The contribution to the authorized capital is the funds contributed by the founders of the organization to carry out business activities. Authorized capital (AC) can be contributed in cash, property, rights of use and represents the amount of assets with which the enterprise is liable to its creditors, and also shows the share of each founder in the total property.
When leaving the business owner, the founder returns the share he contributed as an investment. The size of the initial investment is determined by the participants when creating the company and is indicated in the constituent documents (agreements).
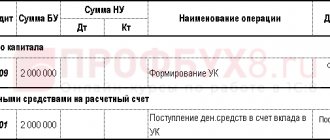
Accounting is maintained on account 80 “Authorized capital”. An increase in the account is calculated on the credit of the account, and a decrease on the debit. The contribution to the authorized capital of the posting is formed by the credit of account 75.01 and the debit of the accounts for accounting for contributed assets.
The authorized capital has been formed and declared - what posting is necessary?
Commercial legal entities (PJSC, JSC, LLC, business partnerships, state unitary enterprises, municipal unitary enterprises) are created with the mandatory formation of an authorized capital (MC).
The size of the management company, the share of participation in it of each of the founders, payment terms, form of contributions and assessment of non-monetary contributions are stipulated in the constituent agreement. The authorized capital is the starting amount of funds with which a legal entity begins its activities. After completion of all activities for making contributions to the authorized capital, postings begin with the corresponding entry made on the date of its registration. It should reflect the accrual of the full amount of the capital provided for by the charter, in correspondence with the debt of the founders on contributions to it: Dt 75 - Kt 80.
Analytics on account 80 (accounting capital account) is organized according to:
- founders (participants);
- stages of formation (in PJSC, JSC and business partnerships);
- types of shares (in PJSC and JSC).
Account 75 is the account for settlements with the founders. The debit balance of its subaccount, reserved for settlements of contributions to the capital account, will show the amount of the unpaid capital account.
For information on how the capital account will be reflected in accounting, read the article “Procedure for drawing up a balance sheet (example)” .
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how the authorized capital is paid. If you have an LLC, this Ready Solution will help you. If AO, this material is for you. If you do not have access to the K+ legal reference system, get a trial demo access for a while. It's free.
Retained earnings: entries
Operations carried out on account 84 and necessary to account for retained earnings and uncovered losses are carried out at the end of the year. NP is reflected by credit turnover, and NU by debit turnover. In both cases - according to account 84 in correspondence with account 99. In the latter, by the way, the financial result is displayed throughout the year.
In this regard, we recall that the accountant must make closing entries with the following content at the end of each month:
| Dt | CT | Operation description |
| 90.9 | 99 | Profit from core activities is taken into account |
Or:
| 99 | 90.9 | The loss incurred from the main activity is taken into account |
Or:
| 91.9 | 99 | Profit received from other activities is taken into account |
Or:
| 99 | 91.9 | The loss arising from other activities is taken into account |
When the year ends and the balance sheet accounts are closed, the ending balance of account 99 should be transferred to the retained earnings account by posting:
| Dt | CT | Operation description |
| 99 | 84 | The company's emergency is taken into account |
Or
| 84 | 99 | The company's loss is taken into account |
As a result of postings at the beginning of the next year, account 99 should be reset to zero. This sequential closing of accounts with the writing off of retained earnings to account 84 and revealing the result is called balance sheet reformation.
Contribution to the capital of another organization from its founder
A commercial legal entity can be created by both individuals and organizations. At the same time, foreigners may be present among both.
By participating in the creation of a legal entity, the founder assumes obligations to pay for the contribution to its management company, in return acquiring the right to part or all (depending on the share of participation) of the property of this legal entity and to receive income from participation in its activities. There is a peculiarity here: when posting, the authorized capital must be reflected both for the founder and for the company receiving the contribution.
On the date of registration of the newly created organization, the founder - a legal entity registered in the Russian Federation, in its accounting shows the debt for the amount of the contribution to the capital specified in the founding agreement, which for it is a financial investment: Dt 58 - Kt 76. Credit balance on the subaccount of account 76, allocated for calculations of contributions to the management company, will show the amount of the management company unpaid by the founder.
The legislation allows payments to the management company both in money and in property or property rights. On the date of making the contribution (the full amount or part thereof), both the founder and the legal entity established by him are repaid the corresponding part of the existing debt.
Legal regulation
The regulation of legal relations regarding deposits in the management company is carried out on the basis of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Article 51) and Federal Law No. 14-FZ of 02/08/1998.
14-FZ allows for an increase in the authorized capital by making additional contributions from the founders. The decision to make additional contributions must be notarized.
