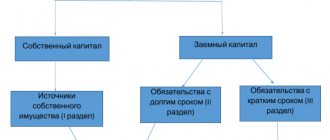
Any enterprise is profitable only if its activities make a profit.
Profit accounting is one of the most important accounting operations, since it indicates the economic efficiency and positive outcome of the organization.
Even if the organization is not commercial, where profit is a priority, income is still accounted for.
A consistently high figure for this indicator in accounting documents indicates the stability of the enterprise in the waves of market fluctuations, its financial success, and the economic efficiency of business methods.
Let's consider what functions does accounting for profit before tax perform, how to correctly calculate it using formulas, and what financial indicators this calculation depends on.
Why is the final result of an organization/enterprise’s activities calculated?
Profit accounting, income and consumables are reflected in the documentation, the responsibility for which is the responsibility of the organization's accountant. The main accounting document is the “Income Statement”.
Counting is required for all types of organizations for a number of reasons:
- to determine the exact amount of net profit and distribute it among participants;
- to calculate taxes required to be paid;
- to compensate for losses in whole or in part;
- to rationalize costs in the future;
- to calculate the accumulated income of the enterprise;
- to account for all third-party ancillary income;
- for the correct repayment of loans/loans, if any.
What are the objects of taxation?
Accounting statements: basic requirements.How to write a business plan for a beauty salon? Read here.
Current income tax - formula
Next, after calculating profit before tax, the current income tax and net profit of the business are determined. The resulting amount of tax payments is reflected in the account. 68 and is payable to the state as a whole for the tax period (taking into account the amounts of advance payments already transferred).
Income tax, formula:
- Income tax on line 2410 = P before tax x 20% (line 2300) +/- PNO (PNA) on line 2421 +/- Changes in IT on line 2450 +/- Changes in IT on page 2430.
If we talk about filling out page 2410 in Form-2, it should be noted that these indicators are only transferred from the income tax return, and the preliminary calculation is carried out according to the rules and regulations of the chapters. 25 NK. The tax amount is always filled in in parentheses. And if the enterprise is not recognized as a profit taxpayer and operates under a special regime (UTII, simplified taxation system, unified agricultural tax), the amount of certain tax obligations in terms of the special regime used - imputation, simplified taxation or agricultural producers - is entered on page 2410.
How to Determine Gross Profit
Gross profit is the total difference between the actual revenue of a business or organization and the cost of goods or services.
The English abbreviation for gross profit is COGS (“cost of sold goods”).
Gross profit and operating profit are different concepts. The second includes the amount before payment:
- Income tax.
- Fines.
- Credit payments.
- Peneus.
Gross profit is calculated as net income minus the cost of goods.
What kind of reporting do NPOs submit to the Ministry of Justice?
Cost and non-production expenses
To determine operating profit, you must first subtract the cost of goods or services from the total revenue. To do this, you need to clearly distinguish which expenses are considered cost. This is reflected in regulatory documents:
- PBU 9/99 “Income of the organization”;
- PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization”;
- Art. 248, 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, etc.
According to general rules, cost :
- salaries for staff;
- contributions to insurance funds;
- costs of raw materials, components, materials, etc.;
- depreciation of equipment;
- communal payments;
- rent, etc.
Non-production expenses are part of the cost. These are the expenses that have to be made to sell already produced products:
- cost of containers, packaging, packing;
- warehouse storage costs;
- costs of transporting goods;
- payment for loading and unloading;
- commissions paid to sales organizations;
- advertising investments;
- administrative expenses, etc.
How to calculate profit/loss before tax
The amount resulting from gross profit minus total non-production expenses. These include:
- product sales expenses;
- administrative;
- managerial.
This type of income has a second name: “operating profit”. It is calculated to cover the organization’s constant operating expenses, taking into account any loans, leasing (operational and financial).
The complete calculation formula is as follows:
Profit (loss) from sales + Income from participation in other organizations – Interest payable + Interest receivable + Other income – Other expenses = Profit (loss) before tax. The total amounts must be entered in line 2300 of the mentioned Report.
