Our new article will talk about the problems and benefits of working as an individual entrepreneur with VAT. A small expected spoiler: there are still more minuses than pluses. But there are often situations when it will not be possible to bypass VAT.
Get a free tax consultation ►
| ✏ Every entrepreneur has the opportunity to determine the optimal tax regime for their activities. In most cases, individual entrepreneurs tend to use special modes (STS, PSN, UTII), which allow them to calculate the minimum number of fees and not pay VAT. However, in practice, situations arise when an individual entrepreneur is forced to work for OSNO, thereby automatically becoming a payer of value added tax. |
This is possible when carrying out activities for which the use of special regimes is prohibited or does not fit into the current restrictions. One of the reasons for using a common tax system may also be cooperation with counterparties on OSNO. In order to retain partners and provide them with a deduction for value added tax, entrepreneurs are forced to switch to OSNO. Let's consider whether an individual entrepreneur can work with VAT, as well as what nuances of work there are.
The essence of the tax
Let us give a clear formulation of the tax. VAT for the buyer is the amount that the seller adds to the price of the purchased goods. For the seller, this is a tax that he has to transfer to the budget. The tax is paid by each participant in the chain, from the manufacturer of the product to the company specializing in cargo transportation and delivering the product.
The following items are considered to be subject to VAT:
- Operations involving the sale of services, property rights, goods, and work in the Russian Federation.
- Transactions involving the transfer of work, goods, and services for one’s own needs.
- Operations for carrying out construction and installation work for your own needs.
- Operations for importing goods into the country from abroad.
The tax base is the markup calculated on the basis of contract prices and advances received. For imported goods, the basis for calculating VAT is the customs value according to the declaration.
Amounts submitted by suppliers when using purchased products or services in activities subject to this tax are considered as VAT deductions. This also includes capitalized services and products for which documentation is drawn up in the form of invoices.
Important! No deductions will be applied to invoices issued incorrectly.
If the tax calculation is negative, this is called “VAT refundable”. To credit such a refund, the entrepreneur will have to undergo a desk audit, based on the results of which VAT is allowed to be taken as an offset to future payments.
Cooperation between LLC and individual entrepreneur: how to overcome contradictions with VAT and not lose money
LLCs often refuse to cooperate with individual entrepreneurs. The main reason is the lack of trust in entrepreneurs and the lack of financial responsibility of individuals. In economic terms, everything is fixable.
In order for you to understand what we are talking about, we will tell you in more detail:
- Individual entrepreneurs almost always choose a taxation system where they do not have to pay VAT - the simplified tax system. Therefore, when paying for a product or service that contains tax, a businessman must reimburse the amount of this tax to the budget by filling out the appropriate declaration. An entrepreneur may face a fine for late submission of documentation.
- LLCs, in turn, operate under the general taxation system (OSNO), where payment of VAT is mandatory. By purchasing a product with VAT, the company will subsequently reimburse 18% through a tax deduction. According to the law, the reduction is made after paying the tax to the budget. If a product or service is purchased from a VAT evader, the company will not be able to obtain a tax deduction, and they will have to pay VAT on the entire income.
As you understand, it is not profitable for an LLC to work with an individual entrepreneur without VAT. For companies, this is a loss, and that is why many refuse to cooperate with individual entrepreneurs, or are looking for partners with VAT.
What should an individual entrepreneur do? Is it necessary to switch to another tax system?
The answer is no.
Entrepreneurs have several options:
- Lure with exclusive products and services. If the individual entrepreneur has no competitors, then the LLC will enter into any agreement with it, even despite VAT.
- Insert VAT invoice. An entrepreneur can issue a VAT invoice to a company (LLC). A declaration is drawn up. The LLC reimburses VAT from its budget.
- Reduce the cost of goods and services by the amount of VAT. In order for the LLC not to overpay 18%, you can discount the goods of the individual entrepreneur. If a product is purchased by a legal entity not for resale, then it is beneficial for it to pay less and not have to worry about returning it from the budget.
The last option is not always in demand, since the individual entrepreneur may lose some of the funds.
Does the individual entrepreneur pay VAT?
Individual entrepreneurs are subject to the obligation to pay this tax. This norm is enshrined in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But in practice, everything depends on what system of individual entrepreneur taxation with VAT is used by the businessman.
Several special tax regimes have been introduced for entrepreneurs. You can choose one of them at your own discretion, sometimes even a combination of several schemes is possible. When choosing, the convenience for the merchant himself is usually taken into account in terms of reporting and the size of the tax rate, as well as contacts with partners.
