VAT when importing equipment is paid at a rate of 18% (except for cases of exemption from payment of indirect taxes when importing certain types of goods into Russia) directly at customs (before the actual release under the chosen customs procedure), except for cases of import from the EAEU countries, when VAT is paid in Inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service at the place of tax registration of the importer. VAT when importing equipment is paid by all organizations (enterprises) and entrepreneurs, regardless of the taxation system applied (i.e. including UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax, simplified taxation system) and whether the total revenue for the three previous calendar months was less than 2 million rubles.
VAT when importing equipment into the Russian Federation is calculated as a percentage of the amount of customs value, customs duties and excise taxes (if the imported cargo is excisable). At the same time, the excise tax itself is considered as a percentage of the amount of customs value and customs duties, and the customs value includes not only the contract price, but also the costs of delivering imported equipment to the Russian Federation. At the same time, the customs authority (Federal Customs Service, Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation) retains the right to apply customs value adjustments (CTS), which will lead to a change in the tax base, and subsequently the amount of value added tax paid.
VAT on equipment is paid regardless of whether the import is carried out independently or through an intermediary (agent). The obligation to pay VAT rests with the declarant, who can be the contract holder (the actual importer) or his intermediary - a customs representative (broker) or even a carrier. If VAT is paid through an intermediary, he will be required to provide payment documents confirming the payment of indirect taxes for subsequent VAT deduction. The agent's payment documents must be accompanied by documents confirming the reimbursement of expenses incurred by the intermediaries by the recipient of the equipment.
VAT on the purchase of imported equipment must be paid within 15 days from the date of receipt of the goods at customs, but no later than the submission of the customs declaration for goods (DT, previously - cargo customs declaration, CCD). If imported equipment is supplied from the countries of the Eurasian Economic Community (EAEC) - Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia or Kyrgyzstan - then VAT must be paid to the Federal Tax Service no later than the 20th day of the month following the month the equipment is registered and registered in the purchase book. In this case, the fact of import and the amount of indirect taxes is confirmed not by the DT, but by the VAT declaration.
VAT is not paid when importing equipment in the following cases:
- is technological equipment, analogues of which are not produced in the Russian Federation and the import of which is carried out without paying VAT (according to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 30, 2009 No. 372 with amendments and additions)
- imported under customs procedures (regimes) or under the conditions stated in Art. 150 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which do not imply use in transactions subject to indirect taxes;
- import of medical equipment is carried out (according to paragraph 2 of Article 150 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 17, 2002 No. 19, vital medical equipment is not subject to indirect taxes);
- if the imported equipment is subsequently contributed to the authorized capital of clause 7 of Art. 150 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax deductions and separate VAT accounting
From 01.07.2019, according to the new edition of Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (as amended by Federal Law No. 63-FZ dated 15.04.2019, hereinafter referred to as Law No. 63-FZ), VAT amounts presented by suppliers of goods (works, services), property rights or paid when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation, they are taken into account by taxpayers for tax purposes in one of the following ways:
- Accepted for deduction (reimbursement):
- if the acquisitions are intended to carry out transactions subject to VAT (Articles 171, 172, 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the acquisitions are intended to carry out operations for the sale of works (services), the place of implementation of which is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation (except for operations provided for in Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) (clause 3, paragraph 2, Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Are taken into account in the cost of purchased goods (work, services), property rights, including fixed assets (FPE) and intangible assets (IMA), if such goods (work, services), property rights:
- are intended for operations for the production and (or) sale (as well as transfer, execution, provision for one’s own needs) of goods (work, services) not subject to VAT (exempt from taxation) (clause 1, clause 2, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) ;
