How is VAT taken into account when leasing?
VAT on a leasing agreement in 2021 has rates: 0% (zero) and 20%.
They depend on the type of property that is leased. Article navigation
- VAT on leasing under the simplified tax system
- VAT on leasing from individual entrepreneurs
- VAT from the lessee
- Tax deduction for leasing
- VAT on assignment
- VAT on early repayment of leasing
- VAT from the lessor
- Postings for VAT under a leasing agreement
- VAT postings from the lessee
- VAT postings to the lessor
The lessee makes leasing payments for the possession and use of the entrusted fixed asset (FPE). They include the lessor's expenses for the acquisition of the necessary property, his commission, and other costs associated with the fulfillment of obligations. These amounts, by their characteristics, are subject to VAT, therefore the contractual value must be increased by the amount of VAT.
VAT on a leasing agreement in 2021 has rates: 0% (zero) and 20%. They depend on the type of property that is leased.
If the leasing company is on a simplified taxation system, then leasing payments are not subject to VAT. In all other cases, the corresponding VAT rate is applied.
Below we will talk about how to determine whether leasing is subject to VAT, in what order this is carried out and about other features of accounting for financial leases.
Related costs
The use of property is associated with associated costs - repairs, service, insurance, etc. The leasing recipient can take into account all these expenses in his costs without special indication in the agreement. The only exception is insurance costs.
This asks for a statement in the agreement that insurance costs are borne by the lessee. Current costs, as well as the costs of all types of repairs, are borne by the leaseholder. Repair costs are included in other costs in the reporting tax period in which they were carried out. At the same time, tax costs reduce the costs incurred.
And in relation to insurance in Art. 21 of the Tax Code of Russia does not establish the rule about who pays for insurance of assets (for example, a car), so a clause is needed in the agreement. If it is present, the leasing recipient takes into account the costs of insurance when taxing income.
Moreover, if the leased property is on the balance sheet of the lease recipient, then these costs are written off on the basis of subclause 3 of clause 1 of Art. 263 of the Tax Code of Russia.
And if the assets remain on the lessor’s balance sheet, then the basis for accounting for insurance costs will be subclause 7 of clause 1 of Art. 263 Tax Code. In both situations, insurance costs are recognized at the reporting time in which money was transferred from the cash desk to pay for insurance.
But if the agreement is concluded for a period of more than three months, the amount of insurance payment must be determined according to the number of calendar days of the agreement in each reporting period and calculated evenly.
VAT on leasing under the simplified tax system
The simplified tax system is a special regime, exempt from VAT (Chapter 26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). There are significantly more simplified lessees than lessor companies that are on the simplified tax system. This is due to the fact that there are restrictions in the application of this taxation system and they depend on the company’s income and the share of legal entities in the authorized capital.
The lessor can issue VAT invoices using the simplified tax system - in this case, he is obliged to pay the entire amount to the budget. He cannot offset VAT on the acquired property. The legislation does not provide him with such a right. A lessee who has chosen the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” takes into account the VAT received upon transfer of a fixed asset as part of its cost. The same condition applies when accounting for rental services under a leasing agreement.
The property is on the account of the leasing company
If the property is in the account of the lease recipient, the Tax Code allows him to begin depreciating such assets. In this case, depreciation charges can be calculated with a large coefficient, and the initial price will be equal to the amount of costs for the purchase of assets made by the lessor.
This means that in the leasing agreement, if it provides for the transfer of assets to the lessee’s balance sheet, it is imperative to indicate the price of the assets and the obligations of the lessor to transfer papers on the amount of costs for its purchase, delivery, and bringing it to the required condition.
Depreciation charges accrued by the leasing recipient will reduce his taxable income in the general manner - every month, based on the accrued amounts in the same way as on his own money.
But then, when taking into account the leasing payment, it will need to be reduced by the amount of monthly depreciation. And if the cost of the redemption is allocated as part of the leasing payment, then the payment, which is taken into account in the costs, is reduced by it.
The transfer of the leased property to the balance sheet of the lease recipient entrusts him with another tax obligation - to pay the asset tax. As for VAT, it is deducted in the same manner as when accounting for the leased asset in the lessor’s account.
VAT on leasing from individual entrepreneurs
If an individual entrepreneur is under the general taxation regime, then he is a VAT payer. The accounting rules for leasing transactions are the same as for the lessee in the LLC form.
An individual entrepreneur cannot be a lessor, since leasing companies are defined by law as commercial organizations with several founders.
If an individual entrepreneur is on special regimes (UTII, simplified tax system, patent) - he is a VAT non-payer. They do not pay VAT on the sale of goods and services, therefore, there is no reason to reimburse it from the budget.
Accounting and tax accounting
Accounting and tax accounting is reflected in the lessor's account - in the amount of the minimum lease payments and the non-guaranteed liquidation price, minus the material income that is to be received, with the recognition of profit from the sale of non-current property.
