State and municipal institutions use various software products in their work. To do this, they purchase the appropriate licenses from copyright holders. Accounting for such expenses raises many questions. How does the license to use the software work? How to reflect the costs of its purchase in accounting and can they be recognized for tax purposes?
Note : Hereinafter, by institutions we will understand state and municipal institutions of all types (state, budgetary, autonomous), as well as state authorities and local governments in terms of their own activities (in accordance with paragraph Art. 161 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation, equated to state institutions institutions).
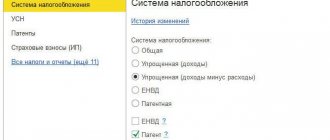
Accounting for license costs under the simplified tax system
Quite often a situation arises in a company when some software or license for a computer is purchased.
And then the accountant is faced with the question: how to correctly take into account this license if the company is on a simplified taxation system? To correctly answer this question, you need to understand what exactly you acquired - rights to the software or a non-exclusive right to use?
- If these are exclusive rights to use a license, and you have the corresponding document in your hands, then it will be an intangible asset, and its accounting will have to be kept on the basis of PBU 14/2007. The holder of such rights can use the result of someone’s mental activity at his own discretion, or permit or prohibit such use by other persons (Article 1229 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- But if you have in your hands an act for the acquisition of a non-exclusive right to use a certain program, then this is a current expense.
We must remember that for companies that have chosen a simplified taxation regime, financial accounting is simplified, and they have the right not to comply with many of the requirements for companies on OSNO. But accounting for fixed assets and intangible assets is mandatory for all companies, regardless of the types of taxes paid.
You can read more about accounting under the simplified tax system in this article.
Accordingly, if you acquire an exclusive right that can be qualified as an intangible asset, then in accordance with PBU 14/2007 you must register it in account 04 at the actual cost of the acquisition and pay off its cost through depreciation. The useful life of an intangible asset must be determined based on the period during which the organization expects to receive economic benefits from it. It is recommended that the established deadlines be reviewed annually and updated if necessary.
On our website you can read more about the procedure for assigning SPI for intangible assets: “How to determine the useful life of intangible assets .
If you have acquired the right to use intangible assets, then payment under the agreement for such rights will be taken into account in the reporting period, and the license itself must be reflected in the off-balance sheet account of the licensor (that is, the company that uses this license).
If your company purchased a software product as a non-exclusive right, then you must remember that, in accordance with the current provisions on accounting, licenses are that rare exception that must be used as deferred expenses (FPR). That is, your company’s accounting should contain the following entries:
- Dt 97 Kt 60 - a license was purchased under a 12-month contract. worth 60,000 rubles. without VAT;
- D 25, 26, 44 Kt 97 - 5,000 rub. monthly - the license is written off as an expense as a RBP.
How to reflect perpetual software in accounting in 2021
/ / Under a license agreement, one party - the holder of the exclusive right to the software (licensor) grants the other party (licensee) the right to use the software within the limits provided for by the agreement. The license agreement is concluded in writing (clause
1, 2 tbsp. 1235 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).By virtue of clause 66 of Instruction No. 157N, the reflection in the accounting of an institution of transactions related to obtaining the rights to use the result of intellectual activity or a means of individualization is carried out on the basis of licensing agreements, commercial concession agreements and other agreements concluded in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. On January 1, 2021, in accordance with the “Fixed Assets” standard and the “Lease” standard, the balance sheet must additionally take into account the property that your institution received for non-operating (financial) lease.
Tax accounting of license expenses under the simplified tax system
Let's first look at accounting for the acquisition of exclusive rights (that is, intangible assets).
Under the simplified tax system, the composition of intangible assets (clause 4 of article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) can include depreciable property worth more than 40,000 rubles, having a useful life of more than 12 months, used by the taxpayer for his own needs. Moreover, if the purchase and sale agreement specifies periodic payments during the term of the agreement, then such objects cannot be classified as intangible assets (subclause 8, clause 2, article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Expenses for intangible assets acquired or created during the period of application of the simplified tax system are written off quarterly in equal amounts until the end of the tax period, after payment and acceptance of the object for accounting.
If we have an act for the acquisition of non-exclusive rights, we will focus on subsection. 2.1 clause 1 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which indicates the costs of purchasing exclusive rights to inventions, computer programs, as well as rights to use the listed developments in accordance with a license agreement.
Such expenses can be accepted for tax accounting at a time, immediately after payment to the counterparty and acceptance of non-exclusive rights for accounting.
Explanations from ConsultantPlus experts will help you reflect your license in your accounting. Get trial access to K+ for free and go to the Deal Guide.
How are the costs of purchasing software products included in the financial result of the current year?
In this case, the following accounting entries are made:
Debit 0 401 20 226 (0 109 Х02 226) Credit 0 302 26 73Х3 - expenses for the purchase of software are reflected;
Increase in off-balance sheet account 01 - the receipt of software is reflected;
Debit 0 302 26 83Х4 Credit 0 201 11 610 (for a government institution - 1 304 05 226), at the same time an increase in off-balance sheet account 18 to account 201 11 - accounts payable to the supplier are repaid;
Decrease in off-balance sheet account 01 - upon expiration of the license, the write-off of an intangible asset received for use is reflected.
An example of how license costs are reflected in KUDiR
In January 2021, Kniga LLC acquired the right to a computer license for its needs on the basis of an agreement and an acceptance certificate. The cost of the license was 100,000 rubles. without VAT. The program was paid for on the day of purchase and was immediately installed on computer workstations. The useful life of intangible assets is set at 3 years.