- intended for operations for the production and (or) sale of goods, the place of sale of which is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation (clause 2, clause 2, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- intended for operations for the implementation of works (services) provided for in Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the place of implementation of which is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation (clause 2.1, clause 2, Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- acquired by persons who are not VAT payers or are exempt from fulfilling taxpayer obligations for the calculation and payment of tax (clause 3, clause 2, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- are intended for the production and (or) sale (transfer) of goods (work, services), operations for the sale (transfer) of which are not recognized as the sale of goods (work, services) in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 4, clause 2 Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If in one tax period a taxpayer carries out operations subject to taxation and operations not subject to VAT, then he is obliged to keep separate records of such operations (clause 4 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and separate records of the amounts of VAT claimed by suppliers (clause 4 of Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When maintaining separate accounting of the amount of input VAT on purchased goods (work, services), property rights (clause 4 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- taken into account when using acquisitions to carry out transactions not subject to VAT;
- are accepted for deduction when using acquisitions to carry out transactions subject to VAT;
- are accepted for deduction or taken into account in their value in the proportion in which they are used for the production and (or) sale of goods (works, services), property rights, transactions for the sale of which are subject to taxation (exempt from taxation) - for goods (works) , services), including fixed assets and intangible assets, property rights used to carry out both taxable and non-taxable (tax-exempt) transactions, in the manner established by the accounting policy adopted by the taxpayer for tax purposes, and taking into account features established by paragraph 4.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Moreover, for the purposes of paragraph 4 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and paragraph 4.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, transactions subject to taxation also include operations for the sale of work (services), the place of implementation of which, in accordance with Article 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation (with the exception of operations provided for in Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) (paragraph 9, paragraph 4, Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In accordance with paragraph 4.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the proportion for maintaining separate accounting is determined based on the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, transactions for the sale of which are subject to taxation (exempt from taxation), in the total cost of goods shipped ( work performed, services provided), transferred property rights for the tax period.
At the same time, for fixed assets and intangible assets accepted for accounting in the first or second month of the quarter, the taxpayer has the right to determine the proportion based on the cost of goods shipped in the corresponding month (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, transactions for the sale of which are subject to taxation (exempt). from taxation), in the total cost of goods shipped per month (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights.
In those tax periods in which the share of total costs for the acquisition, production and (or) sale of goods (work, services), property rights, the sale of which is not subject to VAT, does not exceed 5% of the total total costs for acquisition, production and (or) ) sale of goods (works, services), property rights, the taxpayer has the right not to distribute input VAT. In this case, tax amounts subject to distribution on purchased goods (works, services), property rights, in the specified tax period are accepted for deduction in full.
| 1C:ITS For more information on the rules for maintaining separate records, see the section “Legislative Consultations”. |
Generating purchase ledger entries
This document is needed to reflect deductions for VAT paid. You can find the purchase book in 1C 8.3 in the “Operations” section.
In the list form that appears, click on the “Create” button and select “Create purchase ledger entries.”
Let's fill out the purchase book automatically using the "Fill" button. All three documents that we entered into the program automatically appeared. These documents can be deleted if necessary, or new ones can be added.
After checking and specifying all the necessary data, be sure to post the document, as it creates movements in the appropriate registers.
Distribution of input VAT by operating system in “1C: Accounting 8” (rev. 3.0)
Let's consider an example of how the 1C:Accounting 8 version 3.0 program reflects operations on the distribution of input VAT among fixed assets intended for taxable and non-VAT-taxable transactions.
Please note that in accordance with Federal Law No. 303-FZ dated 08/03/2018, VAT tax rates changed from 01/01/2019: from 18% to 20%; from 18/118 to 20/120 and from 15.25% to 16.67%.
Example
| The organization TF-Mega LLC carries out operations both subject to VAT and exempt from taxation in accordance with Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as operations the place of implementation of which is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation. In addition, TF-Mega LLC sells goods from the warehouse to individuals and is a UTII payer for this type of activity. The organization TF-Mega LLC acquired:
In addition, in July 2021, the organization TF-Mega LLC:
The sequence of operations is given in Table 1. |
Setting up accounting policies, accounting parameters and directories
Due to the fact that the organization maintains separate accounting of the submitted VAT amounts when carrying out operations for the sale of goods (work, services), both subject to VAT and exempt from taxation, as well as operations the place of sale of which is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation, it is necessary to make the appropriate settings of accounting policies and accounting parameters.
On the VAT tab of the Accounting policy
(section
Main
- subsection
Settings
-
Taxes and reports
) you should set the flag
Separate accounting of incoming VAT
and
Separate accounting of VAT by accounting methods
.
