Let's consider the variable costs of an enterprise, what they include, how they are calculated and determined in practice, consider methods for analyzing the variable costs of an enterprise, the effect of changing variable costs at different volumes of production and their economic meaning. In order to easily understand all this, an example of variable cost analysis based on the break-even point model is analyzed at the end.
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
Which costs are variable?
Variable costs are those costs that, during the manufacturing process of a product (or other production process), change in parallel with the dynamics of its output volumes.
However, not only production costs, but also costs not related to the production process can be called variables. An example of the latter are warehouse, packaging, and transportation costs. Conventionally, we can say that variable costs characterize the value of the product produced, while constant costs characterize the price of the company.
How to calculate variable costs: examples, calculation formula
Variable costs are the company's expenses spent on the production or sale of goods and services, the amount of which varies depending on production volumes.
This indicator is used to calculate the possibility of reducing the costs of an enterprise. Any economic indicator serves a single goal - increasing the profitability of the enterprise. Variable costs are no exception.
They allow you to analyze the company’s activities and develop a strategy for increasing profitability. Accordingly, this indicator is not included in the balance sheet, since it is needed not for accounting, but for management accounting. Important!
For example, office rent, training fees, retraining of company employees and other fixed costs. First of all, variable costs are divided into two main subgroups:
- Indirect are expenses related to the cost of a group of goods (services). For example, general plant, general warehouse and other types of general costs that affect the cost of all goods or their individual groups.
- Direct costs are those that are directly related to the cost of the product (service). For example, costs for materials, wages, etc.
Some businessmen believe that variable costs are proportional to production volume.
There should be a clear distinction between fixed and variable costs. The first are those whose amount does not change for a long time.
However, this is not always the case. Based on production volumes, variable costs are divided into three types:
- Progressive.
What are variable costs?
Variable costs include costs for:
- purchase of raw materials and supplies;
- for components and spare parts for production equipment;
- related to the sale of finished products (for transportation, storage, etc.);
ConsultantPlus experts explained how to take into account transportation costs in tax accounting for the supplier and buyer. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution.
- for basic piecework wages for workers;
- for electricity and fuel, which are consumed during production.
Variable and fixed costs of an enterprise in examples and explanations
› Any enterprise planning its activities must draw up a plan for income and expenses. This is necessary to improve operations - reduce costs and, as a result, increase profits. Therefore, having complete information about the company’s costs will allow not only to calculate the cost of production and predict profits, but also to obtain data on the ways of further development of the company in one direction or another. In this article we will explain in detail what fixed and variable costs are and what they include. All costs according to their source of origin can be divided into elements of a fixed and variable nature: Fixed costs are represented by an expense item that does not depend on production volumes and does not participate in the formation of product costs.
For a long time without the influence of external circumstances
Conditionally variable costs
Conditionally variable costs should include costs directly related to the volume of production and sales of commercial products. Throughout the entire production and economic activity of the company, they change in quantity, structure and quality.
Conditionally variable costs can also change due to changes in business activity, although, unlike variable costs, this does not happen so clearly.
An example of such costs is the payment of piecework wages to workers or interest to sales managers.
Accurate calculation of variable costs based on financial statements
During the analysis of their financial statements, the financiers of PVP “Contact” found a way to more accurately calculate the variable expenses of a trading company. All that was needed was an official balance sheet and profit and loss account.
The production and implementation enterprise “Contact” specializes in the supply of medical and dental equipment. The company's branches operate in four cities of the Siberian region. Information about the company LLC Production and Implementation Enterprise "Contact" was founded in 1992 in Krasnoyarsk.
The main activity of the company is wholesale trade in medical equipment, dental equipment, orthopedic products, pharmaceutical and medical goods. PVP is one of the largest representatives of the Chirana-Dental, Chirana-Medical, ECOM factories, as well as a dealer of Bien-Air, NTI, Medin, etc.
Headcount - 150 people, trade turnover - more than 500 million rubles per year. The company has four sales branches. The first is located in Abakan (Republic of Khakassia), the second is in Irkutsk (Irkutsk region), the third and fourth are in Achinsk and Lesosibirsk (Krasnoyarsk Territory).