At the same time, the residual price of the material leasing object is removed from the balance sheet from the sold non-current property. The material income of the lessor is a variation of the amount of rental payments and the price of the leased object and the current price of the prescribed amount, determined at the interest rate.
A financial lease asset recognized as being held for sale is reflected by the lessor in accordance with PBU 27. The lessor's costs for signing the lease agreement are recognized as other costs of the necessary reporting time.
Accounting
When receiving a car under a leasing agreement, it is important to determine who will have the car on their balance sheet.
If the leased property is included on the balance sheet by the lessor, the leaseholder reflects the assets off-balance sheet in account 001 “Leased fixed assets” in the valuation specified in the leasing agreement.
VAT from the lessee
Leasing payments include VAT, which, based on Art. Art. 171, 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the enterprise can offset it from the budget. The monthly payment under the contract includes not only the redemption amount of the equipment, but also the services of the lessor. In this case, the amount of VAT to be offset will be higher than when applying for a loan from a bank. If supporting documents are correctly prepared, VAT on leasing is refundable in full.
However, in practice there are cases when the tax office tries to separate the VAT from the lease payment in the context of rent and payment of fixed assets. But the Ministry of Finance, in letters dated November 15, 2004 No. 03 - 04 - 11/ 203, dated November 23, 2004 No. 03 - 03 - 01 - 04/ 1/ 128, clarified the impossibility of such a division and confirmed the organization’s right to use the deduction in full . Since 2004, Russian arbitration courts have adhered to the same conclusion.
When the property under a leasing agreement is on the balance sheet of the lessee, VAT is deducted monthly. Based on the invoice, the deduction amount is entered into the purchase ledger.
Tax deduction for leasing
A tax deduction is an amount by which payments to the budget can be reduced. The deduction is mainly applied in relation to VAT. The amount of payment of value added tax is reduced by the amount of goods and materials received or services provided.
The leasing system is structured in such a way that the budget must always return VAT to the leasing companies. When paying suppliers for expensive property, they repay VAT on its full cost. After leasing the equipment, the company receives payments significantly less than its value. Thus, the VAT deduction on leasing from the lessor is always greater than the payment.
Reimbursement of VAT when leasing from a lessee in the case where the property is transferred to the recipient’s balance sheet is also fraught with problems. The condition for VAT reimbursement is the fact that inventory items are credited to the organization’s balance sheet or services are provided to it. In this case, companies constantly have VAT to reimburse under the leasing agreement until its expiration.
Problems of VAT refund from the budget arise in cases where the taxpayer cannot provide a complete package of documents or some of them do not comply with the requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Leased property must be fully involved in activities subject to VAT. Then the tax on rental payments is refunded in full. Sometimes an organization conducts its activities in several directions, including those that are not subject to VAT. In this case, the tax on leasing payments is subject to proportional distribution to all types of production. VAT on preferential activities is not deductible.
How to return VAT on leasing
When filling out a VAT return, VAT on leasing payments is subtracted from the amount of tax accrued on sales and advances. In the case when the amount of VAT deduction exceeds its amount payable, according to Art. 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, this amount can be submitted for reimbursement, that is, returned from the budget.
VAT refund on leasing is possible only if the following conditions are met:
- the invoice issued by the lessor complies with the requirements of Art. 169 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- there is confirmation of payment;
- the property is accounted for by the lessee;
- the fixed asset is used by the organization in activities subject to VAT.
To return the amount from the budget you must:
- Write an application to the Federal Tax Service for a refund in any form indicating the amount.
- Provide a leasing agreement, a certificate of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets, documents confirming payment of monthly payments.
- Record the refund amounts in the purchase ledger.
- Submit invoices, work completion certificates, completed in accordance with the law.
An enterprise may be denied a VAT refund if it is in the process of bankruptcy, if the payment under the agreement was made with bills of exchange, assignment agreements or with loans.
VAT on assignment
The assignment of a lease is an assignment. The need for this action arises in most cases due to the insolvency of the lessee. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the transfer of rights to property is subject to VAT.
In case of an assignment agreement, the tax base is established on the basis of Art. 154 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The value is defined as the difference between the amount of the original contract and all payments under it, including advance payments.
According to Art. 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a new party to the agreement can claim VAT for deduction on the amount of remaining payments under the leasing agreement if there is an invoice.
VAT on early repayment of leasing
When purchasing leased property early, accounting features arise for both the lessee and the lessor and they depend on whose balance sheet the object was recorded on.
If the parties have agreed that the lessor accounts for fixed assets on its balance sheet, then early repayment requires postings in the following sequence:
- The lessor writes off the initial cost of the asset, depreciation charges, and residual value; carries out other sales for the amount of early repayment; allocates VAT for payment to the budget.
