For tax and accounting, one of the methods used is the accrual method, which is used by the majority of organizations (individual entrepreneurs use the cash method). The accrual method plays an important role in the correct calculation of income tax and consists in recognizing income and expenses when the results of business transactions are recognized upon actual completion and do not depend on the time of receipt and cash flow associated with the receipts. There are advantages and disadvantages to this method when applied, but it is believed to accurately reflect the organization's performance.
Let's look at accounting using the accrual method.
Reason for using the accrual method
The basis of the accrual method is that the accounting of income and expenses does not depend on the actual flow of funds. That is, the date of receipt of income is the date of transfer of ownership rights to goods (work, services). Thus, revenue from core activities is taken into account at the time of shipment of goods, regardless of whether payment has been received from the buyer. Similarly, for non-operating income, profit accounting does not depend on the fact of payment.
Important! In relation to expenses and for main non-core activities using the accrual method, accounting is carried out in the period in which they are documented and also do not depend on the fact of payment.
Features of the cash method
The cash method is characterized by the fact that income is reflected at the moment when funds are credited to current accounts (received at the cash desk) or property acting as payment has been received (Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Are advances received considered income when using the cash method? The answer to this question is in the ConsultantPlus system. Get free trial access to the system and proceed to the explanations.
Expenses must be recorded when they are actually paid.
It should be noted that not every taxpayer can exercise the right to use this method of accounting for income and expenses. So, you cannot use the cash method:
- Companies whose average revenue for the previous 4 quarters excluding VAT is more than 1 million rubles. for every quarter.
- Banks.
- Credit consumer cooperatives.
- Microfinance organizations.
- Controlling persons of controlled foreign companies.
- Organizations extracting hydrocarbons from a new offshore field, if they have the appropriate license, as well as operators of these fields.
See also the material “What is the procedure (conditions) for recognizing income and expenses using the cash method?” .
Income accrual method
If an organization uses the accrual method of accounting, then income is considered received in the period when the company has them shipped, i.e. there is title (but not yet paid) on the basis that there will be retaliation upon receipt. The timing of payment for goods sold does not matter.
Points of revenue recognition
| Type of implementation | Revenue recognition |
| goods (works, services) | day of receipt of title (shipment) from the seller to the buyer |
| goods (works, services) under a commission agreement by the taxpayer-committee | date of sale of property (property rights), which the commission agent indicates in the notice of sale |
| real estate | date of transfer of such property according to the acceptance certificate or other transfer document |
| valuable papers | date of termination of the obligation to transfer them by offsetting counterclaims |
The date of receipt of income from non-primary is determined at the time of accrual.
If income relates to several periods, the organization distributes it evenly (for work performed over a long period of time - more than a year or started in one year and completed in another, i.e. in two tax (reporting) periods).
Tax accounting provides for the following methods of accounting for revenue:
- evenly (income is divided by the number of months of the contract)
- in proportion to the share of expenses in a particular period according to the estimate for the contract.
General characteristics of the accounting method
The accounting method is a set of methods and techniques that ensure an inextricable, continuous, documented and interconnected reflection in the monetary valuation of the activities of enterprises, organizations and institutions
.
The accounting method includes the following elements: documentation and inventory, valuation and calculation, accounts and the dual reflection of business transactions in them, balance sheet summary and reporting
.
In accounting, the registration of business transactions begins with the preparation of documents. Each business transaction must be formalized with an appropriate document, which is the only basis for its reflection in accounting. The documents provide the content of a business transaction in quantitative (material values) and monetary terms. Drawing up documents is called documentation
. Timely documentation of business transactions is of great importance in ensuring the objectivity and accuracy of accounting data, as well as in ensuring the safety of recorded objects. Inventory plays an important role in this.
Inventory
is a method of determining the actual availability of property and financial obligations (accounts receivable and payable, bank loans, loans and reserves) of an organization and comparing the data obtained about them with accounting data in order to establish the reliability of accounting indicators and clarify them in case of discrepancies.
Example of income distribution
Alpha and Omega LLC uses the accrual method.
In October 2021 the organization entered into an agreement with Beta LLC, whose services should be provided in March 2021. next year. The cost of the contract is 600,000 rubles. It is not possible to determine intermediate results. Revenue according to the contract is reflected in accounting in full (600,000 rubles) in March upon receipt of the results of the work performed.
