Types and functions of off-balance sheet accounts
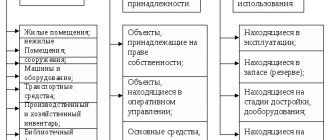
Off-balance sheet accounts (AB) are intended to store information about the objects used by the company. Their key feature is that the company does not have ownership rights to these objects. They are temporarily part of the company. Provided on the basis of various agreements. These objects may include:
Objects temporarily included in the assets, provided under certain agreements, do not belong to the enterprise. However, during a certain period of time, it is the enterprise that is responsible for them, which means it must take them into account in a certain way. But such values cannot be mixed together with those owned by right of ownership within the same accounting accounts.
Budget chart of accounts for 2021
When an institution has its own accounting department, the accounting policy is developed by the chief accountant or another employee responsible for accounting in the institution. If accounting is transferred to centralized accounting, then it develops accounting policies for it. In both cases, the document is approved by the head of the institution, since he is responsible for accounting. Basis - paragraph 8 of the GHS “Accounting Policies”.
We recommend reading: Where does the money for subsidies for young families come from?
To approve a document or make changes to it, issue an order on the accounting policy of a budgetary institution. Do not indicate the year for which it is valid. Set the date from which you will start using the document. For example, write this: “To put the accounting policy into effect from January 1, 2021.”
Postings to off-balance sheet accounts
Off-balance sheet accounting is subject to collateral that the organization receives, as well as obligations that the enterprise issues to counterparties. Obligations and security include pledges, deposits, bank guarantees, letters of credit, sureties, etc. Payment security received under the agreement is recorded in account 008.
The off-balance sheet accounts of the first group take into account non-current assets that were accepted from the counterparty under a leasing agreement, as well as inventory items accepted by the organization for safekeeping. Account 001, which is used to account for fixed assets in a lease, takes into account premises, cars, and equipment that the organization accepts under a leasing agreement.
Examples of basic postings in a government institution
Since January 1, 2021, updated instructions on budget accounting have been in effect, and adjustments have also been made to the current procedure for the formation of KOSGU and the Unified Chart of Accounts - instruction No. 162n. When working with the accounts of a government institution, rely on:
- Law No. 402-FZ;
- federal accounting standards;
- methodological recommendations, letters and explanations from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and other departments.
- ;
- instructions and ;
- ;
We recommend reading: Class of service 3e trains
See examples of postings for government institutions, taking into account the latest changes in the instructions for accounting in the State Finance System. Use the cheat sheet in your work.
Officials also introduced five new federal standards. All these innovations changed the rules of accounting in government institutions. In this article we will look at the main standard transactions for a government institution.
Budgetary accounting of fixed assets in 2021 (nuances)
- Reducing balance method. Suitable for assets whose useful life is very short. Also relevant for objects used in aggressive conditions. This method is necessary for accelerated depreciation.
- A method for determining depreciation in proportion to the volume of goods. The method is relevant for items that have a certain potential. That is, the accountant knows how much goods can be produced over a certain period using the asset. To make calculations, you need to multiply the actual volume of production by the depreciation rate.
- Linear method. Depreciation is accrued in equal installments every month. Accrual is made throughout the entire life of the facility. To determine the payment amount, you need to divide the original cost of the item by the SPI.
The standard established new principles for grouping operating systems.
Please note that we have provided only the basic wiring; see all typical wiring in the reference book above.
Previously, there were only two groups: “Non-residential objects” and “Structures”.
KEC for off-balance sheet accounts and
Good afternoon When you ask a question, please do not forget about the forum rules. Let me remind you: we strive to create a friendly atmosphere on our forum. Therefore, it is customary for us to say hello and also say “thank you” and “please.” Respectful attitude towards forum members, experts and moderators is a requirement of the forum rules.
Off-balance sheet account 17 is intended for cash receipts, and account 18 is for cash payments (clauses 365, 367 of Instruction No. 157n). Article 610 “Disposal from budget accounts” of KOSGU corresponds to off-balance sheet account 18.
Reflection of transactions in the second group
If an institution needs to reflect the receipt of income for the current year according to the corresponding analytical income code, then in parallel with the reflection of the receipt of funds to the personal account or the receipt of cash at the institution's cash desk, it is necessary to generate a posting to the debit account 17.01 or 17.34.
