The patent tax system does not completely exempt people from tax accounting. Entrepreneurs still have the obligation to keep a book of income. For the absence of a book, you can be fined up to 30 thousand rubles.
It would seem that what a difference it makes: on a patent, taxes do not depend on income, 1% of contributions are calculated on potential income, there are no tax returns. But for the tax authorities there is a difference, because she also regularly checks the IP on the patent.
The tax office is interested in:
- Has the individual entrepreneur exceeded the limits? If income exceeds 60 million per year for all patents, this system can no longer be used. Accordingly, the individual entrepreneur must pay tax from the beginning of the year according to the simplified tax system or OSNO, and the budget must receive more money. Of course, there is a danger of such verification in a business with high turnover. They are unlikely to come to an individual entrepreneur with a couple of employees.
- Shouldn't an individual entrepreneur have to pay for multiple patents? For example, they check an interregional carrier. Formally, he must receive all orders in his region. The tax office requests KUDiR, compiles a list of transactions that are interesting to it, and requests the corresponding agreements from the entrepreneur. The agreements were concluded in another region, which means additional taxes can be charged.
Should an individual entrepreneur on a patent keep a book of income and expenses?
An individual entrepreneur on a patent is required to take into account income subject to this taxation system. An income limit has been established for him, upon reaching which the PSN cannot be applied. Confirmation that the size limit has not yet been reached can only be done by accounting in accordance with the rules.
The income of an individual entrepreneur for all patents cannot exceed 60 million rubles per year. If you combine PSN and simplified tax system, income under both tax regimes is considered.
In the book of income and expenses on a patent, an individual entrepreneur must take into account only income from sales. Non-operating income and income under other tax regimes do not need to be reflected.
Reporting methods
As you may have noticed, an individual entrepreneur with employees on staff must submit a fairly large number of documents to various regulatory authorities. But a businessman does not have to deal with these issues himself and waste his time.
At the moment, an entrepreneur can choose one of four ways to submit tax reports and financial statements:
Self-submission of documents is the easiest, in terms of execution, but the most time-consuming and labor-intensive method;
Executing a power of attorney for another person. A representative of an individual entrepreneur can submit reports for him if he issues a notarized power of attorney;
Sending reports by mail
Please note that the date of submission of the report in this case will be considered the date of sending the letter to the regulatory authority. The envelope must contain an inventory of the document signed by the accountant and manager
Experts advise enclosing two copies of the inventory. We recommend sending reports by registered or certified mail. This way you will be absolutely sure that they will reach the addressee;
Sending reports via the Internet. To do this, you need to go to the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia. There you need to get a subscriber ID, install the PC program “Taxpayer Yul”, it is needed to generate documents. Or send reports through special communication operators accredited by tax inspectorates. You also need to issue a power of attorney to submit reports.
Rules for maintaining a book of income accounting for individual entrepreneurs on a patent
KUDiR must be filled out in chronological order. All records are kept only in Russian.
Information about income received is entered on the basis of primary accounting documents - payment orders, bank orders, reports on cash register shifts and other documents that an individual entrepreneur can issue instead of cash receipts. They can be compiled both in Russian and in other languages. In the latter case, interlinear translation is required.
You can keep a book of income and expenses for an individual entrepreneur on a patent either on paper or electronically. It opens every calendar year. After the end of the next year, the electronic document must be printed.
The completed pages of the book should be numbered and laced. The last sheet indicates their number. It is confirmed by the signature of the individual entrepreneur and certified by a seal (if you use it in your activities).
We recommend reading: Should an individual entrepreneur on a Patent keep a cash book and deposit cash in the bank?
Making entries
The title page of the income journal indicates information about the individual entrepreneur, the tax period and details of current accounts.
Records of individual entrepreneurs' income are entered in Section I on the day cash is received or money is credited to the account. Returns are reflected with a minus sign. Replenishing an account with an individual entrepreneur’s personal money, receiving or repaying loans are not considered income, and therefore are not entered into the ledger.
When accounting for acquiring receipts, income is offset by the amounts actually paid by buyers. Money from the bank to the individual entrepreneur’s account is received minus the commission, so reflecting only the amount received is not enough.
Example: On May 15, 2021, 14,600 rubles were received into the individual entrepreneur’s current account under an acquiring agreement, the bank’s commission for the operation was 400 rubles. Therefore, for May 15, you need to reflect income in the amount of 15,000 rubles. (14,600 + 400).
The column “Date and number of the primary document” reflects data on the documents on the basis of which the entry is made, for example, “05/15/2020, 13” or “05/23/2020, 9-11”. Documents of the same type can be grouped into one record by specifying the appropriate range of numbers. Here you are also allowed to specify the type of document, then the entries will become as follows: “05/15/2020, bank order 13” and “05/23/2020, BSO 9-11”.
The entry in the column “Content of the transaction” should reflect its economic essence, for example, “Receipt of proceeds from the sale of goods through acquiring”, “Receipt of proceeds from the provision of services in cash” or “Receipt of an advance payment for the performance of work to the current account”.
Income is recorded in rubles accurate to two decimal places, for example, 500.02. The results are summed up for the entire calendar year.
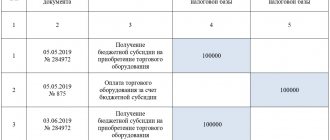
Sample of filling out an income book for an individual entrepreneur on a patent
CUD on a patent is available on the tax website or a specialized reference service for free. You can fill it out according to our sample. It is designed taking into account the most typical retail operations, but can be used as a basis for other types of activities.
