4223 views
News Import accounting is often a complex and confusing procedure. However, knowledge of the specifics of legislation and standard procedures will allow you to protect yourself from mistakes and avoid troubles with the tax authorities. The most popular in Kazakhstan are all kinds of goods imported from neighboring countries that are members of the EAEU. Find out more about how to take into account the import of goods if they originate from EAEU countries...
Customs rules for importing currency
On the border of Kazakhstan with Russia the following currency regulations are allowed:
- Only adult citizens of a particular country can import goods.
- You can carry cash and non-cash funds with you.
- There are no restrictions on the amount that a foreigner wants to bring with him. You only need to declare the import amount if it is more than 3 thousand US dollars. There is no need to pay VAT when importing the specified amount of money.
There are certain restrictions on how much goods imported into Kazakhstan can cost. From January 1, 2021, new rules apply. The total weight of goods should not exceed 25 kilograms, which, when converted into monetary equivalent, should not exceed 500 euros.
This information is relevant for those who cross the border by land (by car, bus or train).
At what rate should imports be recorded?
Import contracts are usually concluded in foreign currency, while accounting in Kazakhstan is carried out in tenge. The question arises: at what rate should import transactions be reflected in accounting?
The procedure for accounting for transactions with foreign currency is enshrined in IFRS 21, which operates with the concepts of “monetary items” and “non-monetary items”. At the same time, for monetary items in foreign currency, recalculation must be made at the end of each reporting month at the rate on the reporting date, and for non-monetary items - at the date of the transaction.
The fact whether an import transaction will be a monetary or non-monetary item in the importer’s accounting depends on whether prepayment or postpayment is used in the calculations.
Thus, if the contract provides for an advance payment from a Kazakh company to a supplier who is a resident of one of the EAEU countries, then the receipt of goods will be considered a non-monetary item (since the importer is waiting for the goods). In accounting, the goods will be reflected at the rate on the date of the advance payment or at the average rate if there were several tranches.
If the condition of delivery was postpayment, and the importer first received the goods and then later transferred money to the supplier, this will be a monetary item that requires recalculation at the rate at the reporting date of each reporting month (taking into account positive or negative exchange rate differences that will arise).
Import of alcohol and cigarettes
Alcohol and alcohol products may be present in the bags of travelers. But you just need to comply with the established restrictions on the import of goods of this kind.
The standards for alcoholic products imported into the republic allow all adult passengers and travelers to carry the following quantities of products:
- Three liters of alcohol (no duties).
- Customs duties begin to apply if a person wants to bring two more liters of drinks. But for each lita you will have to pay 10 euros.
- It is prohibited to transport more than five liters of alcohol per person. It is prohibited to import more alcohol than one person from Russia to Kazakhstan. You should not neglect such rules so that the border guards confiscate the excess from the entering person.
There is no need to pay import VAT to bring other types of goods:
- 15 cigars;
- one kilogram of tobacco;
- 1 thousand cigarettes;
- one hundred liters of gasoline;
- 150 liters of diesel fuel.
Watch the video for Russian customs regulations.
Export from Russia to Kazakhstan
In the structure of Russian exports to Kazakhstan in 2021 (and in 2018), the main share of supplies fell on the following types of goods:
- Machinery, equipment and vehicles (HS codes 84-90) - 25.21% of the total volume of Russian exports to Kazakhstan (in 2018 - 25.31%);
- Metals and products made from them (HS codes 72-83) - 16.34% of the total volume of Russian exports to Kazakhstan (in 2021 - 16.10%);
- Products of the chemical industry (HS codes 28-40) - 14.94% of the total volume of Russian exports to Kazakhstan (in 2021 - 15.43%);
- Mineral products (HS codes 25-27) - 14.45% of the total volume of Russian exports to Kazakhstan (in 2021 - 16.61%);
- Food products and agricultural raw materials (HS codes 01-24) - 12.84% of the total volume of Russian exports to Kazakhstan (in 2018 - 11.77%);
- Wood and pulp and paper products (HS codes 44-49) - 4.62% of the total volume of Russian exports to Kazakhstan (in 2021 - 4.77%);
- Textiles and footwear (HS codes 50-67) - 2.92% of the total volume of Russian exports to Kazakhstan (in 2021 - 2.76%);
- Precious metals and stones (HS code 71) - 2.08% of the total volume of Russian exports to Kazakhstan (in 2021 - 0.25%).
The largest increase in Russian exports to Kazakhstan in 2021 compared to 2021 was recorded for the following product groups:
- Natural or cultured pearls, precious or semi-precious stones, precious metals, metals clad with precious metals, and products made from them; bijouterie; coins (HS code 71) - increase by USD 259,792,044;
- Nuclear reactors, boilers, equipment and mechanical devices; their parts (HS code 84) - an increase of USD 140,588,048;
- Products made of ferrous metals (HS code 73) - increase by USD 140,186,562;
- Ground transport vehicles, except for railway or tram rolling stock, and their parts and accessories (HS code 87) - an increase of USD 85,164,672;
- Cereals (HS code 10) - increase by USD 53,315,291;
- Ferrous metals (HS code 72) - increase by USD 44,792,662;
- Inorganic chemical products; inorganic or organic compounds of precious metals, rare earth metals, radioactive elements or isotopes (HS code 28) - an increase of USD 43,077,314;
- Ores, slag and ash (HS code 26) - increase by USD 42,303,623.
