Astral
September 27, 2021 7758
Lifehack
Charity has long become the norm for many people. Unfortunately, there are people and organizations that need help. Therefore, many entrepreneurs donate money or necessary items to foundations, schools and other organizations. However, the accountant must correctly account for all “good” expenses.
What is included in the concept of charitable assistance?
According to the aforementioned Federal Law No. 135, charitable assistance is any assistance provided on a voluntary basis in the form of:
- transfer (transfer) of money;
- transfer of property, goods, products;
- work performed (services provided);
- transfer of rights to intangible assets;
- other voluntary means of support.
How to use a charitable donation ?
Not every gratuitous operation can be recognized as charity. In particular, the following forms of gratuitous donation are not recognized as charitable assistance:
- Giving. Such an agreement is concluded according to the rules of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Ch. 32. You can give things or property rights as a gift; in addition, exemption from property obligations is also considered a gift. Monetary donation (within the meaning of Article 128 of the Civil Code) can also take place. The concept of “charity” includes not only the fact of donation itself, but also the preferential conditions accompanying such a gratuitous transfer. In addition, gratuitous work and services are also classified as charity, while “gifting” a service (work), according to the law, is impossible. Donations also include donations of goods for purposes beneficial to society (Article 582-1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- Sponsorship. In the course of providing such assistance, for example, when organizing public events, the sponsor receives benefits in the form of advertising of its brand or products, i.e. essentially provides assistance for a fee.
On a note! The question of whether a charitable transfer is classified as a gift transaction has not been fully regulated.
For example, the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow Region, by its resolution No. A40-42066/12-11-389 dated 06/12/12, states that the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation are applicable to charity.
Results
Charitable assistance can be provided through a charitable foundation or independently by legal entities and citizens. In our article we looked at accounting in a charitable foundation, reporting of charitable foundations, as well as accounting in charitable organizations. A special feature is that in foundations, charitable transactions do not affect the financial results accounts; in a regular organization, charitable expenses are other.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 N 66n
- Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Accounting and taxes
The accounting of charitable contributions reflects their type: property, cash, provision of services, etc. In addition, accounting is the basis for calculating tax indicators.
a gratuitously received charitable donation (charitable contribution) reflected
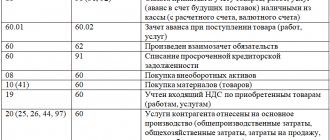
According to PBU 10/99 (clause 12), charitable contributions are recorded in account 91 as other expenses. In the accounting system, the “input” VAT on charity is taken into account, but in the accounting system it is not, which leads to the emergence of tax differences and PIT. Liabilities are calculated by multiplying the tax difference by the income tax rate (PBU 18/02).
For current payments on contributions, benefactors usually use account 76, with the opening of a corresponding sub-account.
Postings:
- D 76 K 51, 50 – transfer, transfer of money for a charitable contribution.
- D 76 K 41, 10, 01, etc. – transfer of materials, goods, property for charity.
- Dt 76 Kt 20, 23, etc. – provision of services, performance of work for charity.
- Dt 76 Kt 60 - the company purchased inventory items, services and transferred them to a third party as a charitable contribution.
- Dt 91 Kt 76 – material assets and money, work are taken into account in other expenses for charity.
- Dt 91 Kt 68 – VAT charged.
- Dt 99 Kt 68 – reflected PNO from the value of money, inventory items, etc.
These are standard entries in the benefactor's accounting.
Are charitable expenses taken into account for income tax purposes ?
Now let's look at the nuances of providing such assistance and reflecting it in accounting. Charity, as a business transaction, is not subject to VAT (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 149-3, paragraph 12). It should be borne in mind that the Tax Code directly indicates compliance of activities with Federal Law No. 135.
If a fixed asset that is not classified as an excisable asset is transferred as a charitable contribution, the VAT on it should be restored and charged to other expenses (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 170-3, paragraph 2). VAT on “charitable” non-excise fixed assets is calculated at the residual value, using the appropriate interest rate.
