Legal entities carrying out economic activities are obliged to timely and fully fulfill their obligations to the state budget, including payment of property taxes.
In 2021, there have been some changes in the rules for its calculation. What changes have occurred in the tax base, who is recognized as a taxpayer in this case, how the rates for enterprises have changed, what benefits exist for the payment of this type of mandatory payments and the deadlines for their payment will be discussed in today’s article. In addition, using a specific example, we will try to consider how this type of mandatory payment and the advance amount for it are calculated.
Changes to the tax base in 2021
In the previous year, movable assets accepted by the company on its balance sheet after January 1, 2013 were not subject to taxation. This rule did not apply to assets that the company received from a so-called dependent counterparty. This exception was introduced in order to eliminate cases of artificially lowering the amount payable to the budget through the transfer of assets between friendly companies. This provision ceased to apply on January 1 of that year.
Now, according to Federal Law No. 335-FZ of November 27, 2017 “On Amendments to Parts One and Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation,” movable assets of enterprises again began to be included in the taxable base.
In addition, in accordance with the new edition of Article 380 of the said code and Article 381.1. benefits applicable to company assets included in depreciation groups 3-10 no longer apply. However, in relation to assets designated in paragraph 25 of Article 381 of the main fiscal document of Russia, from the date of issue of which no more than 3 years have elapsed, as well as assets that are classified as innovative highly efficient equipment, additional benefits may be applied up to the complete exemption of the company from payment of the designated type of obligatory payments to the budget.
Experimental holiday tax in 2018
According to a new government decree, 2021 will be the year the launch of an experimental tax levy - the so-called holiday tax. Its introduction will be carried out in the four most popular resort areas of the Russian Federation today.
Table 1. Popular resort areas in Russia
| Zone | Photo |
| Crimean peninsula | |
| Altai region | |
| Stavropol region | |
| Krasnodar region |
It is to these warm and sunny areas of the country that Russian citizens flock during the hot summer and early autumn months. It should be noted that their patriotism is truly admirable: not only has it been very expensive to vacation in their homeland for a long time, now they will have to pay an additional tax fee.
That’s right, payments for vacation will be made by tourists coming from:
- other regions of Russia;
- foreign countries.
Many Russian citizens consider this newly introduced fee a return to the past. The thing is that it already existed in our country, during its Soviet existence. It came into force in December 1991 and was then repealed in 2004.
However, the resort fee is a unit of global practice. It is also used in such developed countries as:
- Germany;
- Spain;
- Italy;
- France;
- as well as from other leaders of domestic tourism.
The tax will be imposed on all tourists who visit the above resort areas of the country. The category of beneficiaries will include all its traditional representatives, that is:
- minor citizens;
- military veterans;
- students studying in higher educational institutions;
- people with disabilities;
- other similar categories.
The amount of the tax fee for vacation has not yet been determined, however, the amount of deduction is expected to be 100 rubles for one day of stay in an official accommodation facility. By the way, it is possible that rates will vary depending on the season. In addition, their education will be influenced by such nuances of citizens’ travel as:
- purpose of arrival;
- the significance of the area where the tourist is vacationing;
- other, not yet indicated nuances.
One of the most important problems regarding the application of the required tax levy is that it is necessary to remove from the “shadow” such tourist accommodation facilities as guest houses that are not officially registered, beds for private citizens, for example, old people living on pensions. Finding such places to stay overnight in a resort town is easy.
To do this, you just need to ask the locals and they will definitely show you the way
The ongoing experiment causes mixed feelings among taxpayers. On the one hand, the practice is global, which means it takes place. On the other hand, vacationing in your homeland has long become impossibly expensive. And if this price is now added to the need to pay several thousand rubles per family for a standard vacation period, most likely citizens will move to their dachas or go abroad.
Who are the payers?
According to Article 373 of Chapter 30 of the main fiscal document of the country, which is part of the second document signed by the President of the Russian Federation on August 5, 2000 and which entered into force on January 1, 2001, taxpayers of this type of obligatory payment are recognized as enterprises that own capital recognized as an object of taxation according to Article 374 of the country's main fiscal document.