Let us consider the situation in which Institution A receives income from the provision of paid services. To reflect this business transaction in the program “1C: Accounting of a State Institution”, ed. 1.0, you can generate documents “Cash receipt” or “Cash receipt order”. When posting a document, the following transactions will be reflected:
Debit 2.00000000000000000.201.11.510 (201.34) – Credit 2.00000000000000130.205.31
Debit 2. 00000000000000130.17.01.130
Loan 2. 00000000000000130.ND.130 (in case of generating income to the institution’s cash desk)
The amount for this operation will fall into section 1 “Institutional Income” f.0503737 in the corresponding column 5 or 7 according to analytical income code 130. If the institution is obliged to return the excess income from sales (document “Cash Receipt”, “Request for Refund” ) the reflection of operations will be as follows:
Debit 2.00000000000000130.205.31 – Credit 2.000000000000000000.201.11.610 (201.34)
Credit 2.00000000000000130.17.01.130
Credit 2.00000000000000130.ND.130 (in case of generating a return of income through the institution’s cash desk)
Section 1 f. 0503737 will be formed based on data on receipt of income, taking into account their returns in the current year. This reflection of the institution’s income receipts and their return can also be used for other analytical income codes.
Formation of transactions for off-balance sheet accounts 17 and 18
The unified chart of accounts provides for 30 off-balance sheet accounts (hereinafter referred to as o/s) numbered from 1 to 27, as well as 30, 31 and 40. A simple accounting scheme is applied to all these accounts, that is, income is reflected only in debit, and expenses - on a loan, without correspondence.
- to organize control over the safety of property that is located on the territory of the organization, but for which there is no right of operational management or which, according to accounting rules, is not reflected in balance sheet accounts (library fund units, fixed assets up to 3,000 rubles, in use, awards and etc.), as well as other material assets;
- to track settlements and obligations awaiting execution;
- to collect analytical information about other accounting objects, etc.
What to consider from reporting as of January 1, 2021
A number of rules must be applied when preparing reports as of January 1, 2021. Institutions have the right to make changes to analytical accounting during 2021, consolidating the decision in their accounting policies.
Innovations in accounts and their purpose
Entering your own analytical codes of synthetic accounts and off-balance sheet accounts into the working chart of accounts is permitted only taking into account the requirements of the body to which the reports are submitted. The order does not indicate whether this rule applies to additional accounts already established (before the amendments entered into force). It is recommended that all entered accounts be reconciled before submitting reports for 2021.
Income of future periods will be divided according to the dates of recognition in the financial results. Amounts that are planned to be attributed to current year income are recorded in account 401 41. The remaining funds are indicated in account 401 49 “Deferred income for recognition in subsequent years.”
On off-balance sheet account 27, you need to take into account fixed assets for the personal use of employees, which they use, including outside the office and during non-working hours. Previously, such objects were not reflected in the instructions.
The purpose of account 105 01 is brought into line with code 341 KOSGU. This account records all medical products that the institution uses for medical purposes.
Some amendments do not have an exact application date. For example, the instructions include accounts 114 87 and 114 88 to account for the reserve for a decrease in the value of inventories. And although, according to the standard, reserves must be reflected from 2021, new accounts will only begin to apply from accounting for 2021. Also in the instructions from this year, account 106 50 has been introduced to account for investments in treasury property, which is provided for in the Unified Chart of Accounts from 2021. Therefore, it is recommended to agree on the start dates for using accounts and the procedure for submitting reports with the financial authority.
One of the provisions of the order establishes the rules according to which, at the end of the year, in accounts with balances it is not necessary to reset the KOSGU codes under subarticles of articles 560, 660, 730 and 830. It is advisable to apply this rule after agreement with the founder and the financial authority.
Changes in analytical accounting
Analytical accounting requirements have been adjusted in relation to accounts 101 00, 106 00, 205 00, 206 00, 208 00, 209 00, 210 03, 210 10, 302 00, 304 01 and 304 03.