In tax accounting, income from obtaining the result of work is reflected in 2 stages:
- in October, November and December 2021
- in January, February and March 2021
The organization chooses the distribution procedure independently. The following options are possible:
- Evenly
The contract period is 6 months and thus, every month 100,000 rubles will be included in income. (RUB 600,000 / 6 months).
- Proportional to the costs according to the estimate
If an estimate is attached to the contract, according to which stages of work are highlighted with expenses at each stage, for example, 50% of the amount is spent in the first month. Accordingly, 50% of the revenue (300,000 rubles) of Alpha and Omega LLC will be taken into account in October.
Thus, the disadvantage will be that part of the proceeds will be reflected in tax accounting earlier than in accounting and, accordingly, it will be necessary to pay income tax on it earlier than the work performed is received, i.e. taxes will be paid before ownership of the work performed under the contract is obtained. Protect yourself from... that the results of the work will not be provided after 6 months can be explained by the fact that the contract specifies the stages of delivery of the work.
About accounting
Before studying accounting methods, let's talk about the subject of our discussion. What is accounting? What problems does it solve?
Accounting, according to the definition widespread among Russian economists, is a system of monitoring and control over the financial and economic activities of an organization. If accounting as such is, in fact, recording numbers on paper, combining them into “books” (German: Buch) and secure storage (German: Haltung), then together with the accounting function it forms a system that allows the use of financial data for the purpose of extracting practical benefits for the enterprise.
In addition to numbers reflecting cash flows in certain areas of the organization’s functioning, accounting collects other types of significant information - labor or, for example, natural information. However, accounting considers all economic processes as operations in price terms. As a result, the company, using various accounting methods, receives tools that allow it to optimally allocate resources and increase business profitability.
Expense method
Expenses on the accrual basis will be recognized in the period in which they occurred, without taking into account the timing of payments under the contract (payment time).
Similar to the dates of recognition of income, the dates for expenses are also determined.
Points at which expenses are recognized
| Type of consumption | Date of recognition |
| Costs of purchasing raw materials and supplies | Date of transfer of raw materials and materials into production in the part transferred to the production of goods |
| Costs of acquiring the results of production work | Date of signing by the organization of the acceptance certificate |
| Depreciation deductions | In the amount of accrued amounts monthly (Articles 259, 259.1, 259.2, 322 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) |
| Salary | Monthly (Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) |
| Costs for repairs of fixed assets | Upon completion of repairs, regardless of payment |
| Insurance costs: mandatory and voluntary | Date of payment of insurance premiums |
| Amounts of remuneration for commission, rent, etc. | Date of settlements under the terms of the agreements |
| Amounts of compensation paid, such as use of private cars | Date of payment of funds from the current account (from the cash register) |
| Travel expenses, entertainment expenses, etc. | Advance report approval date |
| Amounts of taxes and fees | Date of accrual according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Expenses for purchasing foreign currency | Date of transfer of ownership |
| Negative exchange rate difference | Date of transfer of ownership of foreign currency and last day of the month |
| Fines, penalties and other sanctions for violation of the terms of the contract | Date of recognition as a debtor |
| Cost of acquisition of shares | Implementation date |
| Interest on loans and borrowings with a term of more than one reporting period | Last day of each month of the reporting period |
| Total difference: - from the seller - from the buyer | On the maturity date: – accounts receivable – accounts payable |
Taxes, customs duties and insurance premiums paid by the organization are included in other expenses for production and sales (Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), which are reflected in the accounting of payments on the date of their accrual (Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In tax accounting, the amount of overdue accounts payable must be included in non-operating income. Accounts receivable for which the statute of limitations has expired, in the absence of primary documents confirming the fact of the occurrence of the debt, cannot be taken into account as part of non-operating expenses when taxing profits.
Experts from the Legal Consulting Service GARANT V. Molchanov, O. Monaco
Difficulties in recognizing income and expenses
When using one method or another, the taxpayer often has a question: when should a certain income or expense be recognized? For example, there is a controversial situation regarding the issue of the emergence of non-operating income that arises in the event of the expiration of the statute of limitations on accounts payable (clause 18 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax officials explain that income arises on the last day of the reporting (tax) period in which the statute of limitations expired (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 8, 2014 No. GD-4-3/ [email protected] , letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 12, 2014 No. 03 -03-РЗ/45767). But some arbitrators believe that this income must be taken into account in the period when the manager signed an order to write off such debt (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 15, 2008 No. 3596/08).
