Accounting is a system for collecting and recording data expressed in monetary terms and reflecting debts or obligations, the state of the enterprise’s property. This is done through the permanent recording of all business transactions in special registers for recording homogeneous economic data. One of these accounts is account code 57, which stands for “transfers in transit.” For a clearer understanding of what is happening, it is recommended to learn in more detail the basic information about what transfers in transit are, account 57, postings in this register.
The audit process and why it is needed
Inspections pursue understandable goals - control of reporting for the economically stable existence of the organization. The legality and reliability of the information provided by the accountant are the basis for the correct accounting of the company’s money. The audited company must comply with the following rules:
- provide reliable information on account balance 57;
- timely transfer income from the organization’s activities;
- correctly reflect the accounting of foreign exchange transactions.
The audit is based on a thorough study of all primary accounting registers that lead to the appearance of entries in the “Transfers in Transit” account.
How to conduct operations in a budget institution
Plastic card payments may be reflected differently, depending on the type of organization. Acquiring is a bank service for individual entrepreneurs, LLCs and enterprises that helps make non-cash payments to the company’s account. It can be used by LLCs or individual entrepreneurs who have a bank account.
The main difficulty is that budgetary organizations already have a personal account with the Federal Treasury. But the legislation does not prohibit paying not with cash, but with plastic cards in budgetary institutions. The money will go to your existing account.
If we need to reflect in the report the costs of purchasing/renting a terminal, then the reflection of the transactions will be as follows:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Budget |
| The terminal has been accepted for registration | 3B 01 | – | 60,000 rubles |
| Rent for the terminal has been charged (once a month) | 2 109 90 224 | 2 302 24 730 | 700 rubles |
| Terminal rent listed | 2 302 24 830 | 2 201 11 226 | 700 rubles |
| Services provided for which income was transferred | 2 205 31 560 | 2 401 10 130 | 80,000 rubles |
| VAT charged (if any) | 2 401 10 130 | 2 303 04 000 | 8,000 rubles (if it is 10%) |
| The service was paid for by the consumer using a bank card | 2 201 23 510 | 2 205 31 660 | 80,000 rubles |
| The amount is credited to the personal account | 2 201 11 000 | 2 201 23 000 | 80,000 rubles |
| Commission charged for bank services (2.5%) | 2 109 90 226 | 3 302 26 730 | 2,000 rubles |
| Interest transferred to the bank (2.5%) | 2 302 26 830 | 2 201 11 226 | 2,000 rubles |
Accounting characteristics
57 accounting account is a way of modern description of the process of transferring funds to bank accounts. Almost every trading organization transfers amounts from the cash register and proceeds for the reporting period to the account. The use of account 57 begins with such operations, which allows for more reliable and continuous accounting.
In addition to the funds transferred by the organization, transfers in transit include amounts sent from buyers on account of goods or services received, but which did not manage to be credited to the current account before the end of the reporting period. Funds allocated for currency conversion are also debited in account 57.
Features of accounting
Account 57 is maintained on the basis of the current Chart of Accounts established by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94 of October 31, 2000. It corresponds with the following accounts: 50, 62, 79, 90-91 and others. Credit account 57 corresponds with accounts 50-52, 62, 73.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Maintaining account 57 is regulated by a number of regulatory documents. This, among other things, is the Directive of the Central Bank No. 3210 dated March 11, 2014.
Subaccounts of account 57 “On the way”
Subaccounts are needed for separate accounting of certain operations/actions. For example, these could be transactions with currency, depositing money in a certain way. Account 57 can be divided into these subaccounts:
- 01. Amounts sent to credit organizations are recorded here. These are transfers for which there is no confirmation yet in the form of a bank statement. Example – delivery of proceeds, collected funds. That is, money transferred to a bank account through collectors.
- 02. Actions to purchase currency. A subaccount is needed when there is a need for a difference between the purchase price and the Central Bank exchange rate.
- 03. The sub-account is used in trading to record acquiring transactions. For example, products are paid for through the terminal using special cards. In this case, the money will be credited to the company’s account account after some time. In this case, the owner of the terminal takes a percentage for the transfer.