Among the significant amendments:
- the indicators of account 205 00 in the analytical accounting registers should be divided not only by counterparties, but also by the legal basis for the occurrence of income. It is allowed to maintain records by groups of counterparties, provided that personalized records are maintained outside of balance sheet accounts (management accounting). At the same time, it is necessary to reconcile management and accounting data at least at each reporting date.
- account 302 00 reflects settlements for purchases of goods (works, services) in the context of legal grounds (contracts). Payroll calculations can, as before, be taken into account for a group of counterparties, subject to management accounting and data reconciliation for each reporting date.
- Analytical accounting for accounts 206 00, 208 00 and 302 00 should be carried out, among other things, according to the accounting numbers of monetary obligations, if any.
- If an asset is accepted for accounting after the inventory group has been destaffed, it must be assigned a new inventory number. The inventory number of a complex of objects and internal IDs of objects within the group do not need to be used in the future.
- for off-balance sheet accounts 08 and 20, the procedure for analytical accounting has been clarified.
Technical amendments to the instructions
The instructions set out a number of approaches that companies could previously apply in practice when maintaining records:
- account 103 00 takes into account non-produced assets by responsible persons, location and identification numbers.
- workwear in account 105 05 includes only supplies used by the institution for labor protection, compliance with safety regulations, civil defense and emergency protection.
- on account 105 06 are taken into account including BSO. Forms issued from the warehouse for registration to employees or received by them past the warehouse are reflected in off-balance sheet account 03.
- gifts are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 07.
Off-balance sheet accounts
Off-balance sheet accounts reflect additional information about the obligations of the enterprise and its inventory, which did not have a place on the main accounts. As the name suggests, these accounts are “behind the balance sheet”, that is, they are not reflected in the balance sheet of the enterprise; they do not characterize the financial position of the organization; rather, they highlight the features of its activities.
Video lesson about accounting for off-balance sheet accounts of an organization, describes key accounts in detail, analyzes transactions and typical examples. The lesson is taught by the teacher of the site “Accounting and Tax Accounting for Dummies”, chief accountant Gandeva N.V. ⇓
Instructions for budget (accounting) accounting in 2021: overview of changes
In paragraph 18 of Instruction No. 157n there is a minimal amount of information about correcting errors. This transaction is now governed by the Federal Public Sector Accounting Standard, Accounting Policies, Estimates and Errors. At the same time, paragraph 18 of the updated Instruction No. 157n indicates that accounting records for correcting errors of previous years are subject to separation in accounting and reporting in a separate Journal for other transactions containing o.
At the same time, these orders and, accordingly, changes in the instructions are used in the formation of accounting policies and budget (accounting) indicators, starting from 2021. This is stated in the preamble of each of these orders.
Off-balance sheet budget accounts in 2021
Instruction No. 157n provides for 31 off-balance sheet accounts. The instructions do not limit the rights of the institution to use its additional accounts. Irregularities in accounting for off-balance sheet accounts distort reporting, which can result in fines.
Please note => Okey liter is an all-Russian classifier of units of measurement
• Account 14 “Settlement documents awaiting execution” and account 15 “Settlement documents not paid on time due to lack of funds in the account of a state (municipal) institution).” Accounting for settlement documents is maintained in the Accounting Card for settlement documents awaiting execution, broken down by accounts for each document. • Account 16 “Overpayments of pensions and benefits due to incorrect application of legislation on pensions and benefits, accounting errors.” Keep records in the Funds and Settlements Accounting Card. Registration is carried out on the basis of audit reports, inspections and other similar documents. In account 16, the amounts of overpaid benefits continue to be recorded until they are fully repaid or written off. If repayment or collection occurs over a period of several months, amounts held off balance may also be written off gradually. • Account 17 “Cash receipts” and account 18 “Cash outflows”. Accounts must be opened for balance sheet accounts: 201.00 “Cash of the institution”, 210.03 “Settlements with the financial authority for cash” and 304.06 “Settlements with other creditors” (in terms of cash settlements). Accounting is maintained in a Multigraph Card or Card for Accounting Funds and Settlements in the context of institution accounts, by type of disposals and receipts (in the context of KOSGU). At the end of the year, account balances are not carried over to the next year. Thus, accounts 17 and 18 must be closed as of December 31 of the reporting year. • Account 19 “Unidentified budget revenues of previous years.” Accounting is carried out according to the dates of crediting of uncleared receipts and the dates of their clarification. • Account 30 “Settlements for the fulfillment of monetary obligations through third parties.” Analytical accounting of the account is maintained in the Multigraph Card and (or) in the Funds and Settlements Accounting Card in the context of monetary obligations by type of payment of budget funds or other types of payments.