In the accounting settings settings (section Administration - subsection Program settings - Accounting settings), by clicking on the hyperlink Setting up a chart of accounts, in the line Accounting for VAT amounts on purchased assets, set the value By counterparties, invoices received and accounting methods. To do this, you need to click on the appropriate hyperlink and check the box for the value By accounting methods.
Purchase of MFP
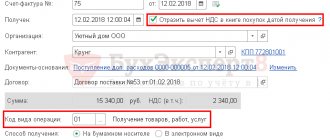
Receipt of a fixed asset (MFP) into an organization (operations 2.1 “Accounting for incoming MFP”; 2.2 “Accounting for input VAT”; 2.3 “Acceptance of MFP for accounting as a fixed asset”) is registered in the program by the document Receipt (act, invoice) with the type of operation Basic funds (section Purchases - subsection Purchases) or the document Receipt of fixed assets (section Fixed assets and intangible assets - subsection Receipt of fixed assets), fig. 1.
Rice. 1. Arrival of MFP
Since TF-Mega LLC carries out both taxable and non-taxable transactions, and the purchased MFP is used in the company’s office, i.e. in all ongoing operations, then in the VAT accounting method
Distributed
is indicated .
After posting the document, the following accounting entries are entered into the accounting register:
Debit 08.04.2 Credit 60.01 - for the cost of the purchased MFP;
Debit 01.01 Credit 08.04.2 - for the cost of the fixed asset accepted for accounting;
Debit 19.01 Credit 60.01 - for the amount of input VAT.
Since the amount of input VAT is subject to distribution, two entries are simultaneously entered into the VAT register submitted: one with the type of movement Receipt and the event Submitted VAT by the Supplier, the second with the type of movement Expense and the event VAT subject to distribution. At the same time, an entry is made in the Separate VAT accounting register for the amount of tax written off in the VAT
.
Register entry Separate accounting
is produced for the further distribution of the amount of input VAT, as well as for the use of data on the acquired fixed asset.
To register a received invoice (operation 2.4 “Registration of a received invoice”), you must enter the Invoice No.
and from the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
(Fig. 1), enter the number and date of the incoming invoice, respectively, and click the
Register
.
Invoice received
will be automatically created (Fig. 2), and a hyperlink to the created invoice will appear in the form of the basis document.
Rice. 2. Invoice received at the MFP
Document fields Invoice received
will be filled in automatically based on information from the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
. Besides:
- in the Received
the date of registration of the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
, which, if necessary, should be replaced with the date of actual receipt of the invoice. If an agreement has been concluded with the seller on the exchange of invoices in electronic form, then the field will indicate the date of sending the electronic invoice file by the electronic document management (EDF) operator, indicated in its confirmation; - in the line Base documents there will be a hyperlink to the corresponding receipt document;
- Operation type code
field the value 01 will be reflected, which corresponds to the acquisition of goods (work, services), property rights in accordance with the Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] ; - The Receipt Method switch will be set to On paper
if there is no valid agreement with the seller to exchange invoices in electronic form.
If there is an agreement, then the switch will be in the position Electronically
.
Since the organization maintains separate accounting, in the Invoice document received
there is no line with the value
Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by date of receipt
, i.e. there is no possibility of a simplified application for input VAT deduction.
As a result of posting the document Invoice received, a registration entry is made in the Register of Invoices. Despite the fact that since 01/01/2015, taxpayers who are not intermediaries (forwarders, developers) do not keep a log of received and issued invoices, and in the document Invoice received in the Amount line it is indicated that the amounts to be recorded in the log book ( “of which by commission”) are equal to zero, the Invoice Journal register entries are used to store the necessary information about the received invoice.
Purchasing a car
Registration of a vehicle receipt operation (operations 3.1 “Accounting for an incoming vehicle”, 3.2 “Accounting for input VAT”) in the program is carried out using the document Receipt (act, invoice) with the operation type Equipment (section Purchases - subsection Purchases) or Receipt of equipment (section OS and Intangible assets - subsection Receipt of fixed assets), Fig. 3.