On this issue, see the material “In what period are overdue accounts payable included in income?” .
When applying the cash method, the amount of accounts payable (including VAT) is also included in non-operating income, while the period of income recognition falls on the date the debt is written off (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 7, 2013 No. 03-11-06/2/31883). This letter refers to a situation in which the taxpayer applies the simplified tax system, but since clause 1 of Art. 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that “simplers” keep records of income and expenses using the cash method, it can be assumed that this approach is used by all taxpayers who use this method. It should be noted that previously such accounts payable were not recognized as non-operating income when applying the cash method (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 26, 2002 No. 04-02-06/3/61).
Thus, in order to avoid controversial situations, it is better to establish the procedure for recognizing a particular income or expense in the accounting policy.
See also the material “What to change in tax accounting policies” .
Example of transactions when using the accrual method
In March 2021, Alpha and Omega LLC shipped a batch of flour worth RUB 590,000 to Beta LLC. (including VAT - 90,000 rubles). Beta LLC transferred funds in April. Alpha and Omega LLC uses the accrual method (according to accounting policy).
The following entries are made in the accounting of Alpha and Omega LLC in March:
D62 K90 subaccount “Revenue” – 590,000 rubles. (proceeds from flour)
D90 sub-account “VAT” K68 sub-account “Calculations for VAT” – 90,000 rubles. (VAT is charged on sales).
And the income tax return for the first quarter of 2021 of Alpha and Omega LLC reflects income from the sale of flour in the amount of 500,000 rubles. (590000 – 90000).
Results
Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation talks about 2 methods of recognizing income and expenses that can be used when calculating income tax:
- accrual method;
- cash method.
However, if any taxpayer has the right to choose the first of them, then the second is only those that meet the conditions established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Having given preference to one method or another, its choice should be reflected in the accounting policy.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Letter from the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 8, 2014 N GD-4-3/ [email protected]
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Accounting structure
Accounting has two main components. Which at the same time form a single system. In fact, these are subtypes of accounting, namely financial and managerial. What is the difference? What specific features do financial accounting methods have, and what are typical for management ones?
Let's answer the first question. Within the framework of management accounting, work is carried out with information intended for use by the company's management structures. The purpose of obtaining, analyzing and interpreting it is to improve the mechanisms of interaction between management and subordinate units and its effective planning. The monetary component in the circulation of this type of information can be either very significant or occupy a very small percentage - it all depends on the specifics of a particular enterprise.
Financial accounting works mainly with information that is used not only in the internal structures of the organization, but is also involved in the process of communication with external entities.
Since in most cases this interaction is based on relations in commodity-money forms, this type of accounting is called financial.
But the information that is processed within the framework of his methodology is not necessarily just monetary figures (although, of course, the absolute majority are).
At the same time, in the Russian methodological school that studies accounting issues, researchers do not clearly draw a clear line between financial and management aspects. We are talking about two, of course, different types of phenomena, but there are a large number of related processes related to both. A simple example: calculating salaries and bonuses for staff. There are elements of both financial - in the aspects of calculating numbers in relation to the company's expenses, and management accounting - in components such as staff motivation or, for example, improving the personnel component of the business model.
Material expenses of an organization in income tax calculations
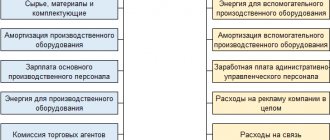
Another group of expenses taken into account in income tax calculations are material expenses. This group, according to Art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, includes acquisition costs:
- materials and raw materials that are intended for production needs;
- materials that are spent on product packaging and other household needs;
- inventory, tools, workwear, devices and other property that is not depreciated;
- components and semi-finished products for subsequent processing;
- energy, water and fuel for technological purposes;
- works and services of third-party organizations and individual entrepreneurs;
- maintenance and operation of fixed assets and environmental property.
The above list is open, since material costs are any expenses that relate to the production process.
Also for tax purposes the following expenses are taken into account:
- for land reclamation and other environmental measures;
- in the form of losses incurred from damage and shortage of food supplies within the limits of current standards;
- in the form of technological losses during production and transportation;
- for mining and preparatory work in the process of mining.
Accounting for materials purchased by an organization is carried out at actual cost, which is obtained from the cost of materials, the costs of their transportation, fees to intermediaries, duties, fees and other similar costs.
