Home • Blog • Online cash registers and 54-FZ • Correction receipt at the online cash register
A correction receipt at the online cash register is needed when making changes to previously made calculations. Such a document is used to correct errors and violations, and its legality is established by 54 Federal Law of 2003 (clause 4 of Article 4.3).
Online cash register service at a discount
Get a discount on annual technical support for KKT on the “Maxi” and “Standard” tariffs - there is a special offer.
Find out more details
When is a correction check needed?
The correction cash receipt is strictly processed when the cash register shift is open. The procedure can be performed any day before the end of the shift. In the event that an error is noticed on another day, a check is also issued when the shift is open.
What are the errors at the checkout:
- The employee entered the check amount incorrectly.
- The employee completely forgot to fill out the fiscal document on the cash register.
- Instead of an adjustment, a return check was issued.
In case of failure at the checkout:
- The cash register turned off due to a power failure.
- The cash register has broken down or the software has crashed.
What is the difference between correction and return?
If the buyer insists on returning the goods, the cashier issues a return receipt. The same thing happens if the broken amount exceeds the purchase amount, and this difference is noticed immediately. When returning, other documents are drawn up - not the same as when adjusting.
The correction document has the following features:
- it is punched when there is more money in the cash register than there should be;
- the details indicate: calculation attribute – correction;
- he breaks through to the detected excess amount;
- names and prices are not indicated;
- together with it, an act and an explanatory note from the cashier are drawn up as the basis for correction.
The fiscal document “Return of Receipt” differs in its main content. Important nuances include:
- it breaks through when a customer returns an item, or a cashier notices an error in the presence of a customer;
- the calculation attribute indicates “Return”;
- it indicates only the excess amount, there are no names and prices;
- The accompanying documents include a return invoice in two copies or a memo issued by the cashier (if an error is noticed in time).
Important! Both the correction check and the receipt return check cannot be punched on another cash register. Fiscal documents are issued exclusively at the cash desk where the purchase was made. These procedures are regulated by tax law.
How to properly draw up a correction check
You cannot issue a check for the entire amount of transactions not carried out on the cash register, with the exception of a massive failure in the operation of the cash registers. It is recommended to generate receipts for each transaction separately, which took place without a cash register.
What details should a correction check contain? Order of the Tax Service of 2021 No. ММВ-7-20/ [email protected] establishes the following mandatory details:
Settlement attribute with value 1 (receipt transaction) - issued when a purchase receipt has not been issued.
Payment attribute with value 3 (expense transaction) - issued when you need to withdraw part of the funds from the online cash register.
According to the rules, a corrective fiscal document can contain only one detail; using two at the same time in a check is unacceptable.
Correction type with a value of 0 - indicates the reason, in this case it is data correction at your own request.
Correction type with value 1 - making changes as determined by the Federal Tax Service when a violation is detected.
Correction description details - indicate the reason for the operation and the document (note, act or other document on the basis of which the correction is carried out).
Document date of the basis for the correction.
Foundation document number.
Cashier details - information about the cashier.
The receipt does not need to indicate the product range and price.
What else needs to be indicated on the check:
|
|
Step-by-step algorithm for issuing a correction check at the online cash register
You must submit 3 documents to the tax office:
- the correction check itself;
- act on the discovery of excess funds;
- an explanatory note from the cashier about the error.
Make a copy of the act, check and explanatory note and submit them to the Federal Tax Service. Keep the originals with you.
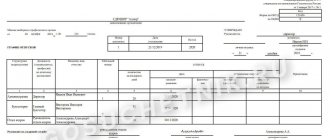
Step 1. With the correction check, you need to draw up a report on the discovery of excess money.
An example of an act on identifying excess funds in the cash register
Step 2. Ask the cashier to write a detailed explanatory note revealing the reason for the error or violation. Be sure to attach it to the act.
Example of an explanatory note from a cashier
Step 3. Notify the Federal Tax Service in writing about the correction check.
