Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system are, as a general rule, not recognized as VAT payers (except for situations expressly defined by tax legislation). Consequently, when selling goods, works, services, property rights, they do not have the obligation to issue invoices, maintain a purchase book and a sales book. At the same time, there is a direct prohibition on the preparation of this document by a “simplified” Ch. 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has not been established.
But in practice, there are often situations when these persons, without receiving any benefit, issue an invoice to buyers at their request. We will talk about the consequences of such “kindness” of organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system in the framework of the article.
Invoice under simplified tax system
All organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system are not VAT payers, which means they do not need to issue an invoice. However, if certain situations arise, such a document will be needed.
These include situations where “simplified” people pay VAT: (click to expand)
- Import of goods;
- Operations under a simple partnership agreement, or trust management of property and concession agreement;
- When a company performs the duties of a tax agent, for example, rents state or municipal property.
In all of the above situations, organizations are required to issue an invoice (
Invoice with o
You are not required to issue an invoice from the company using the simplified tax system. Only companies exempt from VAT put this mark. Organizations that are considered exempt from VAT are recognized in accordance with Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Companies that apply the simplified tax system do not qualify as such “exempt” payers, since they are not initially payers of this tax. Accordingly, there is no need to issue a “simplified” invoice marked “without VAT”.
Some counterparties still insist on an invoice. Such companies should keep in mind that they will not receive a deduction for “input” VAT on such an invoice. And why they continue to demand such invoices is not clear.
“Simplers” are not obliged to fulfill such a request. They have the right to explain to their counterparties that in order to post the purchased goods, documents such as an invoice for payment, an invoice and a statement will be sufficient. And if the counterparty continues to insist and it is impossible to convince him, then you can issue the required document. Please indicate that the purchase does not include VAT.
Such registration of an invoice will not entail obligations to pay tax, as well as the preparation and submission of a VAT return, since the tax will not be highlighted in the invoice (
Issuance of invoices by organizations using the simplified tax system. Tax consequences for the parties to the transaction
Source: “Tax Bulletin”,
In accordance with paragraphs 2, 3 and 5 of Art. 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (TC RF), organizations and individual entrepreneurs applying the simplified taxation system are not recognized as VAT payers, with the exception of this tax payable when importing goods into the customs territory of the Russian Federation. However, they are not exempt from performing the duties of tax agents provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, the provisions of Ch. 21 and 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified taxation system are not given the right to refuse non-recognition of their VAT payers and to pay the tax voluntarily at the request of customers. According to Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when selling (transferring) goods (work, services), persons who are not VAT payers do not issue invoices to buyers. In accordance with paragraph 5 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation when selling goods (work, services), operations for the sale of which are not subject to VAT (exempt from taxation), as well as when the taxpayer is exempt in accordance with Art. 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation from the performance of duties as a VAT payer, settlement documents, primary accounting documents are drawn up and invoices are issued without allocating the corresponding tax amounts. In this case, the corresponding inscription or stamp “Without tax (VAT)” is made on the above documents. In other words, these provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not applicable to persons who have switched to a simplified taxation system. For them, issuing an invoice is a violation (Letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 02/08/2007 N MM-6-03/ [email protected] , Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/11/2004 N 04-03-11/20, Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 03/05/2007 N 18-11/3/ [email protected] ). If persons who are not VAT payers issue an invoice to the buyer with the allocation of the amount of tax, the amount of VAT indicated in the invoice is subject to payment to the budget in accordance with paragraphs. 