- The lessee reflects the transfer of ownership; calculates the amount of early payments based on the invoice, indicating the FPR (deferred expenses) on the account, and allocates VAT from it. In this case, the VAT amount is set for reimbursement, and the amounts according to the terms of the contract are debited from the RBP account to the cost accounts.
If the parties have agreed that the lessee takes fixed assets into account on its balance sheet, then early repayment is recorded as follows:
- The lessor transfers the asset to the lessee, charges early payments, issues an invoice, and charges VAT to the budget.
- The lessee performs the actions described in two paragraphs above.
In both described cases, the transaction is not an advance payment and VAT is offset from the budget or paid on the basis of an invoice.
VAT calculation if no changes are made to the contract
The preferential VAT rate of 10% will remain in 2021.
Therefore, organizations that sell goods subject to VAT at a rate of 10% will apply the tax in the same manner. Also, the changes will not affect the 0% VAT rate for transactions specified in Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in particular, when selling goods for export and providing international transportation services.
Changes to clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (increase in VAT by 2%, i.e. from 18% to 20%) come into force on January 1, 2021 (clause 3 of Article 5 of Law No. 303-FZ) . At the same time, the new VAT rate (20%) will be applied to goods (work, services) shipped from 01/01/2019 (clause 4 of article 5 of Law No. 303-FZ). The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation clarified that for calculating VAT at a rate of 20%, the date of conclusion of contracts does not matter (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06.08.2018 N 03-07-05/55290).
Thus, even if in 2021 or earlier the seller received an advance and calculated VAT on it at the rate of 18/118, when shipping goods (work, services) from January 1, 2021, he is obliged to present to the buyer and calculate VAT at the rate of 20% (of course , if this product is not subject to VAT at a rate of 10% or 0%). In this case, VAT calculated upon receipt of an advance payment received in 2021 is taken as a deduction in the amount of tax calculated from the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services provided), in payment for which the amount of the previously received advance payment is subject to offset according to the terms of the agreement (if any conditions) (clause 8 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Example 1. In 2021, the contractor received an advance payment for the provision of services - 118 rubles, calculated VAT - 18 rubles. (118*18/118). Services will be provided in 2021, the cost of services (by agreement of the parties) was 120 rubles. (including VAT 20%). When providing services in 2021, the contractor will calculate and present to the customer VAT in the amount of 20 rubles. (120*20/120).
At the same time, VAT calculated upon receipt of an advance in the amount of 18 rubles. it will be deductible on the date of provision of services in 2021 (i.e., in accordance with clause 8 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT calculated at the rate of 18/118 from the amount of the advance credited as payment for services rendered is accepted for deduction in our example with 118 rubles). The customer will pay an additional 2 rubles for services provided in 2021.
Many taxpayers who are now entering into long-term contracts want to stipulate in them that a 20% VAT rate is applied to goods (work, services) shipped (performed, rendered) from January 1, 2021.
According to the author, when concluding contracts (additional agreements) in 2021, it is better not to indicate a specific VAT rate. The fact is that in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 422 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the contract must comply with the rules obligatory for the parties, established by law and other legal acts (imperative norms) in force at the time of its conclusion.
Law No. 303-FZ, which increases the VAT rate from 01/01/2019, in this part comes into force from 01/01/2019. Therefore, formally, the parties have no reason to stipulate a 20% VAT rate when concluding an agreement in 2021. At the same time, the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation do not limit the parties in establishing the procedure for determining the price of goods (work, services) taking into account tax.
So, if the delivery of goods will be carried out in 2021, the contract can indicate that “the cost of the goods is 120 rubles. (including VAT at the rate established by clause 3 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).” The wording of the conditions may be different. For example, you can stipulate that “the cost of goods is 100 rubles. excluding VAT.
At the same time, since the norms of civil legislation do not apply to tax legal relations (clause 3 of Article 2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), according to the author, the parties to the contract, having established the price of goods (work, services), have the right to indicate at what VAT rate this tax will be charged to the buyer in accordance with the tax legislation in force at the time of execution of the contract. But unfortunately, the author was unable to find any judicial practice on this issue.
What do the parties risk if, when concluding an agreement in 2021, they indicate a VAT rate of 20%, included in the price of goods (work, services) shipped from January 1, 2021?
According to the author, tax risks do not arise under such contract conditions. In such a situation, only civil legal risks are possible, i.e. the risk of the transaction being declared invalid, but it is practically zero.
If the terms of the contract do not comply with the legislation in force at the time of conclusion of the contract, the transaction is voidable (clause 1 of Article 168 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), i.e. there is a risk that one of the parties to the transaction will challenge its conclusion in court, i.e. the contract may be declared invalid (clause 1 and clause 2 of Article 166 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
According to the author, the indication in the contract that “the cost of goods shipped from 01/01/2019 is 120 rubles, incl. VAT 20%" does not violate the rights of the buyer, since at the time of execution of the contract it will comply with the law, and most importantly, regardless of the VAT rate, the cost of goods is agreed upon and in our example is 120 rubles. Those.
