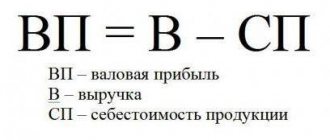What is a financial result?
Financial result is the economic result of the economic life of an organization, which is expressed in the form of profit or loss.
Profit is the amount by which revenue received exceeds expenses incurred. Simply put, when the company remains “in the black”. When an organization has incurred more expenses than it has earned from its activities, it is said to have received a loss. Information about financial results is important not only for internal control and management, but also for external parties interested in information of this kind. These include banking organizations that issue borrowed resources for the use of the company at certain interest rates, insurance companies, property insuring organizations, investors investing in the development of the company, and others. Profit is a relative measure of a company's performance. In general, it symbolizes the positive result of the enterprise. But based on profit analysis, different conclusions can be drawn. For example, after conducting a comparative analysis of profits over several years, a specialist can make a conclusion about an increase or decrease in its value and an increase or decrease in the efficiency of the company.
The resulting loss signals the company's management about the inefficiency of commercial activities and the need to take measures to increase the company's profitability.
For effective analysis, it is important to organize timely and accurate accounting of the financial results of the organization.
Additionally
You noticed that in the financial result formula, I wrote down the expense part like this [90.2....90.8 + 26, 44]. At the same time, I highlighted the cost accounts in bold. Did you notice? I wanted to bring this to your attention and raise a couple of questions from you. Which?
- Why is there no 20, 25 count here when there is 26?
- Why are these accounts highlighted?
Let's take it in order.
Why is there no 20, 25 count here when there is 26
The presence of 20 and 25 accounting accounts is typical for manufacturing companies. And all firms except trading ones have a 26 account. When the procedure for “closing the month” begins for manufacturing firms, accounts 26 and 25 are closed at 20, and 20 is closed at 40.
But 40, if there are deviations between the actual price from production and the planned price at which the products arrived at the warehouse, will partially go into expenses of 90.2 for the goods sold and 43. Probably, the result is a complex proposal. To fully understand it, it will be necessary to analyze production in detail. This is the task of other materials.
For manufacturing enterprises, to obtain the cost of production, all expenses are collected into account 20. But what is included in the financial result formula? Only the cost of goods sold at the time of sale is included. And also expenses from account 44.
Then what does the 26th account in the financial result formula tell us? The presence of account 26, which transfers its amounts to account 90, is typical for companies providing services.
Why do you highlight these accounts in the formula?
Because these accounts do not exist in the formula! That's how it is! I wrote them so that you have an answer to the question “Where will the amounts from the accounts storing costs/expenses go and where will they end up?” These amounts will be in the financial result formula, but will be transferred there to the appropriate subaccounts.
Amounts from cost/expense accounts will be transferred to subaccounts:
- 90.7 “Sale expenses”. Amounts from account 44 will come here (production and trading activities, performance of work)
- 90.8 “Administrative expenses”. Amounts from account 26 (service activities) will come here.
This is where I will end this article. All you have to do is work through it, understand the patterns, basic situations and conditions. This knowledge is enough for each time you draw up a primary document to think about how the entry made will affect the financial result of accounting.
Now in our articles on the website we only have a highlighted basis from accounting theory. The next step is to practice your accounting skills. Stay on the site. All the most interesting things are yet to come.
Strengthen your knowledge
Financial result from ordinary activities in accounting
The types of activities that are fixed in the constituent documentation can be classified as ordinary. Account 90 is intended for recording financial results. It is more convenient to maintain “ordinary” income and expenses in subaccounts opened to it:
- 1 - “Revenue”.
- 2 - “Cost of sales”.
- 3 - “VAT” (sales or “output” VAT).
- 4 - “Excise taxes”.
- 9 — “Profit/loss from sales.” It is in this subaccount that the final result of accounting for financial results is summarized.
Accounting for financial results from the normal activities of an organization can be represented by the following accounting entries:
- Dt 62 Kt 90.1 - sales revenue accrued;
- Dt 90.3 Kt 68 - VAT charged;
- Dt 90.2 Kt 20 (41, 43, 44) - reflects the cost of products, works or services.
Read about the features of accounting for production expenses in our article “Main production in the balance sheet (nuances).”
How to determine whether a company has made a profit or a loss? To do this, you need to compare the total turnover on the debit of accounts 90.2, 90.3, 90.4 with the turnover on credit 90.1. If the credit of the account 90.1 is greater than the debit turnover, then the company can record a profit: Dt 90.9 Kt 99. If the result is the opposite, then they speak of a loss received: Dt 99 Kt 90.9. Note that at the end of the reporting period there should be no balance on account 90.