Send the letter before the tax office notices the violation. Otherwise, the company may receive a fine of 30 thousand rubles. according to paragraph 2 of Art. 14.5 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. If you correct the error before the Federal Tax Service finds it, there will be no fine.
Keep the act and the cashier's explanatory note in case the tax office asks you to explain the reasons for the adjustment.
You might also be interested in:
Online cash registers Atol Sigma - how to earn more
How to make a return to a buyer at an online checkout: step-by-step instructions
MTS cash desk: review of online cash register models
Scanners for product labeling
Shoe marking for retail 2021
Online cash register for dummies
Important nuances
If a shortage is detected (there is less money at the checkout than there should be at the end of the shift), the correction check cannot be punched. Such documents can only be generated if there is a surplus of funds.
The time it takes to break through a correction check may vary. The main thing is that it fits exactly into the time period when reports on the opening and closing of the work shift are compiled. If excesses were discovered after the shift was closed, the correction check can be punched at the start of a new shift, and if even later, when they were discovered. The adjustment date may vary.
The features of fiscalization are defined by law and are equally relevant both for offline trading and for the operation of online stores, as well as points of sale where automated devices are used for payments. The same applies to the seller’s algorithm of actions in the event of a broken cash register or inability to use it. The occurrence of emergency situations requires the intervention of competent specialists who can correct them. All their actions must be open to inspection by the Federal Tax Service.
How to void a bad check
If the cashier enters an incorrect receipt at the online cash register, it can be cancelled.
Canceling a check using cash register technology means canceling the operation of accepting cash from the buyer and further actions with the check. At online checkouts, the check will be canceled if it is not punched. Online cash register software makes it possible to cancel an incorrect receipt before it is printed and submitted to the fiscal data operator. If the cash register is flashed with the Evotor OFD, you can return to the process of entering goods into the cash document, as well as adjust the goods or cancel the receipt.
When a cash document is knocked out, it is impossible to cancel it due to amendments to Federal Law No. 54 “On the use of cash register systems.” Such an error can only be corrected by correcting the check.
In online cash register equipment there is a “receipt return” sign. Calculations can be adjusted in the presence of the buyer. If an incorrectly stamped check is detected, the client who made the payment at the cash desk is issued a new document for the same amount with the calculation sign “receipt return”. This check will have a fiscal indication that it is erroneous. The cashier-operator in his own way cancels an incorrectly stamped document. The buyer gets a new one for the correct amount.
List of the most common errors that need to be corrected with a correction check
Most often, entrepreneurs violate legislation in the field of using cash register equipment out of ignorance. Businessmen often find themselves unaware of the latest innovations and legislative changes. Thus, many of them still do not know that all non-cash payments from individuals should be reflected in the online cash register. After all, this norm was introduced relatively recently.
Tax officials actively take advantage of the fact that ignorance of the law does not exempt from responsibility, and mercilessly fine entrepreneurs who have committed a crime. Therefore, in all cases of violations, even if the legal entity simply did not know that it was necessary to create a check, it should stock up on correction checks that correct these errors. This will allow the entrepreneur to avoid liability for shortages or excess funds in the future.
And here is what the TOP 3 situations look like in which a correction check is needed:
- indication of the incorrect price of the product in the receipt;
- incorrect payment type: cash instead of non-cash or vice versa;
- lack of receipt for any operation.
Learn how to process a partial return of goods using online cash register
It happens that the buyer does not need a full refund - only one or two or more items need to be returned. What to do in this case?
The employee/cashier must be able to process partial returns. The procedure is not much different from conducting a full refund. The only difference is that the electronic receipt must indicate that not the entire amount is paid, and some of the products are returned to the store.
Having discovered deficiencies in the purchased products, the buyer has the right to demand a reduction in its price - in this case, it is necessary to perform the steps described below:
- Create a return transaction for the full purchase price.
- Generate a new check, issue a document with a reduced value to the individual and return the overpaid funds.
Common causes of errors
Very often, as a result of incorrect transactions, surpluses or shortages may occur in the cash register. They occur due to the following errors:
- The seller chose the wrong payment method.