At the same time, enterprises that have switched to a simplified taxation system and own certain assets are recognized as payers.
Also, some property of companies paying unified agricultural taxes is subject to taxation.
At the same time, the objects of taxation for national companies in accordance with the Tax Code are movable and immovable property, which is recorded on the balance sheet as an asset in accordance with the current accounting procedure.
As for foreign organizations operating on the territory of the Russian state through permanent representative offices, the object of taxation for them is movable and immovable property, which is classified as a fixed asset, as well as property transferred under a concession agreement.
For foreign organizations that do not operate through permanent representative offices in the Russian Federation, the tax base includes real estate owned by these companies and located on Russian territory, as well as real estate received under a concession agreement.
The tax base does not include:
- land plots and environmental management facilities;
- cultural heritage sites;
- nuclear installations used for scientific research;
- icebreakers, as well as nuclear technology service vessels;
- space objects;
- vessels registered in the Russian International Register of Ships;
- property included in 1-2 depreciation groups.
Taxation of movable property: history of the issue
From January 1, 2015, fixed assets included in depreciation groups 1 and 2 of the Classification of fixed assets approved by the Government of the Russian Federation ceased to be recognized as objects of taxation (subclause 8, clause 4, article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, other objects of movable property are subject to taxation. Moreover, since 2015, such an object has also included property acquired after 01/01/2013, which was not subject to taxation until 2015. However, simultaneously with the exclusion from non-taxable property, it was included in the preferential property.
Thus, all movable property, except for objects of depreciation groups 1 and 2, from 2015, regardless of the date of registration as fixed assets, began to be regarded as subject to taxation. At the same time, property acquired after 01/01/2013 fell under the exemption.
Changes in rates
As for the current rates for this type of payment in 2021, the maximum rate for movable property tax does not exceed 1.1%.
In 2021, organizations operating under a simplified taxation system are also exempt from this type of obligation to the state budget. For them, only real estate that has a cadastral value at the beginning of the reporting period acts as an object of taxation.
In relation to other business entities that are owners of movable property, taxes are calculated in accordance with regional legislation.
The table below shows the maximum rates provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
| Type of property | Maximum rate, according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| by types of property not included in one of the items listed below | 2.2 percent |
| according to the cadastral value of real estate in Moscow | 1.4 percent |
| according to the cadastral value of real estate for all subjects of the Russian Federation, with the exception of Moscow | 2 percent |
| types of property designated by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 30. 2004 No. 504. When calculating tax on objects put into operation after December 30. 2021, reduction factors can be used. | 1.0 percent |
| along main pipelines, power transmission lines, as well as structures that are an integral part of the facilities listed below | 1.6 percent |
| on objects of main gas pipelines, gas production, production and storage of helium; | exemption from payment |
| for objects, a specific list of which was approved by order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 19.10. 2021 No. 2188-r. When calculating tax for 2021, be guided by the list specified in paragraph 3 of paragraph 1 of the order. | exemption from payment |
Transport tax
There will be no changes in this area, which is undoubtedly one of the most important, tax collection. Transport tax will continue to be mandatory for those citizens who own vehicles. This category includes not only passenger cars, but also:
- motor transport;
- trucks;
- buses;
- pneumatic transport;
- tracked transport;
- snowmobiles;
- watercraft;
- aircraft;
- other types of vehicles.
Regular contributions will continue to be collected in the established manner that is familiar to Russians. Regional government representatives will continue to monitor the implementation of this transport obligation.
As for rates: drivers can exhale, since there are no plans to increase tariffs, despite the protracted economic crisis and the general aggravated situation in the country. However, there will be no reduction either.
So let's rejoice in the absence of change
In view of the difficult economic events we mentioned earlier, it is not possible to completely abandon the transport tax in the conditions of today's Russian realities. According to statistics, transport fees fill the state budget with approximately 146 billion Russian rubles.
However, there will be some changes regarding the timing of payments. Thus, companies that have the organizational form of a legal entity will receive an obligation to pay the tax contribution before the first day of February 2021. In addition, they will also have to immediately transfer the advance payment for the subsequent reporting period to the state balance sheet.
