Why do you need tax accounting?
Each type of accounting is focused on its purpose. The result of the work of accountants is financial statements compiled according to principles approved by the state.
Management accounting also provides information about the financial performance of a business, but in formats convenient for management and owners.
But in both cases, calculating mandatory payments is not a primary task. Therefore, businessmen often have to organize special tax accounting (TA).
Principles and procedure for organizing tax accounting
The general rules for maintaining tax accounting are reflected in Art. 313 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Tax accounting is based on the same basic principles as accounting:
- Monetary measurement - accounting of all transactions in rubles.
- Separation of property - separation of objects owned by the organization from those leased, taken as collateral, etc.
- Continuity – maintaining records throughout the entire “lifetime” of the business.
- Temporary certainty – the procedure for recognizing income. Depending on the type of tax, they can be recognized both as accrual and as payment.
- Consistency – all applicable standards should generally be applied unchanged from year to year. Exceptions are possible if legislation changes or the company adjusts its accounting policies.
- Equalization - income and related expenses should be taken into account in one tax period.
The tax base can be calculated in two ways.
If “ordinary” accounting data is sufficient to calculate the mandatory payment, then the tax is calculated based on these figures.
And if the necessary information is not in the accounting, then the businessman must use additional forms - tax registers. The format of some of them is established by regulations. These are, for example, books of sales and purchases under VAT or a book of income and expenses under the simplified tax system.
If a businessman himself develops tax registers, then they must include a number of mandatory details:
- Name.
- Period (date).
- Type of operation.
- Amount, and if available, quantity in natural units.
- Signature of the responsible person with transcript.
In small enterprises, tax accounting is usually carried out by the same specialists who do accounting. And in medium and large companies, separate divisions can be organized for this purpose.
Tax demand for payment of tax
1.1 What is a tax demand for payment of tax?
The requirement to pay a tax (fine) is an act of authoritative nature by which the tax authorities force the taxpayer to fulfill his tax obligations (obligations to pay a fine) to the budget.
Issuing a requirement to pay a tax is a coercive measure, and the transfer of funds in pursuance of a decision of the tax authority cannot be considered as the voluntary fulfillment by the taxpayer of obligations to pay taxes and fees (Resolution No. 13592/04 of March 29, 2005 of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation).
A demand for tax payment is a written notification to the taxpayer about the unpaid amount of tax, as well as about the obligation to pay the unpaid amount of tax within the prescribed period (Article 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
1.2 Types of tax requirements for payment of tax
Tax authorities are required to issue a demand for payment of a tax sanction (fine) according to the rules established by Article 69 “Demand for payment of tax” of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Forms of demands for tax payment are approved by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees.
Taxpayers report that they receive different types of demands - initial, repeated and updated, a demand to pay a tax (fee), a demand to pay a fine. The type of requirement to pay taxes is uniform; it is defined in the Tax Code.
Article 71 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for only one case of sending an updated requirement - this is a change in tax liability after sending the initial requirement. The absence of conditions for sending an updated request in the presence of an updated request means that the tax authority has sent a repeated request. Tax authorities do not have the right, under the guise of an updated tax claim, to repeatedly send a claim for the same taxes and for the same period. These circumstances will indicate the illegality of the actions of the tax authorities. Repeated submission of demands for payment of taxes for the same period and for the same taxes violates the legal rights of the taxpayer
1.3 What does the tax payment requirement contain?
- amount of tax debt and penalties;
- measures to be taken to collect the tax;
- the grounds for levying the tax, as well as a reference to the provisions of the legislation on taxes and fees that establish the taxpayer’s obligation to pay the tax;
- tax payment deadline;
- deadline for fulfilling the requirement.
1.4 Procedure for submitting a tax payment request
Previously, the tax inspectorate was required to prove the fact of the transfer of a tax claim. All possible actions of the tax authority to force the taxpayer to pay tax payments to the budget could be carried out if the tax authority had information about the delivery or non-delivery of the demand to the taxpayer (for example, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central District dated June 30, 2011 in case No. A14-9429 /2010/335/28).