1 clause 5 art. 173 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, an organization applying a simplified taxation system does not have the right to deduct VAT amounts paid to suppliers of goods (works, services) (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 23, 2007 N 03-07-11/68, Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 30.11.2006 N 18-11/3/ [email protected] , dated 06.03.2007 N 19-11/ [email protected] ). At the same time, readers of the magazine should keep in mind that VAT, unlawfully presented by such business entities in the invoice to buyers, is not accepted for deduction from the buyer (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 23, 2007 N 03-07-11/68, UMTS of Russia for the city Moscow dated 05/04/2004 N 21-09/34816, Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 07/08/2005 N 19-11/48885). If the buyer knew or should have known about the use of a simplified taxation system by his counterparty, his receipt of a tax benefit in the form of a VAT deduction will be recognized in this case as unjustified (clause 10 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated October 12, 2006 N 53). As a rule, organizations and individual entrepreneurs applying the simplified taxation system provide the counterparty with a copy of Form N 26.2-2 “Notification of the possibility of applying the simplified taxation system” in the set of transaction documents. Having received this document, the counterparty cannot claim that he did not know about the tax system applied by his partner, and does not have the right to insist on issuing an invoice to him. A different situation arises with intermediary transactions, in which the commission agent (agent) is a person who applies the simplified taxation system and does not pay VAT, and the principal (principal) is an organization (individual entrepreneur) applying the general taxation regime. The fact is that, in accordance with the provisions of Art. Art. 990 and 1005 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Civil Code of the Russian Federation), within the framework of commission and agency agreements, the commission agent or agent undertakes, on behalf of the principal (principal) for a fee, to carry out one or more transactions in his own name, but at the expense of the principal (principal) or on behalf and for principal's account. As follows from clause 24 of the Rules for maintaining logs of received and issued invoices, purchase books and sales books when calculating value added tax, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 2, 2000 N 914, commission agents selling goods on their own behalf, must issue invoices for the full cost of goods with an allocated amount of VAT in the name of the buyer, and transfer the details of these invoices to the principals. This obligation also applies to the cases we have named (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 03/22/2005 N 03-04-14/03, dated 05/05/2005 N 03-04-11/98, Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 10/12/2006 N 18 -12/3/ [email protected] , from 07/03/2006 N 18-11/3/ [email protected] ). It should be noted that the above procedure for issuing invoices does not lead to the obligation of the commission agent to pay VAT to the budget on goods sold by the principal. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 991 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the principal is obliged to pay the commission agent a remuneration, and if the commission agent has accepted a guarantee for the execution of the transaction by a third party (del credere), also an additional remuneration in the amount and manner established in the commission agreement. In a similar manner, according to Art. 1006 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the principal is obliged to pay the agent remuneration in the amount and in the manner established in the agency agreement. Since the intermediary applies a simplified taxation system and is not a VAT payer, he does not have the obligation to issue an invoice for the amount of his remuneration.
Zero VAT on the invoice
Organizations using the simplified tax system should also not put a real VAT rate of 0% in the invoice. Only companies that are VAT payers can apply this rate. In addition, it must be confirmed by specific documents that organizations submit along with the VAT return to the tax office.
If an accountant decides to meet the buyer halfway and issue a document with zero VAT, the tax authorities have the right to charge it, not at a zero rate, but at a rate of 18%. This will happen because VAT is indicated in the invoice, and it is impossible to confirm that the company’s rate is zero.
How to apply correctly?
The invoice can be displayed through the 1C program , analogues of this program, or filled out yourself. The good thing about the program is that many fields are filled in automatically, but double-checking will not be superfluous. The invoice according to the simplified tax system and the special tax system is filled out in the same way with the difference in the indication of the tax rate.
Is it possible to specify zero percent?
Setting a zero interest rate is a gross mistake. And if it is entered, then despite the form of tax accounting and exemption from their payments, you will have to pay a rate of 18%.
A zero deduction confirms the export of goods to other countries. The organization notifies the tax office by providing a package of export documents :
- Contract;
- customs declaration;
- transport and shipping documents.
The documentation must comply with the forms established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and must also be sealed with a customs stamp. In the case of small trade, with income up to 3 million rubles, under the simplified tax system, the best and legal tax rate is “Without VAT”.
Filling procedure
Correct preparation and completion of the document guarantees high-quality work:
- Filling out the header:
- 1 – document number and date of the extract. When working in the program, you don’t have to enter it yourself - the system will enter it itself.
- 1a – all changes that existed in previous forms. If there were none, then a dash.
- 2 – confirmed name of the Seller company.
- 2a – contacts and location of the Seller.
- 2b – TIN, code assigned to the Seller’s tax authority.
- 3 – name of the shipper. If the goods are sent by the selling company, then the phrase “aka” is indicated.