In addition to Federal Law No. 402 “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011, accounting operations for making contributions during the development of organizations are regulated by the following regulations:
| PBU 9/99 | Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 32n dated 05/06/1999 |
| PBU 6/01 | Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 26n dated March 30, 2001 |
| PBU 10/99 | Order No. 33n dated 05/06/1999 |
| Chart of Accounts | Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000 |
Authorized capital – depositing funds into the current account and cash register
The easiest way to make a deposit is to pay it in money: to a current account or to a cash desk. For foreign participants, payment to a foreign currency account is acceptable.
Postings for contributions to the authorized capital in cash will be as follows:
- at the payee: Dt 50 (51, 52) – Kt 75;
- for the Russian founder: Dt 76 – Kt 50 (51).
Find out how to determine the amount of authorized capital in ConsultantPlus. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
The essence
The authorized capital is the amount that the founders contribute after registering the company. It is displayed in the liability side of the balance sheet, since it is the source of the formation of assets. The founders can make contributions in the form of cash, non-cash funds, materials, fixed assets. The activities of the enterprise are financed from the funds of the management company.
For lenders, this value is a kind of guarantee of return on investment in the event of bankruptcy of the borrower.
Contribution of property
Any type of property and rights to it can be transferred to the deposit: fixed assets, intangible assets, inventories, securities, debt on borrowed funds. The parties transfer the property contributed to the management company at the value agreed upon by them in the constituent agreement. At this value, the contribution is taken into account in accounting. For a contribution to the authorized capital formed in this way, entries are made to the recipient at the cost reflected by the founder. The founder, when forming the amount of the contribution made to the management company, adjusts the actual value of the property to the value agreed upon at the expense of other income and expenses (account 91). Regardless of the cost, records of property received by a legal entity are kept as part of the same type to which it belonged to the founder.
If the transferred property was subject to VAT upon acquisition, and it was presented to the budget, then the founder shall restore the tax either in full or in proportion to its residual value (for depreciable property). Recovered VAT is included in the deposit amount and is indicated in the transfer documents. The transferring party pays it to the budget, and the receiving party can take it as deductions.
The contribution to the authorized capital formed by the property is accompanied by the following transactions:
- For the receiving party:
Dt 07 (08, 10, 11, 21, 41, 58, 66, 67) – Kt 75 - property received;
Dt 19 - Kt 75 - accepted for VAT accounting on it.
- From the founder:
Dt 02 (05) – Kt 01 (04) - the residual value of the disposed depreciable property is formed;
Dt 76 – Kt 01 (04, 10, 11, 21, 41, 58) - property transferred;
Dt 76 - Kt 68 - VAT on transferred property has been restored;
Dt 76 - Kt 91 (or Dt 91 - Kt 76) - the value of the transferred property has been brought to the agreed value.
If you have access to ConsultantPlus, check whether you have correctly reflected the contribution to the management company with property. If you don't have access, get a free trial of online legal access.
Decrease in capital
The minimum amount of capital is regulated by law. Its value is calculated according to the minimum wage and depends on the form of ownership of the enterprise:
- LLC - 10 thousand rubles;
- CJSC - 100 minimum wage;
- OJSC - 1000 minimum wage;
- municipal enterprises - 1000 minimum wage;
- state enterprises - 5000 minimum wage.
The founders may decide to reduce the amount of their own funds by reducing the price of shares or repurchasing the Central Bank. As a result, the participant is paid a remuneration in the amount of the difference between the original and new costs. Income received as a result of reducing the capital capital by changing the value of the share is subject to personal income tax.
If the company has purchased the shares, they cannot be distributed among the owners. The Central Bank must be sold or canceled and, according to general rules, changes must be made to the constituent documents.
Increase in capital: contribution in cash or property
The legislation allows for an increase in the capital capital by decision of its founders (participants) if the following conditions are met:
- the PJSC or JSC has registered an additional issue or conversion of shares in the SBRFR and the Federal Tax Service;
- not only the initial charter capital is fully paid, but also the part by which the increase occurs.
Sources of increase in capital can be:
- retained earnings of a legal entity or its additional capital - in this case, additional payments from the founders (participants) will not be required;
- funds of participants: one, if it is accepted additionally, single or several, if they increase the share of their participation, or all, if the increase in share occurs due to a proportional increase in existing shares or par value of shares.
The procedure for accounting for the accrual and payment of additional contributions to the capital company when it increases is absolutely the same as that used when creating a legal entity. The founders (participants) determine the amounts, form and terms of payment in their decision. Entries for the accrual of obligations are made on the date of the decision to increase the capital and on the date of registration of changes in the charter, and entries for payment - on the actual date of transfer of funds or transfer of property (property rights).