Charity is also not taken into account in the tax base for income tax, simplified tax system (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 270-16, Art. 346.16-1), i.e. Such expenses cannot be recognized by the benefactor.
So, if a previously purchased OS has a residual value of 180,000 rubles and should be donated to charity, you need to make the following entries:
- Dt 91-2 Kt 01 180,000 rub. — fixed assets were disposed of at residual value.
- Dt 19 Kt 68 32400 rub. (180000*18%) – VAT has been restored. From 2019, a basic tax rate of 20% will apply, which should be taken into account in your calculations.
- Dt 91/2 Kt 19 RUR 31,400 — the restored VAT is reflected in other expenses.
- Dt 99 Kt 68 RUR 36,000 — PNO was recorded (180,000*20%).
What are the goals of charitable activities?
Please note that the goals of charitable activities are enshrined in law. Their list is given in Art. 2 of Federal Law No. 135-FZ and looks like this:
- social support and protection of citizens, including improving the financial situation of low-income people, social rehabilitation of the unemployed, disabled people and other persons who, due to physical or intellectual characteristics or other circumstances, are not able to independently realize their rights and legitimate interests;
- preparing the population to overcome the consequences of natural disasters, environmental, industrial or other disasters, and to prevent accidents;
- providing assistance to victims of natural disasters, environmental, industrial or other disasters, social, national, religious conflicts, victims of repression, refugees and internally displaced persons;
- promoting the strengthening of peace, friendship and harmony between peoples, the prevention of social, national, and religious conflicts;
- promoting the strengthening of the prestige and role of the family in society;
- promoting the protection of childhood, motherhood and paternity;
- promoting activities in the field of education, science, culture, art, enlightenment, spiritual development of the individual;
- promoting activities in the field of prevention and protection of citizens' health, as well as promoting a healthy lifestyle, improving the moral and psychological state of citizens;
- promoting activities in the field of physical culture and sports (with the exception of professional sports);
- environmental protection and animal welfare;
- protection and proper maintenance of buildings, objects and territories of historical, religious, cultural or environmental significance, and burial sites;
- training the population in the field of protection from emergency situations, dissemination of knowledge about protecting the population and territories from emergency situations and ensuring fire safety;
- social rehabilitation of orphans, children without parental care, street children, children in difficult life situations;
- providing free legal assistance and legal education to the population;
- promoting volunteerism;
- participation in activities to prevent neglect and juvenile delinquency;
- promoting the development of scientific, technical, artistic creativity of children and youth;
- promoting patriotic, spiritual and moral education of children and youth;
- support for socially significant youth initiatives, projects, children's and youth movements, children's and youth organizations;
- facilitating activities for the production and (or) distribution of social advertising;
- assistance in the prevention of socially dangerous forms of behavior of citizens.”
At the same time, sending money and other material resources, providing assistance in other forms to commercial organizations, as well as supporting political parties, movements, groups and campaigns is not charitable activity. It is also prohibited to conduct pre-election campaigning or explanatory work on referendum issues simultaneously with charitable activities.
Personal income tax
IMPORTANT! A sample agreement for the implementation of free charitable activities by a benefactor - a legal entity from ConsultantPlus is available at the link
Personal income tax and charity are a special case that is worth considering in more detail. Tax Code of the Russian Federation, art. 217-8.2, indicates that accepted charitable assistance is not subject to income tax, however, with one clarification: it must be received through a charitable organization (most often we are talking about a charitable foundation - BF).
Assistance received from an organization not named in Federal Law-135 (Article 6-1) is subject to personal income tax. The tax will have to be calculated and withheld.
On a note. A citizen providing charitable assistance can apply to the tax office for a deduction (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 219-2), since such assistance is exempt from income tax (ibid., clause 1). The deduction is provided only for contributions made through a specialized organization. The deduction is provided in the amount of no more than a quarter of all income subject to taxation for the year.
Legal nuances of donations
At the level of federal legislation, charitable activities are regulated by Law No. 135-FZ of August 11, 1995. Basic definitions are given here and the operating procedure of such organizations is given. According to stat. 1, charity means the voluntary and selfless transfer of various property, including money, to needy individuals or legal entities, as well as the provision of selfless services (work, etc.). According to stat. 5 philanthropists are those individuals who make donations.