Settlement of loss carried forward
In the previous example, we saw what happens to OTA accrued on the amount of tax loss that the organization decides to carry forward. If an organization in NU makes a profit, then it has the right to repay the loss carried forward to the future in the amount of this profit. Repayment can be made in installments over different periods or in full. In this case, ONA is written off for the following loss: Dt 68 Kt 09.
NOTE! The tax loss is carried forward to the future in accordance with the provisions of Art. 283 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and taking into account restrictions.
Accounting for financial results from other activities of the organization
If income and expenses cannot be attributed to ordinary activities, then in this case the concept of “Other types of activities” is provided for them. The list of other income consists of:
- income from the provision of property for rent;
From January 2022, lease transactions are accounted for in accordance with FAS 25/2018, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 16, 2018 No. 208n. You can start applying the Standard earlier by reflecting this fact in the accounting (financial) statements
How to take into account financial leases in accounting and accounting when applying FAS 25/2018, find out in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you don't have access to K+, get a trial demo access for free.
- financial benefits from securities and other investments;
- proceeds from the sale of own assets (for example, fixed assets, intangible assets);
- gratuitous economic benefits;
- fines, penalties and penalties due, as well as compensation for damage caused;
- positive exchange rate differences;
- written off accounts payable after the expiration of the statute of limitations;
- inventory surplus, etc.
The list of other expenses is similar to income:
- cost and expenses related to the sale of assets;
- VAT on sales transactions;
- compensation for damage to third party contractors;
- fines, penalties and penalties intended for payment;
- commission of credit companies for settlement transactions;
- accounts receivable after the expiration of the statute of limitations;
- negative exchange rate differences;
- economic benefits from received loans and borrowings and others.
Others also include income and expenses arising as a consequence of emergency circumstances of economic activity: natural disaster, fire, accident, nationalization, etc. (extraordinary income and expenses).
To account for financial results from other activities, account 91 “Other income and expenses” was approved. Unlike account 90, it is enough to open only 3 subaccounts:
- 1 - “Other income”;
- 2 - “Other expenses”;
- 9 - “Balance of other income and expenses.”
The credit of account 91.1 reflects the income from other activities. It can be in correspondence with various accounts (depending on the source of income):
- Dt 62 (76) Kt 91.1 - rent accrued;
- Dt 62 (76) Kt 91.1 - accrued proceeds from the sale of assets (for example, fixed assets, intangible assets);
- Dt 62 (76) Kt 91.1 - accrued dividends, interest and other income on securities, as well as from participation in the authorized capital of third-party companies;
- Dt 66 (67) Kt 91.1 - interest accrued on previously issued long-term and short-term loans and borrowings;
- Dt 98 Kt 91.1 - income from property received free of charge is reflected;
- Dt 60 (62, 76) Kt 91.1 - accounts payable with an expired statute of limitations are written off;
- Dt 52, 57 Kt 91.1 - a positive exchange rate difference was identified when selling currency;
- Dt 63 Kt 91.1 - the amount of the reserve for doubtful debts is included in other income;
- Dt 50, 10, 41, 43 Kt 91.1 - surpluses were identified based on the results of the inventory;
- Dt 10 Kt 91.1 - materials suitable for further use remaining after damaged fixed assets, goods, finished products are capitalized;
- Dt 76 Kt 91.1 - reflects the amount of insurance compensation for destroyed property if it was insured.
And the debit of account 91.2 is intended to reflect expense transactions:
- Dt 91.2 Kt 01.2 - the residual value of fixed assets intended for sale is written off;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 04.2 - the residual value of intangible assets intended for sale is written off;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 10 - the cost of materials intended for sale is written off;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 68 - VAT is charged on transactions for the sale of fixed assets, intangible assets and materials;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 66 (67) - interest accrued on short-term and long-term loans and borrowings received;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 60 (62, 76) - expired accounts receivable written off;
For more information about the procedure for writing off receivables, read our material “The procedure for writing off receivables.”
- Dt 91.2 Kt 76 - bank commission charged for conducting settlement transactions;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 52, 57 - negative exchange rate difference is reflected;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 01.2, 10, 41, 43 - the residual value of fixed assets, materials, goods and finished products that were damaged as a result of an emergency, for example, in a fire in the warehouses of an enterprise, is written off.
The meaning of calculating the final financial result is completely similar to account 90:
- Dt 91.9 Kt 99 - profit on other operations is reflected;
- Dt 99 Kt 91.9 - loss received from other activities.
