Checking the VAT return on accounting accounts
First of all, the declaration is checked against the accounting accounts. To do this, balance sheets are formed and analysis is carried out on the following accounts:
- 90 and 91 - to check sales in terms of VAT rates;
- 60, 62 and 76 - to check the amounts of advances and VAT;
- 19 - to check the amounts of VAT declared for deduction;
- 68 - to check the total amount of tax payable.
Checking the score 19
We start with an analysis of the postings Dt 68.02 Kt 19. The amount for these postings is the amount of VAT claimed for deduction. In the declaration, this number must be reflected in line 120 of Section 3.
Checking the score 76
We analyze the wiring Dt 76.AV Kt 68.02. Here we see VAT calculated on advances received from buyers. The amount for debit 76.AB falls into line 070 of Section 3 of the declaration. In addition, there are also postings Dt 68.02 Kt 76.AB. This is the amount of VAT on credited advances from buyers. Credit turnover 76.AB should fall into line 170 of Section 3.
Checking the account 90.03
Let's look at the postings Dt 90.03 Kt 68.02. This is the amount of VAT charged on sales. See these postings in the context of applicable VAT rates. If you only use the 20% rate, you will see this amount on line 010 of Section 3 of the VAT return.
Checking the score 62
Information on account 62 must be correlated with turnover on other accounts and the corresponding lines in the declaration. To check the ratio, use the formulas:
- Dt 62.1 * 20/120 = Dt 90.03 = line 010 of Section 3;
- Kt 62.2 * 20/120 = Dt 76.AB = line 070 of Section 3;
- Dt 62.2 * 20/120 = Kt 76.AB = line 170 of Section 3.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
Checking the score 60
For this account, check only one ratio:
Kt 60 * 20/120 = Dt 19.03, which in turn should be equal to line 120 of Section 3.
Checking the account 68.02
We compare the debit and credit turnover of account 68.02. The loan balance is the amount of tax due. It appears in line 200 of Section 3. The debit balance is VAT refundable. It is reflected in line 210 of Section 3.
We check the execution of all purchase and sales documents
Check that all sales and purchase documents have been completed. If you do not have enough sales documents, you will underestimate the amount of tax payable in your return. If purchase documents are not posted, you will not claim part of the VAT for deduction.
Buyers
62.01 K balance = 0 62.02 D balance = 0 don’t forget to make an account. in advance to buyers! 76.AB K balance = 0, also remember the debit balance (62.2*0.18/1.18=76.AB)
So: 1. receipt of goods from suppliers with invoices has been established. 2. Shipments to customers with invoices have been initiated. 3. Advance invoices are issued for the buyers' prepayments
We begin to study Operations - Closing the period - VAT Accounting Assistant . There is also a useful summary report in 1C, see. Reports - Analysis of VAT accounting If payment and shipment (receipt) are in the same period, then everything is taken into account very simply: all my documents “Receipts of goods” in the invoice received have a checkbox “Reflect the VAT deduction in the purchase book by the date of receipt.” Those. here we immediately make entries for VAT refund ( 68.02
Thus, the document formation of the purchase book and sales book is almost empty. And all sorts of advances and other evil spirits ended up there, which makes the life of an accountant bright and eventful. The problem is that if you give up and don’t deal with the advances, then it will all come out anyway. Therefore, we are looking for algorithms for checking advances.
What logic first tells us is that all options (where there are 2 periods, payment in one, shipment in the other) are divided into:
- 1.
- 1.1 client prepayment
- 1.1a счф. for advance payment (76АВ
- 1.2 shipment of goods to the client + regular invoice (there are no postings here, but see its shipment 90.03
- 1.2a we cancel the SCHF. for an advance payment (occurs when creating a purchase book - oddly enough).
- 2.
- 2.1 shipment of goods to the client
- 2.2 payment by the client
- 3.
- 3.1 prepayment to the supplier
- 3.1a supplier to you SCHF. for advance payment ( 68.02 Purchases - invoice for advance payment
- 3.2 receipt of goods from the supplier + regular invoice (68.02
- 3.2a we cancel the SCHF. for advance payment (76VA
- 4.
- 4.1 receipt of goods from the supplier (19.03
- 4.2 payment to the supplier
Please note that for paragraphs. 2 and 4 no SCHF is created. for advance They only appear if payment is made first.
76AB
Checking the VAT return using control ratios
When checking the declaration, the inspector is guided by control ratios. Any taxpayer can find out these ratios in the Federal Tax Service Letter No. GD-4-3/ [email protected] dated March 23, 2015 and the Federal Tax Service Letter No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] dated March 19, 2019.
The letter indicates which article is violated if the ratio is not observed, and what measures the tax authorities will take.
The formulas given in the letter are needed to compare indicators both within and between sections 1-7 of the Declaration, and in conjunction with information from sections 8-12. Here are some of them:
- line 190 of column 3 of Section 3 must be equal to the sum of lines 120, 130, 135, 140, 150, 160, 170, 180, 185 in column 3 of Section 3, if the left side of the equality is greater than the right;
- line 020 of Appendix 1 to Section 9 must be equal to line 230 of Section 9;
- if line 050 of Section 1 is greater than 0, then line 190 of Section 8 is (line 260 + line 270 of Section 9) greater than 0, and so on.
