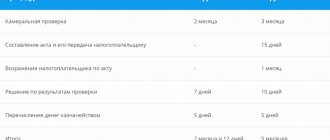
Control over the safety of the property of an economic entity is the most important element of the system of internal control of the facts of economic life (Part 1, Article 19 of the Federal Law “On Accounting”, subparagraph “a”, paragraph 3 of Information of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. PZ-11/2013 “Organization and the implementation by an economic entity of internal control over the facts of economic life, accounting and preparation of accounting (financial) statements." The procedures for internal control of the actual presence and condition of objects include inventory (subclause “e”, clause 8.1 of Information No. PZ-11/2013). Let us consider the features of this procedure for trading enterprises in relation to identifying shortages of goods.
What to pay attention to when conducting an inventory
To carry out an inventory, a permanent inventory commission is created in the organization. In the absence of at least one member of the commission, the inventory results may be considered invalid.
Financially responsible persons of the inventory commission give receipts stating that by the beginning of the inventory, all expenditure and receipt documents for property were submitted to the accounting department or transferred to the commission and all valuables received under their responsibility were capitalized, and those disposed of were written off as expenses.
The results of the inventory must be documented. In practice, they continue to use the forms approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 N 88 “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for recording cash transactions and recording inventory results.”
When conducting an inventory on the basis of recalculation, weighing, remeasurement of inventory items, an inventory list is drawn up separately for each location and financially responsible person or group of persons. This document is drawn up in two copies and signed by the responsible persons of the commission.
According to clause 4.1 of the Method of Indicating discrepancies between the indicators according to accounting data and the data of inventory records, a matching statement is drawn up. This document is needed to reflect the inventory results if the actual data differs from the accounting data. The amounts of surplus and shortage of property in the matching statements are indicated in accordance with their assessment in accounting (form INV-18 and form INV-19).
Based on the results of the commission’s work, documented in a protocol, collation sheet or act, the employer makes a decision on compensation for damage. To do this, an order is issued on the results of the inventory and the withholding of shortages from the guilty persons.
In case of significant violations during the inventory, deductions of shortages from the employee may be considered unlawful.
Therefore, during the inventory, you should pay attention to the following circumstances:
— the absence of at least one member of the commission during the inventory serves as a basis for invalidating the inventory results (clause 2.3 of the Methodological Instructions);
— the participation of the financially responsible person is mandatory. In case of refusal to participate, a corresponding act is drawn up by the members of the commission (clause 2.8 of the Methodological Instructions);
— inventories must contain the signatures of all members of the inventory commission and financially responsible persons (clause 2.10 of the Methodological Instructions).
In addition to properly registering the inventory, the employer is obliged to create all conditions for the safety of property, as well as to properly formalize the employment relationship with the employee and the agreement on full financial responsibility.
Financial liability in the full amount of damage caused is assigned to the employee for damage caused to the employer during the performance of the employee’s job duties (Clause 1, Part 1, Article 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If the employer violated labor laws by not concluding an employment contract with the employee and not familiarizing him with the job description, then he thereby did not inform the employee about his job duties and responsibilities.
Thus, if an employee was allowed to work without formalizing labor relations in the legally established manner, the employer does not have the right to recover from the employee material damage that arose when the employee performed his job duties improperly (Decision of the Leningrad Regional Court dated June 28, 2012 in case No. 33a-2646/2012).
Labor legislation establishes legal norms providing for the financial responsibility of the employee to the employer. The damage caused by the employee must be compensated, regardless of whether he is brought to disciplinary, administrative, or criminal liability or not. This is indicated by Art. 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
When conducting an inventory, shortages of inventory items may be identified from financially responsible persons entrusted to him on the basis of a liability agreement. Shortages of material assets, cash and other property, as well as damage in excess of the norms of natural loss in accordance with clause 5.1. Inventory guidelines refer to the perpetrators.