Read about the nuances of taxation of contributions to a management company in the material “ List of income not taken into account when establishing the size of the profit base in accordance with Art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation " .
Taxation
The rules for taxation of contributions are specified in Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 07-05-06/302 dated December 19, 2006.
Contributions to the management company do not form a tax base either for profit tax (clause 3, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), or for value added tax (clause 4, clause 3, article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition to money, the founders can contribute their share of the capital through property. In such cases, it is necessary to evaluate the property involved. If the value of the property share is more than 20,000.00 rubles, then for the assessment it is necessary to involve an independent expert and obtain a special opinion from him.
If the value of the property contribution is less than or equal to 20,000 rubles, then the monetary value of such OS is determined at the general meeting of the founders and is confirmed by a unanimous decision of all participants.
Making property investments does not create profit or loss either for the shareholder or for the issuer of shares or shares (clauses 1 and clauses 2 of clause 1 of Article 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The taxpayer receives property rights as payment for the shares provided to him, and the shareholder, in turn, transfers his property to receive certain shares of the issuer.
Thus, the calculated difference in the value of the contributed property and the nominal value of the share in the structure of the management company does not affect the taxable base for income tax.
A similar situation arises with the VAT taxation of property investments - the provision of property as a share of the management company is not considered a sale, and therefore is not subject to value added tax (clause 4, clause 3, article 39, clause 1, clause 2, article 146 Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, according to clause 11 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the issuing taxpayer has the right to deduct the VAT restored by the founder or shareholder.
When an accountant determines the property tax base for fixed assets accepted as an investment in the capital company, he must take into account the cost of such fixed assets according to accounting data (Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-05-05-01/80 dated 03.10.2011). The property invested in the charter capital is accounted for at the cost reflected in the balance sheet in accordance with PBU.
Founder's financial assistance
If a company is experiencing financial difficulties, it can be very difficult for it to obtain bank loans. Moreover, such loans, due to high interest rates, can only worsen the situation. In such cases, it is possible to provide assistance from the founders themselves, who are able to provide financial resources on more favorable terms and often save the enterprise from liquidation.
Such financial assistance can be provided in various forms, which determines the way it is accounted for.
Providing financial assistance from the founder:
- Loan of funds (interest-free or with interest accrual)
- Transfer of financial assets or property free of charge
- Transfer of funds by contribution to the capital or property of an enterprise
Financial assistance in the form of a loan
In the case of financial assistance that involves its subsequent repayment, it is issued in the form of a cash loan provided by the founder of the enterprise. For this purpose, a loan agreement is drawn up. When drawing up an agreement, the parties are guided by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The agreement for repayable financial assistance from the founder must reflect the interest rate for using the loan. If the interest rate is not specified, it is considered equal to the current refinancing rate and requires clarification on a monthly basis.
In practice, founders most often provide interest-free loans to their enterprises, which should also be reflected in the contract. According to the Tax Code, borrowed funds received or returned are not included in income (expenses) and are not subject to inclusion in determining income tax. Moreover, with an interest-free loan, the material benefit resulting from the interest savings is also tax-free.
The agreement may also stipulate other conditions, such as: the purpose of using the financial assistance received, the term and procedure for repaying the loan, as well as other clarifications.
The accounting procedure for repayable financial assistance from the founder in the form of a loan depends on the period of provision of funds and the account to which they will be transferred. For loans for a period of no more than a calendar year, the account “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings” (66) is used, for the rest - the account “Settlements for long-term loans and borrowings” (67). Funds are posted to the debit of account 50 “Cash” or 51 “Cash accounts”.
Postings for accounting for financial assistance in the form of a repayable loan:
D51 (50.52) K66 (67) – receipt of a loan issued by the founder;
D66 (67) K51 (50.52) – return of financial assistance to the founder (loan).
Free transfer of financial assistance
The gratuitous transfer of financial resources or property is the most convenient and used way for the founders to provide real assistance to the enterprise. Such assistance involves the provision of funds on a non-repayable basis. However, these funds will not be taken into account in the founder’s share in the assets of the enterprise (authorized capital).
The decision to provide this type of financial assistance is made at a general meeting or individually (with a single founder) and is documented. According to the Tax Code, if the founder’s share in the capital is more than 50 percent, then the funds received are not included in income and are not taxed. Otherwise, they are reflected in the tax base as non-operating income.
The accounting procedure for gratuitously received funds depends on the purposes specified in the written decision to provide financial assistance. In accordance with the Chart of Accounts and Instructions for their application, to account for assets transferred free of charge to the organization, an additional sub-account “Gratuit Receipts” (98-2) is created in the “Deferred Income” account (98). Paragraph 8 of PBU 9/99 contains an instruction to reflect these funds as other income (subaccount 91-1).