Rice. 3. Car arrival
Since TF-Mega LLC carries out both taxable and non-taxable transactions, and the purchased car is intended for use in all activities of the organization, then in the VAT accounting method
Distributed
is indicated .
After posting the document, the following accounting entries are entered into the accounting register:
Debit 08.04.1 Credit 60.01 - for the cost of the purchased car;
Debit 19.01 Credit 60.01 - for the amount of input VAT.
Also, if the amount of input VAT is subject to distribution, then two entries are simultaneously entered into the VAT register presented: one with the type of movement Receipt
and the event
Submitted VAT by the Supplier
, the second - with the type of movement
Expense
and the event
VAT is subject to distribution
.
At the same time, an entry is made in the Separate VAT accounting register for the amount of tax written off in the VAT
.
The Separate accounting register entry is made for the further distribution of the amount of input VAT, as well as for the use of data on the purchased asset.
To register a received invoice (operation 3.3 “Registration of a received invoice”), you must enter the Invoice No.
and from the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
(Fig. 3), enter the number and date of the incoming invoice, respectively, and click the
Register
.
Invoice received
will be automatically created (Fig. 4), and a hyperlink to the created invoice will appear in the form of the basis document.
Rice. 4. Invoice received for the car
Document fields Invoice received
will be filled in automatically based on information from the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
.
Besides:
- in the Received
the date of registration of the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
, which, if necessary, should be replaced with the date of actual receipt of the invoice. If an agreement has been concluded with the seller on the exchange of invoices in electronic form, then the date of sending the electronic invoice file by the EDF operator, indicated in its confirmation, will be entered in the field; - in the line Base documents there will be a hyperlink to the corresponding receipt document;
- Operation type code
field the value 01 will be reflected, which corresponds to the acquisition of goods (work, services), property rights in accordance with the Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] ; - Receipt Method
switch will be set to
On paper
if there is no valid agreement with the seller to exchange invoices in electronic form.
If there is an agreement, then the switch will be in the position Electronically
.
Since the organization maintains separate accounting, in the Invoice document received
there is no line with the value
Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by date of receipt
, i.e. there is no possibility of a simplified application for input VAT deduction.
As a result of posting the document Invoice received
a registration entry is made in the Invoice Journal register to store the necessary information about the received invoice.
VAT distribution
According to paragraph 4 of paragraph 4 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amounts of VAT claimed on goods (work, services), property rights acquired both for taxable transactions and for transactions exempt from taxation are taken for deduction or taken into account in their value in that proportion , in which they are used for the production and (or) sale of goods (work, services), property rights, transactions for the sale of which are subject to taxation (exempt from taxation) - for goods (work, services), including fixed assets and intangible assets, property rights used to carry out both taxable and non-taxable (tax-exempt) transactions, in the manner established by the accounting policy adopted by the taxpayer for tax purposes, and taking into account the features established by paragraph 4.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with paragraph 4.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the proportion for the distribution of the amount of claimed VAT is determined based on the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, transactions for the sale of which are subject to taxation (exempt from taxation), in the total cost of goods shipped (work performed, services provided), transferred property rights for the tax period.
At the same time, for fixed assets and intangible assets purchased in the first and second months of the quarter, the taxpayer has the right to determine such a proportion based on shipment data for the corresponding month.
Despite the presence in paragraph 4 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation indicating the establishment of a proportion between the cost of shipped taxable VAT and non-taxable (exempt from taxation) transactions, when forming the proportion, the amount of revenue from non-taxable transactions will also include revenue from sales transactions that are not subject to VAT. due to the fact that the territory of the Russian Federation is not recognized as the place of their sale in accordance with Article 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 03/06/2008 No. 03-1-03/761, Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 07/05/2011 No. 1407/11).
From 07/01/2019, for the purpose of applying paragraphs 4 and 4.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, operations for the sale of work (services), the place of implementation of which, in accordance with Article 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation (except for operations provided for in Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), relate to transactions subject to taxation (clause “b”, paragraph 3, article 1 of Law No. 63-FZ).
