Home / Labor Law / Personnel Management / Personnel Records
Back
Published: 08/07/2016
Reading time: 11 min
0
953
A timesheet is a basic document for determining the length of service and salary of any employee.
Knowing a few simple filling rules will make it easier to navigate the notations.
- What is it needed for?
- Unified form
- What does the document contain?
- Accounting methods
- Subtleties of filling out Sick days
- Absence from work with permission
- Vacation
- Processing of specialists with irregular working hours
- Part-time exit
- Summarized accounting
- Business trips
Advances under the simplified tax system in 2021
On the simplified tax system, a single tax must be paid annually. At the same time, it is important to make advance payments every quarter during the year. The Federal Tax Service expects payments from organizations and individual entrepreneurs by the 25th of the month following the reporting period. The dates for 2021 and 2021 are as follows:
| Reporting period | 2020 | 2021 |
| 1st quarter | April 27 | 26 April |
| half year | July 27 | 26 July |
| 9 months | October 26 | the 25th of October |
If the 25th falls on a weekend or non-working holiday, then the due date is postponed to the next working day. Due to the coronavirus pandemic, all companies that are required to comply with the non-working day regime have received a deferment on tax payment until May 12. Simplified workers from the most affected industries will be able to pay an advance payment for the first quarter until October 26, and for the half-year - until November 25. There is no formal advance payment for the 4th quarter. It represents the final payment for the year. Organizations and individual entrepreneurs calculate tax according to the simplified tax system, taking into account all previously paid advance payments. Simplifiers at the object “Income minus expenses” calculate a single or minimum tax. You need to transfer taxes to the budget:
| for 2021 | for 2021 | |
| IP | April 30, 2021 | April 30, 2022 |
| OOO | March 31, 2021 | March 31, 2022 |
The deadline for paying the single tax under the simplified tax system in 2021 has been postponed for industries affected by the coronavirus pandemic. For 2021, LLCs can pay tax until September 30, and individual entrepreneurs - until October 30.
Don't ignore down payments. If an entrepreneur decides to calculate and transfer the tax only after the end of the calendar year, he will have to respond in rubles: for each day the advance payment is late, the Federal Tax Service charges penalties - use our free penalty calculator to calculate their amount. If a businessman fails to pay tax for the year, in addition to penalties, he faces a fine of 20% or 40% of the unpaid amount.
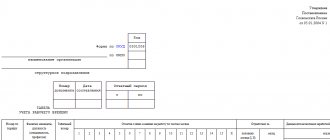
Form T-12
Form 12-F was adopted for use by Rosstat Order No. 247 dated July 13, 2010. The form records data on compliance with the daily routine in the company.
If there are separate divisions in the company structure that work with an independent balance sheet, and also record receipts of funds from the sale of products, work performed, services provided and expenses for the production activities of the department, recording of arrivals to work is carried out for each independent division.
The completed timesheets are sent by the company to the territorial structures of Rosstat at the place of registration of the enterprise or the corresponding structural department of the company.
The head of the institution, by order, appoints a person responsible for monitoring compliance with the daily routine, with the submission of a statistical report to government agencies.
Advance payment for 1st quarter
Calculation of the advance payment for the 1st quarter using the “income” base
Step 1. To calculate the tax, we determine the tax base: we sum up all income from the beginning of the year. This indicator is taken from the 1st section of the Book of Income and Expenses. Organizations and individual entrepreneurs on a simplified basis take into account revenue from sales as income, as well as non-operating income, which are listed in Art. 249 and 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Step 2. The tax amount is calculated using the formula: Income × Tax rate. Check the tax rate for your type of activity and your region - it can range from 1 to 6%. From January 1, 2021, an increased rate of 8% also appeared for those taxpayers who violated the basic limits. We will explain below how to calculate the tax if the limits are exceeded.
Step 3. Simplified workers on the “income” basis have the right to apply a tax deduction and reduce the tax by the amount of insurance premiums paid for employees, as well as sick leave paid by the employer.
- LLCs and individual entrepreneurs with employees can reduce tax by no more than 50%.
- An individual entrepreneur without employees has the right to reduce tax without restrictions by the amount of insurance premiums that he pays for himself.
The trade tax deduction is applied without restrictions.
Now we deduct from the tax amount all paid contributions, fees and sick leave. If the amount of the tax deduction exceeds 50% of the tax (for organizations and individual entrepreneurs with employees), then the tax is reduced only by half.