Reflection of transactions in the first group
If an institution needs to reflect the current year’s expenses according to the corresponding expense type code (KVR), then in parallel with reflecting the outflow of funds from the personal account or the outflow of cash from the cash register, it is necessary to generate a posting to the credit account 18.01 or 18.34 according to the corresponding analytical expense code.
Example.
Using funds to complete a government assignment, Institution A purchased inventories from a supplier. Payment was made by transfer to the supplier's account.
In the program "1C: Public Institution Accounting 8", ed. 1, it is necessary to generate the document “Request for cash expense”, “Cash expense order” or “Cash disposal”, during which the accounting records will be reflected:
Debit 4.00000000000000244.302.34 – Credit 4.00000000000000000.201.11.610
Credit 4. 00000000000000244.18.01.340
Based on these records in f. 0503737 in section 2 “Institutional expenses”, column 5 “Through personal accounts” under expense type code 244 “Other purchase of goods, works and services to meet state (municipal) needs” this amount will be reflected. The scheme for reflecting the expenses of an institution for the current year, executed through a personal account, is universal for other expense type codes, for example, such as “111- Payroll Fund”, “119 - Compulsory social insurance contributions for payments to employees and other payments to employees institutions”, “112-Other payments to personnel of institutions, with the exception of the wage fund”, etc.
Let's consider the reflection of cash expenses through the institution's cash desk. For example, an accountable person was given funds for the purchase of inventories:
Debit 4.00000000000000244.208.34 – Credit 4.00000000000000000.201.34.610
Credit 4. 00000000000000244.18.34.340
Credit 4. 00000000000000244.ND.340
In this case, the expense will fall into section 2 f. 0503737 column 7 “Through the institution’s cash desk” under KVR 244.
Also, in the practice of an institution, quite often it is necessary to restore the cash flow of the current year. In this case, section 2 f. 0503737 will be formed taking into account the restoration of such expenses.
Example.
Institution A transferred more wages to the employee than was required. The employee returned the funds to the institution's cash desk.
In this case, the following transactions will be generated:
Debit 4.00000000000000000.201.34.510 – Credit 4.00000000000000111.302.11
Debit 4. 00000000000000111.18.34.211
Credit 4. 00000000000000111.ND.211
If the expense is restored through the institution’s personal account, an additional entry is generated to the Debit account on 01/18/XXX according to the corresponding expense code.
Why do you need an off-balance sheet account of a budget organization?
Such accounts are auxiliary accounting accounts. The balances for them are not included in the balance sheet and are illustrated behind the results of the main balance sheet, that is, behind the balance sheet. They do not affect the financial result and are not reflected in the periodic and final reports of the organization.
Don't know what an off-balance sheet account is in accounting? In the working charts of accounts used in accounting in both budgetary and commercial and non-profit organizations, main (balance sheet) and off-balance sheet accounts are distinguished. On the main accounts, accountants must conduct transactions related to the movement of cash and other material assets, receipts and disposals, profits and mutual settlements with counterparties; information about various goods and works, as well as advertising and other services are taken into account. Off-balance sheet accounts are used to account for inventory items that are temporarily at the disposal of the organization and do not belong to it as property. Off-balance sheet accounts are also needed to reflect transactions on those obligations that are awaiting fulfillment, and the movement of values not intended for accounting on the main accounting accounts.
Internal cash flows of a state institution in 1C: BSU 8 edition 2
I would like to make a small reservation on the topic of reflecting data on business transactions in the report f. 0503737. This report is filled out on the basis of planned assignments (financial and economic activity plan) and records on analytical accounts 17 and 18.
If one of the cash accounts is involved in the accounting record, then the entry on it is necessarily duplicated by the entry on the off-balance sheet account. In 1C: Accounting of a state institution, the following correspondence is established for these balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts.