Individuals, that is, ordinary citizens and individual entrepreneurs, will have to transfer funds using the details received from the tax service before the first of December next year. Let us remind you that in 2021 the payment deadline remained the first day of October. This means that vehicle owners will have much more time to accumulate the funds due for payment.
The tax rate will continue to be calculated according to the three main characteristics of the vehicle owned by the citizen. These include:
- the year the vehicle was produced at the plant;
- period of use of a specific vehicle;
- engine power (for cars it is measured in so-called horsepower).
Please note that, as before, the coefficient for calculating the amount of the fee will be differentiated according to each subject of the Russian Federation. In other words, different rates will apply in the regions, therefore, it will have to be clarified specifically for any city individually.
Those who decide to change their place of residence should be especially careful. As you move, your rate will also change.
Video - How much more expensive will it be to maintain cars in 2018?
Example of calculating property tax for legal entities and advance payments
We can consider how enterprises and organizations calculate the amount of such obligations to the state budget using a specific example.
Before you begin the calculation, you should decide which property on the organization’s balance sheet is subject to taxation.
Then you should decide whether the company has the right to preferential taxation.
Only after this can you begin to determine the basis for calculating the amount of obligations to the budget, decide on tax rates and calculate the amount.
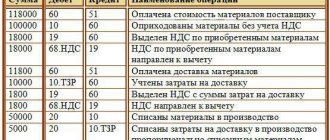
As for advance payments, they should be paid quarterly. To calculate them, the following formula is used:
- in case of calculation based on the average annual cost = (average cost of fixed assets for the reporting period x tax rate)/4;
- in case of calculation based on cadastral value = (cadastral value of fixed assets x tax rate)/4.
Let us consider in more detail how to calculate the amount of tax on fixed assets of organizations based on the average annual cost.
To determine the tax base in this case, it is necessary to add up the residual value of each property on the 1st day of each month and at the end of the reporting period (in Russian rubles):
- 01. – 120 000;
- 02. – 115 000;
- 03. – 110 000;
- 04. – 105 000;
- 05. – 100 000;
- 06. – 95 000;
- 07. – 90 000;
- 08. – 85 000;
- 09. – 80 000;
- 10. – 75 000;
- 11. – 70 000;
- 12. – 65 000;
- 12. – 60 000.
We calculate the advance tax amount for the 1st quarter of the reporting period:
- tax base = (120,000+115,000+110,000+105,000)/4 = 112,500 rubles;
- advance payment amount = 112,500 x 2.2% = 2,475 rubles.
Then you need to determine the advance amount as of July 1:
- tax base = (120,000 + 115,000 + 110,000 + …+ 90,000)/7 = 105,000 rubles;
- advance payment = 105,000 x 2.2% = 2,310 rubles.
Now you need to determine the amount of the advance payment based on the results of the 3rd quarter:
- tax base for calculation = (120,000 + 115,000 + 110,000 + …+ 75,000)/10 = 97,500 rubles;
- advance payment = 97,500 x 2.2% = 2,145 rubles.
After this, the amount subject to additional payment of property tax for the year is calculated:
- tax base for calculation = (120,000 + 115,000 + 110,000 + …+ 60,000)/13 = 90,000 rubles;
- advance payment = 90,000 x 2.2% = 1,980 rubles.
Land tax in 2021
The cost of land plots in the coming year will also be assessed according to the cadastral characteristics. To do this, it is necessary to estimate the market value of the site. Unfortunately, there is an opinion among taxpayers that the cost assessment by bureaucrats is often biasedly inflated. The price is determined by the cadastral chamber and its specialists. Their decision regarding the determination of the price of the plot can only be challenged in court. However, there is a real danger of losing and incurring losses associated with paying for the costs associated with the trial.
The amount of payment due to the state in 2021 will increase by as much as 20%, and its growth will continue immediately until 2020. The main argument of government structures in favor of such an increase is the assumption that the filling of regional budgets, increased through transfer to cadastral value, will have a very positive effect on the development of the infrastructure of each residential locality.