Profit itself is also an object on which tax is imposed, the payment of which is mandatory.
Income is calculated differently for Russian and foreign enterprises and organizations, regardless of whether they are included in tax consolidation or not.
Business without investment: step by step.
Women's business - where to start?Read about special tax regimes in Russia.
Calculation example
Let's look at how profit before tax is determined using an example. Suppose the company earned 83,240 rubles from the sale of its products, while the cost of products sold was 47,583 rubles. The company received 15 thousand rubles from renting out one of the workshops; there was no other income in the period under review. The manager also sent one of the shop managers to advanced training courses and paid 12 thousand rubles for them.
We calculate operating profit:
83,240 + 15,000 - 47,583 - 12,000 = 38,657 rubles.
This does not mean that the company earned 38,657 rubles this month - tax will have to be paid on this amount. Let's assume a company operates under simplified taxation at a rate of 6%. Then the net income will be:
38,657 x 0.94 — 36,337 rubles.
Determination of net profit
Net profit is the share of funds received by an enterprise or organization that remains at the free disposal of the company. It remains after all necessary deductions for taxes, credits and expenses have been made and accounted for.
The concept of net profit is often confused with economic profit, but this is absolutely forbidden. Net profit refers to those incomes that go to the benefit of the enterprise and are used for: investing in fixed assets, investing in the company's turnover, necessary reorganization. From which reserve funds are created and funds for circulating production are increased.
Net profit is calculated as follows:
Income Tax Expense – Income Tax Recovered + Extraordinary Expenses – Extraordinary Revenues + Interest Paid – Interest Received. The result is an amount equal to EBIT, which stands for “earnings before interest and taxes.”
If you add depreciation deductions to the resulting amount and subtract the revaluation of assets, you get the EBITDA value. This indicator is used to level out the impact of income tax payments, borrowed funds and non-current assets.
Operating profit accounting functions
The figure that appears in the financial report is not just an abstract indicator of the abstract concept of “success”. Many factors depend on it, which are reflected in the financial issues of the company. Operating profit is taken into account for the following purposes:
- determine how much net profit is;
- have the opportunity to distribute profits among the founders of the organization;
- correctly determine income tax and other payments that cannot be avoided (fines, loans, obligations, etc.);
- if possible, compensate for expenses or losses;
- add the amount to the funded part of income (if the balance is positive);
- track additional income not related to production;
- optimize costs for the future.
Use of the obtained financial result
In financial calculations, there are several basic concepts called absolute. These terms include the aforementioned EBIT, EBITDA, net profit and operating profit.
The obtained result clearly shows where the company could save, where it took out an extra loan, and where it would not hurt to add funds and invest in development so that income increases in the future.
All data must be entered into the Report, which also stores information about the amount accumulated by the enterprise for the entire period of operation. Despite the seemingly extreme clarity of the term “profit” itself, in practice a huge number of controversial situations arise when it is unclear whether a particular payment is included in the calculations.
Key differences between operating profit and EBIT
This point is actually also very important, since we are talking about two different, albeit very close, indicators. They are often confused. Interestingly, operating profit is the difference between gross profit and operating expenses (OPEX), which typically includes selling and administrative expenses. It is also displayed in Finnish. report, but only on page 2200.
The proximity of these two types of profit is obvious. The difference between them is noted only in composition and display in reporting.
| Indicator name | Display in Finnish report | What does it include | General signs |
| Operating profit | Page 2200 | Exclusively OPEX (operating expenses) | Same nature of origin: |
| EBIT | Page 2300 | This indicator includes non-operating profit (i.e. expenses with income that are not related to normal operating activities) | both indicators are the so-called profit before taxes |
As follows from the data presented in the table, operating profit always includes only OPEX. But EBIT can include both operating (OPEX) and non-operating expenses.
An example of non-operating expenses includes expenses related to interest payments, loans, and depreciation. If the company does not have these and similar non-operating expenses, then EBIT coincides with operating profit.