- If we are talking about the fact that this license will be considered an intangible asset for the company (there is a license agreement, the right is exclusive), then on the basis of Art. 346 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, we must write off expenses incurred in equal amounts over the course of one tax period (100,000 rubles / 4 quarters = 25,000 rubles per quarter). That is, the book of income and expenses for the 1st quarter will look like this:
| No. | Document details | Operation | Income accepted when calculating the tax base | Expenses taken into account when calculating the tax base |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 137 | Total value of column 12 of section 2 for 1 quarter | The cost of the exclusive right to the program is included in expenses | — | 25 000 |
The same entries will appear in the book for 2, 3, 4 quarters. Expenses for the purchase of intangible assets are entered into section 1 of the accounting book on the last day of the reporting or tax period (subclause 4, clause 2, article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
You can find out the procedure for filling out the book of income and expenses here .
Let's see how the acquisition of a new intangible asset will be reflected in the 2nd section of KUDiR:
- If a license was acquired on the basis of a sublicense agreement, then this program will no longer be considered an intangible asset, and, accordingly, the costs of its acquisition can be immediately included in the expenses of the current period in tax accounting. In section 1 of KUDiR, the costs of its acquisition should be reflected in column 5.
| No. | Document details | Operation | Income accepted when calculating the tax base | Expenses taken into account when calculating the tax base |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 45 | Payment order dated January 15, 2020 No. 14 | The cost of the non-exclusive right to the program is taken into account in expenses | – | 100 000 |
In addition, we note some points related to the maintenance of such licenses in tax accounting:
- Programs need to be updated periodically and service companies need to be paid for this. The costs of updating are expressly indicated in sub-clause. 19 clause 1 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and can be taken into account immediately after payment.
- If the contract specifies periodic payments for the use of the program (license), then such expenses are taken into account in tax accounting in accordance with subclause. 32 clause 1 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, that is, also upon payment.
You can read many of the nuances of tax expenses under the simplified tax system in this material .
The Federal Tax Service explained how to take into account the costs associated with purchasing licenses
February 9, 2012 February 9, 2012 The amount of state duty for issuing licenses is written off as a lump sum at the time of accrual.
If the company incurred other expenses related to obtaining licenses (consulting, legal, etc.), they are also taken into account as part of other expenses on one of the dates specified in paragraph 3 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Such recommendations are contained in. In addition, officials explained that the underwritten cost of a license, the validity period of which has been changed to unlimited, can also be taken into account at a time. Since November 3, 2011, a new procedure for licensing certain types of activities has been in effect (approved.
Federal Law dated 04.05.11 No. 99-FZ).
It contains a new list of licensed activities. It has also been established that licenses are now valid indefinitely. In this regard, the question arose: how to take into account the costs
Results
To correctly attribute license expenses to expenses, an accountant needs to know exactly what type of right (exclusive or non-exclusive) the organization received, how it can be used, and how to correctly qualify this expense.
Based on the data obtained, it will not be difficult to correctly determine tax expenses. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
conclusions
- A license is a right. It is not a product - it is a service;
- Because This is a service and the sublicensing agreement does not define how many rights and for which products will be transferred to the end client, it does not require quantitative accounting in the warehouse. There is no need to arrive for the service in advance; it can simply be provided, because you have the right to do so: a sublicense agreement signed with Cleverence!
- The name of the licenses is entered into the “Nomenclature” directory with the mark “Service” and indicating the sales accounting accounts (90 or 91). Royalties can be accounted for in a separate off-balance sheet account;
- To reflect the costs of paying royalties at the end of any agreed period (month, quarter), the licensor (Cleverence) provides the licensee (Partner) with a report and a statement of how many and what licenses were activated by end consumers. Royalty payments are made on the basis of such acts.
Licensed programs: accounting problems
These costs (if you plan to use the program for more than a year) must be reflected in the “Non-current assets” section of the balance sheet. To do this, you can independently enter the line “Licensed programs” or “Deferred expenses” in section 1 of the balance sheet.
Russians, and even then not all of them, buy only a limited set of programs. At the same time, some experts adhere to a different position.
They believe that the costs of acquiring any licensed software are recognized as intangible assets (if the program will be used for more than 12 months), since the exclusive right cannot be a criterion for qualifying costs as an asset.
Main types of state duty for a company
State duties for legal entities can be divided into three types:
- Acquisition of rights or property - state. a fee is paid for their registration.
- Operations related to the organization's activities - a very wide range: urgent issuance of an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, changes in constituent documents, issuance of permits and certificates, provision of licenses, etc.
- Litigation – state. fee for filing a statement of claim in court, complaints, initiation of legal proceedings, etc.
advocatus54.ru
The software is used for its intended purpose for several reporting periods (months), the total costs for the acquisition of such rights, paid in a one-time payment, are initially reflected in the accounting records as the debit of account 97 “Deferred expenses” with their subsequent write-off to the debit of the production costs (expenses) accounts for sale, general business expenses) during the term of the agreement. The following entries are made in accounting: Debit 012 - rights acquired under a license agreement are registered in an off-balance sheet account in an assessment determined based on the amount of remuneration established in the agreement; Debit 97 Credit 60 (76) - expenses associated with the acquisition of rights to use additional modules are reflected as deferred expenses. As expenses are recognized: Debit 20 (26, 44) Credit 97 - part of the expenses attributable to the reporting period is written off.