- 4 – name of the Consignee, all contact details, including postal address.
- 5 – PQR data, including the number and date of its compilation.
- 6 – confirmed name of the Buyer company.
- 6a – contacts and location of the Buyer.
- 6b – TIN, code assigned to the Buyer’s tax authority.
- 7 – a single currency for all goods and services in the document.
- 8 – descriptor of a contract or agreement confirming permission to provide other persons with goods.
- Nomenclature table:
- 1 – nomenclature name of goods or services provided by the seller.
- 2 – unit code. product measurements regulated by OKEI.
- 2a – direct unit of measurement (pcs, kg, m, sq.m, etc.).
- 3 – the number of units of goods or services that the Seller provides to the Buyer.
- 4 – cost of goods/1 unit. change..
- 5 – calculation total of the goods for this nomenclature column.
- 6 – amount of excise tax, if any. If not available – “without excise duty”.
- 7 – tax rate “Without VAT”.
- 8 – the amount of the tax rate “Without VAT”.
- 9 – calculation price of the item, including VAT.
- 10 – code of the country of origin according to OKSM.
- 10a – name of the country of origin.
- 11 – NTD. To be completed if the goods were to be imported from foreign countries.
- After filling out the invoice template, you need to print it out on A4 sheets, sign the person in charge who filled it out, and affix stamps from the Seller.
- After this procedure, both copies are sent to the Buyer and after affixing his signature and seal in the appropriate boxes, one copy is returned to the Seller.
The execution of the document is confirmed by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1137.
If you issue an invoice with VAT
Some organizations, on their own initiative, may issue invoices, highlighting VAT. In this case, they are required to pay tax to the budget and also submit a VAT return to the Federal Tax Service. This must be done before the 25th day of the month following the quarter in which the document was issued. For example, a company issued an invoice using the simplified tax system on February 10, 2021; accordingly, it must submit a VAT return by April 25, 2021.
It is important to understand that issuing an invoice with allocated VAT does not give the simplifier the right to a tax deduction on purchased goods. Only VAT payers have the right to such a deduction, and organizations using the simplified tax system are not such.
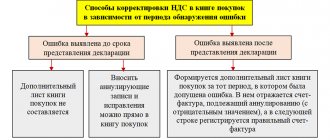
Is it necessary to maintain tax registers on the simplified tax system?
The issue of compiling books of purchases and sales when conducting business on the simplified tax system has always been controversial. After all, books of purchases and sales are registers for VAT, thanks to which you can control the correctness of tax calculation.
The article “Books of purchases and sales under the simplified tax system: the procedure for maintaining” is discussed in the article “Books of purchases and sales under the simplified tax system: the procedure for maintaining them .
As for journals of received and issued invoices, the need for their preparation depends on the types of transaction.
You can learn about them from this section.
Answers to common questions
Question: A simplified company, at the request of the buyer, issued an invoice, highlighting VAT. After that, in accordance with the requirements of the law, I paid this tax to the budget and filed a VAT return. When calculating the simplified tax system, will VAT be included in the tax base? (click to expand)
Answer: The tax base for simplifiers is income, which must first of all be economically profitable. Paid VAT is not a benefit for the company, and therefore should not be included in the base for calculating the simplified tax system. Accordingly, when calculating the tax, the simplified tax system does not need to be included in the VAT base.
How to calculate the amount of VAT payable to the budget?
When you sell goods or services with VAT at the request of a client, to calculate the amount of tax, multiply the cost of goods or services by a rate of 20% or 10%. Since VAT deductions cannot be applied under special regimes, at the end of the quarter, transfer the entire allocated amount of VAT to the budget.
VAT rates:
- 20% – general rate from 2021;
- 10% for certain groups of goods: some products, children's products, medical products;
- 0% for rarer operations.
For transactions of a tax agent, the VAT amount is calculated from the payment amount that is transferred to the seller. This may be the amount specified in the contract, or the amount of the monthly payment when renting from government agencies. Important: the amount of VAT must be withheld from the seller, which means that the calculated rate of 20/120 or 10/110 is used to calculate the tax.