As a general rule, during an inventory, the amount of damage is determined by identifying discrepancies between the actual availability of property and accounting data (Part 2, Article 11 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ “On Accounting”). And in order to determine the perpetrators and the causes of shortages, it is necessary to conduct an internal investigation. This procedure is indicated by the legal norm of labor legislation given in Art. 247 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Agreement on full financial responsibility
Full financial responsibility can be individual or collective (team). The last option is used when sellers work in shifts.
Please note: the lists of works and categories of workers with whom these contracts can be concluded, as well as standard forms of these contracts, are approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 31, 2002 No. 85, and this document is registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia.
Thus, the List of positions and works replaced or performed by employees with whom the employer can enter into written agreements on full individual financial responsibility for shortages of entrusted property includes:
- positions of directors, managers, administrators, other heads of organizations and trade departments, their deputies, assistants, salespeople, commodity experts of all specializations;
- settlement work for the sale (sale) of goods, products and services (including not through the cash register, through the cash register, without a cash register through the seller).
A standard agreement on full financial liability can be supplemented with new conditions that do not contradict the Labor Code. However, the conditions provided for by the regulatory legal act of the Russian Ministry of Labor should not be excluded from it.
In accordance with the Standard Form of a Full Liability Agreement:
- the employee undertakes to participate in inventory, audits, and other verification of the safety and condition of the property entrusted to him (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 15, 2008 No. 07-05-12/16);
- determination of the amount of damage caused by the employee to the employer is made in accordance with current legislation.
Commission to investigate identified deficiencies
To conduct an internal investigation, the manager has the right to create a commission and approve it by order. The order also establishes the terms of the official investigation and the procedure for processing and presenting the results.
It is advisable to regulate the procedure for conducting an investigation by local regulations of the organization. However, the absence of such a document cannot hinder the investigation. At the same time, the commission studies documents, including acts, inventories, primary accounting documents, actually carries out a recount, takes explanations from various employees, studies reports (official) notes, etc.
The result of the commission's work should be an act of internal investigation, in which it is necessary to indicate the composition of the commission, the date of compilation and period of the investigation, the prerequisites for the conduct and the facts established by the commission, the conclusions it made with justification (the presence or absence of circumstances excluding the financial liability of the employee; illegality of the employee's behavior; the employee’s guilt in causing the damage; the causal relationship between the employee’s behavior and the damage that occurred; the presence of direct actual damage to the employer, the amount of damage, etc.).
A separate conclusion may be drawn up based on the results of the investigation. It usually reflects a summary of the results of the investigation. The act and conclusion must be signed by all members of the commission. After this, the financially responsible persons who are found guilty of the shortage must be familiarized with the act and conclusion under personal signature.
And one more document that can be drawn up based on the results of the investigation is an act that is drawn up in the event of a refusal to familiarize or to affix a personal signature to the familiarization by the financially responsible person.
Accounting entries: deduction of shortfalls from wages
After carrying out all the necessary procedures, the accountant is obliged to deduct the relevant accounts and withdraw the required amount from the employee’s salary.
| Debit | Credit | Description |
| 73 | 10 (01, 41,…) | A shortage of material assets (OS, money, goods, etc.) has been detected. |
| 70 | 73 | Withholding the shortfall from the employee's salary |
| 50 | 73 | Voluntary compensation for damage by an employee |
| 91.2 | 73 | Write-off for other expenses in case of incomplete compensation of the deficiency by the employee |
| 73 | 98 | Reflection of the amount intended for reimbursement |
| 98 | 91.1 | As the employee makes up for the shortfall, the amount is included in other income |
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from Scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) purchased by {amp}gt; 8000 books |
The employee must write an explanatory note
In accordance with the requirements of Part 2 of Art. 247 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a financially responsible employee whose shortage is detected must be required to provide a written explanation. Refusal to provide an explanatory note must be reflected in the act.
In practice, to carry out this procedure for bringing to responsibility, you can proceed as follows.
