Opening special accounts
To carry out certain operations, organizations on their own initiative can open special accounts in banks (Article 30 of the Law of December 2, 1990 No. 395-1, clauses 2.1 and 2.8 of the Bank of Russia Instruction of May 30, 2014 No. 153-I).
Funds are credited to special accounts from settlement or foreign currency accounts of organizations. Also, the source of funds in a special account can be a loan provided by the bank.
Typically, special bank accounts are opened:
- for settlements under letters of credit;
- for payments by checks;
- for accounting of deposits (deposits);
- for payments using bank cards.
In addition, on their own initiative, banks open to organizations:
- loan accounts – for the movement of funds provided under loan agreements;
- transit currency accounts - to record receipts in foreign currency. Regardless of the organization’s wishes, a transit currency account is opened simultaneously with a current currency account.
A special account can be opened both in rubles and in foreign currency. To do this, you need to submit an application to the bank (in a form approved by the bank) and attach a payment order for the transfer of funds.
Cost of special accounts in Sberbank and service tariffs
| Account opening and maintenance | for free |
| Interest on balance | 0,01% |
Blocking on a special account for email. sites:
| 50 rubles |
| Unblocking | no commissions |
| Connection and maintenance of Internet banking | |
| SMS notification |
Open a special account in Sberbank
Accounting: special accounts
In accounting, reflect the movement of money in special accounts on account 55 “Special accounts in banks.” The following sub-accounts can be opened for account 55:
- 55-1 “Letters of credit”;
- 55-2 “Checkbooks”;
- 55-3 “Deposit accounts”;
- 55-4 “Special card account”, etc.
Accounting for the availability and movement of funds in rubles and foreign currencies should be kept in different sub-accounts opened for account 55 (for example, in the sub-accounts “Special card account in rubles”, “Special card account in foreign currency”).
Funds in special accounts in foreign currency are converted into rubles at the Bank of Russia exchange rate on the date of transactions in foreign currency, as well as on the reporting date (clauses 4–7 of PBU 3/2006). Include positive exchange differences that arise in this case as part of other income (clause 7 of PBU 9/99), negative ones - as part of other expenses (clause 11 of PBU 10/99).
Loan and transit currency accounts are internal accounts of banks and are opened by them for control functions. In the accounting of organizations, transactions carried out on them are not reflected in account 55. To record debt on loan accounts, use accounts 66 and 67. To reflect transactions on the transit currency account, you can open a separate subaccount of the same name to account 52.
How to find out if an application has security
Information about the application security in contracts under 44-FZ is reflected in the Unified Information System in the procurement notice. To see it, you need to click on the code of the purchase you are interested in:
UIS, purchase selection
Next, scroll down the screen to the “Application Security” section:
The amount of security is reflected in the “Application security” section
If you use third-party services, for example, Kontur.Purchases, then this information can be obtained there by logging into the bidding card:
Amount of application security in Kontur.Purchases
Payments by checks
The procedure for settlements by checks is regulated by Articles 877–885 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and the Regulations approved by the Bank of Russia on June 19, 2012 No. 383-P.
Check blanks are prepared by the bank. The bank establishes the form of checks, a list of its details (mandatory and additional), as well as the procedure for filling it out in its internal rules (clauses 8.1−8.4 of the Regulations approved by the Bank of Russia on June 19, 2012 No. 383-P, Article 878 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) .
The organization receives checks from the bank in the form of a checkbook (clause 1.8.10 part 3 of the Rules approved by the Regulations of the Bank of Russia dated July 16, 2012 No. 385-P).
To obtain a checkbook, you need to submit an application to the bank (in the form established by the bank). For issuing a checkbook, the bank charges a fee in accordance with the bank account agreement (Article 851 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Checks are strict reporting forms and are accounted for the balance in account 006 “Strict reporting forms” in the conditional valuation. As they are used, checks are written off from account 006 (clause 22 of the instructions approved by the GMEC protocol of June 29, 2001 No. 4/63-2001).
In accounting, reflect the receipt of check books by posting:
Debit 006 subaccount “Checkbooks” – checkbooks are accepted for accounting.
Reflect the bank's commission for issuing a checkbook with the following entries:
Debit 91-2 Credit 60 (76) – reflects the bank’s commission for issuing a checkbook;
Debit 60 (76) Credit 51 – the bank wrote off the commission for registering a checkbook.
As you use checks, write them off by posting:
Credit 006 – used checks are written off.
In banking practice, there are two types of checks: cash and settlement. This conclusion can be drawn from paragraph 2 of clause 5.2 of the Bank of Russia Regulation No. 318-P dated April 24, 2008, paragraphs 8.1−8.4 of the Bank of Russia Regulation No. 383-P dated June 19, 2012.