An example of calculating an advance payment for Kopyto LLC for the 1st quarter of 2021
Tax base “income”, rate 6%.
The enterprise's income from the beginning of the year to the end of March amounted to 150,000 rubles.
- Advance payment for the 1st quarter: 150,000 × 6% = 9,000 rubles.
We may reduce this amount by the amount of fees paid. The organization has two employees, the salary of each of them is 30,000 rubles. Insurance contributions are paid from the salary in the amount of 30%, that is, 18,000 rubles per month. Over the past quarter, the organization transferred insurance premiums in the amount of 54,000 rubles (18,000 × 3). Sick leave was not paid.
We see that the amount of contributions is greater than the amount of tax, but we can still only reduce the tax by half:
- 9,000 × 50% = 4,500 rubles.
Thus, the organization must pay 4,500 rubles by April 25.
Calculation of the advance payment for the 1st quarter using the “Income minus expenses” base
Step 1. Determine the tax base. The amount of income is taken from section 1 KUDIR - the total amount for the reporting period, column 4. Simplified people must take into account income in the tax base in accordance with Art. 249 and 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The amount of expenses that we will deduct from income is taken from column 5 of section 1 KUDIR. Under the simplified tax system, economically justified and documented costs are recognized as expenses, which are listed in paragraph 1 of Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. You can read about how to keep track of expenses under the simplified tax system in our article.
Step 2. The tax amount is calculated using the formula: (Income – Expenses) × 15%. Check the tax rate for your region and type of activity, it may be less than 15%.
A separate question: what to do with insurance premiums? In accordance with clause 1.7 of Art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, simplified versions include paid insurance premiums as expenses. This applies to contributions for employees and contributions from entrepreneurs “for themselves.” Paid insurance premiums reduce the tax base and the tax itself.
An example of calculating an advance payment for an individual entrepreneur A.V. Petrov for 1st quarter.
Tax base “income minus expenses”, rate 15%.
The income of the individual entrepreneur from January to the end of March amounted to 120,000 rubles. The individual entrepreneur's expenses for 3 months amounted to 40,000 rubles. Individual entrepreneur Petrov pays insurance premiums for himself in each quarter of 10,220 rubles, he included this amount in expenses.
- Advance payment amount: (120,000 – 40,000) × 15% = 12,000 rubles.
Thus, the individual entrepreneur must pay 12,000 rubles by April 25.
How to keep a timesheet
By law, the employer has the right to choose one of the following methods:
- continuous - registration of appearances, absences and any deviations from the normal work schedule, such as work on holidays, overtime, business trips;
- for deviations - registration of only absences and deviations from the standard work regime.
In practice, everyone uses the continuous method, and accounting for deviations is almost never used. This is due to the fact that personnel records are almost completely automated, and electronic processing of forms T-12 and T-13 does not allow leaving empty cells.
Advance payment for 2nd quarter
The procedure for calculating the advance payment for the second quarter is similar to the first. It is important to keep in mind that advance payments paid in the last quarter must first be subtracted from the calculated tax amount.
An example of calculating an advance payment for LLC “Kopyto” for the 2nd quarter
The enterprise's income from the beginning of the year to the end of June amounted to 270,000 rubles. Of these, 150,000 rubles for the 1st quarter and 120,000 rubles for the 2nd quarter. Advance payment for the 1st quarter - 4,500 rubles.
- Tax amount for the half year: 270,000 × 6% = 16,200 rubles
We can reduce this amount by the amount of contributions paid, which for the first six months amounted to, say, 108,000 rubles. Sick leave was not paid. We see that the amount of contributions is greater than the amount of tax, but the tax can still only be reduced by half:
- Tax amount for half a year with deduction: 16,200 × 50% = 8,100 rubles
Now from this amount we must subtract the advance payment of the 1st quarter: 8,100 – 4,500 = 3,600 rubles.
Thus, the organization must pay 3,600 rubles by July 25.
Calculation of the advance payment for the 2nd quarter using the “Income minus expenses” base
The procedure for calculating the advance payment for the taxable base “Income minus expenses” is also similar to the first quarter. But the advance paid in the first quarter must first be deducted from the amount of tax calculated in the second quarter.
An example of calculating an advance payment for an individual entrepreneur A.V. Petrov for the 2nd quarter.