- 21. Actions performed in currency.
If required, the accountant can create auxiliary subaccounts.
Credit and debit account 57
Account 57 is considered an active balance account. Its features are in two areas:
- Debit. Money allocated for enrollment.
- Credit. Subsequent transfer of money for its original purpose. In particular, this is the posting of funds to the cash desk, the receipt of money in foreign currency.
Postings are used to reflect certain transactions. They record certain actions/operations.
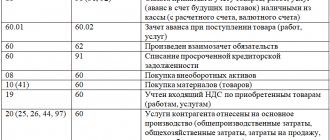
Standard postings to account 57
Entries on account 57 can be very diverse. However, we can highlight the most commonly used wiring:
- DT57/01 KT50. Revenue comes to the company's account with the bank at the end of the month. Primary – bank receipt.
- DT50-52 KT57. The money “on the way” arrived at the cash desk/banking institution.
- DT57/02 KT50. Directing proceeds to a banking institution through collectors.
- DT51 KT57/02. The money is credited to the account through the collection service.
- DT57/03, 04 KT51,52. Transfer of money for the purchase/sale of currency.
- DT57 KT62.76. Transfer from a debtor to pay a debt that has not yet been credited. When this transfer arrives at the company's account, you need to post it back.
Each entry is made on the basis of the primary document. As a rule, these are bank papers (receipts, etc.). Let's look at the wiring that is used in specific situations.
Receipt of money to the company's bank account
When money is received into the account, these entries are used:
- DT50 KT90/01. Company revenue.
- DT57/02 KT50. Money accepted by the collector.
- DT51 KT57/02. The money is credited to the company's account.
- DT91/02 KT51. Bank commission for money transactions.
As is obvious, a subaccount appears in almost every posting. It is needed to detail the operation.
Acquiring accounting
Acquiring is payment by payment cards, that is, non-cash. Such transactions are reflected in accounting using these entries:
- DT50 KT90. The proceeds have been credited to the account.
- DT57 KT90. Fixation of revenue by bank transfer.
- DT90/03 KT68. VAT accrual on sales.
- DT51 KT57. Receipt of money by bank transfer, taking into account bank commission.
- DT91 KT57. Fixation of bank commission for non-cash payments.
The accountant must take into account the fact that the transactions were carried out in a non-cash manner.
Purchasing currency
The company can purchase foreign currency. In this case, the following wiring is used:
- DT57 KT51. Transfer of money for the purchase of currency.
- DT52 KT57. The currency was converted and credited to the organization’s account.
- DT57 KT91/01. Fixing a positive exchange rate difference.
- DT91/02 KT57. Fixing a negative difference between courses.
Primary documentation: accounting certificate, bank statements.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! The primary document is needed to confirm the amounts recorded in the accounting records.
Account application
Account 57, according to the order of the Minister of Finance of the Russian Federation, serves as a source of information about the movement of money in ruble and foreign currency equivalent. It is used in cases where the transfer of funds to a bank account is delayed for a period of 1 day or more from the moment of sending. In addition to the bank, the organization uses the services of savings banks and post offices for settlement transactions.
It is necessary to have a basis in the form of primary accounting documents. These are receipts from executive agencies, as well as accompanying statements for the delivery of proceeds to collectors and other accounting registers. The movement of foreign currency funds must be organized separately from other transfer operations.
Tax accounting of acquiring
As a result of the acquiring transaction, the businessman receives in his current account an amount less than what the buyer paid, since the bank withheld a commission. But to calculate income tax, VAT or the simplified tax system (USN), the revenue must be taken into account in full.
Example. Alpha LLC operates at OSNO. According to the acquiring agreement, the bank commission is 1.5%. Revenue per day from cards is 120,000 rubles.