Automatic distribution of the amount of input VAT (operations 4.1 “Distribution of VAT on MFIs by accounting methods”; 4.2 “Distribution of VAT on a car by accounting methods”; 4.3 “Accounting for VAT on a car in the cost of a non-current asset”; 4.4 “Accounting for VAT on MFIs in the cost of a non-current asset” asset"; 4.5 "Accounting for VAT on MFIs in the cost of fixed assets") is carried out by the regulatory document Distribution of VAT
(section
Operations
- subsection
Period closure
).
The distribution of the presented VAT amount is carried out according to those fixed assets, upon acquisition of which the value Distributed is specified in the VAT accounting method (MFP and car)
.
According to established arbitration practice and clarifications of the Federal Tax Service of Russia and the Ministry of Finance of Russia, when purchasing fixed assets, the buyer has the right to claim a tax deduction of the presented amount of VAT in full within 3 years from the date of acceptance of the fixed assets for registration, including in account 08 “Investments in non-current assets "(Clause 1, 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 09/04/2018 No. 03-07-11/63070, dated 12/19/2017 No. 03-07-11/84699, dated 04/11/2017 No. 03-07 -11/21548).
Consequently, input VAT on all acquired fixed assets, both accepted for accounting on account 01 (MFP) and accepted for accounting on account 08 (car), is subject to distribution in the month of acquisition.
Since fixed assets were purchased in July 2021 and the proportion of VAT distribution will be formed based on shipment data for the corresponding month, then in the VAT Distribution
the date must be set to 07/31/2019.
To calculate the proportion of VAT distribution, you must execute the Fill
.
After executing this command on the Sales Revenue tab, the following will be automatically calculated:
- the amount of revenue (the cost of shipped goods (work, services, property rights)) from activities subject to VAT (including the amount of revenue from the sale of non-commodity goods for export and the amount of revenue from the sale of services, the place of sale of which is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation according to Article 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, i.e. services not on the territory of the Russian Federation);
- the amount of revenue from activities not subject to VAT (not UTII);
- the amount of revenue from activities not subject to VAT (UTII);
- the amount of revenue from sales subject to VAT at a rate of 0% (except for the export of non-commodity goods).
Thus, the proportion indicators for the distribution of VAT for July 2021 will be:
- revenue from taxable activities (cost of shipped goods, works, services, property rights) for July 2021 excluding VAT - RUB 672,600.00. (RUB 600,000.00 (sale of goods subject to VAT at a rate of 20%, excluding VAT) + RUB 72,600.00 (provision of advertising services to a foreign person));
- revenue from activities not subject to VAT (not UTII) - RUB 19,200.00. (transfer of goods for advertising purposes);
- revenue from activities not subject to VAT (UTII) - RUB 350,000.00.
In addition, it should be noted that when carrying out activities taxed in accordance with different regimes (general tax regime and UTII), and distributing costs between these types of activities, the share of VAT included in the cost of purchased goods (works, services) is taken into account accordingly. . To do this, in the Article fields to include VAT in the costs of activities
should be indicated (Fig. 5):
- in the field not subject to VAT (not UTII) - the value Write-off of VAT on expenses (For activities with the main taxation system);
- in the non-taxable VAT (UTII) field - the value Write off VAT on expenses
(
For certain types of activities with a special taxation procedure
).
Rice. 5. Calculation of the proportion for the distribution of VAT
Automatic distribution of the input VAT amount will be reflected on the Distribution
document
Distribution of VAT
.
According to the calculated proportion:
- the share of VAT accepted for tax deduction will be 64.56134% (RUB 672,600.00 / (RUB 672,600.00 + RUB 19,200.00 + RUB 350,000.00) x 100%), which according to MFP it corresponds to 22,928.96 rubles. (RUB 35,515.00 x 64.56134%);
- the share of VAT included in the cost of acquisitions will be 35.43866% ((RUB 19,200.00 + RUB 350,000.00) / (RUB 672,600.00 + RUB 19,200.00 + 350,000.00 rub.) x 100%), which according to MFP corresponds to 12,586.04 rubles. (RUB 35,515.00 x 35.43866%).