Like the score 90, the score 91 assumes there is no balance on it.
Read about the procedure for determining exchange rate differences in our article “Accounting for foreign exchange transactions (PBU, postings).”
If the company operates at a loss
If you do not take into account charity, then all the activities of the enterprise are aimed at generating income. In accounting, this concept implies all means that affect the growth of assets with the exception of material support for the founders. As a rule, these are funds that were received as a result of the transfer of goods or services by their customers. The following are not considered income:
- makings;
- advances;
- VAT amounts received from counterparties;
- funds used to repay previously received borrowings;
- money received under commission or agency agreements in favor of third parties;
- pledges that pass into the possession of the pledgee under the terms of the agreements.
Operating
In the classification of income, operating income is considered to be income, the receipt of which is not related to the implementation of the main type of activity. They are reflected in the credit of subaccount 91/1. These include income received from renting out property, if this is not the profile of the organization. In addition, this includes benefits received from the paid transfer of patents and industrial designs. The enterprise's participation in the capital of third-party companies, the sale of fixed assets, interest on loans issued - all this is operating income.
Non-operating
Non-operating income, as the name suggests, has a different origin. These include profits earned from exchange rate differences, assets received by the organization free of charge, and profits from previous years that were identified only in the current period. This includes all kinds of payments in the form of fines and penalties for non-fulfillment of concluded contracts.
Organizations do not always manage to make a profit from their activities. And if it turns out that the advance payment for the next reporting period was less than for the previous one, then you need to adjust the data. For example, the amount of the accrued advance payment for the first quarter of 2021 was 100,000 rubles, and for the first half of 2021 - 70,000 rubles, then the following transactions are drawn up.
| Operation | Wiring | Amount, rub. |
| Advance income tax accrued for the first quarter of 2019 | Debit of account 99 “Profits and losses” - Credit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, subaccount “Income Tax” | 100000-00 |
| An advance for the first quarter of 2019 was transferred to the budget | Debit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, subaccount “Income Tax” - Credit of account 51 “Settlement accounts” | 100000-00 |
| The advance payment for income tax for the first half of 2019 has been adjusted (RUB 70,000 – RUB 100,000) | REVERSE Debit account 99 “Profits and losses” - Credit account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, subaccount “Income Tax” | 30000-00 |
How to determine the final financial result?
Taking into account the financial results for ordinary and other activities, we figured it out. But how to determine the overall financial result for the enterprise as a whole? First, let's define what it consists of.
The final financial result includes:
- financial result obtained from ordinary activities;
- financial result identified from other activities;
- accrual of income tax.
The result of accounting for financial results for ordinary activities is reflected:
- Dt 90.9 Kt 99 - profit;
- Dt 99 Kt 90.9 - loss.
The balance of accounting for financial results for other activities is as follows:
- Dt 91.9 Kt 99 - profit on other operations is reflected;
- Dt 99 Kt 91.9 - loss received from other activities.
Income tax is required to be assessed and paid by Russian and foreign companies that operate within the territory of our country and apply the general tax regime. It is reflected in the following entry in the accounting accounts:
Dt 99 Kt 68.4 - income tax is charged, which is intended to be transferred to the budget system of the Russian Federation.
You can learn how to determine the amount of income tax from the publication “How to correctly calculate corporate income tax?”.
For the entire financial year, the balance of profits and losses in accounts 90 and 91, as well as accrued income tax, are accumulated in account 99. At the end of each year, the result of accounting for financial results is determined and final entries are made using account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”:
- Dt 99 Kt 84 - net profit received.
- Dt 84 Kt 99 - the loss of the financial year is reflected.
Thus, account 99 is completely closed at the end of the year and cannot have a balance.
At the end of the year, all organizations transfer information from the 90th accounts to the financial results report. Let us remind you that at the end of 2021, fill out the information on the updated form. Read about what has changed in the form here.
ConsultantPlus experts told us how to correctly fill out a financial results report. Get trial access to K+ and learn how to fill out Form 2 for free.
You can download a sample of filling out a report in the new edition with comments on the design from K+ experts in the ConsultantPlus reference and legal system. To do this, get a free trial demo access to the system:
Meaning
The indicator under consideration, among other things, characterizes the rational use of material and labor resources. In general, accounting profit is the difference between the income and expenses of an enterprise.
| Profit indicator | Explanation |
| Positive | Evidence that the company has received financial benefits from its activities |
| Income equals expenses | The break-even point has been reached: no profit or loss has been made |
| "Negative profit" | There shouldn't be such a thing. After all, when expenses exceed income, we cannot talk about any profit. |
Based on the value of the PWB, calculations are made to assess the effectiveness of the activity. For example, analysis is carried out in relation to material resources using various indicators. But the general one for them is profit per 1 ruble. material costs . The resulting coefficient is equal to the quotient of the extracted profit from the main activity (P) to the amount of material costs (MZ):
The growth of this value positively characterizes the activity of the enterprise. In practice, specialists conduct such analysis in more depth, using various factor models and establishing the reasons for changes.
