that it maximally corresponds to the company’s development plans for the near future.
Which method is better?
It depends on situation.
The cash method is easier to implement because... is based on data from payment systems, which is very easy to collect - they are reflected in the cash register or banking system and are always confirmed by primary documents. In addition, the result of this method - profit - coincides with the cash balance, i.e. can be easily verified (by cash count).
The accrual method is more complicated, and its profit does not coincide with the cash balance, but it is more accurate in the sense that if the profitability or efficiency of the enterprise is calculated by the profit received, then it makes more sense, because income, expense and profit are interrelated.
The difference between them can be illustrated by the example of gasoline consumption in a car. Gas mileage is something we use to measure the “efficiency” of a car (and driving style). The lower the gas mileage, the better.
The “accrual method” is when we compare the distance traveled during a period with the volume of gasoline consumed during the same period. For this we use the on-board computer. We can drive 100 km in one week and spend 7 liters (7 l/100km), and drive 1000 km in another week and spend 60 liters (6 l/100km). Obviously, in the second week we drove more economically or “more efficiently”.
The “cash method” is when we compare the distance traveled during a period with the volume of gasoline purchased (filled in the tank) during the same period. We can fill 50 liters in one week and drive 1 km (5000 l/100km), and the next week add another 1 liter and drive 100 km (1 l/100km). Obviously, the results are not comparable, they make no sense.
Determination methods
Currently there are two definition options:
- By accrual.
- Upon receipt of funds.
The second method of revenue recognition can only be used by small enterprises that are considered such in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 4 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2007 No. 209-FZ. In accordance with paragraph 4 of Art. 6 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ of December 6, 2011, they have the right to conduct simplified accounting and not apply a number of existing Accounting Regulations (Information of the Ministry of Finance PZ-3/2015). All others must use the accrual method.
Corporate income tax
Any operating organizations that do not use preferential tax regimes are recognized as payers of income tax. These include Russian and foreign institutions operating on the territory of the Russian Federation.
The following categories of entities are not obligated to charge this tax:
- enterprises related to the organization of the 2014 Olympic Games (until the beginning of 2021), the organization of the 2021 Football World Cup;
- organizations using preferential systems (USN, Unified Agricultural Tax, UTII).
Profit is understood as the income received by an economic entity during the reporting period, reduced by the amount of costs incurred. Receipts can be sales, that is, received as a result of the main activity (sale or resale of goods, provision of services), and non-sales (exchange differences, interest on deposits). However, not all income contributes to the formation of profit. According to the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, these include:
- funds received as a deposit, advance;
- amounts of indirect taxes (VAT);
- property or property rights as a contribution to the management company;
- funds received as gratuitous assistance;
- funds received as a result of concluding credit agreements and obtaining loans;
- special-purpose financing;
- other funds received that are not recognized as income according to the law.
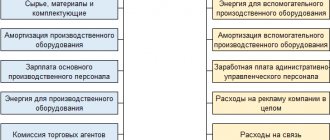
Expenses are of great importance when determining profit and calculating subsequent taxes. It is worth considering that in this case, taxpayers have the right to take into account only economically justified costs that are directly related to profit-making activities.
Expenses include material costs, staff salaries, rent, utility payments, expenses for obtaining necessary services, payment of the cost of goods, and others.
For tax purposes, expenses must not only be justified from an economic point of view, but also documented. Otherwise, regulatory authorities have the right to declare the illegality of reducing the tax base.
Like income, expenses are divided into sales (participating directly in the main activity, for example, purchase of goods, payment for services) and non-operating (payment of banking services, credit and borrowed interest).