It is necessary to notify the employee about requesting an explanation from him regarding the shortage of inventory items.
If the employee refuses to give them, he should be given written notice requesting an explanation and required to sign for receipt of the notice.
If the employee refuses to sign the notice, it should be read aloud to the employee in the presence of witnesses.
If after this the employee refuses to give a written explanation, then in this case an act of refusal or evasion of the employee from giving an explanation is drawn up. The employee must also be familiarized with the act against signature; in case of refusal, a corresponding note is made about this.
The Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation in Resolution No. 52 actually established a presumption of guilt in relation to financially responsible persons, that is, if the employer has proven the legality of concluding an agreement with an employee on full financial responsibility and creating conditions for the safety of entrusted valuables, then if this employee has a shortage, the latter is obliged to independently prove the absence of his guilt in causing damage. Thus, it is not the employer who must prove the employee’s guilt, but the employee who must prove that the shortage was not his fault. However, we still do not recommend punishing financially responsible persons without conducting an investigation and appropriate documentation.
In what cases will it not be possible to recover?
Most often, problems with collecting the shortage do not arise. However, the deficiency cannot be recovered if:
- the exact damage has not been established;
- the employee’s guilt has not been proven;
- if the shortage arose due to management’s failure to comply with the necessary rules for the storage and protection of material assets;
- the employee caused damage to the enterprise in the event of acceptable self-defense or when absolutely necessary.
As you can see, the list of circumstances under which the deficiency cannot be recovered is small.
Recovery of damages
Before making a decision to collect shortfalls from an employee, the employer must have the following package of documents:
— documents confirming the results of the inventory (inventory lists, matching statements, report of identified discrepancies);
— a written explanation from the employee about the reasons for the shortages (or an act of refusal to give explanations);
— An act (conclusion) of the commission based on the results of an internal investigation, which records the guilt of the employee, the illegality of his actions, as well as the cause-and-effect relationship between his actions and the damage incurred by the employer.
The employee (his representative) has the right to familiarize himself with all materials of the internal inspection.
Based on the results of the investigation, the manager must decide whether to recover damages from the guilty party or not. Labor legislation (Article 240 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) gives the employer the right, taking into account the specific circumstances in which the damage was caused, to fully or partially refuse to recover it from the guilty employee. In any case, this decision must be formalized in the form of an order (instruction) for the organization. To recover the amount of damage from the guilty employee, the head of the organization must issue a withholding order. The order must be issued no later than a month after the commission establishes the amount of damage.
Based on the order, deduct the cost of damage from the employee’s income, not exceeding his average monthly salary. Taking into account this rule, it is necessary to recover damages both in cases where the employee bears limited financial liability, and in cases where financial liability arises for the full amount of damage.
I would like to draw your attention to one significant point. In accordance with Art. 239 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employee’s financial liability is excluded in cases of damage due to force majeure, normal economic risk, extreme necessity or necessary defense, or the employer’s failure to fulfill the obligation to provide adequate conditions for storing property entrusted to the employee.
Failure by the employer to fulfill the obligation to provide adequate conditions for storing property entrusted to the employee . This fact may serve as a basis for refusing to satisfy the employer’s claims if this was the cause of the damage. As an example, let us cite the Decision of the Golovinsky District Court of Moscow dated April 11, 2012 in case No. 2-1170/12. The court found that the employer did not create the appropriate conditions necessary to ensure the complete safety of the property entrusted to both the employee and the team (crew), and did not take measures to identify and eliminate the reasons preventing the safety of the entrusted property. In this regard, the claim was denied. In addition, the judges also pointed out that the inventory was carried out in violation of the requirements contained in the Guidelines for the inventory of property and financial obligations.