The bank commission will be:
120,000 × 1.5% = 1,800 rubles
Money will be credited to your bank account:
120,000 – 1,800 = 118,200 rubles
Revenue excluding VAT for income tax:
120,000 / 120% × 100% = 100,000 rubles
The costs of paying the acquiring commission reduce the taxable base, both for income tax and for the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” or Unified Agricultural Tax. It is impossible to deduct VAT from the bank commission, since it is not subject to this tax.
The procedure for recognizing revenue in tax accounting depends on the taxation regime. Under the simplified tax system and unified agricultural tax, income is taken into account only by the cash method, that is, on the date of payment. In this case, it is important to include in the proceeds all funds received from the buyer, otherwise the tax base will be underestimated.
To calculate income tax, the accrual method is usually used - revenue is recognized at the time of accrual, that is, when you transfer the goods or provide the service to the buyer. Small enterprises with revenues of up to 1 million rubles per quarter have the right to calculate income tax using the cash method. But in practice, almost no one does this so that there are no deviations between accounting and tax accounting.
Correspondence with other accounts
Account 57 is active, which means that any inflow of funds is recorded in debit, and write-off is recorded in credit. At the end of the reporting period, a debit balance is formed, or the account is closed if the funds in transit have managed to transfer to the main bank accounts. Based on the characteristics of the account, it is possible to distinguish between its correspondence in debit and credit with other accounts.
Account “Transfers in transit” is debited to the following accounts:
- monetary (accounts 50, 51 and 52, “Intra-economic settlements”);
- settlements with buyers and creditors (accounts 62, 64, 76);
- settlements with dependent organizations (account 78);
- sales of products (accounts 45 and 46);
- profit and loss (account 99).
Closing account 57 - loan correspondence - is most often performed from the account. 50, 51, 52 and 64, 73. Complete posting confirms the fact that funds have been credited to the destination account.
Reflection of account balances 57 on balance sheet accounts
In order to calculate the liquidity ratios of an enterprise (current, urgent), use the data from line 1250 of the balance sheet, called “Cash and cash equivalents”. Using these ratios, information is provided about the possibility of repaying the subject's current short-term obligations using its own funds. Cash and short-term financial investments are recognized as liquid assets.
Composition of line 1250 balance
| Balance section | Account debit | What is it formed from? |
| Current assets | Debit 50 | Cash on hand |
| Current assets | Debit 51 | Account balances |
| Current assets | Debit 52 | Currency bank accounts |
| Current assets | Debit 55 | Special accounts - deposits, letters of credit |
| Current assets | Debit 57 | Amounts of transferred money transfers that did not reach their destination |
| Current assets | Debit 58 | Cash equivalents of short-term financial investments (bills and other securities) |
| Current assets | Debit 76 | Other cash equivalents of short-term financial investments |
The total value of the listed indicators gives an idea of the content of line 1250 of the balance sheet. Cash in transit helps to reflect the actual picture of the financial condition of the enterprise at a particular moment, preventing assets from getting lost due to time intervals between the issuance of cash and crediting for its intended purpose.
But high performance here is not always seen as a positive sign. Rather, it means that the organization’s money is not working. A well-developed monetary policy of an institution should create conditions not only for the speedy repayment of obligations, but also for the timely investment of funds into circulation, bringing additional profit to the enterprise.
Postings to account 57 when depositing money from the cash register
The transfer of money from the cash desk using the “Transfers in transit” account is carried out in the case when the duration of the operation will take more than 1 day. Amounts are deposited from the organization’s cash desk in the following cases:
- you need to top up your current account;
- to avoid exceeding the cash limit;
- you need to transfer money to your corporate card account.
Additionally, you can consider the situation when a transfer occurs from one current account of an organization to another.