How exactly and to whom generally beneficial assistance can be provided is defined in the stat. 582 Civil Code. And specific goals are included in the statistics. 2 of Law No. 135-FZ. In order for charitable assistance to be correctly reflected in accounting, entries must be made in accordance with Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000.
Invoice
From January 1, 2014, when performing transactions that are not subject to VAT in accordance with Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there is no need to issue invoices, keep logs of received and issued invoices, purchase books and sales books. Changes have been made to clause 5 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and clause 3 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The mentioned obligations remain for taxpayers who apply tax benefits under Art. 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Such persons draw up invoices without allocating the corresponding tax amounts (clause 5 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Postings with gratuitous financing
Let's consider typical operations carried out by an enterprise accountant when receiving financial assistance.
Account assignments made when accepting a gift for accounting
| Dt | CT | Characteristics of a business transaction |
| 51 | 98.2 | Funds received free of charge |
| 60 | 51 | The money was used to pay for purchased supplies |
| 10 | 60 | Materials accepted for accounting |
| 98.2 | 91.1 | Part of the financial assistance amount is included in non-operating income |
| 66 | 51 | Funds of gratuitous support for loan repayment were transferred |
| 68 | 99 | Tax asset accrued on profit from financial assistance |
| 19 | 60 | Accepted for accounting for VAT on excisable goods received free of charge |
After using financial assistance funds, they must be reflected in the item of non-operating income.
How to transfer money to charity
Citizens can transfer their funds to charity in the following ways:
- through the accounting department at the place of work, submitting a corresponding application to the chief accountant;
- from a bank account or in cash through a bank;
- through the cash desk of the organization to which the citizen provides assistance.
Transfer through an organization
An organization that is a citizen’s source of income can transfer funds to charitable purposes only on the basis of his written application. The application can indicate the frequency of transfers, specific amounts or shares (percentages) of wages and other information. And be sure to provide the account details of the beneficiary organization. The application form is free.
In this case, the documents confirming the expenses incurred will be copies of payment orders for the transfer of money for charitable purposes with the bank’s mark on execution. When filling out a payment order, in the “payment purpose” field, you must indicate: “From full name to help the boarding school”, “From full name to carry out statutory activities”. Some tax authorities require, in addition to copies of payment receipts, to also submit a certificate from the organization about the transfers made.
Transfer via bank
If the taxpayer transferred funds from his bank account, then the expenses are confirmed by a bank statement confirming the transfer of funds for charitable purposes.
It is convenient to transfer money through branches of Sberbank of Russia. I draw your attention to the fact that when filling out a document according to form No. PD-4, in the line “name of payment” you should write “transfer of funds for charitable purposes.” A receipt for this form with a bank mark is submitted to the tax authority.
If a citizen deposits money directly into the cash desk of an organization to which he provides financial assistance, then the supporting document will be a receipt for the receipt order indicating the purpose of using the deposited funds. For example: “Charitable assistance for sporting events.”
Documentation of donation of property
The provision of gratuitous financial assistance must be recorded in documents. The exception is cases of transfer of funds to non-profit organizations that do not pursue the goal of using the funds for business activities. In other cases, the company must have the following documents on hand:
- agreement with the party receiving financial assistance;
- copies of accounting registers on the acceptance by beneficiaries of amounts for accounting;
- confirmation of the intended use of the funds received.
The list contains the main papers that are necessary to formalize the act of charity. In some cases, additional documents may be required.
Filling out a tax return
According to the Procedure for filling out a VAT return, approved. By Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 N ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] , transactions that are not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation) are subject to reflection in section. 7 VAT returns. In column 1 on line 010 section. 7 of the declaration reflects the transaction codes established in Appendix 1 to this Procedure. For the gratuitous transfer of goods and/or property rights (for the gratuitous performance of work or provision of services) within the framework of charitable activities, code 1010288 is provided.