And one more important point. When calculating EBIT, as well as operating profit, it is necessary to correctly determine which income and expenses need to be taken as data for the calculation. In this case, it is recommended to be guided by the standards PBU10/99 (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 33n dated 05/06/1999), as well as PBU 9/99 (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 32n dated 05/06/1999).
PBU 10/99 establishes what is recognized as expenses for commercial structures (legal entities of the Russian Federation). Provides a clear definition and explanation of what constitutes expenses for ordinary activities and how they are generated. In addition, this PBU lists the composition of other expenses and explains how their value for accounting purposes is determined. accounting. So, for example, according to PBU 10/99, swearing is recognized as expenses for ordinary activities. expenses, wages. “Other” includes: interest on loans, credits, as well as losses from previous years that were recognized in the current year.
PBU 10/99 contains almost similar provisions, but only for the income of commercial structures. Accordingly, here you can find information about what is income and what types it is divided into. Particular attention is paid to income from ordinary activities and other income. The issue of recognizing income in accounting is discussed separately. accounting Thus, as a standard, “ordinary” income includes revenue received from products sold and cash receipts from work performed. “Other” includes: exchange rate differences, profits for past years identified in the current period.
Video: how to calculate the difference and summarize financial results
More information about preparing a financial results report - how to correctly calculate and calculate, determine the balance - is described in this video:
Particular attention should be paid to calculations of compensation payments for municipal organizations, since the amount received was paid by the owner of the enterprise. Such funds are part of income and cannot be designated as targeted funding. That is, they are also subject to tax.
To summarize, it is worth noting that the concept of “profit” has many subparagraphs: gross, net, operating; before and after taxes and other expenses. All these concepts, despite the obvious similarity, should be clearly distinguished in order to avoid errors in regulatory documents, including the “Report on Financial Results”.
How to calculate EBIT: calculation options
So, to calculate EBIT, it is necessary to correctly determine the value of all income and expenses for the period of interest. The following general calculation formula should be used:
The formula is cumbersome, but at least it displays all the basic indicators that are usually required for calculation. All of them are displayed in the corresponding financial lines. report. If you substitute the financial line indicators into the specified formula. report, the calculation will take the following form:
These two formulas are basic. If we talk about calculations in detail, then when calculating EBIT, you can go a slightly different way. First, calculate VP - gross profit (subtract cost of sales from revenue). After this, calculate the profit from sales (subtract commercial and administrative expenses from the gross profit). Then, already knowing the amount of profit from sales, calculate the EBIT value.
Schematically, the entire process of the second calculation option looks like this:
As a result, the company receives the amount of loss or the total amount of profit, from which it will then need to withhold taxes and make other required deductions. The presence of profit indicates that the enterprise’s income for the period under study exceeded expenses and this is the norm. In contrast, the presence of losses will confirm the excess of expenses over income, i.e. it will show a negative result.
When calculating EBIT, it is very important to accurately and correctly take into account all income and expenses, and correctly write down the calculated amount of the indicator in financial terms. report. That is, a positive result is indicated with a plus, and a negative result with a minus. In addition, the final amount of EBIT must correspond to the account balance. 99 and the estimated amount. If these rules are not followed, or if errors are made, the calculation result may be distorted. Accordingly, the loss or profit will be overestimated.
What is profit before tax
The value under consideration is also called operating profit - that is, that which remains in the organization as a result of deducting a number of indicators:
- Cost of services or products sold. This category includes labor costs, depreciation, marketing and advertising costs;
- Administrative expenses;
- Commercial expenses;
- Costs that do not relate to sales.
Thus, this value can be used to cover tax obligations and subsequent use as available funds for other purposes. This means that this value acts as a kind of link between the indicators of gross and net profit.
What factors influence the indicator
The goal of every company is to make a profit. Only if it exists, the enterprise is considered profitable. Accounting for this indicator is an important task for an accountant, since the efficiency of the company depends on it. Even if the organization is a non-profit, income accounting is still required.
As an accounting value, profit is represented by the difference between income from the sale of goods and the costs associated with their production. Getting it is the main task of every enterprise. It is associated with risk, therefore, the higher the risk of a businessman, the more income he receives.