What to consider on off-balance sheet account 02 in 2021
The column “Target function of the asset” reflects information about possible ways to involve inventory objects in economic circulation, use them to obtain economic benefits (extract useful potential) or, if this is not possible, about ways to dispose of the object. For example, for fixed assets: “commissioning”, “repair”, “mothballing of the facility”, “retrofitting (retrofitting)”, “write-off”, “disposal”.
Please note => Child benefits for part-time workers
At the same time, individual items of property that are owned by the accounting entity not for the purposes of their operation (do not bring useful potential, do not ensure the receipt of economic benefits), but ensure that the institution performs certain functions, are subject to reflection in the composition of fixed assets (clause 3 of the Methodological Recommendations on the application of the Standard “Fixed Assets”, communicated by letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 15, 2017 No. 02-07-07/84237, hereinafter referred to as Methodological Recommendations).
Changes in accounting and reporting of municipal and state institutions in 2021: answers to questions
Therefore, in the program “1C: Public Institution Accounting 8”, edition 1 and edition 2, for counterparties, which we define as individual entrepreneurs based on the presence of OGRNIP, registration date, have account 40802, we enter type 6.
In accordance with clause 12.1.7 of the Procedure for the formation and application of budget classification codes of the Russian Federation, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/08/2021 No. 132n as amended on 03/06/2021 No. 36n, hereinafter referred to as Order No. 132n, operations
taxpayers - state (municipal) autonomous and budgetary institutions
for the assessment of taxes, the object of taxation for which is the income
(profit) of the institution,
for the assessment of value added tax
on income from sales made, work performed, services rendered, taxed in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees, value added tax, and on the accrual of corporate income tax, calculated based on the results of the tax (reporting) period, subject to payment to the budget,
are included in the article of the analytical group of subtype of budget income 180 “Other income”
.
Application of off-balance sheet accounts 17 and 18 in budget accounting
Since the control agencies have not come to a common position, the organization can independently choose the option of generating records. It is logical to assume that refunds of funds must be indicated on the account loan. 17, and restoration of expenditure payments - on the account loan. 18.
- Refund of amounts previously received from counterparties.
- Payment of tax obligations regarding reduction of income (VAT, profit).
- Payments to the budget of receivables incurred by the recipient of financing in the process of executing the budget estimate.
Accounting policy 2021
3.2. Tax deductions to individuals for whom the institution acts as a tax agent are provided on the basis of their written applications using forms independently developed by the institution and given in the Appendix to this Accounting Policy.
2.11. The book value of an item of fixed assets of the types “Machinery and Equipment”, “Vehicles” increases by the cost of costs for replacing its individual components, provided that such components, in accordance with the criteria for recognizing an item of fixed assets, are recognized as an asset and in accordance with the procedure for operating the object (its components) such replacement is required, including during major repairs.
Accounting for off-balance sheet accounts in 1C
The movement in off-balance sheet accounts is reflected as follows: the debit account takes into account the increase in the values of the account, and the credit account for the decrease, since all accounts are active. Recording on accounts, unlike balance sheet accounts, is simple; a corresponding account is not needed to generate postings.
1. Account 01 accounted for each individual object of non-financial assets with inventory numbers assigned by the balance sheet holder and indicated in the transfer and acceptance certificate. In this case, the accounting object was assessed at its value indicated by the balance sheet holder. In the absence of a valuation of objects, it is allowed to take into account the conditional valuation - 1 object = 1 ruble.
Chart of accounts for accounting 2021 in budgetary organizations
All these organizations are part of the system of the so-called state accounting policy, which is a strictly defined procedure for budget accounting in state, territorial, municipal authorities, extra-budgetary funds, etc.
We recommend reading: Who is Equated to the Liquidators of the Chernobyl Accident
The new budget chart of accounts contains about two thousand synthetic accounting accounts. For its own accounting needs, a state (municipal) enterprise develops its own PS on the basis of an approved one, which includes only the accounts necessary for this organization.
Off-balance sheet accounts
- generalization of information on the availability and movement of valuables temporarily in use or disposal of the organization (leased fixed assets, material assets in safekeeping, in processing, etc.), contingent rights and obligations;
- control over individual business transactions.