The income of the individual entrepreneur from January to the end of June amounted to 230,000 rubles. Of these, 120,000 were for the 1st quarter, 110,000 were for the 2nd quarter. The individual entrepreneur's expenses for 6 months amounted to 85,000 rubles. Of these, 40,000 for the 1st quarter, 45,000 for the 2nd quarter. Advance payment in the 1st quarter - 12,000 rubles. Individual entrepreneur Petrov pays insurance premiums for himself in each quarter of 10,200 rubles, he included these amounts in expenses.
- Tax amount for half a year: (230,000 – 85,000) × 15% = 21,750 rubles
Now we subtract the advance payment for the 1st quarter from this amount: 21,750 - 12,000 = 9,750 rubles.
Thus, the individual entrepreneur must pay 9,750 rubles by July 25.
Who is responsible for recording time worked in the organization?
According to the instructions for using and filling out forms of primary accounting documents:
- the working time sheet is compiled and maintained by an authorized person;
- the standards indicate who signs the time sheet - the head of the department and the HR employee;
- after which it is transferred to the accounting department.
Management has the right to appoint anyone to perform this task. To do this, an order is issued indicating the position and name of the responsible person. If an order to appoint such an employee is not issued, then the obligation to keep records is specified in the employment contract. Otherwise, it is unlawful to require an employee to keep records. In large organizations, such an employee is appointed in each department. He fills out the form within a month, gives it to the head of the department for signature, who, in turn, checks the data and passes the form to the personnel officer. The HR department employee verifies the information, fills out the documents necessary for his work based on it, signs the time sheet and passes it on to the accountant.
In small companies, such a long chain is not followed - maintaining time sheets for employees is entrusted to the personnel employee, and he submits the completed document to the accounting department on a monthly basis.
Advance payment for 3rd quarter
Calculation of the advance payment for the 3rd quarter using the “income” base
The procedure for calculating the advance payment for the third quarter is similar to the first. It is important to keep in mind that advance payments paid in the first and second quarter must first be subtracted from the calculated tax amount.
An example of calculating an advance payment for LLC “Kopyto” for the 3rd quarter
Tax base “income”, rate 6%
The enterprise's income from the beginning of the year to the end of September amounted to 420,000 rubles. Of these, 150,000 rubles for the 1st quarter, 120,000 rubles for the 2nd quarter and 150,000 for the 3rd quarter. Advance payments for the 1st quarter - 4,500 rubles, for the 2nd quarter - 3,600 rubles.
- Tax amount for 9 months: 420,000 × 6% = 25,200 rubles.
We can reduce this amount by the amount of contributions paid, which over the past 9 months amounted to 162,000 rubles. Sick leave was not paid. The amount of contributions is greater than the amount of tax, but we can still only reduce the tax by half:
- Tax amount for 9 months with deduction: 25,200 × 50% = 12,600 rubles
Now from this amount we must subtract the advance payments of the 1st and 2nd quarters: 12,600 - (4,500 + 3,600) = 4,500 rubles.
Thus, the organization must pay 4,500 rubles by October 25.
Calculation of the advance payment for the 3rd quarter on the basis of “income minus expenses”
The procedure for calculating the advance payment for the taxable base “Income minus expenses” is also similar to the first quarter. But advances paid in the first and second quarters must first be deducted from the tax amount calculated in the third quarter.
An example of calculating an advance payment for an individual entrepreneur A.V. Petrov for the 3rd quarter
Tax base “Income minus expenses”, rate 15%
The income of the individual entrepreneur from January to the end of September amounted to 380,000 rubles. Of these, 120,000 were for the 1st quarter, 110,000 for the 2nd quarter and 150,000 for the 3rd quarter.
The individual entrepreneur's expenses for 9 months amounted to 125,000 rubles. Of these, 40,000 for the 1st quarter, 45,000 for the 2nd quarter and 40,000 for the 3rd quarter.
Advance payments in the 1st quarter - 12,000 rubles, in the 2nd quarter - 9,750 rubles.
Individual entrepreneur Petrov pays insurance premiums for himself in each quarter of 10,200 rubles, he included these amounts in expenses.
- Tax amount for 9 months: (380,000 – 125,000) × 15% = 38,250 rubles.
Now we subtract from this amount the advance payments of the 1st and 2nd quarters: 38,250 – (12,000 + 9,750) = 16,500 rubles.
Thus, the individual entrepreneur must pay 16,500 rubles by October 25.