When deciding whether to compensate an employee for damages, the following must be taken into account. The amount of damage must be determined by actual losses, calculated on the basis of market prices prevailing in the area on the day the damage was caused, but not lower than the value of the property according to accounting data, taking into account the degree of its wear and tear. Moreover, if it is impossible to determine the day the damage was caused, the employer has the right to calculate the amount of damage as of the day it was discovered (clause 13 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of November 16, 2006 No. 52).
Please note that financial liability in the full amount of damage caused is assigned to the employee only in those cases specified in Article 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, these may be situations in which:
- such responsibility is assigned in accordance with applicable laws;
— a shortage of valuables entrusted to the employee on the basis of an agreement on full financial liability or received by him under a one-time document has been identified;
— the damage was caused as a result of the employee’s criminal actions established by a court verdict or as a result of an administrative violation;
- the employee acted intentionally or while under the influence of alcohol or drugs, as well as when he did not perform his job duties.
In other cases, the amount of damage that can be recovered from the employee is limited to his monthly earnings. This is stated in Article 241 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. That is, regardless of the amount of damage caused, the employee is obliged to compensate an amount that does not exceed his average monthly salary (decision of the Moscow Regional Court dated June 17, 2010 No. 33-11823).
When calculating the average salary, all types of payments provided for in the remuneration system and used in the organization are taken into account. In this case, the calculation is made based on the actual accrued wages and the time actually worked by him for 12 calendar months (Article 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
You also need to keep in mind that the amount of deduction should not exceed 20 percent of earnings, and, therefore, recovery of damages may take several months.
Payroll
Reflect the deduction in the employee’s payroll using the Payroll document through the Salaries and Personnel section – Salary – All accruals.
Please indicate:
- Salary for - July 2018 , month of accrual;
- from - 07/31/2018 , date of salary calculation.
The tabular part of the document is filled in automatically by clicking the Fill :
- Employee - A.P. Ivanov ;
- Accrued — 40 000;
- Personal income tax - 5,200 , 13% personal income tax on the amount Accrued .
To reflect the amount of damage deducted from the employee’s salary, in the Payroll , create a new Deduction by clicking the Deduction - New Deduction button.
In the Retention , indicate:
- Name - Shortage identified during inventory ;
- Amount - 3,600 , 20% (1/5) of the market value of the shortage identified as a result of the inventory.
A new column Withheld in the tabular part of the Payroll .
in the Withheld - 3,600 .
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt Kt - calculation of wages to the employee;
- Dt Kt 68.01 - Personal income tax is withheld from the salary;
- Dt Kt 69 - insurance premiums are charged.
In the postings of the Payroll , the deduction of damage from the employee's salary will not be reflected. Withholding in this document must be made so that the amount of damage is reflected in the payroll and pay slip, and is also taken into account when determining the amount to be paid.
A situation where an employee admitted his guilt
If the employee admits his guilt and does not mind compensating for the damage voluntarily, it is better to take a receipt from him with an obligation to repay the amount of material damage within the time period agreed upon by the parties. According to Part 4 of Art. 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee guilty of causing damage to the employer may voluntarily compensate it in full or in part; By agreement of the parties to the employment contract, compensation for damage by installments is allowed. In this case, the employee submits to the employer a written obligation to compensate for damages, indicating specific payment terms.
According to the receipt given by the employee as an obligation to repay the damage, the employee has the right to repay the amount of debt and more than the average monthly earnings - in the amount specified by him in the receipt. There will also be no violation of early repayment of debt by an employee in an amount of regular payments greater than that specified in the receipt - until the entire amount of damage is covered. There are no restrictions in this case established by law. Even if the employee quits and refuses to pay the balance of the debt for damages, the employing organization, on the basis of this written obligation, will be able to collect the debt from him in court.
By virtue of Part 1 of Art. 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the total amount of all deductions for each payment of wages cannot exceed 20%, and in cases provided for by federal laws - 50% of wages due to the employee.
How to calculate the specified limit: from the entire accrued amount or after withholding personal income tax? According to representatives of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia, the amount of deductions from an employee’s salary is calculated from the amount remaining after taxes are withheld (Letter dated November 16, 2011 N 22-2-4852).