The average number of employees of the company is about 150 people. Despite the fact that the Contact company was founded almost 20 years ago, in 1992, a full-fledged financial service was created only three years ago.
Now this service includes not only the accounting department, but also the economic planning department.
The main reason for creating such a financial unit was
Variable costs of an enterprise (calculation examples). Calculation formula in Excel
Let's consider the variable costs of an enterprise, what they include, how they are calculated and determined in practice, consider methods for analyzing the variable costs of an enterprise, the effect of changing variable costs at different volumes of production and their economic meaning. In order to easily understand all this, an example of variable cost analysis based on the break-even point model is analyzed at the end.
Variable costs of an enterprise (English: Variable Cost, VC) are the costs of an enterprise/company that vary depending on the volume of production/sales.
All costs of an enterprise can be divided into two types: variable and fixed.
Their main difference is that some change with increasing production volume, while others do not. If the company's production activities cease, then variable costs disappear and become equal to zero.
Variable costs include:
- Wages of working personnel (part of the salary depends on the standards met).
- Taxes that have a tax base based on the size of sales and sales: excise taxes, VAT, unified tax on premiums, tax according to the simplified tax system.
- The cost of raw materials, materials, fuel, electricity and other resources involved in production activities.
- Percentages on sales to sales managers and other bonuses. Interest paid to outsourcing companies.
- Cost of manufactured products.
★ (calculation of Sharpe, Sortino, Treynor, Kalmar, Modiglanca beta, VaR ratios) + forecasting exchange rate movements
Variable Cost Examples
According to financial reporting standards accepted in the international environment, variable costs in production are divided into indirect and direct. Indirect production costs include expenses that demonstrate a direct dependence on changes in the volume of economic activity, but due to a number of technological production nuances they cannot be directly attributed to the products produced by the enterprise. At the same time, direct variable costs in full, based on primary accounting data, can be directly attributed to the cost of production.
Read more about dividing costs into groups in our article “How to divide income tax expenses into direct and indirect?”.
Examples of direct variable costs are:
- for remuneration of workers involved in the production process, including accruals on their salaries;
- basic materials, raw materials and components;
- electricity and fuel used in the operation of production mechanisms.
Examples of indirect variable costs:
- raw materials used in complex production;
- costs for scientific development, transportation, travel expenses, etc.
We also advise you to familiarize yourself with the procedure for dividing expenses into indirect and direct for tax purposes. Read more about this in the article “How to divide income tax expenses into direct and indirect?” .
Accountant's Directory
05/27/2018 Contents The manual is presented on the website in an abbreviated version. This version does not include testing, only selected tasks and high-quality assignments are given, and theoretical materials are cut by 30%-50%.
I use the full version of the manual in classes with my students. The content contained in this manual is copyrighted.
Attempts to copy and use it without indicating links to the author will be prosecuted in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation and the policies of search engines (see provisions on the copyright policies of Yandex and Google). When we looked at the periods of production of a company, we said that in the short term the company can not change all the factors of production used, while in the long term all factors are variable.
It is precisely these differences in the possibility of changing the volume of resources when changing production volumes that forced economists to divide all types of costs into two categories:
- variable costs.
- fixed costs;
Fixed costs (FC, fixed cost) are those costs that cannot be changed in the short term, and therefore they remain the same with small changes in the volume of production of goods or services.
We recommend reading: How much land is allocated to large families
Fixed costs include, for example, rent for premises, costs associated with maintaining equipment, payments to repay previously received loans, as well as all kinds of administrative and other overhead costs.
How to calculate variable costs (examples, formula)
> > May 30, 2021 Variable costs are one of the main economic components of any enterprise, involved in most financial formulas.
Let's say it is impossible to build a new oil refining plant within a month.
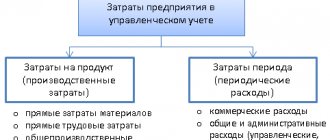
Costs (expenses) incurred by a legal entity for the purposes of management accounting are divided into 2 large groups:
- Variables that make up the actual cost of production (direct costs of production). Their volume directly depends on the volume of production and changes with it.