What to do if you are late on your quarterly advance payment
Sometimes an entrepreneur does not have available funds to pay an advance payment and makes the payment later - closer to the end of the year or together with the payment of tax calculated at the end of the year. This means that the businessman will have to pay a penalty for each day of delay. If the advance had to be transferred before April 25, then the first day for accrual of penalties for non-payment is April 26. The last day for accrual of penalties is the day on which you paid the advance payment.
Penalties are calculated differently for organizations and individual entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs charge penalties as follows:
1/300 of the refinancing rate × amount of non-payment × number of days of delay.
The amount of penalties for organizations depends on the number of days of delay. If the delay is less than 30 days, then the formula is similar to the formula for individual entrepreneurs. But if the delay is more than 30 days, the formula becomes more complicated:
(1/300 of the refinancing rate × amount of non-payment × 30) + (1/150 of the refinancing rate × amount of non-payment × number of days of delay from 31 days)
Pay attention to the refinancing rate. Since 2016, it has been equal to the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, and in recent months the Central Bank has often reduced it. In November 2021, the key rate is 4.25%. To avoid making mistakes in your calculations, use our free online penalty calculator.
An example of calculating penalties for non-payment of an advance payment in the 3rd quarter
The individual entrepreneur was supposed to pay 12,000 rubles in advance by October 26, but he was able to transfer these funds only on November 10. The delay is 16 days. The key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in November 2020 is 4.25%.
- 1/300 × 4.25% × 12,000 × 15 = 25.5 rubles.
Thus, the penalty will be 25.5 rubles. The individual entrepreneur will have to pay this amount along with the advance payment on November 10.
In what cases is the NN code used?
The NN code, or the absence of an employee for unknown reasons, is entered every time and as long as the employee is not at work and the responsible person does not have documents about the reasons for his absence. Even if the manager of the absent person swears that the employee is absent (PR code), do not rush to put this code in the primary accounting documents, wait until the person brings a document explaining his absence. Otherwise, it may happen that a time sheet with an incorrect code is submitted to the accounting department, and then it turns out that the employee was absent for a good reason, and then changes will have to be made to the primary accounting documents.
Single tax according to the simplified tax system for the year (payment for the 4th quarter)
There is no advance payment under the simplified tax system for the 4th quarter. The fact is that the tax is paid in installments at the end of each reporting period, and 4 quarters of the year are the tax period. Therefore, for the 4th quarter, it is not an advance payment that is paid, but a tax based on the results of the year or all quarters. When calculating it, all advance payments made during the year are taken into account. Tax payment deadlines differ for organizations and entrepreneurs:
| for 2021 | for 2021 | |
| IP | April 30, 2021 | April 30, 2022 |
| OOO | March 31, 2021 | March 31, 2022 |
Calculation of the single tax according to the simplified tax system for the year using the “Income” base
The rules for calculating the single tax according to the simplified tax system are established by Article 346.21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The tax is calculated using the formula:
TAX = Tax base × 6% – Advance payments for the year
Step 1. Determine income for the period. Let's sum up the income received for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th quarters on a cumulative basis. This indicator can be found in the first section of the Income and Expense Accounting Book. Organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system take into account revenue from sales as income, as well as non-operating income, which are listed in Art. 249 and 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Step 2. Determine the amount of insurance premiums . The calculated tax is reduced by the amount of insurance premiums paid for the period.
- LLCs and individual entrepreneurs with employees can reduce tax by no more than 50%;
- An individual entrepreneur without employees has the right to reduce tax without restrictions by the amount of insurance premiums that he pays for himself.
Step 3. Determine the tax base. From the amount of income received for the year, we subtract the amount of insurance premiums paid for the year. If the amount of the tax deduction exceeds 50% of the tax (for organizations and individual entrepreneurs with employees), then the tax is reduced only by half.
Step 4. Calculate tax according to the simplified tax system . We multiply the resulting tax base by the tax rate and subtract all advance payments transferred to the budget during the year.
An example of calculating a tax payment for Kopyto LLC for 2020.
Tax base “Income”, rate 6%
LLC "Kopyto" works on a simplified basis with the object of taxation "income". The organization has two employees, the salary of each of them is 30,000 rubles. The company's income for the entire year amounted to 580,000 rubles:
- 1st quarter - 150,000 rubles;
- 2nd quarter - 120,000 rubles;
- 3rd quarter - 150,000 rubles;
- 4th quarter - 160,000 rubles.