Speaking about the rules of accounting, we noted that one of the main accounting principles is the principle of property separation. Based on this assumption, the accounting policy of the organization should be formed for accounting purposes (clause 5 of PBU 1/2008). The principle of property separation provides that the assets and liabilities of an organization exist separately from the assets and liabilities of the owners of such an organization, as well as the assets and liabilities of other organizations and individuals. In this case, how do you keep records of, for example, leased fixed assets or inventories received for safekeeping? After all, the organization that received them is responsible for this property, and therefore must keep records of them. However, it is impossible to take into account such values along with your own on the same synthetic accounts. For similar and other purposes, there are off-balance sheet accounts. As the name suggests, the data from these accounts is not used in preparing the organization's balance sheet. Information about them is disclosed separately in the reporting, “off the balance sheet”.
Account 02: how to use it when writing off a fixed asset
If it is impossible to restore a fixed asset or it is not economically feasible to use it, the object is deregistered due to moral or physical wear and tear.
Please note: these are two different concepts.
The differences are in. The procedure and reasons for writing off federal property have been approved. A government institution cannot dispose of property that is assigned to it under the right of operational management, without the consent of the owner (). That is, you need to get consent to write off even old furniture. The approval procedure depends on the basis on which property the institution was created: federal, regional or municipal.
We will tell you further about how to correctly write off unusable assets. There are no differences in the procedure for writing off an underdepreciated object and property with zero residual value.
The institution must create a permanent commission. This commission must: The write-off act is approved by the head of the state
Systematization of accounting
Postings to off-balance sheet accounts 17 and 18 must be reflected by government agencies, government bodies and other structures using the Unified Chart of Accounts, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 157n. We will tell you about the rules for using these accounts in our article.
Please note => Reprimand based on the results of the audit order
The unified chart of accounts provides for 30 off-balance sheet accounts (hereinafter referred to as o/s) numbered from 1 to 27, as well as 30, 31 and 40. A simple accounting scheme is applied to all these accounts, that is, income is reflected only in debit, and expenses - on a loan, without correspondence.
Results
Entries under s/s 17 and 18 must be made if there are transactions in accounting that affect the DS accounting accounts and the account for settlements with the financial authority for cash DS. The double entry method is not applied to off-balance sheet transactions, that is, receipts are reflected only on a debit basis, and disposals - on a credit basis. Off-balance sheet accounting of the movement of assets helps to control these assets, and also allows for detailed analytics, which is necessary for drawing up some forms of reporting.
Sources: Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Off-balance sheet budget accounts
Budgetary accounting of MCs on the balance sheet is carried out in a simple way: receipts are subject to reflection on the debit side of the accounts, disposals - on the credit side. Corresponding records are not used when using them. Budgetary organizations can open additional off-balance sheet accounts to collect information necessary for management accounting and internal control over the safety of property.
Fixed assets on an off-balance sheet account in the budget are taken into account according to the primary document, which confirms their entry at a conditional valuation or at book value, depending on the procedure provided for by the accounting policy of the budget organization.
How to keep records of low-value fixed assets
Not a day without instructions × Not a day without instructions
- Services:
Low-value fixed assets 2021 are the property of an organization, the value of which does not exceed the limit established by law, and it can be taken into account as part of expenses at a time, and not through depreciation charges. Let’s figure out which fixed assets are considered low-value and how to properly account for them in a budget organization, taking into account the changes in 2021.
January 11, 2021 Author: Natalya Evdokimova To determine which objects can be classified as low-value fixed assets, from what amount for 2021 to count and how to count, we will determine the maximum limits. Cost limits have been adjusted.
Now, fixed assets subject to immediate write-off on the balance sheet should include objects that cost 10,000 rubles or less. Let us recall that until 2021, fixed assets with a value of up to 3,000.00 rubles were recognized as such property.
Application of off-balance sheet accounts
At the same time, information in monetary terms about the state of property located at the institution, but not assigned to it under the right of operational management, including during the period of state registration of the right of operational management, is subject to reflection on off-balance sheet accounts (clause 3, 332 of Instruction No. 157n).