Currently, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides the tax authority with three separate and independent ways to submit a claim :
- personal transfer to the head of the organization (its legal or authorized representative) or an individual (his legal or authorized representative) against signature;
- sending by registered mail. If the specified request is sent by registered mail, it is considered received after six days from the date of sending the registered letter;
- transmission in electronic form via telecommunication channels.
It happens that the tax authority sends a request by registered mail. The fact that the letter was delivered to the taxpayer is not tracked. Indeed, in accordance with Art. 54 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a legal entity bears the risk of negative consequences of non-reception of correspondence addressed to it, if, with the degree of care and prudence required from it, it does not take measures aimed at receiving this correspondence at its location (example - resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated September 6, 2011 on case No. A72-8864/2010).
Judicial practice on such issues is emerging, but two main points can be distinguished:
- the demand for tax payment must be served on the taxpayer after the deadline for its execution;
- the request must be sent by registered mail to the address corresponding to the tax records.
Important: The fact that the tax authority has identified arrears is recorded in a document in the prescribed form. This document on identification of arrears is not sent to the taxpayer.
1.5 Deadline for submitting a tax payment request
The general deadline for sending a claim has been established - no later than 3 (three) months from the date of discovery of the arrears . If the tax payment requirement is sent to the taxpayer electronically via telecommunication channels, then the deadline must be no later than the deadline established by clause 1 of Art. 70 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but not earlier than 75 calendar days from the date of discovery of the arrears.
The deadline for sending a request based on the results of a tax audit (including sent electronically via telecommunication channels) is within 20 (twenty) days from the date of entry into force of the relevant decision.
Consequences of missing the deadline for submitting a tax demand. In practice, there are often situations when the tax authority misses the established deadline for sending a request to the taxpayer. The Tax Code does not provide for changing the course of the period or its termination. Thus, the tax authority missing the deadline for sending a demand for tax payment does not exclude the possibility of taking further measures to collect the arrears.
1.6 Deadline for fulfilling the tax payment requirement
The minimum period for fulfilling the requirement that the tax authority is obliged to provide to the taxpayer for voluntary payment of arrears: 8 (eight) days from the date of receipt of the specified requirement, unless a longer period of time for paying the tax is specified in this requirement (Article 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the demand for tax payment is sent to the taxpayer electronically via telecommunication channels, then according to clause 4 of the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 9, 2011 No. YAK-4-8 / [email protected] “On the procedure for sending a demand in electronic form » the deadline for fulfilling the requirement to pay a tax, fee, penalty, fine sent to organizations and individual entrepreneurs electronically via telecommunication channels must be at least 20 calendar days, and for individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs - at least 30 calendar days .
Before the expiration of the period for voluntary compliance with the requirement, the tax authority does not have the right to apply subsequent measures to force the payment of taxes, penalties and fines.
Grounds for appealing a tax payment requirement
- lack of information informing the taxpayer about the existence of a debt;
- lack of information about the beginning of its procedure for enforcing the obligation to pay tax and measures to collect and ensure the fulfillment of the obligation to pay tax;
- failure to provide the taxpayer with the minimum established period for voluntary compliance with the requirement;
- violation of the procedure for serving a demand.
Failure to comply with the tax requirement to pay taxes leads to the procedure for indisputable collection of arrears (penalties, fines, interest). To ensure compliance with the requirement to pay tax, the tax authority has the right to apply the following measures to compel payment:
- penalties are the amount that a taxpayer pays in addition to accrued taxes and fees if payment occurs later than the established deadlines. The penalty for each day of delay is determined as a percentage of the unpaid amount of tax or fee. The rate is equal to one three hundredth of the refinancing rate.
