When it is impossible to conclude a GPC agreement
It is not always illegal to enter into such a contract. Officials provided specific conditions. If the employer violates them, the labor inspectorate will impose a substantial fine. A budgetary institution does not have the right to conclude a PPPC if:
- The position in which the contract worker works is provided for in the staffing table of the government agency.
- The internal labor regulations apply to the mercenary. For example, such an employee works during working hours that are established for core personnel.
- Work is carried out in a specially created workplace. For example, a doctor in a medical facility.
If at least one of the conditions is met, then enter into an employment contract. There are no exceptions. In 2021, taxes and contributions under the GPC agreement will be collected without fail.
What fees should I pay?
Insurance coverage for payments under DHPC is calculated according to the usual rules, but with reservations. The base for insurance premiums when renewing a GPC agreement is determined depending on the type of insurance premium. Here are the contributions employers are required to pay under the GPC:
- Compulsory pension insurance, or compulsory pension insurance, is calculated in full. The tariff for insurance premiums for compulsory health insurance is determined in accordance with the tariff applied by the institution in relation to payments under employment contracts.
- Compulsory health insurance, or compulsory medical insurance, is charged in full at the rate applied by the organization.
- Contributions to pay for temporary disability and in connection with maternity, or VNIM, are not charged. According to paragraphs. 2 p. 3 art. 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payments under PGPC are non-taxable in terms of insurance for temporary disability and in connection with maternity.
- Insurance against accidents and occupational diseases, or accidents and illnesses, is accrued only if such an obligation is expressly stated in the terms of a civil contract.
Procedure and deadlines for paying personal income tax to the budget
- following the day of actual receipt of income by taxpayers (for income paid in cash),
- following the day of actual deduction of the accrued personal income tax amount (for income received by the taxpayer in kind or in the form of material benefit).
The more employees an organization (IP) has who receive various incomes (wages, vacation pay, temporary disability benefits, material benefits, etc.), the more attention the accounting department has to pay to the calculations with the budget for personal income tax.
Calculation example
Payment will be made based on the results of the provision of services. There are no advance payments. There are no contributions for injuries under the terms of the agreement.
The institution pays insurance coverage at generally established rates.
Let's calculate what fees and taxes for civil partnership with an individual the organization will have to pay:
Contributions such as VNiM, NS and PZ are not charged.
The article is devoted to taxes and contributions under the GPC agreement in 2021. It describes in detail what exactly needs to be paid, in what volume, and who exactly should do it.
If you need a specific specialist to do a certain job for you, you can hire him. And for this it is not always necessary to conclude an employment contract. In some cases, a civil law agreement will be optimal. It is also called a GPC agreement.
This agreement differs from an employment agreement in that the parties to it are not the employer and the employee. It is regulated by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Article 420), and not by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The essence of the contract comes down to the performance by one person of a second volume of work or the provision of specific services for a monetary reward.
In this regard, the question arises: are taxes paid under a civil partnership agreement? Yes, there are no exceptions in this regard in the legislation. Therefore, the relevant issues need to be dealt with.
Who deals with payments under the GPC agreement
Expert opinion
Semenov Alexander Vladimirovich
Legal consultant with 10 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
It is very important to understand who pays taxes under the GPC agreement. In fact, everything here is quite simple and depends on with whom exactly such an agreement is drawn up:
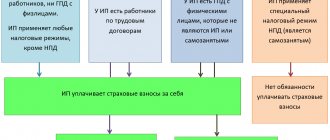
- if we are talking about an individual, then in this case the customer company acts as a tax agent. That is, she will have to deal with the payments;
- if the executor means an individual entrepreneur, then the individual entrepreneur must pay everything for himself.
The issue of calculating taxes on GPC should be resolved as early as possible. This way you will definitely avoid claims from the tax authorities.
Regulatory framework for 2021
The main regulation for this type of relationship is the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. In Art. 702 states that a work contract acts as a transaction for the contractor to perform certain works that are paid for by the customer. Based on the terms of a specific agreement, in practice the following types of work contracts :
- Household (performing work to meet the customer’s household needs). The standard used is Law No. 2300-1 of February 7, 1992 “On the Protection of Consumer Rights,” as well as the Rules for Consumer Services in the Russian Federation.
- Construction (carrying out construction work and everything connected with it - capital, installation, reconstruction work). The standard is Federal Law No. 39 of February 25, 1999 “On investment activities in the Russian Federation” and Federal Law No. 160 of July 9, 1999, as well as the Land and Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation.