Moreover, if the employee agrees to repay the material damage caused and assumes the obligation to compensate for the damage on a voluntary basis, this means that he has the right to submit a corresponding application to the employer to withhold the amount of damage from wages in excess of 20% (Definition of the St. Petersburg City court dated January 16, 2013 No. 33-303/2013, Appeal ruling of the Supreme Court of the Republic of Bashkortostan dated June 28, 2012 in case No. 33-7367/2012, etc.).
The easiest way is for the employee to immediately deposit his personal funds into the employer’s cash desk in an amount corresponding to the assessment of the damage caused by him. Also, with the consent of the employer, the employee can transfer equivalent property to compensate for the damage caused or correct what is damaged.
A combined option is also possible - when the employee repays part of the amount of damage immediately (in cash, property or another way), and the rest is deducted monthly from his salary until the debt is fully repaid.
Please also pay attention to the following. Clause 5.3 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory establishes that mutual offset of surpluses and shortages as a result of re-grading can be allowed only as an exception for the same audited period, from the same audited person, in relation to inventory items of the same names and in identical quantities.
Financially responsible persons provide detailed explanations to the inventory commission about any misgrading. In the case when, when setting off shortages with surpluses by re-grading, the value of the missing values is higher than the value of the values found in surplus, this difference in value is attributed to the guilty parties.
In this case, the employer has the right to refuse to offset the surplus when determining financial liability to the guilty person, since clause 5.3 of the Inventory Guidelines states that such offset is allowed only as an exception, i.e. The employer's obligation to offset is not established.
Step-by-step instruction
Based on the results of a planned inventory of goods in the warehouse, a shortage of goods was identified:
- set of curtains “Versailles” – 2 pcs. (cost price 8,000 rub./piece).
The financially responsible person (MOL) - Ivanov A.P. was recognized as the culprit.
The shortage is subject to recovery from him at the market value of the goods.
The amount to be collected is 18,000 rubles.
An agreement on full financial responsibility was not concluded with the employee.
The average monthly salary of an employee is 30,000 rubles.
By agreement between the employee and the Organization, the amount of the shortage is withheld for 5 months in equal shares by deduction from the employee’s salary.
On July 31, the employee received a salary of 40,000 rubles, personal income tax amounted to 5,200 rubles.
20% (1/5) of the market value of the shortage is withheld from the employee’s salary - 3,600 rubles.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Attribution of the amount of the shortfall to the guilty party | |||||||
| July 01 | 73.02 | 94 | 16 000 | 16 000 | 16 000 | Attribution of the amount of the shortfall to the guilty party | Manual entry - Operation |
| 73.02 | 91.01 | 2 000 | 2 000 | 2 000 | Reflection of the difference between the book value and market value of the goods | ||
| Payroll | |||||||
| July 31 | 26 | 70 | 40 000 | 40 000 | 40 000 | Payroll | Payroll |
| 70 | 68.01 | 5 200 | 5 200 | Withholding personal income tax | |||
| 26 | 69.01 | 1 160 | 1 160 | FSS accrual | |||
| 26 | 69.11 | 80 | 80 | FSS accrual (accidental) | |||
| 26 | 69.03.1 | 2 040 | 2 040 | FFOMS accrual | |||
| 26 | 69.02.7 | 8 800 | 8 800 | Pension Fund accrual | |||
| Withholding damage from an employee's salary | |||||||
| July 31 | 70 | 73.02 | 3 600 | Withholding damage from an employee's salary | Manual entry - Operation | ||
For the beginning of the example, see the publication:
- Shortage of goods and materials. The culprit has been identified
A situation where the employee did not admit his guilt
If the employee does not want to voluntarily compensate for the damage, the employer must issue an order to recover the amount of damage caused from the culprit. Based on it, you can recover an amount not exceeding the average monthly salary. Such an order is drawn up in any form and can be made no later than one month from the date of completion of measures to determine the amount of damage and the causes of its occurrence.