Cash checks are used to withdraw cash from a current account for the current needs of the organization (for the payment of salaries, business needs and for other purposes agreed with the bank). Unlimited check books are provided for cash checks (the amount of cash issued under such books by banks is not limited).
To withdraw cash from a current account, an organization fills out a check, certifies it with the signatures of authorized persons and the organization’s seal, and submits it to the bank.
In accounting, reflect the receipt of cash from the current account by posting:
Debit 50 Credit 51 – money received from the bank by check.
Payment checks are used for non-cash payments with counterparties.
If an organization decides to pay for purchased goods (works, services) by checks, it must deposit (reserve) the funds necessary for this in a special bank account. To do this, simultaneously with the application for issuing checks, you need to submit a payment order to the bank to transfer the required amount from the current account to a special account.
Limited check books are provided for settlement checks. The amount of settlements under such books is limited to the total amount credited to the special account. In this case, the amount of settlements per check is not limited.
A settlement check is a written order to the bank to transfer a certain amount of money from the payer's account to the recipient's account. A settlement check, like a payment order, is issued by the buyer (customer), but unlike a payment order, the check is transferred not to the bank, but to the seller (executor) at the time of the business transaction. After this, the seller (executor) presents the check to his bank and receives funds from a special account from the payer’s bank. This procedure follows from paragraphs 8.1−8.4 of the Regulations approved by the Bank of Russia on June 19, 2012 No. 383-P.
In accounting, reflect the movement of funds in settlement checks in account 55-2 “Check books”.
In accounting, the movement of money in checkbooks is reflected by the following entries:
Debit 55-2 Credit 51 (52) – funds deposited for settlements by checks;
Debit 60 (76) Credit 55-2 – funds on checks presented for payment are written off.
In some cases, part of the organization's settlement checks may remain unused. For example, this is possible if the organization refuses to make payments by checks, if the checkbook has expired, as well as when closing a bank account or changing the name of the organization. Unused checks must be returned to the bank, after which it will credit the balance of the deposited funds to the organization's current (currency) account. In accounting, reflect these transactions with the following entries:
Debit 51 (52) Credit 55-2 – unused funds previously deposited for payment of checks are credited to the current (currency) account.
Analytical accounting for account 55-2 is maintained for each checkbook received.
An example of how transactions related to the opening and use of a limited checkbook in rubles are reflected in accounting
To make payments on checks, Alfa CJSC received from the bank a limited checkbook with 100 checks and transferred funds in the amount of 300,000 rubles to a special account. In accounting, check books are reflected in account 006 in a conditional valuation equal to 1 ruble. for one check.
The bank commission for issuing a checkbook was 150 rubles. (debited from the organization's current account).
Amount 250,000 rub. was paid in five checks to Alpha suppliers. Unused amount RUB 50,000. was returned to the organization's current account, and 95 unused checks were returned to the bank.
Alpha's accountant made the following entries in the accounting records:
Debit 91-2 Credit 76 – 150 rub. – reflects the bank’s commission for issuing a checkbook;
Debit 76 Credit 51 – 150 rub. – the bank has written off the commission for issuing a checkbook;
Debit 55-2 Credit 51 – 300,000 rub. – funds for settlements by checks have been deposited;
Debit 006 – 100 rub. (100 checks × 1 rub./check) – a limited checkbook has been accepted for off-balance sheet accounting;
Debit 60 Credit 55-2 – 250,000 rub. – funds from checks presented for payment are written off;
Credit 006 – 5 rub. (5 checks × 1 rub./check) – used checks are written off;
Debit 51 Credit 55-2 – 50,000 rub. – unused funds previously deposited to pay checks are credited to the current account;
Credit 006 – 95 rub. – unused checks are written off.
Background to the emergence of special accounts
The concept of special accounts for public procurement was introduced on the last day of 2021 by law 504-FZ. He changed paragraph 10 of Article 44 of Law 44-FZ and established that from July 1, 2018, application security will be charged in a new way. Each supplier must open an account in an authorized bank , the list of which is approved by the Government, and deposit funds into it. It is from this money that sites must collect application security. Previously, funds were blocked for this purpose on the participant’s personal account on the ETP.
A little later, on April 12, 2021, the Government, by its Resolution No. 439, introduced the following rule: customers are required to establish application security only if the contract amount exceeds 1 million rubles. In cheaper auctions, customers have the right to establish bid security, but they do not have such an obligation.