Rationale. In accordance with clause 339 of Instruction No. 157n, off-balance sheet account 04 “Debt of insolvent debtors” is intended to account for the debt of insolvent debtors from the moment the institution’s commission for the receipt and disposal of assets makes a decision to write it off from the institution’s balance sheet. The provisions of this paragraph are given taking into account the latest changes made by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 1, 2016 No. 16n (hereinafter referred to as Order No. 16n).
Login for clients
Off-balance sheet account 18 “Outflows of funds from the accounts of the institution” reflects the outflows of funds (except for returns of receipts), as well as returns of expenses (excessive transfers made) for the current year. In this case, operations on receipts from reimbursements of expenses are reflected in off-balance sheet account 18 with a minus sign.
According to clause 365 of Instruction No. 157n, off-balance sheet account 17 “Cash receipts” reflects cash receipts (with the exception of receipts from refunds of expenses of the current financial year), as well as the return of excess income received (income from advances). In this case, transactions for transferring returns of income accounted for in the corresponding analytical accounting accounts of off-balance sheet account 17 are reflected with a minus sign.
Off-balance sheet accounts in budgetary institutions in 2021
- By analogy with the use of off-balance sheet accounts by private organizations, accounting on off-balance sheet accounts in budgetary institutions involves the use of simple entries - without correspondence, only by debit or credit.
- is not the property (or a counter-obligation to the counterparty when ownership rights arise) of the organization or is not under the operational management of the institution;
- is not regularly used in business activities (as an option, it is transferred for use to another person and most of the time it is used by him);
- came into use of the organization temporarily;
- has a very low cost in comparison with the typical cost of accounting objects of the same name, which are usually placed on the balance sheet as assets or liabilities.
Chart of accounts for budgetary accounting of a government institution in 2021
In 2021, Instructions 157n and 162n are applied in new editions. We tell you what amendments have been made to the relevant orders of the Ministry of Finance, whether the structure of the chart of accounts has changed and where you can see the correct accounting entries.
- Non-financial assets - fixed assets, financial assets, intangible assets, legal acts, investments in non-financial assets, depreciation, production costs, impairment and rights of use.
- Financial assets - cash in hand and in banks, financial investments, all types of securities, income from various sources, advances issued, settlements with accountable persons, for damages and shortages, with other debtors.
- Liabilities - settlements for payments to personnel, accruals for wages, Social Insurance Fund benefits, taxes, contributions, debts, loans, with counterparties for goods, works and services, intradepartmental transfers, for payments from the budget.
- Financial result – income and expenses of the current, past and future periods.
- Authorization of expenses - estimated assignments, accepted budgetary obligations and monetary obligations received by LBO and budgetary allocations.
Off-balance sheet accounting
Example An organization provided grain storage services. The contractual value of the transaction is 100 thousand rubles. The services are valued at 15 thousand rubles, the costs of the custodian are 10 thousand rubles. In the accounting system this operation is reflected as follows:
Off-balance sheet accounts with inventory items can now also contain information about the movement of valuables that are subject to write-off due to wear and tear or due to the impossibility of further use. Conclusion To record values that are in the temporary use of an organization and do not belong to it, special off-balance sheet accounts are used. All capitalization transactions are displayed as a debit, and write-offs as a credit. If necessary, you can add off-balance sheet 1C accounts and keep records without violating the law. All cost items and subcontos are already built into the basic version of the program. Standard transactions and reporting are generated using standard documents.
15 Nov 2021 marketur 235
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Compensation for damage to health in case of an accident under compulsory motor insurance
- Payment after donating blood in Vladimir
- Additional agreement to the contract on postponing work due to unprepared territory
- Where to get a certificate of family composition in Irkutsk Urik
KPS for budgetary institutions decoding 2021 accounts 105 and 101
A full (26-bit) account for allocating expenses for the write-off of materials, including for inventory balances that existed at the beginning of the year and accounted for at “zero” KPS, is indicated in the header of the document and must include the current KPS of the “KRB” type. (See Fig.2)
To which KPS should we assign expenses for writing off materials and calculating depreciation in “1C: Accounting of a state institution 8” Dt 040913Ya0002110244 1.105.36 340, Kt 040913Ya0002110244 1.302.34 730 (according to Appendix 2 to Instruction 162n ).