- The price indicated for the item is incorrect.
- A technical glitch has occurred.
If you are contacted by a buyer who wants to return a purchased item, you will need a return receipt. They will also have to be used in case of an incorrectly entered value. If the transaction amount at the cash register turns out to be excessive or there is no information about the purchase in the cash register database, you will need to create a correction document.
Please note that you only have a couple of days to make changes.
Additional documents for adjustments
The correction check is a fiscal document. Consequently, as a result of the adjustment made in the online cash register, it goes to the tax authorities, and they have the right to monitor the fact of compliance with the law when working with cash registers. In this regard, the adjustment must be accompanied by a document, for example:
- cashier's explanatory note;
An example of such an explanatory note can be seen here.
- act of adjustment;
- memo, etc.
The current legislation does not currently contain clear explanations of exactly how this should be done. Therefore, the choice of documentation method remains with the cash register user. The relevant document must include a rationale for the operation and other information explaining the reasons for the adjustment.
Correcting data entry errors at the online cash register
If a data entry error is detected at the online cash register (a receipt has not been issued, some items are missing on the receipt) due to the fault of the cashier or due to a technical malfunction of the machine, a correction check is generated.
The purpose of the procedure is to bring real sales information into conformity with those subject to accounting in the National Tax Service (fiscal). You can make adjustments to decrease or increase sales volume at any time after an error is discovered. There are two possible situations.
Situation 1. If the cashier rejects a cash document for an amount less than actually received, a situation arises where unaccounted sales revenue appears. Tax authorities may interpret this fact as concealment of the share of income subject to taxation and illegal non-use of cash registers.
In order to avoid penalties for tax payments, you need to generate a correction check. If an error is discovered on your own, the punched check, along with the act and an explanatory note containing the time and date of the error, is sent to the operator (OFD).
After which the organization (at its own request, but not necessarily) can contact the Tax Service department and notify that a discrepancy has been detected and eliminated. Upon receipt of an order from a tax structure that has received information about unaccounted sales, a correction check is generated indicating the NS order as the basis, which is sent to the operator and to the TS along with the organization’s obligation to pay a fine (Article 14 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Situation 2. If the cashier punches a cash document for an amount greater than actually received, an excess of sales proceeds over fiscal data (shortage) is formed. Creating a correction check is not mandatory due to the absence of suspicion of non-use of cash register equipment. The cashier should punch a document for the return of receipts for the missing amount and prepare an explanatory note explaining the reason for the lack of money in the cash register.
When a check for an incorrect amount was punched in the presence of the buyer, it is also possible not to create a correction check. The employee generates a document for the return of receipts in the amount of an erroneous amount, and then punches a cash document for receipts in the correct amount. The correct check is handed over to the buyer, the incorrect one is returned to the cashier, and the correct data will be sent to the OFD and TS.
For your information! If necessary, a correction check should be created in the interval between the creation of a report on the opening of a shift and a report on its closure (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Kazakhstan No. 03-01-15/28914, 05/12/2017). But this does not mean that corrections cannot be made after the shift that made the error ends.
When closing the next shift, the amounts corrected in cash documents and checks are used by the fiscal drive to generate final information for the shift (Federal Law No. 54, 05/22/2003). Therefore, creating a correction check after the end of the shift is acceptable, provided that it reflects the moment the violation was committed (date, time). For example, a document drawn up on 10/11/17 to correct an error made on 09/02/17 may contain a description of the correction in the form: “A cash receipt with an incorrectly specified amount was generated at 10:10 on 09/02/2017.”
Tax officers are able to remotely discern errors in cash calculations
The use of online cash registers brings fiscal interaction between merchants and tax authorities to a new modern level. Now the latter do not have to come out for inspection to identify errors in cash calculations. This is achieved through the exchange of information between 4 participants in the process:
- buyer;
- owner of an online cash register with a fiscal drive;
- serving the specified owner as a fiscal data operator (FDO);
- authorized officials of the Federal Tax Service.