This indicator is influenced by factors:
- price of raw materials
- labor productivity
- prices set by competitors
- production efficiency
- number of similar organizations on the market
Attention! If a company is a monopolist, then it can set prices without taking into account the policies of competitors, which significantly increases profitability.
Indicator value
Profit before tax is important for:
- management and internal management of the company;
- external users of financial data from the company's operating activities.
By excluding the amount of tax payments, profit before taxes minimizes the impact of an additional variable, which may contain various indicators that affect the way the company's financial data is analyzed
For example, one industry may have significant tax benefits that will positively impact the net income of an organization in that industry. Conversely, a company in another industry will be negatively impacted by unfavorable tax policies.
Eliminating tax expense will allow the two companies' operations to be better compared, regardless of how tax policies determine their bottom line.
These tax differences can also exist between companies within the same industry, as age, use of capital and geographic location will all play a role in how much tax a business has to pay.
Important! Earnings before taxes eliminate any impact that tax policies may have on a company's financial information.
Thus, the indicator is a performance measurement that highlights the overall operations of a business. Although the metric can be used to compare any company, it is most useful when applied within the same industry.
Ignoring taxes, profit before taxes focuses solely on a company's ability to generate profits from operations and business, ignoring variables such as tax burden. The ratio is a particularly useful indicator because it helps determine a company's ability to generate enough profit to be effective in the marketplace, pay off debt, and finance ongoing operations.
Earnings before taxes are also useful for investors who are comparing multiple companies with different tax situations.
For example, an investor is thinking about buying shares in a company, the pre-tax earnings figure can help determine the company's operating profit before taxes in the analysis. If the company received tax breaks or tax rates were reduced, net income would increase.
Earnings before taxes help analyze companies operating in capital-intensive industries, meaning that they have a significant amount of fixed assets on their balance sheets. Fixed assets are physical assets, plant and equipment that are typically financed through borrowing. For example, companies in the oil and gas industry are capital intensive because they have to finance their drilling equipment and oil rigs. As a result, capital-intensive industries incur high tax costs. Earnings before taxes help investors in such companies analyze operating performance and profit potential while removing tax payments.
Calculation of gross profit
It is represented by the difference between revenue and costs associated with the production or purchase of goods. Revenue consists of various cash receipts related to the main activities of the enterprise. In the calculation process, indicators excluding VAT are taken into account.
Costs include expenses associated with the purchase or production of goods. If a company provides services or performs any work, then all expenses related to this activity are taken into account.
The following indicators are not included in the cost:
- business expenses
- administrative expenses
- other costs
VP calculation is carried out at the end of each month, quarter and year. It can be determined for almost any period, for which only official payment documents are required.
The formula used for calculation is:
VP = sales revenue – cost
Attention! The cost includes only expenses associated with the main and not additional activities, therefore, if a company is engaged in different types of business, then double accounting is carried out.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Question No. 1: The calculation of profit before tax (EBIT) gave a negative result, that is, it showed a loss. Does this mean that loss and EBIT are the same indicator?
Yes, according to economic theory, we are talking about one indicator (EBIT), only in the situation under consideration, based on the calculation results, it turned out to have a negative value. As is customary, it is shown in brackets on page 2300 fin. report.
A loss does not bode well for a company. It points to the inefficiency of its activities and the deterioration of its financial situation.
Question #2: Is it possible to calculate the tax amount by multiplying EBIT by the tax rate?
No you can not. Tax and accounting. accounting differ in many ways. Therefore, EBIT is not always accepted as the tax base for tax calculation. To avoid distortions, it is recommended to carry out calculations separately, taking into account the norms of PBU 18/02 (see the original source, Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 114n dated November 19, 2002)
Enterprise profit structure
The profit of an enterprise includes various economic indicators that demonstrate the results of each area of the company’s economic activity.
The structure includes the following sources of cash receipts:
- Sales of products (provision of services, performance of work).
- Sale or management of real estate that is at the disposal of the enterprise.
- Foreign exchange transactions, interest on stocks, bonds, etc.
- Financial transactions (investments, dividends).