During the year, advance payments were transferred for the 1st quarter - 4,500 rubles, for the 2nd quarter - 3,600 rubles, for the 3rd quarter - 4,500 rubles.
- Tax amount for the year: 580,000 × 6% = 34,800 rubles
We may reduce this amount by the amount of fees paid. From the salaries of two employees (30,000 rubles each), insurance premiums are paid monthly in the amount of 30% - 60,000 × 30% = 18,000 rubles per month. Over the past year, the organization transferred insurance premiums in the amount of 18,000 × 12 = 216,000 rubles. Sick leave was not paid.
We see that the amount of contributions is greater than the amount of tax, but we can still only reduce the tax by half.
- Tax amount for the year with deduction: 34,800 × 50% = 17,400 rubles
Now from this amount we must subtract advance payments for three quarters:
- 17,400 – (4,500 + 3,600 + 4,500) = 4,800 rubles.
Thus, the organization must pay 4,800 rubles by March 31, 2021.
Calculation of the single tax according to the simplified tax system for the year using the “Income minus expenses” base
Step 1. Determine the tax base. We take income and expenses from the Income and Expense Accounting Book. Income is recorded in the first section of KUDIR in column 4. “Simplified” must take into account income in the tax base in accordance with Art. 249 and 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Expenses are indicated in column 5 of the first section of KUDIR. Economically justified and documented costs, which are listed in clause 1 of Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Unlike the simplified taxation system “Income”, under the “Income minus expenses” system, insurance premiums cannot be deducted. They are immediately included in expenses and reduce the tax base and the tax itself.
Step 2. Determine the tax amount. The tax is calculated using the formula:
Tax = (Income - Expenses) × 15%.
Check the tax rate for your region and type of activity, it may be less than 15%.
Step 3. Calculate the amount of tax payable for the year. From the calculated tax amount, we subtract advance payments that were made in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd quarters.
An example of calculating a tax payment for an individual entrepreneur A.V. Petrov. for 2020
Object of taxation “income minus expenses”, rate 15%
IP income for 2021 amounted to 470,000 rubles, and expenses amounted to 160,000 rubles. Of them:
Quarter Income Expenses 1st quarter 120,000 rubles 40,000 rubles 2nd quarter 110,000 rubles 45,000 rubles 3rd quarter 150,000 rubles 40,000 rubles 4th quarter 90,000 rubles 35,000 rubles Petrov pays quarterly insurance premiums for himself of 10,200 rubles, he included these amounts in expenses.
Advance payments during the year amounted to: 1st quarter - 12,000 rubles, 2nd quarter - 9,750 rubles, 3rd quarter - 16,500 rubles.
- Tax amount for the year: (470,000 - 160,000) × 15% = 46,500 rubles.
Now we subtract advance payments for the year from this amount:
- Tax amount for the year minus advance payments: 46,500 – (12,000 + 9,750 + 16,500) = 8,250 rubles.
Thus, the individual entrepreneur must pay 8,250 rubles by April 30, 2021.
Are days off noted on the timesheet when an employee is sick?
When an employee is on sick leave, code B (temporary disability) is assigned for the entire period of temporary disability, including weekends and holidays.
Read more: How sick leave is paid on weekends
A similar complete registration is carried out when employees are on maternity leave (P), on parental leave when they reach the age of three years (OZ) and unpaid leave (UP).
Calculation of the minimum tax according to the simplified tax system 15%
It is not always possible to make a business profitable. At the end of the year, expenses may exceed income or differ only slightly. In this case, the tax base will be very tiny or even negative. In this case, the state will not pay you any compensation, but will oblige you to pay a minimum tax. The minimum tax is calculated based on all income received during the tax period at a rate of 1%.
Therefore, at the end of the year it is necessary to calculate the tax in the standard way and the minimum tax. The amount that turns out to be greater is subject to payment to the budget.
An example of calculating the minimum tax for Tea House LLC.
In 2021, income amounted to 180,000 rubles, and expenses amounted to 170,000 rubles.
- Tax amount for the year = (180,000 - 170,000) × 15% = 1,500 rubles per year.
- Minimum tax = 180,000 × 1% = 1,800 rubles.
With a slight difference in income and expenses, the amount of the minimum tax was 300 rubles higher than the amount of tax calculated in the usual way. In this case, Tea House LLC will pay the minimum tax for the year - 1,800 rubles.
The difference between the minimum tax and the tax you would have paid under the standard rules can be taken into account when calculating your tax for subsequent tax periods.