- Constants that ensure the operation of the entire enterprise as a whole, but are not directly related to the main production process. They do not depend on production volumes and occur even if production is temporarily not functioning. These include, for example, the costs of maintaining the management apparatus, taxes, rent, organizing sales, advertising, information and consulting services, communication services, and personnel training.
The classification of costs as fixed or variable costs of an enterprise is quite conditional.
Let's look at what they are and how to calculate them in our article.
They are determined by many factors and in reality reveal more complex dependencies, incl.
hours and on production volumes. The determination of their sizes, and, consequently, the reliability of economic calculations and the reliability of the conclusions that are drawn on their basis depend on the correctness of dividing costs into these 2 groups. Variable costs include the costs of the production process itself, which vary with its scale.
Results
Due to the fact that variable costs change in direct proportion to production volume, and the same costs per unit of finished product usually remain unchanged, when analyzing this type of cost, the value per unit of product is initially taken into account.
In connection with this property, variable costs are the basis for solving many production problems related to planning. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Systematization of accounting
09.09.2021 Contents Briefly:
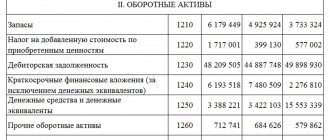
- Line number in the balance sheet: 1210.
- Purpose of the article: reflection of information about reserves.
- Account number according to the chart of accounts: Debit balance - 10, 11, 15, 16, 20, 21, 23, 28, 29, 43, 41, 44, 45, 97, Credit balance - 14, 42.
Inventories refer to the tangible property of enterprises with the help of which final production products are manufactured.
By reflecting them in the balance sheet, the company shows what resources it has at the end of the reporting year. Inventories on the balance sheet consist of several categories:
- goods for sale.
- materials, raw materials;
- unfinished production;
- Future expenses;
- finished products;
Raw materials and materials that were not given for the manufacture of products, in line 1210 of the balance sheet, information is collected on the balances of debit and credit accounts: The specifics of raw materials can be very diverse depending on what the enterprise does.
We recommend reading: Statute of limitations for utility payments
Fixed and variable costs include.
What variable costs include on the balance sheet
Finance December 30, 2015 All enterprise costs are divided into variable and fixed. Their main difference is that some change with increasing production volume, while others do not.
However, fixed and variable costs include costs related to production and sales. When production activities cease, part of the expenses disappears and becomes zero. Let's look at what variable costs include. An example of costs will also be given in the article.
Variable costs include: Commercial expenses (percentages from sales to sales managers and other remunerations, as well as% that are paid to outsourcing companies). Cost of goods produced. Salaries of working personnel (part of the salary, which depends on the standards met). Cost
Returnable and sunk costs
Costs are grouped depending on whether the money invested will be returned back or not.
Return costs
It is assumed that this group of costs will come back sooner or later. For example, this is a large part of production costs. After all, first the company invests money in production, then sells the finished product, thereby returning the costs incurred and making a profit. Examples of such costs: costs of raw materials, wages, and so on.
Sunk costs
The company bears these costs, but will never be able to return them. That is, they do not participate in the creation of profit. For example:
- costs of creating and registering a company;
- insurance costs;
- expenses for banking services and so on;
- expenses for failed research projects.
How to reduce costs?
One of the options for reducing variable costs is the use of “economies of scale”. It appears with an increase in production volume and the transition from serial to mass production of products. The graph of the “economies of scale” shows that as the size of output increases, a certain point is reached. In it, the relationship between the amount of expenses and production volume becomes nonlinear. At the same time, the rate at which variable costs change is lower than the intensity of growth in output/sales of goods. The reasons for this effect include:
- Reducing management personnel costs.
- Application of scientific developments in improving technology.
- Narrowing of product specialization. By focusing the production complex on the implementation of a number of specific tasks, the quality of work increases and the number of defects decreases.
- Release of a product similar in the technological chain, additional utilization of production capacity.
What it is?