Thus, from the above, we can conclude that it is better not to indicate a specific VAT rate in the contract. But if the parties nevertheless agreed in 2021 on the cost of goods (work, services) shipped from January 1, 2021, indicating a VAT rate of 20%, then, according to the author, the risks of such contracts being invalidated tend to zero.
If the concluded agreement, which will be in force in 2019, stipulates a VAT rate of 18%, then in order to avoid disputes with counterparties about the cost of goods (work, services) that will be shipped from 01/01/2019, it is necessary to draw up an additional agreement to the agreement, establishing a new cost of goods (works, services) taking into account the rate of 20%. Moreover, it is not necessary to increase the cost of goods (work,...
In other words, it is possible that the parties will want to keep the same price, but taking into account 20% VAT. For example, the cost of services is currently 118 rubles, including 18% VAT. The parties to the agreement agreed that from January 1, 2021, the cost of services is 118 rubles, including 20% VAT. Or they could set the cost of services at 120 rubles. (and more or less), including 20% VAT.
When concluding additional agreements in 2021, as already mentioned, it is better to set the cost of goods (work, services) without specifying a specific VAT rate of 20%, i.e. it is better to make a reference to the rate established by clause 3 of Art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Note! Even if the cost of goods (work, services) that will be supplied in 2021 in the contract (or invoice) is agreed upon with a VAT rate of 20%, upon receipt of advance payment in 2021 there are no grounds for applying the VAT rate of 20/120, since changes in p. .3 art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation have not yet entered into force. Therefore, when receiving an advance payment for the supply of goods (works, services) before 01/01/2019, VAT is calculated at the rate of 18/118, even if upon their shipment VAT will be charged at a rate of 20% and this rate is provided for in the contract.
Victoria Varlamova Deputy Head of Consulting Department, Chief Tax and Accounting Expert
Example 2. The contract for the provision of services in January 2021 was concluded in 2018. The cost of services is 120 rubles, including VAT at the rate established by clause 3 of Art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In December 2021, a 100% advance payment in the amount of 120 rubles was transferred. The Contractor will calculate VAT at the rate of 18/118, the VAT amount will be 18.31 rubles. (120*18/118).
When providing services in 2021, costing 120 rubles. (including VAT), the contractor will present VAT to the customer at a rate of 20%, i.e. 20 rubles. At the same time, he will deduct the VAT calculated upon receipt of the advance in 2021 - 18.31 rubles. (i.e., VAT calculated at the rate of 18/118 on the amount of the advance taken into account as payment for services rendered, i.e., from 120 rubles, is accepted for deduction).
Determining the cost of services (goods, work) with a VAT rate of 20% depends on the terms of the contract.
Option 1: if the cost of goods (work, services) is established in the contract including VAT.
For example, it is indicated that the cost of services is 118 rubles, incl. VAT is 18%, then in this situation, according to the author, the seller will have to pay the “extra” 2% VAT at his own expense, i.e. the seller's costs will increase. If he is ready to enter into disputes with the buyer, then under certain conditions the contract can be terminated or modified by the court (but this, in the author’s opinion, is unlikely).
Let us explain our position. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 422 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the contract must comply with the rules obligatory for the parties, established by law and other legal acts (imperative norms) in force at the time of its conclusion. The execution of the contract is paid at the price established by agreement of the parties (clauses 1, 2 of Article 424 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
If, after the conclusion of an agreement, a law is adopted that establishes rules binding on the parties, other than those that were in force at the conclusion of the agreement, the terms of the concluded agreement remain in force, except in cases where the law establishes that its effect extends to relations arising from previously concluded agreements (Clause 2 of Article 422 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The Law on increasing the VAT rate to 20% does not directly state that its effect applies to contracts concluded before 01/01/2019. And, in the author’s opinion, the clarification that “the new rate applies to goods (works, services) shipped from 01/01/2019” - as an indication that the new rules apply to “old” contracts is not possible (clause 4 of Art.
5 of Law No. 303-FZ). In other words, according to the author, in order to calculate VAT, the seller is obliged to calculate the amount of tax at a rate of 20%, but in accordance with the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the seller has no grounds for automatically increasing the cost of goods (work, services) established by an agreement concluded before January 1 2021, at 2% VAT, i.e. the total cost specified in the contract, including VAT, must remain unchanged.
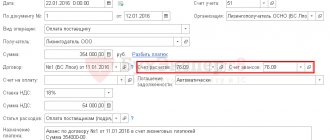
Postings for VAT under a leasing agreement
Accounting for leasing transactions is regulated by the relevant order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 17, 1997 No. 15. The leased object can be recorded on the balance sheet of one of the parties: the lessor or the lessee. This procedure is fixed in the contract or in an additional agreement to it.