Registration in the ERUZ UIS
From January 1 2020 , in order to participate in bidding under 44-FZ, 223-FZ and 615-PP, registration in the ERUZ register (Unified Register of Procurement Participants) on the EIS (Unified Information System) portal in the field of procurement zakupki.gov is .ru.We provide a service for registration in the ERUZ in the EIS:
Order registration in the EIS
On July 13, 2021, Government Order No. 1451-r , which provided a list of 18 banks authorized to open special accounts for government procurement. However, the implementation of this mechanism was postponed, as was the transfer of trading to electronic form, until October 1, 2021 (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 25, 2021 No. 24-06-08/43650). This happened due to the fact that by that time the Ministry of Finance had not yet approved the list of sites for conducting auctions under 44-FZ. At that time, only auctions were still held in electronic format, that is, everything remained the same, including securing the application.
On October 1, 2021, the new system finally started working. Now all auctions (with rare exceptions) have been transferred to electronic format and are held on newly approved electronic trading platforms. There are now 9 of them: the usual procedures are carried out at 8 sites, and another one - AST GOZ - is intended for bidding within the framework of the state defense order. At the same time, the mechanism for using special accounts began to be implemented.
The list initially approved by the Ministry of Finance included 18 banks. But on February 13, 2021, 2 government orders were signed at once (No. 213-r and No. 214-r), which changed this list. Now there are 21 banks, and their SPMS looks like this:
New list of banks for opening special accounts
Deposit account
If an organization has available funds and intends to receive income from placing them in a bank, then a special deposit account is opened for it, on which the bank will accrue interest monthly. The bank opens such an account on the basis of a bank deposit agreement (Articles 834, 835 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), which stipulates:
- type of deposit;
- the amount that is deposited or transferred to the deposit;
- the amount of the deposit account maintenance fee;
- shelf life;
- liability of the parties;
- terms of termination of the contract;
- other conditions as agreed by the parties.
After the deposit period expires, the bank will return the money from the special account to the organization’s current account.
In accounting, the movement of money in deposits is reflected in account 55-3 “Deposit accounts in banks.”
Reflect the transfer of funds to the deposit by posting:
Debit 55-3 Credit 51 (52) – funds were transferred to a special deposit account.
When the bank returns the deposit amount, make a reverse entry.
When calculating and paying interest on a deposit, make the following entries in your accounting:
Debit 76 Credit 91-1 – interest accrued on the deposit;
Debit 51 Credit 76 – interest on the deposit was credited to the current account.
The bank deposit agreement may provide for the payment of the entire amount of interest on the deposit upon expiration of the period of storage of funds on deposit. In this case, interest accumulates in the deposit account during the entire period of storage of the money, and then the bank transfers it to the settlement (currency) account of the organization. Reflect such transactions in accounting with the following entries:
Debit 55-3 Credit 76 – interest on the deposit was credited to the deposit account;
Debit 51 (52) Credit 55-3 – interest on the deposit was credited to the current (currency) account.
Analytical accounting for account 55-3 “Deposit accounts” is maintained for each deposit separately.
Since deposits are recognized as financial investments (clause 3 of PBU 19/02), they can be accounted for in account 58 “Financial investments”. The organization establishes the method of accounting for the movement of money on deposit in its accounting policy.
How long to open
One special account is enough to participate in government procurement. Electronic platforms signed agreements on interaction with each of the banks from order 1451-r. This is one of the advantages of the innovation: now they no longer keep money on several electronic platforms. One account is used for all trades.
It is not prohibited to have them in several banks. This is confirmed by the position of the Ministry of Finance.
Payment for winning the auction under 44-FZ
In 2021, many changes were made to Federal Law 44, which also affected payment by potential suppliers for their participation in the tender. This is how clause 4 of Article 24.1 appeared in it, according to which ETPs acquire the right to set fees for companies’ participation in procurement. The resolution specifies the maximum possible amount of such remuneration; exceeding it is not allowed.
In situations where the contract will be concluded with the participant who took second place according to the results of the procurement procedure, the site operator does not have the right to charge him a fee. This is indicated by paragraph 3 of resolution No. 564.
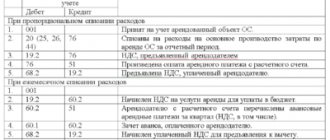
Bidding: how to take into account the costs of holding or participating
The winning bidder's accounting after signing the contract will depend on what exactly was won. If this is the right to enter into a lease, then you will subsequently record lease transactions. If you win a construction contract, then you will have “construction” transactions.
The auction participant must be prepared to raise the price, and the competition participant must develop some special project, for which it may be necessary to attract new workers and purchase additional materials.