Important! For some counterparties, the application of VAT is a mandatory condition for doing business. This applies, for example, to large foreign companies.
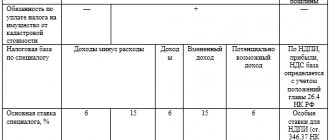
To determine whether an individual entrepreneur is a VAT payer, it is enough to know the taxation scheme used by him. Payment of tax is not required when conducting activities under the following regimes:
- simplified tax system or the so-called simplified tax system.
- UTII is a system for calculating taxes according to a specific scheme. From 2021, you can switch to this scheme at your own discretion, but it only works for certain types of activities.
- Unified agricultural tax is a special regime for agricultural producers.
- The patent system is now separated into an independent regime and is valid for specific services.
Individual entrepreneurs who use OSNO in their work must pay VAT.
Individual entrepreneurs working under UTII can combine this regime with the general regime for different types of activities. In such cases, VAT is paid for that part of the activity that is subject to taxation under the general regime.
Under the simplified tax system, an entrepreneur does not have to pay VAT, as well as some other fees: on profit and property. But there are exceptions here. A simplified businessman is a VAT payer when he performs the functions of a tax agent.
The second case is issuing an invoice to the counterparty when this tax is highlighted in the document. This category does not include sales under intermediary agreements with domestic customers, when the individual entrepreneur is an agent or commission agent. An individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system must include data from issued invoices in the declaration. If the intermediary entrepreneur is not a tax agent, he submits a journal of invoices to the tax authorities instead of a declaration.
There are also exceptions for UTII payers. In this mode, VAT will have to be paid when issuing invoices, performing the duties of a tax agent and importing goods into the Russian Federation.
As for the combination of UTII and OSNO, an important nuance must be taken into account. If an individual entrepreneur purchases services or products for use exclusively in activities on UTII, then the amount of VAT will be taken into account in the cost of these goods and works. If you plan to use them in activities on OSNO, the tax amount is deductible according to the current tax rules.
If it is impossible to ensure separate accounting, “input” VAT is distributed in proportion to the use of goods and services in activities in both modes. An example of such a situation would be paying utility bills and renting premises.
According to Article 9 of Law No. 335-FZ of November 27, 2017, from 2021 individual entrepreneurs on the Unified Agricultural Tax will become VAT payers. However, entrepreneurs in this regime are exempt from paying tax if certain conditions are met. The first concerns businessmen who switched to the Unified Agricultural Tax and declared an exemption from VAT within one calendar year. The second provides for receiving total income excluding tax within the limits:
- 100 million rub. in 2021
- 90 million rub. in 2021
- 80 million rub. in 2021
- 70 million rub. in 2021
- 60 million rub. in 2022 and subsequent years.
Individual entrepreneurs on the Unified Agricultural Tax, who have been exempted from VAT, will not be able to waive this right in the future. If an entrepreneur exceeds the above amount of income, from the same month he becomes obligated to pay VAT. You will not be able to receive the benefit again.
Important! Exemption from VAT is not provided to entrepreneurs who have sold excisable goods for 3 months in a row.
In the patent system, exceptional cases in which VAT is paid are the import of goods into the country, transactions under agreements of a simple or investment partnership, trust management, and concession agreements.
Summary
VAT is a tax that can be paid:
- legal entities registered in the Russian Federation;
- foreign business entities (through the mediation of a Russian tax agent, which in cases provided for by law may be an individual entrepreneur);
- IP;
- citizens not registered as individual entrepreneurs;
- government agencies.
Individual entrepreneurs and legal entities that work under a special regime are exempt from paying VAT - simplified tax system, PSN (individual entrepreneur only), UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax, but only if they:
- did not issue an invoice for the counterparty on their own initiative;
- did not import goods or services from abroad.
At the same time, the procedure for paying VAT and submitting reports on it, depending on what is imported - a product or a service, and also depending on which country the product or service is imported from, can vary greatly.
How to get started with this tax
Every businessman who needs to pay tax should know how an individual entrepreneur works with VAT. First, it’s worth understanding the features of determining tax rates:
- For exported products, VAT is 0%.
- Some items are subject to a 10% tax. These are printed products, books, medicines, medical products, food and goods for children.
- In other cases, the rate is set at 20%.
Individual entrepreneurs on OSNO issue an invoice to clients, in which the tax is allocated. At the end of the quarter, the data is entered into a special book.
The status of VAT payer is assigned to an individual entrepreneur from the moment of registration with the tax authorities. Conducting activities without registration and generating profit can be proven based on the main criteria, and then the individual is equated to entrepreneurs, regardless of registration. In this case, you have to pay all additional taxes, to which penalties and fines will be added. It is much easier to open an individual entrepreneur in the prescribed manner and pay the necessary taxes.