By the way, this filling will increase approximately 6-8 times
Tax benefits
In accordance with Article 381 of Part 2 of the Tax Code, introduced by Federal Law No. 139-FZ of November 11, 2003, the following are exempt from payment:
- institutions and organizations working in the penal system, in relation to those fixed assets that are used to perform the functions assigned to them;
- religious organizations in terms of property used for religious activities;
- national public organizations of people with disabilities, among whose members at least 80% are people with disabilities and their representatives, in terms of fixed assets used to carry out their statutory activities;
- organizations engaged in the production of pharmaceutical products, in terms of fixed assets used for the production of veterinary immunobiological agents aimed at combating the epidemic;
- material objects of enterprises engaged in the production of prosthetic and orthopedic products, etc.
This article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains 26 points indicating enterprises and organizations exempt from paying this type of mandatory payments.
Corporate income tax
Legal entities pay income tax to the state treasury at a fixed rate, which currently amounts to 20% of the funds received by them. Let us remember that profit is not income, that is, the proceeds of an enterprise, but money earned, from which all production costs have been subtracted.
Let's give an example. You run a store where you sell vegetables and herbs that you grow yourself. Let’s assume your revenue for a certain tax period amounted to 50 thousand rubles. In the process of arranging greenhouses and growing vegetables, as well as for the purchase of packaging and other necessary production expenses, you previously paid about 25 thousand rubles. To calculate the taxable base (profit), you need to subtract expenses from revenues. We will receive: 50-25 = 25 thousand - the net profit of your vegetable shop.
The changes regarding the income tax did not affect the rate itself, but the distribution of the proceeds collected from the taxpayer. Now the federal budget gets 3% of the amount received, while the remaining 17% goes to the regional treasury.
Corporate income tax 2018
In addition, in 2021, local authorities received the right to independently differentiate rates in each individual situation. In the new year, everything will remain the same, however, representatives of some categories of taxpayers will have the opportunity to work at a minimum rate. Previously it was 13.5%, now it is 12.5%.
Corporate income tax plays a major role, however, in some specialized taxation regimes it is not deducted to the treasury, since they require simplified accounting. Let's talk about this in detail in a special article.
Payment period
According to Article 383 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of the designated type of mandatory payments and the amount of advance payments for it are subject to payment in the manner and within the time limits established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
During the reporting period, taxpayers must pay advance payments to the budget, unless otherwise provided by the legislation of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. At the end of the reporting period, an additional payment for this tax is made for the year.
Taxpayers are required to submit calculations for the specified tax within a maximum of 30 calendar days after the end of the relevant reporting period.
As for tax returns based on the results of the reporting year, taxpayers are required to submit them no later than March 30 of the year following the expired fiscal period.
Who pays for the property and who doesn't?
The determination of the rate is relevant for legal entities that have taxable property in accordance with Art. 374 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The following companies and organizations are subject to a zero tax rate in 2018.
- Religious organizations;
- Charitable foundations based on voluntary contributions;
- Organizations involved in improving the lives of socially vulnerable segments of the population, including people with disabilities;
- Sports associations and federations led by FIFA;
- Organizations serving FIFA and its subsidiaries.
Pay - and don't cry
Citizens must receive notices to pay property taxes by November 1. Photo: Mikhail Frolov / Komsomolskaya Pravda
What has changed in the tax notices that citizens receive this year?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: In order to simplify the tax payment procedure, reduce budget costs for the delivery of tax documents and prevent the dissemination of false receipts under the guise of fiscal payment documents, all details for paying taxes from this year are included in the tax notice itself. Separate receipts for payment of taxes specified in the notice are not sent.
For the first time, land tax was calculated taking into account a limiting coefficient: an increase of no more than 10 percent compared to the previous year
Some media reported that scammers began sending fake tax notices to citizens. How to understand that the notification received is genuine, especially if a person does not have a personal account on the Federal Tax Service website?