Recommended articles on this topic:
- Pricing methods and recommendations for their use
- Doing business: from developing a plan to choosing software
- Methods for reducing costs in a company and enterprise without small sacrifices
The first item on the list is the main source of cash flow, since it has a greater impact on the profit received, and also serves as the basis for analytical and statistical calculations, forecasts, and strategic plans.
It is the production and sale of products that is the main channel for the receipt of funds that can be directed to business development or distributed among the founders (shareholders).
In order to optimize business activities and look for ways to improve its efficiency, financial statements are analyzed monthly and the costs and profits of the enterprise are calculated.
An experienced manager who is able to think strategically and knows how to operate with financial indicators can influence the size of each index, as a result of which the activity will become more profitable.
Determination of profit from sales
This indicator allows you to find out how effective and appropriate the strategy chosen by the company is. Organizational leaders must strive to increase this value in order to continue to operate in the market.
The analysis takes into account the contents of the profit and loss statement, as well as the balance sheet. Additionally, the financial plan is examined to determine whether the planned values have been achieved. To calculate the indicator, the formula is used:
PP = VP - administrative and commercial expenses
Costs associated with commercial work or managerial decisions are recorded in official documents.
Why are values revealed?
Timely determination of PDN makes it possible to achieve the following goals:
- identification of the tax base for paying taxes, therefore possible debts are prevented
calculation of coefficients to determine the state of the business- determination of net profit
- if a loss is recorded, the amount of monetary compensation is determined
- cost-benefit analysis
- entering information into accounting documentation
All actions are carried out by the company’s accountant, who has access to payment documentation.
What is the indicator used for?
The amount of net profit most reliably characterizes the efficiency of the enterprise. An increase in this amount compared to the previous period indicates the high-quality work of the company, a decrease indicates an incorrect policy of management personnel.
The indicator is used by many internal and external users of information about the organization:
- Owner and shareholders . Using this data, the company owner evaluates the results of the enterprise's activities and the effectiveness of the selected management system. This amount is also used to calculate dividends and attract individuals as investors in the authorized capital.
- Director . He evaluates the financial stability of the company, the correctness of management decisions, and also develops new development strategies. The indicator directly affects profitability, which is why analysis of the balance of available funds is important for top managers.
- Suppliers . It is especially important for them that the organization is able to pay for raw materials, and the indicator is used to assess the stability of the company. If she has little money, then some suppliers may refuse to enter into an agreement because they will not be sure of payment for services and materials.
- Investors . Based on the indicator, they consider the possibility of financial investments. The higher the amount of free income, the more attractive the company is for investors. First of all, they plan to receive additional income from shares.
- Creditors . Borrowers determine the solvency of the company. Money has the greatest liquidity, that is, the ability to be quickly sold. The more of them an organization has at its disposal, the faster it can pay off its debts. Accordingly, there is a greater chance of getting a loan from a bank.
Indicator analysis
In addition to using conventional formulas, the company's economist analyzes the indicators. With its help, significant problems are solved:
- actual values will be equal to planned ones
- the reasons for deviations from the planned financial result are determined
- weaknesses and shortcomings of the company's work are identified
- sources of loss are located
- a list of reserves is compiled that will allow minimizing losses in the future and increasing cash receipts
All types of profit are analyzed. The structure, dynamics over several periods and deviations from the plan are examined. The analysis is carried out on the basis of data available in financial statements and other documents. To do this, you are allowed to use special programs. If dynamics are taken into account, then the amount of inflation is determined during the calculation.
It is recommended to compare the value with revenue or cost. Additionally, it is calculated in relation to the authorized capital or asset value. If an in-depth analysis is needed to identify factors that influence the financial result, then data from the balance sheet is used, as well as external features represented by the economic crisis, changes in the refinancing rate, an increase in the dollar exchange rate or a sharp drop in demand for goods sold.
Profit before tax is represented by a significant parameter by which the financial result is assessed. It allows you to determine the tax base. With the help of analysis, factors influencing the efficiency of the enterprise are identified. For calculations, data from the balance sheet, as well as other payment documents, is used.
Top
Write your question in the form below