Funds received from the founder are considered income from an accounting point of view, but the income tax base does not increase. Therefore, a difference arises in accounting, forming a permanent tax asset. It must be reflected in the accounting accounts.
Let's look at the procedure for receiving gratuitous financial assistance from the founder using the following example.
Example:
CJSC Spetsstroy received gratuitous assistance in the amount of 10,000,000 rubles from the founder, who owns 51 percent of the shares. Transactions for receiving gratuitous financial assistance will look like this:
D51 K98-2 –10,000,000 – receipt of free assistance;
D98-2 K91-1 – 10,000,000 – funds are accounted for as other income;
D68 K99 – 2,000,000 (20% of 10,000,000) – permanent tax asset.
Reduction methods and corresponding postings
When there is an obligation to reduce, situations are divided into two groups:
- Part of the Criminal Code is not actually paid and must be cancelled. These are shares (shares) at the disposal of the business entity. They are taken into account in account 81. When conditions arise for reducing the capital, a posting is made for them Dt 80 Kt 81.
- The activities of the legal entity are unprofitable or ineffective, as shown by the ratio of the net asset value to the capital asset. By reducing the capital in this case, the loss is covered or the retained earnings are increased by the amount missing to pay off the share in the LLC: Dt 80 Kt 84. In relation to each participant (shareholder), there will be a commensurate decrease in his share or the nominal value of the shares.
Procedure for changing and leaving a founder from an LLC
The founder's withdrawal is a procedure that represents the termination of the participant's obligations to the company. In this article we will understand how the founders of an LLC leave the company, how to change the founder, and how to become one.
The procedure for the founder to leave the LLC
A participant’s exit can occur in two scenarios:
- By the participant himself on a voluntary basis upon a written application addressed to the head of the body, in accordance with the Charter, which determines the composition of the founders. This may be the general director - the executive body, or the chairman of the constituent meeting.
- The founding meeting of the company or the general director. As a rule, in this case, the founder refuses to leave his post and the management of the company must file a claim in court to deprive the participant of the right to own and manage the company.
The procedure for exclusion from the list of founders is subject to registration with the tax authority with mandatory amendments to the constituent documents of the company. It is also worth considering that the participant’s share in the authorized capital is transferred to the company and is subsequently distributed among the founders or put up for sale. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation obliges the company to pay the withdrawing participant the full value of his share in cash or property within 3 months from the date of filing his application or the date of issuance of the court decision, unless otherwise provided by the Charter of the organization. It is important to remember that the law prohibits the removal of the sole founder or all founders simultaneously from the LLC.
Documents for leaving the founders of an LLC
After receiving an application from a participant, an accountant or lawyer must collect the necessary package of documents and submit it to the tax authority within 1 month. Documents required to register changes in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities:
- application on form 14001 (notarized)
- minutes of the meeting on changing the composition of LLC participants or the decision of the sole participant, if only one founder remains
- application for withdrawal from LLC
- original passport of the applicant (the tax inspector makes a copy and returns the passport)
Documents can be submitted in person or by mail, but as practice shows, it is better to submit them in person.
Documents on making changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities will be ready in 5 working days. You can receive them by proxy in person or expect to receive them by mail. The last step in the withdrawal of the founder from the LLC is the payment to the withdrawing participant of his share.
Change of founder in LLC
Often, the withdrawal of the founder from the LLC coincides with the entry of new participants into the company. How to change the founder in an LLC? In this case, it is recommended to proceed in the following order:
- First, accept new members.
- Withdraw the required participants.
This algorithm for replacing a founder in an LLC is especially relevant in cases where it is necessary to change the sole founder. Moreover, this procedure is more consistent with the concept of change.
The process of removing a founder was discussed above, now we will learn more about the procedure for including new participants.
How to become a founder?
In order to become a member of an LLC, you must adhere to the following procedure:
- Those wishing to become founders of the company submit applications indicating the expected size of the share and the option of contributing the share (cash or property).
- The minutes of the general meeting or the decision of the sole participant approves the new composition of the founders of the LLC.
- Within three days, a package of documents is submitted to the Federal Tax Service to register changes in the constituent documents:
- Charter of the new edition in two copies
- Form 14001 (notarized)
- Extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities
- Minutes of the meeting or decision of the sole participant to change the composition of the founders of the LLC
- Certificate of state registration of LLC
- Receipt to confirm payment of state duty
After five working days, you must collect from the tax authority documents confirming the changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
Now you can safely move on to the procedure for removing the founder(s) from the LLC.
Important: the documents are signed by the participants in the new composition, as well as by the new director, if there has been a change in the head of the executive branch.