- suspension of transactions on the taxpayer's accounts (limitation of the taxpayer's rights to dispose of his funds in the amount of the demand submitted, the tax authority makes an appropriate decision, in case of repayment of debts to the budget, the decision must be canceled within 2 days);
- guarantee (the guarantor is obliged to pay all amounts of taxes and fees, penalties and fines in the event that the taxpayer does not do this within a certain time frame, formalized by an agreement);
- bank guarantee (the bank is the guarantor of payment of the taxpayer’s debts to the budget; a number of requirements are presented to the bank providing the bank guarantee, which are set out in Article 74.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- pledge of property (formed by an agreement between the tax authority and the organization; in case of failure to pay the required amounts within a certain time frame, the tax authority makes the payment independently at the expense of the value of the pledged property);
- seizure of property (performed only with the approval of the prosecutor and only in cases where there are sufficient grounds to believe that the taxpayer may escape or take measures to conceal the property; can be either full or partial).
If, after sending the request, the amounts of arrears, penalties or fines have changed (for example, shortcomings have been identified as a result of reconciliation of payments), then the tax authority will send an updated request for payment. Thus, submitting a demand for tax payment is an integral part of the procedure for enforcing the taxpayer’s obligations to the budget.
Income tax
Many businessmen, when they talk about tax accounting, mean, first of all, income tax. Not surprising - the calculation of this particular mandatory payment is associated with many nuances.
Although formally the tax base for profit is similar to the accounting result - the financial result for the period, in practice everything is much more complicated.
The procedure for accounting for many types of income and expenses for income tax differs significantly from that adopted in accounting. Here are just a few examples:
- Depreciation. Accounting policies may stipulate that different methods of calculating depreciation are used in accounting and tax accounting.
- Reserves formed for various expected expenses. For example, reserves for the payment of vacation pay or for doubtful debts do not need to be created in tax accounting, but in accounting they must be required (except for small enterprises).
- Limited costs. Some types of expenses, for example, travel or entertainment expenses, are recognized in full in accounting, and in tax accounting - within established limits.
There are so many discrepancies between accounting and tax accounting that businessmen often keep parallel records of all income and expenses in separate registers to calculate income tax.
Maintaining registers
Fill out tax accounting registers in chronological order. Tax registers can be maintained in the form of forms: independently developed tables, statements, journals. Do this on paper (machine) or electronically.
If an error is found in the tax accounting register, only the employee responsible for maintaining the register has the right to make a correction. Moreover, the correction must not only be certified by the signature of the latter (indicating the date), but also justified in writing.
This procedure is provided for in Article 314 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not specify how to make corrections to the tax register. Therefore, this can be done, for example, by including a correction entry (if the register is generated electronically) or by crossing out the incorrect amount (if the register is compiled on paper).
VAT
The main registers for calculating VAT are the books of sales and purchases (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137). Payers of this tax enter invoices issued and received in them. Then, based on the results of the quarter, the total amount of accrued and deducted VAT is determined, as well as the total to be paid or reimbursed from the budget.
There is also an additional register - a log of received and issued invoices. It is used by commission agents, agents, forwarders and developers. Those. in this case we are talking about businessmen who act in the interests of others.
Unified agricultural tax
The calculation of the unified agricultural tax is in many ways similar to the calculation of income tax: it is necessary to determine the difference between income and expenses.
The law allows legal entities to determine the taxable base for the Unified Agricultural Tax on the basis of accounting data (clause 8 of Article 346.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, you need to keep in mind that income and expenses under the unified agricultural tax are determined “by payment”, so it will not be possible to directly use accounting data.
Individual entrepreneurs may not keep accounts at all, so a special book for recording income and expenses under the Unified Agricultural Tax has been developed for them (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 11, 2006 No. 169n).
UTII and patent system
When using these modes, the tax is determined based on physical parameters. This may be the number of employees, area of premises, number of vehicles, etc. Each taxpayer determines the procedure for accounting for these indicators himself.