- Design and survey (the customer prepares documents based on the results of the work performed - the results of economic, natural research, technological, constructive, architectural solutions).
- Public (the purpose of creation is to meet state or municipal needs).
In Art.
432 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that an agreement is considered concluded from the moment an agreement is reached on significant issues. The subject of the transaction is described in Art. 743 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The work performed is recognized as it. As for the cost for the work, it is considered significant if it was agreed upon by the parties in advance, in accordance with the provisions of Art. 709 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Why do they enter into a GPC agreement with employees? The answer is in the video below.
What taxes and fees do you need to pay?
So, you have figured out that in this case you cannot get rid of taxes. Now you need to understand what exactly to pay. That is, you need to understand what taxes the GPC is subject to in 2021. We are talking about the following:
- Personal income tax (personal income tax) – 13% of income if we are talking about an individual. An individual also has the right to use standard tax deductions, but they will only apply to the period during which such an agreement was in effect;
- insurance premiums - only contributions to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund and the Pension Fund will be mandatory. Everything else is determined by the text of the contract. Insurance premiums are as follows:
- to the Pension Fund or the Pension Fund – 22%;
- in the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund – health insurance, the rate will be 5.1%.
Please note that if the customer has the right to apply reduced rates, then he has the right to use it in the described case. That is, this right also applies to payments under GPC.
Also, when deciding what taxes and contributions to pay under the GPC agreement, you need to take into account the Social Insurance Fund or social insurance. And this has its moments.
Thus, contributions are not made for disability or maternity benefits. But there may well be premiums for insurance against injury or occupational disease if they are provided for in the text of the agreement.
How to reduce taxes and contributions under a GPC agreement
The issue of tax optimization worries many today. And he did not ignore civil contracts. It should be taken into account that there is a possibility of reducing payments if the customer belongs to a preferential group. Then such a person can use the reduced tariffs legally.
It is also very important to correctly formulate the terms of the contract. That is, so that it is possible to correctly establish without any problems the amount that the customer owes for work and materials. The more specific you are, the fewer problems you will have with the tax authorities later.
When carrying out any activity that involves making a profit, you need to deal with taxes and fees. This will help you not to encounter unpleasant questions from the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation later. And the GPC agreement is no exception.
In addition to the permanent staff enrolled in the enterprise, the employer may attract additional workers on a temporary basis to provide certain services. In this case, the relationship between the parties is regulated by a civil contract.
The proposed material examines how insurance premiums are withheld under a GPC agreement in 2021, taking into account legal norms and general principles of taxation in the Russian Federation.
- Peculiarities of civil law contracts (GPC)
- Are GPC agreements subject to insurance premiums in 2021?
- What insurance premiums are charged under GPC agreements?
- Amounts of contributions under GPC agreements
- How can you reduce the base for insurance premiums?
- Features of payment of insurance premiums under GPC agreements
- Deadlines for payment of contributions from the GPC agreement
- How reporting is generated when paying fees under a GPC agreement
- 2-NDFL
- 6-NDFL
- Payment document for insurance premiums
- Video on the topic of the article
Accounting as part of income tax expenses
Accounting for income tax expenses deserves special attention. The dates on which the certificate of completion of work was received cannot be reflected by the accountant in the costs of purchasing work results, since the drawn up contract does not indicate high-quality and timely provision of services by the counterparty. If the deadlines for completing the work are violated, this will not be taken into account as an error in the accounting department.
Costs incurred by the customer for the purchase of services are recognized as part of the costs for classic areas of activity at the time of signing the relevant act. The cost of work beyond the scope of the main activity of the enterprise is classified as other expenses and is recorded as a debit to account 91. The main entries look like this:
- Dt 20 (26, 44, 91) Kt 76 – carrying out settlement transactions under the GPC agreement;
- Dt 76 Kt 51 – payment of remuneration to the contractor.
Expenses incurred to pay the contractor's remuneration are recognized as expenses that are justified and have documentary evidence. In order to confirm costs that are taken into account for taxation, primary documents are used.
Peculiarities of civil law contracts (GPC)
Expert opinion
Semenov Alexander Vladimirovich
Legal consultant with 10 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
A civil contract is an agreement concluded by an employer with an employee, without the latter being included in the staff of the enterprise, to perform certain work.
The GPC agreement has the following features:
- performing pre-agreed work or providing a service, without taking into account corporate rules and the need to comply with labor regulations at the enterprise;
- determining the deadlines for the fulfillment of obligations by the involved employee;
- setting prices by mutual agreement.