Accounting entries are also prepared using account 57. Basic quotes for correspondence between accounts 50, 51 and 57
| Dt | CT | Amount, rub. | Characteristics of an accounting transaction |
| 57 | 50 | 20.000 | money in rubles was handed over from the cash register for transfer to a bank account |
| 51 | 57 | 20.000 | the transferred money was successfully credited to the bank account |
| 57 | 51.01 | 140.000 | the amount was transferred from current account A to current account B |
| 51.02 | 57 | 140.000 | funds were transferred from current account A (51.01) to current account B (51.02) |
| 57 | 50 | 85.000 | money is sent to a corporate card account |
| 55.01 | 57 | 85.000 | funds have been received into the organization’s corporate card account |
It is important not to forget to use account 57 when transferring amounts from the cash register to the bank account. It is possible that posting Dt 51 Kt 50 more simply describes the process of transferring the cash contents of the cash desk to a bank account, but this operation is not reliable. After all, funds are not credited at the same moment when they were sent. Only after the actual execution of the transaction is it possible to carry out such a quotation.
Retail sales report
When reflecting retail sales at an automated point of sale, use the “Retail Sales Report” document in the “Sales-Retail Sales” menu section.
Fig.28 Retail sales report
This document generates transactions both for the sale of goods and for the reflection of revenue, including those received by paying with a payment card.
To reflect the fact of payment by payment cards in the document, you must fill out the “Non-cash payments” tab, indicating the type of payment.
Fig.29 Tab “Cashless payments”
We will process the document and generate a report on the movement of the document. The document generated the following transactions.
Fig.30 Report movements
Dt 90.02.1 Kt 41.01
- the cost of the goods is written off;
Debit 62.Р Credit 90.01.1
- revenue from the sale of goods is reflected;
Debit 57.03 Credit 62.R
- payment by payment cards is reflected;
Debit 90.03 Credit 68.02
- VAT on sales is reflected.
Account 57.03 reflects the amount received when paying with payment cards.
Currency operations
Accounting for foreign currency funds is carried out on active account 55. Circulation is carried out both in rubles and in foreign equivalents in various payment forms, except for bills. Each of the payment forms involves opening a corresponding sub-account.
When converting currency, companies use account 57. Depending on the type of operation being carried out, sub-accounts are opened:
- 57.1 – currency for sale;
- 57.2 – currency for sale deposited by the bank;
- 57.3 – funds in rubles for the purchase of foreign currency.
It is worth noting that account 57.3 remains open until the organization purchases currency in the amount of transferred rubles.
Subaccount 52.2 reflects currency transactions that are carried out outside the Russian Federation on the accounts of foreign companies. It is debited when transfers are made by foreign firms in favor of the organization, as well as when bank interest is calculated for the use of funds. The account credit shows transactions related to:
- transfer of funds to the main bank account of the company;
- fee for servicing a foreign currency account;
- payment of expenses to employees of the organization;
- transfer of funds related to the maintenance of a foreign branch.
Payment of expenses to employees can be made from account 52.2 only with special permission from the Bank of the Russian Federation.
The exchange rate difference arising on account 57 is written off to the credit of subaccount 91 “Other income”. If it is negative in the reporting period, the account corresponds with the debit of subaccount 91 “Other expenses”. Postings are made only on the basis of an accounting certificate.
When is 57 count used?
This accounting account should be used only in cases where it takes a certain amount of time, but not less than one day, to carry out an income or expense transaction on a DMC. That is, if the operation of crediting or debiting money from a company’s DMC takes two or more days, then the company is obliged to use account 57 in accounting.
Let us note situations in which it is not necessary to use accounting account 57:
- Organizations receiving revenue in cash, the amount of which does not exceed the established cash limit.
- Firms that use exclusively non-cash payments.
- Companies that spend the proceeds on paying salaries to staff, issuing travel allowances, and making payments to suppliers.
Postings for currency transactions
Currency transactions are an important component of monetary accounting and settlements.
To transfer funds in foreign equivalents, organizations use accounting account 57. The transactions common in the process of conducting transactions are considered in the table: Currency transfers in transit
| Dt | CT | Characteristics of an accounting transaction |
| 57.3 | 52 | currency transferred for conversion into rubles |
| 91 | 57.1 | The total from the sale of foreign currency was written off in rubles |
| 76 | 57.2 | after transferring funds to a foreign branch, the currency in rubles was written off from the account |
| 57 | 91.1 | positive difference in the exchange rate is recognized |
| 91.2 | 57 | a negative difference in the exchange rate is recognized |
Correct preparation of correspondence accounts will reduce the risk of errors in accounting registers and financial statements.