In this case, income and expenses are not needed to calculate the tax itself. But for those who use PSN, income accounting is necessary to control the limit. The fact is that a patent can only be used if annual revenue does not exceed 60 million rubles. To track revenue, entrepreneurs using PSN must keep an income book (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 22, 2012 No. 135n).
Registration in the Russian Federation
Tax authorities are responsible for registration. Registration occurs from the moment information is received in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, Unified State Register of Legal Entities, Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs or on the basis of an application. It is necessary to register at the place of residence or location of the organization, its property, and branches. The registration procedure takes 5 days, regardless of what status the taxpayer has - an individual or a legal entity. The following are registered:
- physical persons registering individual entrepreneurs;
- physical persons conducting notary or lawyer's private practice;
- persons who own transport/real estate property;
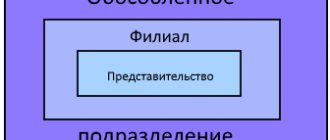
- organizations creating separate institutions;
- organizations with the status of “largest taxpayer”;
- foreign citizens and organizations.
In case of expansion of the company and opening of branches, the taxpayer is obliged to register a separate structure where it is actually located. The procedure for registering an organization is generally the same. But there are a number of differences in the documentation for registration and after it.
Individuals
Citizens are registered automatically from the moment information is received from the relevant authorities:
- From services that register citizens at the place of residence or temporary stay, as well as from consular offices and diplomatic missions.
- From the authorities that register real estate with the state.
- From the traffic police.
- From guardianship and trusteeship authorities.
- From notary services.
- From the authorities involved in issuing passports and changing documents.
In order for registration to proceed faster, you can independently contact the tax authority with an application.
Citizens (who do not have individual entrepreneur status) engaged in the provision of services are required to notify the tax service about their activities and register. Self-employed individuals work under a special regime, often patent. After registration, they do not receive a document or notice of registration from the tax office. In all other cases, notification is sent by mail.
After registration, a special document is issued - TIN, which, at the request of the taxpayer, can be included in the passport. The account is entered into the Unified State Register of Real Estate. If an individual registers as an individual entrepreneur, he is issued a registration certificate confirming receipt of a TIN, and the data is entered into the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs. Registration of an individual entrepreneur takes five days. If an individual entrepreneur ceases its activities, the tax service deregisters it and an extract is made from the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs.
Legal entities
Registration of organizations in tax accounting occurs at their location. The same rule applies to branches, representative offices, and company property. As soon as an entry is made in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities about the creation of a company, the Tax Service registers this organization within five days.
If the company has separate structures (for example, branches), you should register them yourself. That is, in this case, you need to submit an application to the tax office where the branch or other separate structure is located. This can be done within a month after opening. To register you will need:
- Certificate of registration of the organization itself.
- It is necessary to provide an extract from the State Register of Legal Entities, which provides information about the separate structure.
- Documentation confirming the creation of a branch or other separate organization.
IMPORTANT: Branches may be located within the same region. In this case, they can only be registered with one tax service. Moreover, its choice remains at the discretion of the organization.
Registration is required in the following cases - creation of a company, reorganization of an existing structure, liquidation to another location. All these operations are subject to registration with the National Tax Service within 10 days. To do this, a certain package of documents is collected:
- certificate of state registration;
- constituent documents;
- documentation confirming the establishment of the enterprise.
Before you apply, go to your local tax office and find out exactly what documents will be needed. The set of documentation may vary; each region has its own additional requirements. If an organization has ceased operations, the taxpayer notifies the Tax Service about this and submits an application. The withdrawal procedure consists of an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities and direct deregistration.
Registration of a vehicle, as well as real estate, occurs automatically. The relevant authorities, the traffic police or the Federal Registration Service, send information to the tax office. On their basis, registration takes place. The tax office sends the taxpayer the appropriate registration document.