Of course, the order (order) to recover damages must also contain the signature of the guilty employee indicating his familiarization with and agreement with the contents of the order.
If the month period has expired or the employee does not agree to voluntarily compensate for the damage caused to the employer, then it can only be recovered through the court.
It will be necessary to recover damages in court in cases where:
- the employee does not agree to voluntarily compensate for damages that exceed his average monthly earnings (Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- the employee gave a written obligation to compensate for damage, but then quit and refused to fulfill it (Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The following must be taken into account. Based on Art. 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer has the right to go to court in disputes about compensation by the employee for damage caused to the employer within one year from the date of discovery of the damage caused. If you miss the deadlines established by Parts 1 and 2 of Art. 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, they can be restored by the court (Appeal ruling of the Omsk Regional Court dated September 19, 2012 in case No. 33-5469/2012).
Reflected in the book of income and expenses
There is no need to carry out the shortfall in the tax base. The use of damage compensation accounting does not cause any particular difficulties for specialists.
Its order consists of the following points:
- the fact of a shortage cannot be considered a reason for recognizing expenses;
- but the amount of funds that was received from the person at fault must be reflected in the income book.
Such norms are provided for by law. Compliance with them is mandatory for all companies and organizations.
Insurance premiums
If an organization recovers damages from an employee, there is no need to pay insurance premiums. Indeed, in this case, there is no object for taxation of contributions (Article 7 of the Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ, Article 20.1 of the Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ).
Situation: is it necessary to charge insurance premiums if an organization paid an administrative fine for an employee (for example, for violating traffic rules on the organization’s car)?
Answer: yes, it is necessary.
As a general rule, an administrative fine must be paid by the one who was brought to justice (Part 1 of Article 32.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). That is, in this case it is the employee himself.
If the organization paid the fine for it, then in this case the employee receives income. At the same time, the list of amounts exempt from contributions does not provide for the payment of an administrative fine for an employee. This means that contributions must be calculated in the general manner (Articles 7 and 9 of the Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ, Articles 20.1 and 20.2 of the Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ).
These rules also apply when paying an administrative fine for an employee who violated traffic rules in an organization’s car. It does not matter how the violation was recorded: by a photo/video recording camera or directly by a police officer.
Shortage at the cash register, deduction from the cashier's salary
Finding an insufficient amount of money in the cash register is also a damage. If such a precedent occurs, it is necessary to conduct an audit of the cash register. The procedure for conducting an audit must be fixed by internal legal documents. As when conducting an inventory (an audit is one of the forms of inventory), it is necessary to make sure that the amount of the shortage exceeds the natural rate of loss determined by law.
Having carried out the necessary procedure to record the fact of the shortage and familiarize the perpetrators with the documents on the audit, the organization has every right to recover the amount of the shortage from the salary, if it does not exceed the average monthly salary. The collection procedure is endorsed by the General Director in a special order, which must be issued within a month after all acts are drawn up, otherwise the shortage may be withheld by order of the executive authority.
Amount of salary deduction
Salary deductions can be classified as:
- Mandatory: personal income tax, withholding according to executive documents.
- Retention at the initiative of the employer.
According to labor laws, the maximum possible amount of deduction from wages is 20% of the salary, unless otherwise provided. Only if there is a justified reason can the employer count on a larger amount not exceeding the average monthly salary. Although in some cases a court decision may order compensation of an amount several times greater than the employee’s salary, this is the exception rather than the rule and depends on each specific case within the framework of existing legislation.
| Maximum amount (in %), part of salary | Rationale |
| 20 | Personal income tax, executive documents |
| 50 | Cases provided for by the Federal Law of the Russian Federation |
| 70 | Alimony, personal injury, crime |
| 100 | Shortages, damage if there is a legal basis |
| More | The court's decision |