Taxation system for paying VAT
The fact of registration of a new tax payer in the form of an individual (without creating a legal entity) is recorded in the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs (USRIP). At the same time, the newly created business entity must be registered with the Federal Tax Service. From this moment until filing an application for the application of special regimes or fiscal exemptions, the entrepreneur is considered a payer of OSNO and potentially VAT.
In accordance with the requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, persons using special regimes (chapters 26.3 and 26.5) cannot be considered a VAT payer. However, the Code does not prohibit carrying out activities in parallel with the general requirements. This means that an individual entrepreneur (it doesn’t matter whether he works on PSN and UTII) can combine them with OSNO, as well as report and transfer VAT to the country’s budget.
Pros and cons of VAT
An entrepreneur has the right to decide for himself whether to work with VAT or not. In the first option, the businessman chooses OSNO, in the second - a suitable special mode. In this case, you need to take into account the advantages and disadvantages of the tax.
The main advantage of working with VAT is that buyers can deduct the tax imposed by the entrepreneur-seller. Accordingly, if two individual entrepreneurs offer one product at the same price, the buyer will choose the one who works with VAT. True, this applies to cooperation with organizations.
The advantages include the very essence of OSNO. Thus, an individual entrepreneur working in this mode does not have to monitor his compliance with the requirements for special modes.
The disadvantages of working with VAT are:
- The need to calculate tax.
- Regular payment of a certain amount to the budget.
- Preparation of invoices for buyers.
- Obligation to submit a tax return.
- Concluding an agreement with the operator for filing declarations in electronic format and paying for the relevant services.
Businessmen work with VAT on OSNO, but they also need to pay personal income tax and property tax. Such individual entrepreneurs are more actively controlled by tax authorities.
Tax forms
BASIC
By default, all entrepreneurs are subject to the common tax system. This regime is quite labor-intensive from an accounting point of view and has an increased fiscal burden compared to special regimes (they are the only ones who pay VAT and personal income tax).
Therefore, there are not many entrepreneurs willing to work for OSNO. The
the tax regime is justified in the case of doing business in the segment of importing goods into Russian territory or when there is a predominance of VAT payers among partners.
By default, only OSNO entrepreneurs are required to pay VAT. Taxpayers transfer to the budget the difference between “outgoing” (the one that was presented to buyers in invoices for goods shipped and rendered (the one that was received in invoices from suppliers) VAT.
Sometimes the input VAT exceeds the output VAT, then the individual entrepreneur has the right to receive compensation for the difference from the budget.
The default tax rate is 18%.
Let's give an example of VAT calculation.
The individual entrepreneur shipped goods worth 5 million rubles, including VAT of 762,711.86 rubles. During the same period, he purchased raw materials for 3 million rubles, including VAT of 457,627.12 rubles, and also ordered repairs in the office in the amount of 500 thousand rubles, including VAT of 76,271.19 rubles. VAT payable to the budget will be calculated as follows: (762711.86 – 457627.12-76271.19) = 228,813 rubles.
How and when to pay value added tax
Individual entrepreneurs must submit a VAT return to the Federal Tax Service quarterly, and do this before the 25th day of the month following the reporting period. If this date falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is moved to the first of the following business days. Declarations are accepted exclusively in electronic format. It is possible to transmit a document in only one way: through the communication channels of the TKS and the special operator.
The tax is paid in stages, one-third of the quarterly amount per month. For example: the first third of the payment for the first quarter is due by April 25, the second by May 25, and the third by June 25. The tax is calculated as the difference between the output VAT on sales and the input VAT from suppliers. Both components are highlighted in the calculations.
The declaration should be filled out using tax registers (books, journals and other documentation). Tax authorities have the right to check the correctness of maintaining such registers.
Is it possible not to pay VAT on OSNO
The Tax Code provides for the possibility of exemption from VAT for a year. This happens if:
- The entrepreneur’s revenue for the quarter did not reach 2 million rubles.
- The individual entrepreneur registered as a VAT payer less than 3 months ago.
- The businessman applied for tax exemption and attached a journal of invoices, KUDiR, and a sales book for 3 months.
The minimum amount of revenue must be confirmed by an extract from the relevant documentation. Some entrepreneurs, in order to be exempt from tax, increase expenses by carrying out repair work and purchasing equipment. Another option is leasing payments.
Important! After the 12 months of VAT exemption have expired, you can collect the papers and resubmit them.