An example of filling out the CUD on a patent for retail trade:
Combining the patent system with other regimes
An entrepreneur using a patent tax system can combine it with any other tax regime. This conclusion follows from paragraph 1 of Article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
At the same time, in relation to the same type of activity, an entrepreneur has the right to combine the patent system with a different tax regime for the following types of activity:
road transportation of passengers (subclause 10, clause 2, article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
road transportation of luggage (subclause 11, clause 2, article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
transportation of passengers by water transport (subclause 32, clause 2, article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
transportation of goods by water transport (subclause 33, clause 2, article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
catering services (subclause 47, clause 2, article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
retail trade carried out through a stationary retail chain with a sales floor area of no more than 50 sq. m for each object (subclause 45, clause 2, article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
retail trade carried out through objects of a stationary trading network that do not have sales floors, as well as through objects of a non-stationary trading network (subclause 46, paragraph 2, article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For example, an entrepreneur received a patent for retail trade through a stationary retail chain with a sales floor area of no more than 50 square meters. m (subclause 47 clause 2 of article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, he conducts retail trade in stores with a different floor area. In such a situation, an entrepreneur can:
for trade through halls with an area of no more than 50 square meters. l – apply only the patent system;
for trade through halls with an area of more than 50 sq. m and up to 150 sq. m – pay UTII;
for trade through halls with an area of more than 150 sq. l – apply a simplified or general taxation system.
In a similar manner, an entrepreneur can combine the patent system with a different tax regime for catering services.
For the services of transporting passengers or luggage by water or road transport, an entrepreneur can combine the patent system with another tax regime in the following order:
for vehicles specified in the patent, it is necessary to apply the patent taxation system;
For vehicles not declared in a patent, a different tax regime can be applied.
This is stated in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 5, 2013 No. 03-11-10/11254 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 7, 2013 No. ED-4-3/10450. The documents are posted on the official website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
For example, an entrepreneur has seven cars that are used in passenger transportation activities. He received a patent for five of them. Consequently, with respect to income from five cars, the entrepreneur must apply the patent system, and for the remaining two he can apply a different taxation regime.
Situation: can an entrepreneur who leases out real estate objects apply the patent taxation system only to that part of such objects that are indicated in the patent, and apply a different tax regime for the remaining objects?
Yes maybe.
An entrepreneur has the right to apply a patent taxation system if he leases residential and non-residential premises, dachas, land plots that belong to him by right of ownership (subclause 19, clause 2, article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the patent system applies only to those leased objects that are specified in the patent. If an entrepreneur owns other real estate properties that are rented out, but which are not indicated in the patent, then he has the right to apply other taxation regimes with respect to income from the rental of such real estate. For example, a simplified or general taxation system.
This is stated in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 5, 2013 No. 03-11-10/11254 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 7, 2013 No. ED-4-3/10450. The documents are posted on the official website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
For example, an entrepreneur has five real estate properties that he rents out. The entrepreneur received a patent for three of them. Consequently, in relation to income from three objects, the entrepreneur must apply the patent system, and for the remaining two he can apply a different taxation regime.
It should be noted that previously representatives of the tax service took a different point of view. Letter No. ED-3-3/1116 of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 28, 2013 stated that the patent system should be applied to leasing activities in general. That is, if an entrepreneur who owns real estate located in one constituent entity of the Russian Federation decides to apply the patent system, he must apply it to all such objects (i.e., by type of activity as a whole). However, with the release of letter No. ED-4-3/10450 of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 7, 2013, the previous clarifications lost their relevance.
Shelf life of KUD
The patent income book must be kept for at least 5 years. The specified period begins on January 1 of the year following the reporting year. Before its expiration, the tax office has the right to request the CUD to conduct an audit. If you do not provide it within 10 days, you will be charged a fine of 200 rubles.
We recommend reading: Individual entrepreneur on a patent and VAT: in what cases you need to pay.
Official instructions
The main document of legal regulation of the taxation system, the Tax Code (TC), does not provide an explanation of the legal concept of the income book of an entrepreneur applying a patent (KUD). Article 346.53 only mentions that the form of this document and the procedure for its maintenance are approved by the relevant ministry.
Thus, the Ministry of Finance of our country, by its regulatory document (order), determined the form of the CUD, as well as the procedure for maintaining and filling out this book. This document was adopted on October 22, 2012 No. 135n. Its form is quite simple and includes the following information:
- indication of the period (year) for which this book is opened;
- start date of document maintenance (i.e. specific day and month of a given year);
- name of the taxpayer applying the simplified system in the form of a patent. Since only an individual entrepreneur can pay taxes in this way, his last name and first name are indicated (if there is a patronymic, this is also indicated);
- identification number that was indicated in the document on registration of this individual as a business entity (SPD);
- the validity period of the issued patent in the form of the initial and final dates of its validity;
- unit of measurement. It is already indicated in the form of the document and represents the Russian ruble (in no case can records be kept in other currencies, even in generally accepted dollars or the currency of the European Union);
- place of residence of the individual entrepreneur;
- details of the entrepreneur’s accounts, as well as the banks in which they are opened;
- The only section of this book is Income, presented in table form.
Documents for download (free)
- Download the KUD form in Word
- KUD form in Excel
If difficulties arise, the entrepreneur can get advice free of charge from the tax service or follow the advice in this article.