Svetlana Bondarchuk : The Federal Tax Service does not have information about any confirmed cases of sending out so-called fake tax notices. In any case, it is advisable to pay attention to the information contained in the notification.
Svetlana Bondarchuk: Benefits for pre-retirees will be applied for the first time in 2021. Photo: nalog.ru
The taxpayer’s personal data is indicated there: last name, first name, patronymic, residential address or a note that the tax notice was sent through the taxpayer’s personal account, taxpayer identification number, detailed information about the taxable property owned by the taxpayer: cadastral or registration number, ownership period, tax base, tax amount, tax benefits.
Mandatory elements of the tax notice also include details for transferring taxes to the budget system, indicating a unique payment identifier, information about the recipient of taxes represented by the Federal Treasury and tax inspectorates.
The tax amount in the text of the tax notice coincides with the tax amount indicated in the electronic payment details; this is the QR code and barcode in the tax notice.
As you can see, such a set of information “linked” to the recipient of a tax notice is almost impossible to falsify, much less use as recipients of tax payments indicated in the tax notices of some individuals.
If you have any questions about the contents of the tax notice, you can contact any tax office, including to receive a copy of the tax notice, or contact the contact center of the Federal Tax Service of Russia by phone.
What percentage of notifications did the tax service send out by mail this year, and what percentage did they send out electronically through your personal account on the Federal Tax Service website?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: 52.7 million tax notices were sent by mail in 2021. This is 76 percent of the total number of tax notifications generated. 16.5 million taxpayers received such documents electronically.
The “six hundred square meters” tax deduction now applies to parents with many children. If the area of the plot does not exceed 600 square meters, they will not have to pay tax at all
The number of users of the taxpayer’s personal account on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia is growing. At the same time, the share of tax notices that are sent in paperless format is also increasing. This year it reached 24 percent, while four years ago it did not exceed 11.5 percent.
What new has happened in the system for calculating property taxes that citizens will have to pay for 2018?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: Let's start with land tax. One of the most important innovations concerns the introduction of a coefficient limiting the annual marginal tax increase to 10 percent compared to the previous year.
If a citizen has not received a tax notice by November 1, it makes sense to contact the Federal Tax Service. Lying low and waiting is a bad strategy
The exception is plots for housing construction, when calculating the tax for which an increasing factor is applied due to their untimely development.
There is also a ban on recalculating tax if it entails an increase in previously paid tax. That is, they can recalculate the paid land tax downward, but not upward?
Svetlana Bondarchuk : Yes. Another innovation concerns the application of the cadastral value of a land plot due to a change in its type of permitted use, category of land or area. Now such changes are taken into account from the date of entry into the Unified State Register of Real Estate information that serves as the basis for determining the new cadastral value. Previously, the new cadastral value was used for taxation starting next year.
RG experts discuss the legal subtleties of taxation in the “Legal Consultation” section
What new federal benefits have appeared for land tax?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: For the first time, citizens with three or more minor children are provided with a tax deduction that reduces the amount of tax on the cadastral value of 600 square meters of the area of one land plot.
For the first time, a non-declaration procedure for providing tax deductions has been established for preferential categories of taxpayers - pensioners, disabled people, large families. So, if the tax authorities already have information about such citizens, for example, the information was received from the Pension Fund of Russia or a disabled person previously applied for transport tax benefits, the pensioner took advantage of the benefit that exempts him from paying apartment tax, he does not have to re-apply for the deduction need to. It is applied automatically.
What has changed in the calculation of the tax that Russians pay for their apartments and houses?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: In seven regions, the tax was calculated for the first time taking into account the cadastral value. These are Kaluga, Lipetsk, Rostov, Saratov, Tyumen, Ulyanovsk regions and Perm region.
Due to the fact that the cadastral value is used as a tax base there for the first year, when calculating the tax, a coefficient for the tax period equal to 0.2 was used. (At the start of the “cadastral reform”, in order to make the tax increase not so sharp, a special coefficient was included in the formula for calculating it for the transition period, which increases as the region switches to cadastral valuation of real estate. - Ed.)