Accounting for the use of profits
Profit is a positive result of the company's activities as a whole. Every enterprise is interested in increasing it. But making a profit alone is not enough for the further development of the organization. Its rational and effective use is of great importance. Net profit is the profit remaining at the disposal of the enterprise after paying income tax. It is reflected in the credit of account 84 and is subject to further distribution.
Find out how to analyze a company’s net profit from our article “Procedure for analyzing a company’s net profit.”
The main directions of distribution of net profit:
- Creation of reserve capital. For joint-stock companies, its creation is a prerequisite; other enterprises can create it at their discretion:
Dt 84 Kt 82 - reserve capital was formed at the expense of net profit.
- Repayment of losses from previous years:
Dt 84 Kt 84 - the loss of previous years is repaid.
- Accrual and payment of dividends to company participants:
Dt 84 Kt 75 (70) - dividends are reflected.
Account 70 is used when the shareholders are employees of the enterprise.
Based on the results of the financial year, the enterprise may receive a loss, which is also reflected in account 84. It can be covered in several ways:
- Using additional capital:
Dt 83 Kt 84.
- At the expense of the amount of reserve capital that was created in previous reporting periods after the distribution of net profit:
Dt 82 Kt 84.
- Due to additionally attracted contributions from company participants:
Dt 75 (70) Kt 84.
Thus, the rational use of profits allows the enterprise to remain more sustainable in the future. Modern economists consider the creation of reserve capital to be one of the most effective ways to use net profit. It will help the company in the future to cover losses from its activities, which are possible in an unstable economic situation.
Documentation of distribution of net profit
The decision on the distribution of net profit is drawn up in the form of a protocol.
The protocol specifies what part of the net profit is to be distributed and for what specific purposes the net profit will be directed.
Thus, in a limited liability company, the owners draw up the minutes of the general meeting of participants (Clause 6, Article 37 of Law No. 14-FZ).
In a joint stock company, the founders draw up the minutes of the general meeting of shareholders (Article 63 of Law No. 208-FZ).
Its difference from the minutes of the general meeting of participants is that it is drawn up in two copies.
And it has mandatory details.
This is the place and time of the meeting; the total number of votes possessed by shareholders - owners of voting shares; the number of votes of the founders participating in the meeting.
As well as information about the chairman and secretary of the meeting, the agenda. Such requirements are established in paragraph 2 of Art. 63 of Law No. 208-FZ.
But in companies created by a single founder, minutes of meetings are not drawn up at all.
This follows from Art. 39 of Law No. 14-FZ and paragraph 3 of Art. 47 of Law No. 208-FZ. The founder determines the directions for spending the net profit by his written decision.
For an accountant, the founders’ decision on the distribution of profits is the primary document on the basis of which business transactions will be carried out in accounting and the amounts listed in this document will be paid.
Analysis of the financial results of the organization's activities
The financial result of the financial year shows the effectiveness of the commercial activities of the enterprise. Timely and complete accounting of financial results is important from an economic point of view, as it allows you to obtain the most reliable data and conclusions. Analysis allows you to identify the weaknesses of the enterprise and find a more rational use of available resources. Analysis data can be used for current and strategic planning of the company's activities in the future.
The main purpose of analysis, as well as accounting for financial results, is to assess the state of the enterprise as a whole. Such data is necessary not only for the management of the enterprise, but also for the company specialists responsible for its further development. Basically, the analysis uses a deductive method, that is, a movement from general data of accounting for financial results to specific ones.
Accounting for financial results involves the preparation and submission of financial statements. Profit occupies one of the key places when carrying out analytical calculations. A distinction is made between the analysis of accounting and economic profits of an enterprise. The difference between them lies in the manner in which profit is determined.
The calculation of accounting profit is based on accounting data. It is this profit that we see in the income statement. Accounting profit recognizes only explicit costs for real and documented business transactions. When determining economic profit, experts also take into account implicit costs. Because of them, the difference between accounting and economic profit is formed. Implicit costs represent alternative resources or lost economic opportunities (benefits). For example, a company has a savings deposit with a credit institution. If it had additionally invested certain financial resources into it during the year, then the income on the deposit could have increased. The amount of possible, but not received interest on the deposit will be lost economic profit.