A GPC agreement differs from an employment agreement:
- the fact that the hired employee is not included in the staffing table with a permanent contract;
- no need to provide a workplace.
In this case, the agreement is temporary and does not imply the assignment of wages. Piece remuneration is expected if the work is completed in accordance with the requirements and on time.
The difference between a GPA and an employment contract
When concluding a civil law contract (CLA), it is necessary to carefully ensure that its terms exclude even the small possibility of being classified as a form of employment agreement.
In judicial practice, such requalification is not uncommon, and its consequences are fraught not only with the payment of an administrative fine, but also with additional assessment of insurance premiums and penalties for their late payment. IMPORTANT! Labor relations with an employee are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and civil relations with an individual are regulated by civil law.
To avoid possible problems, the following features must be observed in the terms of the contract:
1. The subject of the GPA is the provision of a certain service, performance of work or transfer of property rights, and not the performance of a labor function by profession. The result of the work should be a tangible result in the form of, for example, a completed project or assembled equipment. Accordingly, the basis for payment is not a time sheet, application or order, but an act of work performed (services rendered).
2. An employee under such a contract is not a full-time employee, which means that he cannot be subject to requirements for compliance with internal regulations and subordination in accordance with the hierarchical structure of the company, as well as standards for setting salaries in accordance with the staffing table. This means that there will be no such conditions in the GPA.
3. The procedure for payment under the GPA is determined by agreement of the parties and is not regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, payment of remuneration is possible only after completion of the work (their stages) stipulated by the contract or transfer of rights to property, unless its conditions indicate the need for an advance payment.
4. Unlike an employment agreement, such an agreement, regardless of its subject matter, status of the parties and special conditions, always has a finite period of validity.
5. In the case of providing services under the GPA, special attention should be paid to the frequency of their provision. If, under the contract, certificates of work performed or services provided are regularly issued for amounts of a comparable amount, this will be considered a clear sign of a disguised labor relationship and will attract the attention of inspectors.
About situations in which the courts regard the GPA as a labor one, read the material “GPA with an individual for the provision of services - the risk of reclassification as a labor one.”
Are GPC agreements subject to insurance premiums in 2021?
The question of whether insurance premiums are charged under civil law agreements interests many.
The legal basis for the procedure for withholding insurance premiums under GPC agreements is determined by the provisions of the current Civil and Tax Codes of the Russian Federation.
The provisions of the listed standards require mandatory payment of contributions for pension and health insurance within the framework of the taxable amount accepted as the calculation base for a civil contract.
Insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund are not subject to payment. An exception applies to injury deductions, the manner of withholding of which may be determined by the terms of the agreement entered into by the parties.
A similar legal procedure is provided for when concluding contract agreements with individuals. This rule must be observed, regardless of the tax system under which the company operates.
The specified legal conditions apply to insurance premiums for the employment of individuals under contract with these employees for the following purposes:
- to perform this or that work;
- when providing services;
- for copyright orders;
- when transferring copyrights to use products.
Note! Insurance premiums cannot be deducted from compensation payments that reimburse the employee for the costs incurred by him in connection with the fulfillment of the terms of the contract.
These accrued amounts are not taken into account in the calculation base and are not subject to insurance premiums, since they are not related to making a profit, but are aimed at compensating for damage suffered by an individual.
Results
Despite the obvious attractiveness of using GPA agreements due to the possibility of charging insurance premiums for the payments they provide for in a smaller amount, their legal component requires accuracy in the wording of the terms of the agreement. For an accountant, the presence of freelance workers will mean the need to carefully collect and study documents confirming the possibility of non-payment of insurance premiums, as well as work together with a lawyer to exclude language from civil liability agreements that implies negative consequences for the business.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 6, 2019 No. 1407
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 28, 2018 No. 1426
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 18, 2019 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 10, 2016 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
- Resolution of the Board of the Pension Fund of December 6, 2018 No. 507p
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What insurance premiums are charged under GPC agreements?
Taking into account the legal framework provided for by law, within the amount payable under the terms of the GPC agreement, the employer is obliged to pay the following insurance premiums:
- according to the compulsory medical insurance system;
- for pension insurance.
Current legal norms exempt the employer from paying insurance premiums related to maternity and temporary loss of ability to work, the recipient of which is the Social Insurance Fund. The parties have the right to separately stipulate the procedure for withholding insurance premiums for injuries (in connection with accidents or occupational diseases), providing for or eliminating the need for these payments.