In accounting, it is usually shown in the fixed assets account. If the property is accounted for on the lessor’s balance sheet (account 01 “Fixed assets”), then the lessee reflects its value on off-balance sheet account 001 (“Leased fixed assets”).
Accounting for all payments under the leasing agreement is made on account 76, with separate analytics for payments: advance payment (for accounting for advances), current payments (monthly payments), redemption value (cost of property upon redemption). Next, all the nuances of accounting for the seller and buyer of leased property are taken into account.
VAT postings from the lessee
Under a leasing agreement, the lessee's property will be accounted for in an off-balance sheet account. He will not make depreciation deductions, since off-balance sheet accounts do not provide for changes in value before the transfer of ownership. Other transactions under the agreement are reflected in accordance with the documents provided by the lessor. Accounting entries:
- Debit 001 - the fixed assets received under the leasing agreement were placed in an off-balance sheet account.
- Debit 20 Credit 76 - payment under the leasing agreement is reflected in expenses (posting is done monthly).
- Debit 19 Credit 76 - VAT is reflected on the monthly lease payment.
- Debit 68 Credit 19 - VAT is accepted for deduction (monthly posting).
- Debit 76 Credit 51 - transfer of the obligatory lease payment.
After making all mandatory payments, the lessee reverses the amount from the off-balance sheet account, making an entry to credit 001. At the same time, the property is placed on the lessee’s balance sheet account (Debit 01 Credit 02 - the amount of the fixed asset minus VAT, since the amount of VAT on the property was accepted for offset against the issued lessor's invoices).
Actions of suppliers and buyers in various situations of transition
Supplier: if goods (works, services) are sold in 2021, and payment is received in 2021, then VAT must be charged in 2021 at a rate of 18%. When receiving payment in 2021, there is no need to adjust the VAT amount previously presented to the buyer. Starting from January 1, 2021, sales are carried out at a rate of 20%.
Buyer: if goods (work, services) are received from a supplier in 2021 and paid for in 2021, then input VAT is deductible at a rate of 18%. All subsequent payments for goods (work, services) received are based on the VAT rate in effect at the time of shipment and reflected by the supplier in the invoice.
For further sales in 2021 and later of the specified goods purchased in 2021, input VAT is deductible, as stated above, at a rate of 18%. Starting from January 1, 2021, VAT on sales is charged at a rate of 20%.
Supplier: if in 2021 a 100% prepayment is received for the sale of goods (works, services), which will take place in 2021, then VAT on the advance received in 2021 is charged at the calculated rate of 18/118. The same amount of VAT in 2021 is accepted for deduction when selling goods (works, services), which occurs at a VAT rate of 20%.
If in 2021 a partial prepayment is received for the sale, which will take place in 2021, then VAT on the advance received in 2018 is accrued for payment at the calculated rate of 18/118. When selling goods (works, services) in 2021 at a rate of 20%, VAT on a partial advance in the amount calculated at the rate of 18/118 is deductible.
Buyer: if goods (work, services) are fully paid for in 2018 and received in 2021, then VAT on the advance payment issued in 2018 is deductible at the calculated rate of 18/118. In 2021, after goods (works, services) are accepted for accounting, VAT from a previously paid advance is restored at the calculated rate of 18/118 based on the supplier’s advance invoice, VAT is accepted for deduction at a rate of 20% based on the invoice issued by the supplier at implementation.
If goods (work, services) were partially paid for in 2018 and received in 2021, then VAT on the amount of the partially paid advance in 2021 is deducted at the calculated rate of 18/118. In 2021, after goods (works, services) are accepted for accounting, VAT on a partially paid advance is restored in the amount in which it was previously accepted for deduction and, based on the supplier’s invoice for sales, VAT is accepted for deduction at a rate of 20%.
Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 23, 2018 No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] “On the procedure for applying the VAT tax rate during the transition period.”
Example: a contract concluded in 2021 stipulates that the buyer in 2021 pays an advance in the amount of 50% of the contract amount. The cost of goods (work, services) in accordance with the contract is 118,000 rubles, including VAT 18%. The parties signed an additional agreement to the contract, providing for the preservation of the cost of goods (work, services) without VAT and an increase in the amount of VAT due to changes in the rate. As a result, the final amount of the contract changed to 120,000 rubles, including VAT.
59,000 x 18/118 = 9,000 ₽.
The buyer deducts VAT in the amount of RUB 9,000 based on the supplier's advance invoice.
In 2021, when selling goods (works, services) using a VAT rate of 20%, the total sales amount is 120,000 rubles, including VAT 20,000 rubles.