In 14 regions where cadastral value is used for the second year, the coefficient increased from 0.2 to 0.4. This also applies to the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), Krasnodar, Khabarovsk territories, and Orenburg region (a complete list of regions is on the Federal Tax Service website. - Ed.).
The coefficient of 0.6 was applied in 21 regions: including St. Petersburg, Stavropol Territory, Voronezh, Chelyabinsk regions. There, the cadastral value is used as the tax base for the third year.
This year, citizens must pay property taxes no later than December 2. Photo: Ivan Makeev / Komsomolskaya Pravda
For regions where the cadastral value serves as the basis for calculating tax for at least three years, the law provides for a maximum 10% limit on tax growth compared to the previous tax period. This year, the Federal Tax Service applied such a limiter to 49 regions, including Moscow, the Moscow region, Bashkortostan and Tatarstan.
Some regions have not yet begun “cadastral reform” in 2021. How was the tax calculated there?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: Based on the inventory value of real estate using a deflator coefficient, it is established by the Ministry of Economic Development. For 2017 it was 1.425, for 2021 - 1.481.
By the way, as in the case of land tax, a ban on recalculation has been introduced for property tax if it entails an increase in previously paid tax.
Tax is not charged in respect of a completely destroyed or destroyed capital construction project. An important point: accrual stops based on the taxpayer’s application from the first day of the month when the object was destroyed. The date of registration of termination of the right to it in the Unified State Register of Real Estate does not matter.
What about the benefits?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: Parents with three or more minor children have for the first time received the right to additional tax deductions that reduce the amount of tax on the cadastral value of 5 square meters of the total area of an apartment, room and 7 square meters of the total area of a residential building per each minor child.
For beneficiaries, including pensioners, disabled people, citizens with many children, by analogy with land tax, a non-declaration procedure for providing tax benefits has been applied.
If a person became a pensioner at the end of January 2021 and he has two apartments, and pensioners are exempt from paying tax for one object, will he not pay the tax for 2021 completely on one object or will the tax be charged for that part of January when he has not yet became a pensioner?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: If the right to a benefit that exempts you from paying tax arises, the tax is not calculated from the period when such a right arose. For the period when the owner of taxable property was not a benefit recipient, the tax is calculated in the general manner.
Are there any innovations regarding transport tax?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: Vehicles that are wanted in connection with their theft or theft are now not subject to tax until the month of their return to the rightful owner, and not until the date the search ceases due to the expiration of its period, as before.
In what ways and where can citizens pay property taxes today?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: This can be done through banking organizations, including using their electronic mobile applications, through the taxpayer’s personal account on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, in authorized multifunctional centers for the provision of state and municipal services, in federal postal offices, and in local administrations.
If the taxpayer has not received a notice, does he have an obligation to report this to the tax office or can he lie low and wait?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: By law, tax notices are sent to taxpayers no later than 30 days before the tax payment deadline. This year the deadline is December 2. Thus, the notification must be sent or posted in your personal account before November 1.
There are several situations provided by law when it is not sent. Firstly, in the presence of a tax benefit, tax deduction, or other legal grounds that completely exempt the owner of the object of taxation from paying tax. Secondly, if the total amount of taxes reflected in the tax notice is less than 100 rubles, with a number of exceptions.
In all other cases, if the taxpayer has not received the notification before November 1, it is advisable for him to contact the tax office or send information through the “Personal Account of the Taxpayer” or using the Internet service “Contact the Federal Tax Service of Russia.”
Owners of real estate or vehicles who have never received tax notices on their taxable object and have not claimed tax benefits in relation to the corresponding taxable object are required to report the presence of such objects to any tax authority. For failure to fulfill this obligation, a fine of 20 percent of the unpaid tax amount in respect of the real estate or vehicle is provided.
Russia has adopted a law on benefits for pre-retirees. When will they start working?
Svetlana Bondarchuk: From the tax period of 2019, that is, these benefits will be applied for the first time in 2021 when calculating taxes for the tax period of 2021.