When determining the tax base, it is important to take into account that the legal norms of relations between the parties under a GPC agreement are regulated not by the Labor Code, but by the Civil Code, and that the involved employee is not part of the company’s staff.
The payment provided for the performance of work under the GPC agreement is necessarily included in the personal income tax base. In this situation, the customer acts as a tax agent, and therefore is obliged to calculate, withhold and transfer the tax to the state treasury.
It is necessary to take into account the peculiarity that such a role does not apply to the customer if we are talking about attracting an individual entrepreneur who will pay the tax himself, based on his own profit.
Expert opinion
Semenov Alexander Vladimirovich
Legal consultant with 10 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
At the same time, the legal norms of the legislation in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation do not detail how to prove that payment under the GPC agreement was made to the entrepreneur.
The personal income tax rate for payments under the GPC agreement is 13 percent, as for any other type of income. An individual is given the right to use the possibility of a standard tax deduction, but within the validity period of the GPC agreement.
The reporting of an enterprise as a tax agent must be submitted no later than the beginning of April in the year following the reporting year. In addition to the annual report, these documents, with increasing indicators, should be submitted every quarter, half year and nine months.
In the 2-NDFL report, which is a standard form for providing information to the tax department, this type of income is indicated by code 2010. The recording date of the specified income is noted on the day the money is paid to the employee.
There is no need to specify personal income tax payment in the agreement itself, since here the parties take into account the requirements of legal regulations.
Considering that payments under GPC agreements are among those that are subject to the calculation of insurance premiums, reporting documentation on these deductions must be submitted by the 30th day of the month following the reporting month.
Since payments under these agreements are not subject to insurance premiums for temporary loss of ability to work and maternity, the specified employee is not included in the number of persons for whom contributions are paid.
The parties must agree in the concluded GPC agreement on the need for the employer to pay contributions for injuries. If such deductions are made, the employee will be protected in the event of injury. Otherwise, he is not covered by the possibility of receiving payments from the Social Insurance Fund in the event of an accident or occupational illness.
If such conditions are provided for in the contract, the relevant data should be reflected in the 4-FSS report. Otherwise, the information is not entered there.
Personal income tax
Russian organizations and individual entrepreneurs are required to calculate, withhold from an individual (counterparty under a civil contract) and pay for him the amount of personal income tax as a tax agent.
This obligation also arises for notaries engaged in private practice, lawyers who have established law offices, and in some cases, for separate divisions of foreign organizations in the Russian Federation (clause 1 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
There is an opinion that the burden of paying tax can be shifted from the organization directly to the individual himself. However, such actions will violate the law, since, as a general rule, this responsibility lies with the organization that pays remuneration under a civil contract.
An exception to this case is payments to individual executors who have the status of an individual entrepreneur or are self-employed. In relation to the latter, this exception can be applied only if there has been no labor relationship between the organization and the self-employed for at least two years. These persons independently calculate and pay personal income tax to the budget.
Personal income tax rates depend on whether the individual - the executor under the contract - is a tax resident of the Russian Federation.
Note: tax residents in 2021 are recognized as individuals who are actually located on the territory of the Russian Federation for at least 183 calendar days over the next twelve consecutive months (clause 2 of Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). An exception is 2021: the minimum period of stay in the Russian Federation has been reduced to 90 days.
The period of a person’s stay in Russia is not interrupted if he travels outside the state for short-term (less than six months) treatment or training, as well as to perform labor or other duties related to the performance of work (provision of services) in offshore hydrocarbon fields.
The tax rate for personal income tax for tax residents of the Russian Federation is 13 percent, for non-residents - 30 percent (clause 1, clause 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). There is also an exception to this rule: if the non-resident person involved in the work is a highly qualified specialist, then the personal income tax rate remains the same - 13 percent.
Note: a highly qualified specialist is a foreign citizen who has work experience, skills or achievements in a specific field of activity (for example, science, medicine, etc.), if the conditions for attracting him to work in the Russian Federation require him to receive a salary (remuneration) in the amount not lower than those established in Article 13.2 of the Federal Law of July 25, 2002 No. 115-FZ “On the legal status of foreign citizens in the Russian Federation”. The minimum monthly salary (remuneration) for such specialists is established by law at a level of 58,500 rubles.