The supplier charges VAT on sales in the amount of 20,000 ₽ and at the same time deducts VAT on the previously received advance in the amount of 9,000 ₽.
The buyer deducts VAT in the amount of 20,000 rubles based on the supplier's invoice for sales and at the same time restores the payment of VAT from the previously issued advance in the amount of 9,000 rubles.
As a result, the buyer must pay an additional 61,000 rubles to the supplier in 2019 (120,000 – 59,000 rubles).
If in 2021 the supplier sold goods (works, services) subject to VAT at a rate of 18% and issued an invoice to the buyer, and in 2021 the parties agreed to change their price or quantity, then the VAT rate is indicated in the adjustment invoice, valid on the date of sale, that is, 18%.
If in 2021 the supplier sold goods (works, services) subject to VAT at a rate of 18% and issued an invoice to the buyer, and in 2021 a technical error was discovered in this invoice, then the supplier issues a corrected invoice with the VAT rate, indicated on the original invoice, i.e. 18%.
Please note: in situation 5 we are talking only about services provided by foreign performers in electronic form, and not about all services.
Services provided in electronic form, for example, include advertising services on the Internet and the provision of advertising space on the Internet (for the list of services, see Article 174.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Services provided electronically do not include:
- sale of goods (work, services), if they are ordered via the Internet, but delivered (performed) without using the Internet (for example, by mail, courier);
- implementation (transfer of rights to use) computer programs, databases on tangible media (disks, flash drives);
- consulting services provided via email (correspondence);
- Internet access.
When paying an advance to a foreign supplier in 2021, the tax agent calculates VAT at the rate of 18/118. After accepting works (services) for accounting on the basis of documents received from a foreign supplier, the tax agent has the right to deduct VAT.
If the final settlement with a foreign supplier is made after receiving the results of work performed (services provided) in 2021, then the tax agent calculates and pays VAT at the rate of 20/120, taking for deduction the VAT previously calculated on the advance payment at the rate of 18/118.
Moreover, if the contract does not provide for changes in the cost of work (services) or the foreign supplier does not agree with the increase in the cost of the contract, then the difference in the amount of VAT is paid by the tax agent (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated April 3, 2012 No. 15483/11).
Please note that from January 1, 2021, the obligation to calculate VAT is assigned to a foreign organization providing services in electronic form, regardless of who the buyer is: an individual, an individual entrepreneur or a legal entity (Article 174.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law No. November 27, 2017 No. 335-F).
Consequently, for services provided by a foreign organization in electronic form in 2021, payment for which is made in 2019, VAT is calculated and paid at the rate of 18/118 by the foreign organization.
If services were provided electronically by a foreign organization in 2021, and the Russian buyer paid for them in 2021, the latter must remit VAT. At the same time, in 2021, Russian buyers can no longer deduct VAT from payments made in 2021, since they are no longer tax agents.
If you have contracts with foreign organizations for the provision of services in electronic form, you need to pay attention to the payment procedure so as not to lose VAT on deduction (Information of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 5, 2017).
When renting state (municipal) property from authorities and management, VAT is withheld and paid to the budget by the tax agent-tenant of this property. If he made an advance payment in 2018, he must transfer VAT to the budget at a rate of 18/118.
If a tax agent-tenant transfers payment in 2021 for rental services provided in 2021, then the tax agent must transfer VAT to the budget also at the rate of 18/118, since the VAT rate of 20% applies to the sale of goods (works, services), which were committed after January 1, 2021.
Representatives of regulatory authorities believe that the return by the buyer of a quality product, which is carried out by agreement with the supplier, is a reverse sale. If in 2018 the supplier sold goods subject to VAT at a rate of 18%, and in 2021 the buyer returns these goods on the basis of a return agreement concluded with the supplier, then the specified return is processed as a regular sale. Then the former seller becomes the buyer, and the former buyer becomes the seller, applying a VAT rate of 20%.
In general, the return of defective goods from the buyer to the supplier, in terms of Art. 518 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, is not a separate transaction, since it is carried out within the framework of the original purchase and sale agreement. Therefore, the buyer has the right to present a claim to the supplier related to defects in goods (defects detected after the buyer accepted the goods for accounting), provided that the defects (defects) were discovered within the time limits established by Art. 477 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and not exceeding two years from the date of transfer of goods to the buyer.
In this case, the supplier of goods always issues an adjustment invoice, and it does not matter:
- whether the goods are accepted for accounting by the buyer or not;
- when was the shipment - before 2021 or after;
- the entire shipment of goods or part of it is returned.
The adjustment invoice indicates the same VAT rate that was in the originally issued invoice (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 23, 2018 No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] ).
On the application of the VAT rate in relation to the services of leasing property, Letter No. 03-07-11/64576 of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 10, 2018 was issued. It states that a 20% rate applies to services for the provision of property for rent provided after January 1, 2021, including on the basis of contracts concluded before that date. Therefore, invoices issued in 2019 must contain a VAT rate of 20%.