When purchasing a product, the buyer receives a KKM receipt. He has the right to check his details through a special application and send information about the violation to the tax authorities. The cashier working at the online cash register transmits information about the punched check to the OFD. The latter accepts this information, confirms the fact of receiving the data and stores it. The main purpose of the OFD is a connecting link between the owner of the online cash register and the tax authorities, to whom he sends the received information within the prescribed time frame.
In the process of monitoring the information received, the tax service identifies offenses, sends the owners of cash registers the instructions necessary to comply with them and holds them accountable.
This is a brief summary of the modern process of interaction between the tax authority and other persons involved in the procedure for using online cash registers. If a check is entered through an online cash register by mistake, it may be visible to the tax authorities. It is advisable to resolve the error before it comes to their attention.
To get more information about interacting with tax authorities, read the article “How to get a tax deduction when purchasing an online cash register?”
What does the format of fiscal data have to do with it?
To correct the error correctly, you will have to find out which version of the fiscal data format (FDF) the cash desk uses to draw up documents. In general, in FFD 1.05 errors are corrected with a return check, and in FDF 1.1 with a correction check. But if the mistake is that two receipts were knocked out for one purchase, then different rules apply. We have summarized everything in a table.
How to correct errors depending on the FDF
| error type | FFD 1.05 | FFD 1.1 |
| Error in details (cost, VAT, name of product or service, payment method, SNO) | Returned check | Correction check |
| Two receipts for the same purchase, buyer at the cash register | Returned check | Returned check |
| Two receipts for the same purchase, the buyer left | Returned check | Correction check |
You can see which version of the fiscal data format (FDF) the cash register uses to generate documents in two ways: in the report on the opening of a shift at the cash register and in your personal account Kontur.OFD. To view the FFD in your personal account, in the “Cash Offices” section, upload the list of cash registers into Excel. The format will be indicated in the FFD column opposite the desired cash register:
Correction check or refund check? Advantages and disadvantages
Many accountants are afraid to use correction checks because they believe that they are a definite signal to the tax inspectorate: they say that this company needs to be taken into account. They advise their colleagues to use refund checks rather than correction checks to correct errors.
Indeed, in certain situations, you can get by with a return check - for example, when the cashier immediately noticed his mistake: an incorrectly indicated cost or the wrong type of calculation. In this case, the seller must immediately issue a return receipt with the calculation sign “return of receipt”. After that, he knocks out a new, correct receipt, and gives the buyer both receipts - both the return receipt and the correct one. An erroneous receipt is not given to the buyer, but information about it is stored in the system.
IMPORTANT! You can get by with a refund check only in cases where the error was discovered immediately or when the buyer himself asked to cancel the payment. If the violation was noticed only at the end of the shift or some kind of check was not found at all, you will have to issue a correction check.
Typically, tax authorities calmly react to correcting errors on their own if the company does not hide them from the inspection. Such businessmen are also not subject to special control. But if an entrepreneur tries to hide the fact of an error, and the tax office discovers it, this will result not only in a fine, but also in special attention from tax authorities in the future. Therefore, it is better to use correction checks whenever there is doubt about the correctness of payments.
What error can there be in a fiscal receipt?
There are not many mistakes that a cashier can make when making a purchase. These include, in particular:
- incorrect indication of the payment form in the check: “cash” instead of “electronic” or vice versa;
- incorrect price of goods;
- incorrect quantity of goods.
Tax authorities believe that it is necessary to correct such errors immediately after they are discovered. Sometimes this is what a correction check is for. 54 of the Federal Law provides for this possibility, but does not provide a clear algorithm for action in this regard. After all, in addition to the correction check, there is also a cash receipt for the refund. Unfortunately, sellers and accountants often confuse these concepts. A return document is used when the buyer wants to return the product and get the money back, or if the cashier accidentally indicated the wrong price for the product. The corrective one is needed when excess funds are identified, for example, when the amount of the transaction in the cash register turned out to be underestimated or was not included in it at all. The tax office automatically assumes that in this situation there is unrecorded revenue, so the adjustment check needs to be issued only in extreme cases.