Recognition of material expenses occurs in a manner that depends on the tax accounting method used by the company. If the cash method is used, expenses are recorded upon payment; if the accrual method is used, expenses are recorded in the period to which these expenses relate. In this case, materials and raw materials are written off as expenses in the part in which they were released into production and used at the end of the month (clause 5 of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, material costs can be classified as direct costs, in which case materials are written off as expenses in the process of selling products.
The release of materials and raw materials into production occurs in one of three ways established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- by cost per unit of inventory;
- at average cost;
- according to FIFO.
The company must record the chosen method in its accounting tax policy.
The composition of an organization's material expenses affects the procedure for calculating income tax. For example, the company takes into account inventory losses within the limits of natural loss. However, it must be borne in mind that this only applies to material assets for which the rules apply. If standards for industrial production have not been approved, they cannot be taken into account in income tax expenses (clause 2, clause 7, article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Accounting methods
Let's look at the main accounting methods used by Russian financiers. We again make allowances for the fact that we mean the conduct of the corresponding procedure, and not its essence.
- Documentation . This accounting method is used when the task is to record facts that are significant from the point of view of assessing the financial and economic activities of an enterprise. This procedure is carried out using standardized document forms (approved by law or at the level of corporate regulations).
- Inventory . This tool allows you to monitor the amount of property at the disposal of the enterprise. Some experts believe that inventory is an element of the accounting method. There is a “compromise” point of view. In accordance with it, inventory as an accounting method is a full-fledged and fully established component of farming. The main criterion here is this: there is not only a calculation of available property, but also possible obligations for its transfer by the organization in favor of third parties and the identification of other prospects for the use of resources. However, if inventory plays the role of only a calculation tool, then in this case it is still an integral element of the method (in this case, documentation, the first on our list).
- Valuation is also considered a common accounting method. Is it more of a statistical tool or more of an analytical tool? Some experts believe that the former predominates, arguing that an assessment is, first of all, a set of strict rules that do not require any additional conclusions after their implementation. The result of using this tool will be only statistics. But there is another point of view. According to it, the assessment may contain elements of the accounting method with properties that make it possible to study not only current statistical data, but also to interpret them and predict their impact on business processes. That is, analytical work is also implied here.
- Calculation . This type of tool is used mainly for expenses associated with production. These are most often costs that form the cost of goods produced or services provided. A distinctive feature of calculation is the ability to derive some numbers based on others according to certain rules (including appropriate formulas). That is, for example, documentation is working with current indicators. But as soon as elements appear in it related to obtaining data of a different nature on the basis of this information, then this method turns into calculation (or is supplemented by it).
These accounting methods, as well as their constituent elements (we have already said this above), as a rule, are not applied individually, but in aggregate (despite the fact that some of them will be leading, and others will be auxiliary) . In addition, the boundary between elements and methods as such is not very clear. Regarding the elements, we noted the same pattern. An example is inventory. It is considered as an accounting method if it implies a comprehensive study of financial and economic processes. As an element of another process (documentation), only if its function is reduced to collecting information.
Continuing contracts
According to the Russian Ministry of Finance (see, for example, Letter No. 03-03-05/3/59 dated July 14, 2004), expenses are subject to distribution only under contracts that provide for the receipt of income over several periods. At the same time, as follows from the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated March 14, 2006 N 20-12/19599, the tax authorities believe that the taxpayer is obliged to take into account expenses evenly for any ongoing contracts, and not only for those that provide receipt of income over several periods.
Amendments to terminology
It is very important, before continuing to study various aspects of accounting, to decide on the conceptual apparatus. The fact is that the term “method” has several meanings depending on the context. And therefore, in some cases there may be confusion with its interpretation. Phrases that sound almost identical can refer to completely different phenomena.
A simple example is the phrase “accounting method.” Its meaning will vary greatly depending on the specific context. The main criterion here is how often the word “method” is used. If only, then the possible interpretations of the phrase are as follows:
- “accounting” itself as an independent procedure;
- one of the accounting tools.
If the word “method” is used in the plural, then it would be correct to identify this phrase in meaning with the second option. That is, if we write “accounting methods,” we mean the tools for maintaining it. In turn, when working with a singular term, you need to read the context. Depending on it, by “accounting method” we can understand accounting as such or, again, one of the tools for maintaining it.