Bank commission accounting
The interest transferred to the bank for using the acquiring service is set by the bank itself. Each organization has its own. At Sberbank, the interest rate for non-cash payments is 1.6% and higher.
The commission depends on the direction in which the organization operates, how much monthly turnover is, what type of acquiring service is used: trade, mobile (wireless terminal) or Internet acquiring.
The postings indicate the percentage specified in the agreement with the bank. Or rather, the amount in rubles that makes up this percentage.
For example, a financial institution has set a commission of 2.2%. The goods were sold for the amount of 3,000 rubles. Then 2.2% of this amount will be 66 rubles. This figure is indicated in expenses Dt 91.2 Kt 51.
The table shows 3 banks and their acquiring commission amount that you must pay:
| Bank | Trade | Internet |
| Tinkoff | 2.1% – 2.79% – basic tariff; 1% – 5.8% – for gastrointestinal tract services; 1.55% – 5.6% – for airlines. Tariffs are calculated based on monthly turnover | From 2.19% |
| Dot | 1.3% to 2.3% | 2, 8% |
| Module | 1.65-1.9% – standard and 1.8-2.5% depending on the payment system | From 1 to 4% |
There is no need to pay for setting up the terminals; the costs reflect only the amount of rental or purchase of the device.
Acquiring operations
Acquiring is the process of paying for goods or services using a special card. Payment can be made either through online resources or during a regular purchase in a store. Payment cards are plastic cards of the VISA, MasterCard and other classes issued and serviced by the bank. The POS terminal serves as a means of communication between the service user and the banking organization.
The company using acquiring operations enters into an agreement with the bank. The latter is due a set percentage of the commission for the instant payment services provided. The transfer of revenue to the organization occurs only after receiving a fiscal receipt - slip. This is a document confirming a payment transaction using a payment card. One of its copies is transferred to the accounting department of the organization.
Existing subaccounts
As already mentioned, foreign currency in the register is held, like itself, separately. In particular, it has several sub-accounts that are entered as needed. Among them:
- 57.1 – “Funds transferred to the bank or not credited during the reporting period” (at the end of the month without confirmation in the submitted statement);
- 57.2 – “Funds transferred to the bank through collection services.” Most often used by retail entrepreneurs who enter into an agreement with a bank to deposit money through a collection service;
- 57.3 – “Funds in the national currency of Russia for exchange for foreign currency.” Describe the processes of purchasing foreign currency;
- 57.4 – “Funds in foreign currency for exchange for the Russian ruble” Describe the processes of selling foreign currency.
1C tool provides accounting automation
Important! You should pay attention to the fact that when a report is generated on the movement of DS on account 57 in the accounting department, they (DS) must be reflected in this reporting. You also need to include the turnover of SCH 57 Debit in the reporting. Any transactions with foreign currency, according to Accounting Regulations 3/2006, must be converted into Russian rubles. The order of this process is also regulated by Regulation 3.
Reflection of acquiring in accounting
Profit from the sale of goods or provision of services through payment through a POS terminal is transferred to the company’s account only after a bank verification and deduction of commission.
To correctly reflect accounting transactions, use “Transfers in transit” - account 57. The transactions that occur in this case can be seen in the table:
Acquiring Accounting
| Dt | CT | Characteristics of an accounting transaction |
| 57 | 90.1 | Profit from sales paid by bank card is recognized |
| 90.3 | 68 | VAT is charged on the amount received |
| 51 | 57 | the amount of profit is credited to the organization’s bank account |
| 91.2 | 57 | reflects the company's expenses for acquiring services |
Depending on the method of accrual of income, its recognition will be carried out at different times. The accrual method implies the use of posting Dt 57 Kt 90.1, regardless of the period in which the funds were received, and considers the date of receipt of income as the date of sale. If the company uses the cash method, the amount is written off to income when the money from the sale is credited to account 51.