Policy of Yarus LLC regarding the processing of personal data
Yarus LLC
Legal and actual address:
Actual address: 115280 Moscow, st. Leninskaya Sloboda, 19, building 4
Legal address: 117292, Moscow, Nakhimovsky Prospekt, 52/27, room B
General provisions
1.1. This document (hereinafter referred to as the Policy) defines the goals and general principles of processing personal data, as well as the implemented measures to protect personal data at Yarus LLC (hereinafter referred to as the Operator). The Policy is a public document of the Operator and provides for the possibility of familiarization with it by any person.
1.2. The policy was developed in accordance with and on the basis of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, Federal Law dated July 27, 2006 N 152-FZ “On Personal Data”, Federal Law dated May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ “On the use of cash register equipment when making cash payments and (or) settlements using electronic means of payment”, as well as other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, local acts of Yarus LLC.
1.3. The policy is strictly followed by managers and employees of all structural divisions and branches of Yarus LLC.
1.4. The Policy applies to all personal data of subjects received and processed by Yarus LLC using automation tools and without the use of such tools.
Definitions
2.1. Personal data - any information relating to a directly or indirectly identified or identifiable individual (subject of personal data).
2.2. Processing of personal data is any action (operation) or set of actions (operations) with personal data performed using automation tools or without the use of such tools. Such actions (operations) include: collection, receipt, recording, systematization, accumulation, storage, clarification (updating, changing), extraction, use, transfer (distribution, provision, access), depersonalization, blocking, deletion, destruction of personal data.
2.3. Personal data subject is any person whose personal data is processed by the personal data operator.
2.4. The personal data operator is Yarus LLC.
Processing of personal data
3.1. The processing of personal data is carried out taking into account the following requirements:
— only personal data that meets the purposes of their processing are subject to processing;
— the content and volume of personal data processed must correspond to the stated purposes of processing;
— the personal data processed should not be redundant in relation to the stated purposes of their processing;
— when processing personal data, the accuracy and sufficiency of information in relation to the purposes of processing personal data must be ensured.
3.2. The content and volume of processed personal data are determined based on the statutory goals of the Operator’s activities, on the basis and in pursuance of the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation, including Federal Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ “On the use of cash register equipment when making cash payments and (or) settlements using electronic means of payment.”
3.3. The main categories of personal data subjects whose data is processed and/or may be processed by the Operator in accordance with the purposes for obtaining it include individuals:
- persons who are and have been in labor and civil legal relations with the Operator and/or the Operator’s counterparties;
- candidates for vacant positions;
- persons who have a civil law contractual relationship with the Operator, or are at the stage of pre-contractual or completed relationships of a similar nature;
- persons who provided their personal data in the process of interaction with the Operator, including by connecting to the Operator’s services and/or signing legal documents with the Operator.
3.4. For these categories of subjects, information may be processed, including that requested on the Operator’s services, including, but not limited to: last name, first name, patronymic; year, month, date of birth; place of birth, address; Family status; social status; property status; education; profession; income; TIN, SNILS, contact information (telephone, address, email address, etc.), as well as other information necessary for processing purposes.
3.5. The operator has the right to process personal data of subjects, including in the following ways:
collection, recording, systematization, accumulation, storage, clarification (updating, changing), extraction, use, transfer (distribution, provision, access), depersonalization, blocking, deletion, destruction of personal data.
3.6. The operator processes personal data using automation tools and without the use of automation tools.
3.7. The processing and storage of personal data is carried out no longer than required by the purposes of processing personal data, unless there are legal grounds for further processing.
Measures to ensure the security of personal data
4.1. The Operator takes technical and organizational security measures to protect personal data from accidental or unlawful destruction, loss or modification, as well as from unauthorized disclosure or access to personal data.