The amount of input VAT to be included in the cost of acquisitions will be additionally distributed between types of activities (general taxation system and UTII).
Since the car was accepted for accounting (on account 08) also in July 2021, the distribution of VAT on it should be made in the same way as the distribution of input VAT for MFIs.
| 1C:ITS For more details, see the explanations of O.S. Duminskaya, Advisor to the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation, 2nd class of the Value Added Tax Department of the Department of Taxation of Legal Entities of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, in the section “Consultations on Legislation” and in the article “Distribution of Input VAT on Fixed Assets”. |
If the transaction for purchasing a car was not automatically reflected on the Distribution tab of the VAT Distribution document, then you need to click on the Add button to enter information in the tabular section by filling out the following columns: Invoice, Total, Type of value, VAT account, % VAT, Batch, Cost account , Subconto.
To distribute the reflected amount of VAT (to fill out the columns: Accepted for deduction, Taken into account in the cost, Taken into account in the cost (UTII)), you must click on the Distribute button (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Distribution of input VAT by MFP and vehicle
According to the calculated proportion for the car:
- the share of VAT accepted for deduction will be RUB 127,831.45. (RUB 198,000.00 x 64.56134%);
- the share of VAT included in the cost of acquisitions will be RUB 70,168.55. (RUB 198,000.00 x 35.43866%).
After posting the VAT Distribution document, the following entries will be made in the accounting register:
- the amounts of input VAT on the purchased MFP and car will be transferred from the credit of account 19.01 with the third sub-account. Distributed to the debit of account 19.01 with the third sub-account. Accepted for deduction
and
taken into account in the cost
in accordance with the calculated proportion; - the amount of input VAT to be included in the cost of the car will be written off from the credit of account 19.01 with the third sub-account Included in the cost in the debit of account 08.04.1;
- the amount of input VAT to be included in the cost of the MFP will be written off from the credit of account 19.01 with the third sub-account. Taken into account in the cost
in the debit of account 08.04.2 with a subsequent write-off to the debit of account 01.01.
Receipt will be entered into the VAT register presented
with the event, VAT is distributed to the amount of VAT presented by the supplier and subject to deduction after distribution.
VAT-exempt transactions
register will record the amount of VAT that is not accepted for tax deduction and relates to activities with the main tax system.
in the Separate VAT accounting
:
- with the type of movement Expense
- for the VAT amounts presented by the supplier and subject to inclusion in the cost of acquisitions after distribution; - with the type of movement Receipt
- for the VAT amounts presented by the supplier on acquired fixed assets, taken into account at the time of distribution as part of non-current assets (on account 08).
Source documents
During a desk audit of a tax return, the tax office may require documents from the taxpayer that would confirm the correctness of the tax calculation. In particular, documents confirming the right to deduct VAT on fixed assets may be required. What kind of documents are these?
First of all, these are the primary accounting documents:
- act of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets (form OS-1);
- inventory card for accounting of fixed assets (form OS-6), etc.
In addition, at the request of the tax inspectorate, the taxpayer must submit invoices and payment documents confirming payment for fixed assets and work on their assembly (installation). When paying for them by third parties, you must be prepared to present official letters from counterparties, acts of offset of mutual claims and other documents confirming the fact of the transaction.
If a fixed asset requires state registration, the tax office may need documents confirming the fact of registration or submission of materials for registration.
If primary documents, settlement documents or invoices are drawn up incorrectly, VAT cannot be deducted.
E.V.Klochkova
RNC Expert
| The procedure for including VAT amounts in expenses | |
| VAT on advances when setting prices in conventional units |
Fresh materials
- Clarification on 4 FSS When it is necessary to adjust 4-FSS The calculation presented in the FSS in form 4-FSS does not need adjustments if...
- Social tax 2021 Tax accrualIn accounting, the amounts of advance tax payments are reflected in the credit of account 69 (68)…
- Why do they buy gold? Selling gold competently is a process that will require you to spend some free time. It will be necessary to find out...
- Tax planning Tax planning in an organization Tax planning can significantly affect the formation of the financial results of an organization,…