How to close account 57 in accounting
When funds are credited and written off, or when there is an exchange rate difference during a foreign exchange transaction, there is a need to close. How to close account 57? If material resources are received on one day and spent on another, then such an operation will be called a transit operation. The formation of transactions by currencies must be carried out in accordance with Accounting Regulations 3-2006, which determines the recalculation of amounts from foreign currencies into the Russian ruble. The differences that arise will relate to the expenses and income of the organization, which are written off to 91 accounts.
Schematic of active and passive registers
The transactions that should occur when account 57 is closed suggest:
- Debit 57 Credit 91.1 – plus the difference when the Central Bank exchange rate increases;
- Debit 91.2 Credit 57 – minus the difference when the Central Bank rate decreases;
- Debit 91.2 Credit 57 – bank commission amount.
An example of acquiring accounting at an enterprise
Let's consider the process of accounting for non-cash payment by bank card at a conditional enterprise X. The cashier at the end of the work shift generates a Z-report, which contains the following information: the amount of revenue from sales by bank transfer - 180,000 rubles. (of which VAT is RUB 27,457.63). The data is transmitted to the accountant who makes the following entries:
- Dt 57 Kt 90.1 – receipt of revenue from sales via bank cards is reflected – RUR 180,000.
- Dt 90.3 Kt 68 – VAT charged on sales – RUB 27,457.63.
- Dt 51 Kt 57 - money was received into the company’s account minus the commission - 177,300 rubles.
- Dt 91 Kt 57 – shows the commission for banking services provided 1.5% = 2700 rubles.
57 accounting account is one of the main cash accounts used by the enterprise to make payments in rubles and foreign currency.
Reflection of sales and reflection of payment
Next, for a more complete consideration of our example, we will reflect the operation “Sales (acts, invoices)” in the “Sales” section.
Fig. 10 Reflection of implementation
We will not dwell on filling out the document in detail; this should not cause any difficulties. Let's move straight to the next step. From the completed document “Sale of goods” we will create a document “Payment card transaction” based on the “Create based” button.
Fig. 11 Create a payment card transaction
All data from the sales document has been transferred to the document that opens, and all we have to do is indicate the “Type of payment”. Please note that the “Type of transaction” is indicated automatically - “Payment from the buyer”.
Fig. 12 Operation “Payment from buyer”
Let's review our document and analyze the accounting entries that we received as a result of these transactions. You can view the transactions generated by the document by clicking Dt/Kt at the top of any document.
Fig.13 Posting check button
We are posting settlements with customers Dt 62.01 Kt 90.01.1 for the amount of revenue and VAT is allocated - Dt 90.03 Kt 68.02.
Fig. 14 Movements of the receipt document
For payment card transactions, the posting is Dt 57.03 Kt 62.01 for the amount of funds received from the buyer for payment by payment card.
Fig. 15 Document movements by operations
In this situation, the document reflecting the implementation was posted first, and then payment was made. In the case of an initial payment, and after it a reflection of the fact of sale, the postings would look like this:
- First, payment by payment card is reflected;
Fig. 16 Document movements by operations
- Then the fact of sale of the goods is reflected. In this case, it is necessary to pay attention to the timing of the document.
Fig. 17 Movements of the implementation document
As we can see from the document movement report, in this case account 62.02 “Calculations for advances received” is involved. When carrying out the implementation, the program generates an additional entry to offset the advance received.
By clicking on the “More” button in our implementation document, we can view other documents related to it.
Fig.18 “More” menu
From this structure you can quickly navigate to any document entered based on the current one.
Fig.19 Related documents
If you do not see where your generated document is located - “Payment card transaction”, then through the settings button, selecting the “Navigation settings” command, we can add to the desktop any document logs and other menu items that are not displayed.
Fig.20 Navigation settings
Having selected the desired item, use the “Add” button to move it to the right window.
Fig.21 Navigation panel settings
By opening the “Buyers’ Documents” journal, we will have access to all the documents in this section, including our “Payment by payment card” document.
Fig. 22 Buyers' documents