Situation 10. Leasing
The explanations in the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 10, 2018 No. 03‑07‑11/64576 regarding rental services fully apply to leasing agreements, which are a financial service, a type of lease.
Acceptance of the transferred property for accounting by the recipient party
When an object is accepted for accounting by the lessee, accounting entries under the leasing agreement will be made using accounting accounts 08 and then 01 (clause 8 of Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 15), i.e., as if this property were its own.
On account 08 it will appear at a cost equal to the amount of full payment under the contract (together with the repurchase price), but excluding VAT from it. The corresponding account in this posting will be account 76: Dt 08 Kt 76 “Rental obligations” (clause 8 of Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 15). At the same time, an entry will be made reflecting the allocation of VAT related to the cost included in account 08 (Dt 19 Kt 76 “Rental Obligations”), and this will lead to the formation in subaccount 76 “Rental Obligations” of the full amount of the recipient’s debt for payments stipulated by the agreement.
Further accounting operations will be the same as for fixed assets owned by the recipient: the object is put into operation (Dt 01 Kt 08) and depreciated monthly (Dt 20 (23, 25, 26, 29, 44, 91) Kt 02) . The duration of the depreciation period may correspond to the duration of the contract, but is also determined by other criteria: with reference to the period of either expected use with planned operating parameters, or planned physical wear and tear (clause 20 of PBU 6/01, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n). It is permitted to establish a coefficient of 3, which accelerates the calculation of depreciation (clause 9 of Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 15).
But in tax accounting (TA), such property will be taken into account at a different value. It will be determined by the amount spent on the purchase by the transferring party (clause 1 of Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The amount of this amount must be reflected in the contract. The difference in the initial costs of the object will lead to different amounts of depreciation charges for it in the accounting system and in accounting, even if the same period for writing off this cost and the same acceleration factor are established. This, accordingly, will lead to the need to apply the rules contained in PBU 18/02 (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n), and use entries for accounts 09 and 77 in accounting.
Results
In relations arising under a financial lease agreement, it is allowed to delegate to the recipient of the property the right to take into account the subject of this agreement in the balance sheet. This leads to the appearance of accounting entries that differ significantly from those performed in a situation where the object is accounted for by the lessor.
The recipient's object is accepted into the OS through the usual transactions (using accounts 08 and 01) at the total cost given in the agreement, excluding VAT, the amount of which is debited to account 19. In the same usual manner, the object is accrued depreciation, the amounts of which are included in costs.
Lease payments are not included in accounting expenses. They are calculated by reducing the total amount of payment stipulated by the contract. VAT is deducted in parts as invoices are received for each lease payment. The last of the payments and the last deduction are made in relation to the cost of redemption, if the agreement does not provide for the return of the property. The return of the leased object will be reflected in the transactions as the sale of fixed assets.
For the purchased object, no changes in accounting in the amount of its accounting value and the procedure for calculating depreciation occur.
You only need to make entries that clarify the analytics of ownership of the property. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Advantages and disadvantages
- The financial flow for such a transaction is less than when purchasing for cash or on credit.
- You should not collect a lot of paperwork for leasing.
- The leasing recipient does not worry about the service of the property (car), and also receives 24-hour support.
- The organization saves on taxes.
- Short rental time.
- The risk of losing the leased item, as well as the accrual of fines for non-payment.
- The recipient of the lease is completely dependent on the leasing company, because its balance sheet contains the assets leased.
- Leasing can be more expensive than a loan.
When leasing property, the parties to the transaction are required to pay taxes. VAT when leasing from the lessee is determined by the parameters of the leasing agreement.
How to get a cash loan without certificates and guarantors from Rosselkhozbank? The answer is in the link.
Find out more about a cash loan without proof of income.
When assessing taxes, the rules determined by Art. 171-172 of the Tax Code, according to which in order to obtain a VAT extract, a company must fulfill the necessary conditions. And all related services are taken into account.
VAT refund for leasing companies
For leasing companies, the traditional situation of VAT reimbursement during leasing remains painful, but currently it has improved somewhat. Market participants note that the tax office no longer sets itself the goal of not refunding, but puts forward specific claims for individual transactions. This positive trend was facilitated by the arbitration court, which recently ruled in favor of taxpayers.
The leasing system is structured in such a way that the budget must constantly reimburse the amount of VAT. When purchasing a leased item, the company pays the supplier once, including VAT. After transferring the property for rent, the company receives lease payments including VAT. The company does not pay the received VAT to the budget, but adds it to what was previously paid. Since leasing payments are spread over years and the amount of taxes involved is insignificant, the company has the right to demand compensation from the tax authorities for the excess amount of VAT.