In practice, accountants do not reconcile control ratios manually. All this is done by the accounting program in which they keep their books. Sometimes the check can be performed by the service through which the declaration is submitted to the tax office.
Settlement of advances
Let's say the seller received an advance payment, transferred VAT from the advance payment to the budget, but did not ship the goods (did not perform work, did not provide services). The general rule is that in this case he can accept VAT as a deduction only after he returns the advance payment to the buyer. This is provided for in paragraph 2 of paragraph 5 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In some cases, the offset of the advance is equivalent to the return of the advance. Offsetting the advance also allows the seller (performer) to deduct the VAT previously paid to the budget on this amount.
Such cases include:
- mutual offset of advances transferred by counterparties to each other (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 22, 2010 No. 03-07-11/262);
- The seller and buyer have two contracts. The parties terminate one contract. But instead of returning the advance under this agreement, the seller counts the advance towards repayment of the buyer’s debt under another agreement (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 11, 2012 No. 03-07-08/268, dated November 12, 2012 No. 03-07-11/ 482).
In the first case, the parties draw up an act of offset of mutual claims. The seller (performer) must reflect the offset in accounting. Then, on the date of reflection of the offset in accounting or later, the seller can accept VAT from the prepayment for deduction. Attention: the seller can accept VAT for deduction no later than one year after drawing up an act on the offset of mutual claims. This follows from the provisions of paragraph 4 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the buyer (customer) is obliged to restore the VAT accepted by him for deduction (subclause 3, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In the second case, the seller can accept VAT from the prepayment as a deduction after he ships the goods (work, services) under another agreement . Such conclusions are in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 1, 2014 No. 03-07-RZ/14444, dated November 12, 2012 No. 03-07-11/482, dated August 29, 2012 No. 03-07-11/ 337. You can also take advantage of the deduction on the date the offset is reflected in accounting, but no later than one year after drawing up the act on the offset of mutual claims (clause 4 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition to offset agreements, the parties can enter into an agreement on novation among themselves. As a result of the novation agreement, the obligation to supply prepaid products is “transformed” into debt obligations. That is, the advance received becomes a loan that the buyer provided to the seller. In such a situation, the seller does not return the advance payment to the buyer, and therefore cannot accept VAT as a deduction (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 1, 2014 No. 03-07-RZ/14444). However, after the novation of the advance, this amount of VAT should be considered as overpaid. After all, receiving loans is exempt from taxation (subclause 15, clause 3, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, the seller who received the loan has no tax obligations. This means that he can contact the tax office with an application for a refund or offset of the overpayment of VAT (Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The legality of this approach is confirmed by the ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 19, 2015 No. 310-KG14-5185. In letter dated July 17, 2015 No. SA-4-7/12693, the Federal Tax Service of Russia also refers to this definition and recommends that tax inspectorates take into account the position of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation in their work.
Situation: can the seller deduct VAT from the advance payment under the purchase and sale agreement? The organization repays its obligations to the buyer for the advance received by offset, assigning to the buyer the right to claim the debt of a third party.
No, he can not.
After all, VAT can be deducted from an advance payment only in two cases:
- goods have been shipped (work performed, services provided) (clause 8 of Article 171, clause 6 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the parties terminated or changed the contract, and the supplier returned the advance to the counterparty. A prerequisite for deduction is that the seller had to transfer VAT on the advance payment to the budget (clause 5 of Article 171, clause 4 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The following can be equated to the return of an advance in cash if certain conditions are met:
- mutual offset of advances transferred by counterparties to each other (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 22, 2010 No. 03-07-11/262);
- offset by the seller (executor) of the advance received under one agreement to pay off the debt of the buyer (customer) under another agreement (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 1, 2014 No. 03-07-RZ/14444, dated September 11, 2012 No. 03 -07-08/268, dated November 12, 2012 No. 03-07-11/482).
However, in the situation under consideration these conditions are not met. Having received an advance payment from the buyer under the purchase and sale agreement, the organization, instead of shipping goods against the received prepayment, entered into an assignment agreement with the buyer. The subject of this agreement is the assignment of the right to claim a debt incurred by the organization in relations with a third party.
In such conditions, an advance received by an organization and repaid by offset is not considered returned. It should be qualified as payment of the right of claim acquired by the buyer. Since there is no real refund to the buyer, the advance remains with the organization. In such a situation, the norms of paragraph 2 of paragraph 5 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation do not apply. Consequently, the organization does not have the right to deduct VAT.
Checking the correctness of filling in invoices
In addition to checking control ratios and information on accounting accounts, pay attention to the correctness of invoices. If this document is filled out incorrectly, VAT cannot be deducted. The rules for maintaining documents used in calculating VAT are enshrined in Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1137 of December 26, 2011.