Each type of profit can be analyzed using basic techniques:
- Comparative analysis, which involves comparing the same indicators over similar periods of time, and also reveals deviations between them, up or down.
- Structural analysis aimed at calculating the structure of each indicator in the total weight of all data and the dynamics of its change.
- Factor analysis, which is used to determine the influence of each factor on the economic result and identify the relationships between them.
Each enterprise that is interested in further increasing profits must choose those analysis methods that best suit its specific activities and industry.
Formulas for calculating the main indicators that characterize the company’s activities can be found in the article “Basic financial ratios and formulas for their calculation.”
When should net profit be spent on purposes determined by the owners?
After approval of the owners' decision on the distribution of net profit, payments should be made for the purposes specified in this document.
In this case, the payment deadline specified in the decision must be observed.
If a period is not specified, then the general period of time established by law is taken into account.
Thus, for limited liability companies, the deadline cannot exceed 60 days from the date on which the corresponding decision was made (clause 3 of Article 28 of Law No. 14-FZ).
And for joint-stock companies, the terms are calculated depending on the status of the recipient (it is determined by the board of directors).
Results
The financial result is the result of the financial activities of the organization. It shows how effective the company's activities were as a whole. Profit is a relative indicator of an organization's performance. It indicates a positive result of the activity. However, after conducting analytical procedures, other conclusions about the efficiency of the enterprise can be made.
Accounting for financial results for ordinary types of activities is carried out on account 90, for other types of activities - on account 91. The final financial result is determined on account 99 and consists of the balance of income and expenses for ordinary and other types of activities, accrued corporate income tax.
At the end of each year, account 84 reflects the amount of net profit or uncovered loss. Net profit is subject to distribution and must be used rationally from an economic point of view. The loss of the reporting period can be covered using additional and reserve capital, as well as by attracting additional contributions from company participants.
Currently, a large number of techniques for analyzing financial results are used.
They are carried out by different services and management levels of the enterprise. The analysis can be carried out on the basis of accounting or economic profit. Each type of analysis and accounting of financial results is closely related to each other. Without the final accounting data of financial results, it is impossible to carry out any type of analysis. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Regulatory framework
Today in the Russian Federation there is a large list of standards, regulations, which in one way or another affect the accounting activities themselves, accounting and analysis of financial results. Firstly, this is the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, where special attention is paid to taxable profit and the federal law “On Accounting”. In addition, there are a number of other documents:
- PBU “Organization expenses” (No. 10/99);
- PBU “Income of the organization” (No. 9/99);
- Account correspondence;
- PBU “Accounting statements of an enterprise” (No. 4/99);
- Charts of accounts;
- PBU “Accounting Policy of the Organization” (No. 1/2008);
- International Financial Reporting Standards;
- PBU “Information by segments” (No. 12/2010), etc.
What is the result of the company's work?
This indicator depends on the volume of sales of goods/services, the productivity of the company's property, income from transactions not related to sales and many other indicators. The financial result can be expressed as follows: the company receives either income or loss. Therefore, the activities of the enterprise are considered as:
- Profitable if the income received covers the costs incurred;
- Unprofitable when costs (production and other) exceed income.
However, they begin to analyze the company’s activities after they have already received the results of the work. We will look at how to calculate the financial result.
Approach: How to Calculate Accounting Profit
According to the Regulations on accounting and reporting in the Russian Federation (Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 34-n, clause 79), the indicator under consideration is the final financial result for the reporting period. It is determined based on:
- accounting documents for all business transactions;
- balance sheet items.
Thus, all sources of income are summed up. And the formula for accounting profit looks like this:
PRb = D – Zav
Where: D – the company’s income for the period under review; Claims are obvious costs, which include labor costs, equipment purchases, utility bills, etc.
EXAMPLE 1
Based on accounting documents and the balance sheet, she received income in the amount of 10 million rubles in 2021. The table shows the costs associated with financial and economic activities. What will be the accounting profit ?
| Costs | Amount, rub. |
| Payment for bank services | 500 000 |
| Salary to employees | 6 000 000 |
| Communal payments | 1 500 000 |
| Other expenses | 900 000 |
Solution: 10,000,000 – 8,900,000 = 1,100,000 rubles.
EXAMPLE 2
Income for the past year amounted to 6.5 million rubles, and expenses were approximately the same 6.5 million rubles. What will be the accounting profit?
Solution: Since both indicators are equal, the activity brought neither profit nor loss to the organization.