Personal income tax must be withheld from each payment (regardless of whether this amount is a prepayment or an advance payment, as well as in what tax period the final payment will be made after signing the certificate of completion of work/services rendered) - see the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 21 July 2021 No. 03-04-06/46733.
The transfer of the amount of calculated and withheld tax is made no later than the day following the day of payment of income to the taxpayer (clauses 3, 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If a tax agent organization has not fulfilled its obligation to withhold and (or) transfer the amount of tax, it may be held liable in the form of a fine in the amount of 20 percent of the amount subject to withholding and (or) transfer (clause 1 of Article 123 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Amounts of contributions under GPC agreements
The tariff rates for those items of social insurance contributions that the employer is subject to under these agreements are no different from similar deductions in any other situations.
In accordance with Art. 425 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the legal framework of the legislation requires the withholding of such insurance premiums:
- within the framework of mandatory pension payments - 22 percent of the limit specified by law, with an addition of 10 percent of the excess of this amount;
- for compulsory health insurance – 5.1 percent, regardless of the amount of deductions.
The procedure for calculating insurance premiums is easier to understand using a specific example.
Taking into account the tariffs established by legal norms, the amount of contributions will be:
If the employer resorts to reduced tariffs, the specified limit on contributions to the Pension Fund does not apply.
Reduced tariffs may be assigned in situations where similar conditions apply to full-time personnel. This possibility is provided for certain categories of employees, the list of which is quite limited and approved by law.
With a reduced tariff, the amount of contributions can be reduced to 15 percent.
It’s more complicated with legal regulations regarding additional tariffs. An increase in contributions is expected if the work offered to the employee under a civil process agreement involves an increased degree of harmfulness or danger and corresponds to certain professions that fall under a similar list.
In this case, contributions increase in accordance with the amounts provided for by law.
How can you reduce the base for insurance premiums?
When calculating the base for insurance premiums, you should adhere to certain limits that provide for the appointment of additional payments.
The following limits are established for pension insurance (depending on the year, in thousands of rubles):
- 2019 – 1 150;
- 2020 – 1 292.
In practice, organizations resort to various tricks to comply with legal regulations and reduce the size of the tax base. Instead of a regular GPC agreement, a mixed agreement may be concluded that has features of both types of documents.
For example, hiring a citizen to sell products may involve, in addition to these responsibilities, installation and configuration of equipment.
Considering that contributions are not paid under lease agreements and in relation to purchase and sale, there is no need to highlight services as a separate item. In this case, the tax base will be uniform.
Expert opinion
Semenov Alexander Vladimirovich
Legal consultant with 10 years of experience. Specializes in the field of civil law. Member of the Bar Association.
But if you indicate that the subject of the contract involves the involvement of a specialist not in the profession, but, for example, to sell a dress, insurance premiums will not be withheld.
Features of payment of insurance premiums under GPC agreements
As follows from the above-described features of the taxation of payments under GPC agreements with insurance premiums, the following points must be taken into account:
- deductions can be withheld solely from agreements for the performance of work or provision of services, or for the transfer of intellectual property rights;
- GPC agreements on property transactions (purchase and sale or lease) concluded with volunteers or involving the provision of services outside the Russian Federation are excluded from the list subject to withholding of contributions;
- Only payments to the Pension Fund and Compulsory Medical Insurance are withheld;
- contributions for injuries are deducted if such a condition is provided for in the contract;
- When assigning deductions, standard tariff rates are applied, with the use of general established limits, increased or reduced tariffs.
There are no other differences in the deduction of insurance premiums under GPC agreements. If the legal situation does not imply insurance payments, this is not reflected in the reporting documentation.
Peculiarities
The conclusion of such an agreement is associated with some nuances:
| The need to pay taxes | The GPC agreement does not relieve an individual from the need to pay taxes and other deductions. This function is undertaken by the employer. The exception is when the contractor is an individual entrepreneur. This means that he pays the fees himself. |
| Validity | The deadline is indicated based on the time spent by the performer on solving a specific task. As a rule, such contracts are recognized as short-term. Concluding several agreements in a row with one contractor can be considered an employment contract. The duration of the contractor’s work is counted as length of service, since he pays insurance premiums. |
| Entry in the work book | There is no need to sign up for employment. This is done only when concluding a full-fledged contract with a specialist for a long period. |
| Conclusion procedure | The contract is drawn up and signed by the parties with prior agreement on each item. The document is drawn up in two copies, one each for the customer and the contractor. Any disputes arising during the execution of work must be resolved on the basis of the provisions of the contract and the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. |