Leasing accounting
Initially, it is necessary to pay an initial advance for leasing a car, which is not an expense for the buyer. And if the buyer has all the necessary documents along with the deed, the advance amount added to the accounting can be posted in several ways
- On the date of payment of the first leasing payment (one-time payment).
- On the date of payment of the last leasing payment (one-time payment).
- Throughout the entire period of payment of leasing payments under the contract, evenly and, thereby, reducing the amount of the monthly payment.
After the leasing company has received the first advance payment, it has the right to present the buyer with an invoice for the amount of the advance payment within 5 days. In this case, you can calculate the amount of VAT using the estimated rate. The buyer can accept input VAT from the advance payment as a deduction, but in the presence of all the necessary documents.
Each time you pay a monthly payment and receive an invoice from the leasing company, the amount of VAT declared by the company is deducted when the advance leasing payment is credited. Carefully read the agreement with the specified equal offset of the advance payment throughout the entire term of the agreement; the expense will be qualified as an expense for a future period, and will also be taken into account evenly in tax accounting.
Leasing, taxation
An advantage for calculating the tax base, namely the possibility of reducing it, is leasing. Taxation in this case has a number of features. For example, a company must take into account leasing payments to calculate the profit tax base . If the lessee has taken the received property into account on his balance sheet, then he must deduct the amounts associated with accrued depreciation from the amount that is written off as lease payments expenses. When the property is accepted on the balance sheet by the lessor, then from the amounts that are written off as expenses of lease payments, it is necessary to subtract an amount equal to the redemption value of the property accepted for lease .
This is due to the acquisition of depreciable property and the costs associated with it, which are not taken into account in the income tax base. The redemption cost of the equipment will be equal to exactly these expenses, and it will be written off gradually through depreciation . This is permitted only after the property acquires the status of ownership of the lessee. Then the property is purchased by the lessee at its residual value and the lease ends. Taxation will be calculated differently in the future.
Pros and cons of using leasing
What is the benefit of buying a car for the general population and legal organizations, because you can just go and get a loan in your name, and then pay according to the same scheme? But in order to take out a loan, it is often necessary to prove the ability to repay the loan and provide property as collateral. But not every organization has such property on its balance sheet, so it’s faster and easier to lease a car. Thus, the loan gives the authority to pay income tax, and leasing is completely interpreted as additional costs, and if you also pay VAT, then all obligations to the state in the form of taxes are significantly reduced.
When purchasing a car from a leasing company, you can easily solve all problems related to repairs, maintenance, insurance and servicing of the car by the leasing company. And also in the event of car accidents or accidents, breakdowns or malfunctions, all questions and problems fall on the shoulders of the management of the leasing company.
If you correctly conclude an agreement with the company, the car leased may be subject to return before the expiration of the agreement or earlier. To calculate payments, depreciation is also taken into account, which makes it possible to practically not pay the last payment. This type of acquisition of movable property is most beneficial for small businesses.
With all the many advantages, this type of service also has disadvantages. By taking the main burden of responsibility on the leasing company, the cost of the car is much higher than it could be on credit. The rates of payments made monthly, the down payment for a car, will also be higher, and if payments are late, the car can be taken away legally.
We recommend reading: At what distance from a populated area is hunting allowed?
The list of negative aspects of using leasing also includes the low prevalence of such companies throughout the Russian Federation, so buyers from the outback cannot always find a similar organization in their region that provides leasing services. The leasing system has not been developed, and very often organizations providing leasing services have to join a banking structure. The buyer of a car through leasing is prohibited from renting out or using this property as a means of collateral. The buyer is obliged, at any time convenient for the parties, to provide complete reporting on the availability, use or any other information about the subject of the contract.
Tax authorities are very often picky about each item, and it is not always possible to recover the VAT deduction, therefore an important stage in concluding a leasing agreement is to take into account all possible shortcomings and quibbles on the part of the tax authorities.
Leasing system
There are many examples of using this method of buying a car: a fleet of minibuses or taxis, a fleet of executive cars, or a simple purchase of a car by an individual. Leasing companies have different conditions for providing services, but the main criteria remain the following.
- Car purchase price.
- Advance at the time of purchase.
- Bid.
- The duration of the lease under the signed contract.
- Frequency of payments.
- Redemption cost.
- Payment method.
Leasing, tax accounting
Leasing also participates in the system of summarizing information for the purpose of calculating the tax base. Tax accounting is based on the formation of the initial cost of leasing property. The lessee accepts the leased asset for an amount equal to the original cost of the property . The initial cost is considered to be the sum of the lessor's total expenses for construction, acquisition, delivery and other actions, as a result of which the subject of the contract acquired a form suitable for its use, with the exception of those amounts provided for in the Tax Code.
After leasing is concluded between the parties, the lessee’s tax accounting will consist of depreciation deductions and all, taking into account the deduction of depreciation amounts, leasing payments .