Calculation of advance payments and tax for the year at an increased rate
From January 1, 2021, increased rates began to apply for the simplified tax system. They must be used when basic limits are violated. This happens when:
- Income since the beginning of the tax period exceeded 150 million rubles, but did not reach 200 million rubles;
- The average number of employees in the reporting period exceeded 100 people, but remains less than 130 people.
The increased rate for the simplified tax system “income” is 8%, for the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” - 20%. The size of the increased rates is fixed; they must be applied if the limits are violated, even if there are reduced rates in your region or you are on a tax holiday.
The increased rate applies to the portion of the tax base that falls on the period from the beginning of the quarter in which the excesses occurred.
Calculation procedure
Step 1. Calculate the down payment for the period before exceeding the limits. To do this, determine the advance payment without taking into account deductions by multiplying the tax base by the standard tax rate.
Step 2 . Calculate the advance payment for the period in which the limits were violated. To do this, take the amount calculated in step 1 and add to it the difference between the tax base for the period with excess and the tax base for previous periods, multiplied by 8%. Use the following formula:
Advance payment for the period in which the limits were exceeded = Tax base for the reporting period preceding the quarter in which the limits were exceeded × Tax rate + (Tax base for the reporting period in excess - Tax base for the previous reporting period in which the limits were met) × Increased tax rate
Step 3. If you are calculating the payment for the simplified tax system “income”, additionally reduce the accrued advance payment or additional tax by tax deduction.
An example of calculating an advance payment at a rate of 8% for the simplified tax system “income”
LLC "Bashmachok" on the simplified tax system "income" exceeded the income limit for 9 months and was forced to apply an increased rate of 8%. At the end of the 1st quarter, revenue amounted to 50 million rubles, at the end of the half year 100 million rubles, and at the end of 9 months - 152 million rubles. Advance payments for the 1st quarter and half of the year are calculated in the standard manner:
- Advance payment for the 1st quarter: 50,000,000 × 6% = 3,000,000 rubles.
- Advance payment for six months: 100,000,000 × 6% – 3,000,000 = 3,000,000 rubles.
The accrued advance payment for 9 months of 2021 must be calculated at an increased rate.
- Advance payment for 9 months: (100,000,000 × 6%) + ((152,000,000 - 100,000,000) × 8%) = 10,160,000 rubles.
The advance payment accrued at the end of 9 months can be reduced by tax deductions (450,000 rubles in insurance premiums for 9 months) and previously paid advance payments.
- Advance payment for 9 months for additional payment: 10,160,000 - 450,000 - 3,000,000 - 3,000,000 = 3,710,000 rubles.
Based on the results of 9 months, Bashmachok LLC must pay an additional 3,710,000 rubles to the budget.
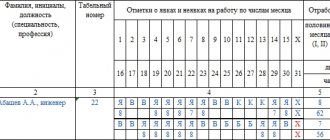
Methods for filling out the T-13 form, basic codes for filling out the timesheet
When working with timesheets, different methods are used to control the time worked by staff.
- One way is to display staff presence at work on a daily basis.
- Another way to work with a report card is to control absences and tardiness, with a description of the reasons for such violations.
To simplify the work with the time sheet, specialized codes have been adopted, thanks to which data is entered simply and quickly. Today, the following codes are used in timekeeping:
- Arrival of personnel at work according to the established schedule is displayed with the symbol “I”, or the number “01”
- A working person's scheduled vacation is indicated by the symbols “FROM” or the number 09.
- Maternity leave is assigned the code “P”, or the number 14.
- If an employee goes on leave to support a child, the code “OZH” or the number 15 is displayed.
- Vacation at your own expense is indicated by the symbols “BEFORE” or the number – 16.
- When a person is on a business trip, the symbol “K” or the number 06 is displayed.
- If you miss work due to unknown circumstances, fill in the symbols “НН” or the number 30.
- The provision of sick leave is marked with the symbol “B” or the number -19.
All company personnel involved in monitoring the daily routine and payroll are required to study the codes. Ignorance of the designation of codes can lead to incorrect calculation of wages to an employed person or to the imposition of an unreasonable punishment.
The timesheet displays all data on the work of the company’s personnel in symbolic or numerical notation. Thus, the T-12 form contains all the conditional codes that must be used when working with the report card. This ensures that errors are avoided when working with the form, as well as when deciphering the entered information by accounting employees.