4.2. To prevent unauthorized access to personal data, the Operator applies the following organizational and technical measures:
- appointment of officials responsible for organizing the processing and protection of personal data;
- limiting the number of persons who have access to personal data;
- organization of accounting, storage and circulation of information carriers;
- checking the readiness and effectiveness of using information security tools;
- restriction of user access to information resources and software and hardware for information processing;
- registration and recording of actions of users of personal data information systems;
- use of protection means and means of restoring the personal data protection system;
- organization of access control to the Operator’s territory, security of premises with technical means for processing personal data.
Rights of personal data subjects
5.1. The subject of personal data decides to provide his personal data and consents to their processing freely, of his own free will and in his own interest. Consent to the processing of personal data can be given by the subject of personal data or his representative in any form that allows confirmation of the fact of its receipt, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
5.2. The subject of personal data has the right to withdraw consent to the processing of personal data by sending a corresponding written request to the Operator.
5.3. The subject of personal data has the right to receive information regarding the processing of his personal data, including containing:
- confirmation of the fact of processing of personal data by the Operator;
- legal grounds and purposes of processing personal data;
- the purposes and methods of processing personal data used by the Operator;
- name and location of the Operator, information about persons (except for the Operator’s employees) who have access to personal data or to whom personal data may be disclosed on the basis of an agreement with the Operator or on the basis of federal law;
- processed personal data related to the relevant subject of personal data, the source of their receipt, unless a different procedure for the presentation of such data is provided for by federal law;
- terms of processing of personal data, including periods of their storage;
- the procedure for the exercise by the subject of personal data of the rights provided for by the Federal Law “On Personal Data”;
- information about completed or intended cross-border data transfers;
- name or surname, first name, patronymic and address of the person processing personal data on behalf of the Operator, if the processing has been or will be assigned to such a person;
- other information provided for by the Federal Law “On Personal Data” or other federal laws.
5.4. The subject of personal data has the right to demand from the Operator clarification of his personal data, blocking or destruction of it if the personal data is incomplete, outdated, inaccurate, illegally obtained or is not necessary for the stated purpose of processing, as well as take measures provided by law to protect his rights .
5.5. If the subject of personal data believes that the Operator is processing his personal data in violation of the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation or otherwise violates his rights and freedoms, the subject of personal data has the right to appeal the actions or inaction of the Operator to the authorized body or in court.
Access to the Policy
6.1. The current version of the Policy on paper is stored at the location of the Operator’s executive body at the address: 115280 Moscow, st. Leninskaya Sloboda, 19, building 4
6.2. The electronic version of the current version of the Policy is publicly available on the Operator’s website on the Internet: here
Updating and approval of the Policy
7.1. The policy is approved and put into effect by the head of Yarus LLC.
7.2 The Operator has the right to make changes to this Policy.
Responsibility
8.1. Persons guilty of violating the rules governing the processing and protection of personal data bear responsibility under the legislation of the Russian Federation, local acts of the Operator and agreements governing the legal relations of the Operator with the subject of personal data and/or third parties.
Final provisions
9.1. The Operator has the right to make changes and additions to this Policy regarding the processing of personal data at any time without prior notice to Users.
In this case, the subject of personal data is obliged to independently monitor changes and additions to this Policy. In case of disagreement with the terms of this Policy and/or its individual provisions, as well as changes and additions to it, the Operator asks you to refrain from visiting and using the Operator’s services and not to provide your personal data. Otherwise, the Operator has the right to process personal data in accordance with the Policy and does not bear any liability in connection with this.
How to generate a correction check in the cash register module of Kontur.Market (FFD 1.05): step-by-step instructions
In the upper left corner of the checkout screen, click the menu icon.
Next, you can work in any of two sections: “Information” or “Receipts”. In both tabs you need to select the “Adjustments” tab.
We will describe the creation of adjustments in the “Receipts” section. Going to the “Adjustments” tab, click “Create adjustment”:
Fill in the fields in the window that opens. All items are required except the “Reason” field. The sequence of actions depends on the format of fiscal documents (FDF) that the cash register supports - these are formats 1.05 and 1.1. The updated Market cash module uses only format 1.05.