First of all, check that the seller’s TIN and KPP are filled out correctly. The official service of the Federal Tax Service has been developed for this purpose. If the service indicates that the TIN and KPP are not in the database, request the correct information from the counterparty.
Check the details of issued and issued invoices. When checking, the tax office correlates your Sections 8 and 9 of the VAT Declaration with the corresponding sections of the declarations of your customers and suppliers. If it turns out that you indicated an invoice from a supplier, but he did not register it, the tax office will require clarification or an updated declaration. This function is performed by the automated system ASK VAT-3. Therefore, a difference in even one number or letter in the invoice number will lead to the system not finding the invoice from the buyer or supplier.
Examples of entries for accounting for VAT on advances
Example of an operation for advances received
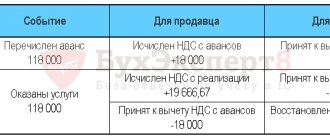
Harmony LLC, under an agreement with the buyer Amalgama LLC, must supply a consignment of goods in the amount of 212,400 rubles, incl. VAT — 32,400 rub. 07/10/2016 "Amalgam" transfers an advance payment of 50% of the contract amount: 106,200 rubles. VAT on advance: 106,200 * 18/118 = 16,200 rub.
We reflect in the postings VAT on advances received from the buyer:
| Dt | CT | Wiring Description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 51 | 62.2 | Reflection of the advance received | 106 200 | Bank statement |
| 76.AB | 68 (VAT) | VAT charged on advance | 16 200 | SF issued |
In August, Harmony ships a consignment of goods to Amalgam. Sales transactions and deduction of VAT from advances received:
| Dt | CT | Wiring Description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 62.1 | 90.1 | Sales of goods reflected | 212 400 | Act |
| 90.3 | 68 | VAT charged on sales | 32 400 | SF |
| 62.2 | 62.1 | The offset of the buyer's advance is reflected | 106 200 | Accounting information |
| 68 | 76.AB | VAT on advance payment is deductible | 16 200 | Book of purchases |
Transactions on advances issued
Let's consider the same operation from the buyer's side. The accountant of Amalgama LLC will reflect VAT on advances issued by postings:
| Dt | CT | Wiring Description | Amount, rub | Document |
| 60.2 | 51 | Advance paid to supplier | 106 200 | Payment order ref. |
| 68(VAT) | 76.VA | VAT on advance payment is deductible | 16 200 | Invoice, purchase book |
| 41 | 60.1 | Goods receipt reflected 0) | 180 000 | Invoice |
| 19 | 60.1 | Incoming VAT reflected | 32 400 | SF |
| 60.1 | 60.2 | The offset of the advance is reflected | 106 200 | Accounting information |
| 76.VA | 68(VAT) | Recovered VAT from advance payment | 16 200 | Sales book |
After receiving the goods, VAT is deducted from the delivery:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 68 | 19 | VAT deduction upon receipt of goods | 32 400 | Book of purchases |
Sales book sheet form with explanations:
Reconciliation with the tax office for VAT
After submitting the declaration and paying the tax, check with the inspectorate. To do this, ask the tax office for a reconciliation report or a certificate about the status of settlements with the budget. Documents are prepared within 5 working days.
In the act you will see whether your VAT calculations coincide with the information from the Federal Tax Service. If everything is correct, the act can be signed and submitted to the inspection. If not, sign the deed with Fr. After this, the tax office will ask you to provide evidence confirming the correctness of your calculations.
We recommend you the cloud service Kontur.Accounting. When filling out a VAT return, our program automatically checks all control ratios. And the report lines are filled in in accordance with the accounting accounts. We give all newbies a free trial period of 14 days.
VAT on advances issued
An organization that has paid an advance to a supplier has the right to claim for deduction the VAT paid. Necessary conditions for obtaining a VAT deduction from an advance payment:
- the condition for advance payment must be clearly stated in the contract with the supplier;
- the advance payment must be presented to the SF (no later than 5 days after payment).
VAT deduction is provided in the tax period when the advance was transferred. When the final payment for the delivery occurs, that is, the goods are received from the supplier under the acceptance certificate, the organization is obliged to restore the amount of VAT previously claimed for deduction.
In addition to the receipt of goods, the obligation to restore the deduction arises for the organization in the following cases:
- changes in the terms of the contract;
- termination of the contract and return of the advance.
VAT is restored in the same amount in which it was previously accepted for offset. If the terms of the contract determine that the delivery of goods occurs after receiving 100% advance payment, the buyer can transfer the advance in installments. In this case, the amount of VAT reflected in the SF for the supply is restored. In any case, this value coincides with the amount of VAT on all advance tax payments for this supply.
Where might the discrepancies come from?
There are many reasons for the incorrect operation of VAT on advances, for example: this may be due to the irrelevance of mutual settlements, the use of “manual operations” on mutual settlement accounts or on VAT accounts on advances, incorrectly reflected debt adjustments.
Correcting these errors is a big topic for another article, but thanks to this one you can be sure that you have checked the correctness of VAT calculations on advances.
If you have questions about checking VAT on advances, then leave a request on our website and we will definitely contact you.