0.02 percent is a penalty on the unpaid amount of tax for each day of delay. The penalty is calculated based on 1/300 of the Central Bank rate in effect at that time
Firstly, citizens of pre-retirement age will be exempt from paying property tax for one piece of real estate of a certain type, provided that it is not used in business activities. Such an object can be a residential building or part of it, an apartment or room, a garage or parking space, or an outbuilding with an area of no more than 50 square meters. It will be possible to select one object from each category and not pay tax on it.
Secondly, a tax deduction of 6 acres will be extended to citizens of pre-retirement age. When calculating land tax, the amount of tax will be reduced by the cadastral value of 600 square meters for one land plot. If the plot is 6 acres or less, you will not have to pay tax at all. If it is larger, the tax will be calculated for the remaining area.
A citizen who has two or more plots can choose the one for which the deduction will apply and send a notification about this to any inspection. By default, the deduction will be applied automatically to the single parcel with the highest tax amount.
Is it possible to challenge the assessed tax amount?
Citizens often wonder why this or that tax might increase?
Bondarchuk: Since taxes are calculated based on tax rates, benefits and the tax base determined at the regional and municipal levels, the reasons for changes in the amount of taxes in a specific situation should be clarified with the tax office or by contacting the Federal Tax Service contact center by phone: 8 800-222- 22-22.
There are also general grounds for changing the tax burden. For example, an increase in transport tax may be due, among other things, to the use of an increasing coefficient. They apply to passenger cars with an average price of three million rubles. The list of such vehicles is determined every year and published on its website by the Russian Ministry of Industry and Trade.
For land tax, growth may be associated with changes in tax rates or the abolition of benefits, the authority to establish which falls within the competence of representative bodies of municipalities at the location of the land plot. More information about this can be found in the section “Reference information on rates and benefits for property taxes” on the Federal Tax Service website.
The same factors may be responsible for an increase in property taxes. Plus - an important point - the change in the coefficients for the tax period, which we have already discussed.
If, in the taxpayer’s opinion, the tax notice contains outdated or incorrect information, for example, about the period of ownership of the object, tax base, address, then to check and update it, you need to contact the tax authorities. Users who already have access to the “Taxpayer’s Personal Account” can send a request through this service. For all other citizens, our website offers the “Contact the Federal Tax Service of Russia” service. You can also send a letter by mail or make clarifications in person at any tax office. Challenging the amount of tax itself, regardless of the basis for its calculation: the application of a certain period of ownership of the object of taxation, tax rate, tax base, benefits, etc., is not provided for by law.
Claiming benefits is now easier
Since 2021, a new procedure for confirming the right to benefits has been in effect (Law No. 286-FZ dated September 30, 2017, as amended by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Now, to receive a property tax benefit for individuals, it is not necessary to submit supporting documents to the Federal Tax Service. The fact is that since 01.01.2018, the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 14, 2017 No. ММВ-7-21/897 has been in force, which approved a new application form for benefits on three taxes - for land, transport and property:
Starting in 2021, this application form looks more like a tax return. In any case, the structure and filling principle have become similar.
But the essence of innovation is not only in the form of a statement. From 2021, an individual property tax payer can choose from two options:
1. Immediately submit to the Federal Tax Service, along with the application, documents justifying the right to the benefit.
2. Just indicate the details of these documents.
In the second case, the tax authorities themselves will make a request to those bodies/organizations that issued the documents indicating the basis for the benefit specified in the application. And then the individual will receive an answer about whether the benefit is approved or not.
If the Federal Tax Service does not receive the necessary data at its request, the owner of the property will be informed of the need to still submit supporting documents.
Thus, from 2021, citizens can choose whether or not to submit documents to the Federal Tax Service for a property tax benefit.
All information on the consideration of an application for a property tax benefit for individuals can be seen in your personal account on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia. If one is not connected, you can choose another method of notification:
- at the tax office;
- MFC (“My Documents”) through which the application was submitted;
- by mail.
You can apply for a property tax benefit for individuals at any Federal Tax Service Inspectorate, as well as through the individual’s personal account on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
Also see “What will change in 2021: taxes, insurance premiums, reporting, accounting and a new fee.”
Read also
08.12.2017