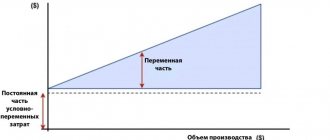
For the purposes of analyzing the break-even of activities, the total expenses of an enterprise are usually divided into two main categories:
- — costs, the amount of which directly depends on the volume of production and sale of services (depending on the chosen direction of the company’s operation), i.e., in fact, they are directly proportional to any fluctuations in the volume of core activities;
- fixed costs are costs the amount of which does not change in the medium term (a year or more) and does not depend on the volume of the company’s core activities, i.e. they will exist even if the activity is suspended or terminated.
Having considered fixed costs using the example of an enterprise, it is easier to understand their essence and interdependence with the volume of core activities.
So, they include the following expense items:
- depreciation charges on the company's fixed assets;
- rent, tax payments to the budget, contributions to extra-budgetary funds;
- bank expenses for servicing current accounts, loans of the organization;
- wage fund for administrative and managerial personnel;
- other general business expenses necessary to ensure the normal functioning of the enterprise.
Thus, the essence of fixed costs of any organization comes down to their functional necessity for the implementation of activities. They can and most often change over time, but the reason for this is external factors (changes in the tax burden, adjustments to the terms of service at the bank, renegotiation of contracts with service organizations, changes in utility tariffs, etc.).
Internal factors influencing changes in fixed costs are a significant change in corporate policy, the personnel remuneration system, a significant change in the volume or direction of the company’s activities (not just a change in volume, but a radical transition to a new level).
Under the influence of all these factors, fixed costs change; they are usually characterized by sharp fluctuations in expenditure amounts.
For the purposes of accounting and analysis, enterprise expenses are usually divided into constant and variable, using the following methods:
- Based on experience and knowledge, through a management decision, a certain category is assigned to expenses. This method is good when the company is just starting its activities and there are simply no other ways to attribute costs. It is characterized by a high level of subjectivity and requires revision in the long term.
- Based on the data of the analytical work carried out to search, evaluate and differentiate all expenses by category based on their behavior under the influence of the factor of changes in the volume of core activities. It is the most acceptable, since this method is more objective.
To see which expenses should be assigned to which group, watch the following video:
Properties of direct costs
- Direct costs increase in direct proportion to the volume of production and are described by the equation of a linear function in which b=0. If there are direct costs, then in the absence of production they should be equal to zero, the function will begin at point 0. In financial models, it is possible to use coefficient b to reflect the minimum wage of employees due to downtime due to the fault of the enterprise, and so on.
- There is a linear relationship only for a certain range of values. For example, if, with an increase in production volumes, a night shift is introduced, then the pay for the night shift is higher than for the day shift.
Important point
The model discussed above usually operates on linear relationships between production volume and profit/expenses. In practice, these dependencies are often nonlinear. This situation is due to the fact that the size of production is influenced by a number of factors. These include:
- Seasonality of demand.
- Technologies used.
- Activities of competitors.
- Taxes.
- Macroeconomic indicators.
- "Effect of scale."
- Subsidies and more.
To ensure the accuracy of the model, it must be applied in the short term to products with stable demand.
conclusions
Summarizing the above, we note that variable costs are the most important component of the activities of any enterprise, and their minimization is one of the main tasks of business planning. To properly plan expenses as part of developing the overall concept of the organization, we advise you to download a ready-made example of a business plan for an enterprise similar to yours. This will allow you to take into account all the necessary sections, and will also facilitate financial modeling. It would also be a good option to contact specialists in the field of business planning to develop a concept for your enterprise in a turnkey format.
Break even
Let's consider the role of variable costs in its determination. The break-even point directly depends on these costs. When a company reaches a certain production volume, a moment of equilibrium occurs. At this point, the amount of losses and profits coincides. In this case, net income is equal to 0, and marginal income equals fixed costs. This point indicates the minimum critical production level at which the enterprise is considered profitable. The company’s task is to create a safety zone and create a level of production and sales of products that would ensure the maximum distance from the break-even point. The further the enterprise is from this point, the higher its financial stability, profitability, and competitiveness. As variable costs increase, this point moves.