The largest reduction in Russian exports to Kazakhstan in 2021 compared to 2021 was recorded for the following product groups:
- Mineral fuel, oil and their distillation products; bituminous substances; mineral waxes (HS code 27) - reduction by USD 146,190,209;
- Soaps, organic surfactants, detergents, lubricants, artificial and prepared waxes, cleaning or polishing compositions, candles and similar products, modeling pastes, plasticine, “dental wax” and dental compositions based on gypsum (HS code 34) - reduction by $50,388,704.
Russian exports to Kazakhstan in 2021 by product groups
| HS Code | Name of product group | Exports in 2021, US dollars | Share in total exports, % | Exports in 2021, US dollars | Changes in 2021 relative to 2021, % |
| 01 | Live animals | 28 302 640 | 0,20 | 17 385 093 | 62,80 |
| 02 | Meat and edible meat by-products | 46 148 172 | 0,33 | 43 064 428 | 7,16 |
| 03 | Fish and crustaceans, molluscs and other aquatic invertebrates | 27 642 944 | 0,20 | 23 898 098 | 15,67 |
| 04 | Milk products; bird eggs; natural honey; edible products of animal origin, not elsewhere specified or included | 107 111 020 | 0,76 | 95 937 204 | 11,65 |
| 05 | Animal products not elsewhere specified or included | 1 722 013 | 0,01 | 1 220 566 | 41,08 |
| 06 | Living trees and other plants; bulbs, roots and other similar parts of plants; cut flowers and decorative foliage | 2 297 054 | 0,02 | 1 010 330 | 127,36 |
| 07 | Vegetables and some edible roots and tubers | 7 601 965 | 0,05 | 6 361 405 | 19,50 |
| 08 | Edible fruits and nuts; citrus fruit peel or melon rind | 28 208 130 | 0,20 | 17 503 841 | 61,15 |
| 09 | Coffee, tea, mate, or Paraguayan tea, and spices | 28 525 561 | 0,20 | 29 660 726 | -3,83 |
| 10 | Cereals | 72 668 588 | 0,52 | 19 353 297 | 275,48 |
| 11 | Products of the flour and cereal industry; malt; starches; inulin; wheat gluten | 24 341 690 | 0,17 | 19 966 880 | 21,91 |
| 12 | Oilseeds and fruits; other seeds, fruits and grains; medicinal plants and plants for technical purposes; straw and fodder | 41 005 605 | 0,29 | 13 446 773 | 204,95 |
| 13 | Natural shellac, unrefined; gums, resins and other plant juices and extracts | 2 837 749 | 0,02 | 2 718 162 | 4,40 |
| 14 | Plant materials for making wickerwork; other products of vegetable origin, not elsewhere specified or included | 481 719 | 0,00 | 110 204 | 337,12 |
| 15 | Fats and oils of animal or vegetable origin and their breakdown products; prepared edible fats; waxes of animal or vegetable origin | 152 206 937 | 1,08 | 149 310 654 | 1,94 |
| 16 | Prepared products of meat, fish or crustaceans, molluscs or other aquatic invertebrates | 85 700 621 | 0,61 | 73 063 395 | 17,30 |
| 17 | Sugar and sugar confectionery | 134 329 308 | 0,96 | 114 847 133 | 16,96 |
| 18 | Cocoa and cocoa products | 138 273 043 | 0,98 | 122 381 890 | 12,98 |
| 19 | Prepared products from cereal grains, flour, starch or milk; flour confectionery products | 205 909 325 | 1,47 | 178 863 911 | 15,12 |
| 20 | Processed products of vegetables, fruits, nuts or other plant parts | 133 836 124 | 0,95 | 124 772 591 | 7,26 |
| 21 | Various food products | 171 605 074 | 1,22 | 161 194 093 | 6,46 |
| 22 | Alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks and vinegar | 123 819 234 | 0,88 | 108 476 210 | 14,14 |
| 23 | Residues and waste from the food industry; ready-made animal feed | 64 936 048 | 0,46 | 54 515 358 | 19,12 |
| 24 | Tobacco and industrial tobacco substitutes | 174 224 336 | 1,24 | 142 183 503 | 22,53 |
| 25 | Salt; sulfur; earth and stone; plastering materials, lime and cement | 57 493 692 | 0,41 | 70 140 739 | -18,03 |
| 26 | Ores, slag and ash | 371 825 363 | 2,65 | 329 521 740 | 12,84 |
| 27 | Mineral fuel, oil and their distillation products; bituminous substances; mineral waxes | 1 600 817 966 | 11,39 | 1 747 008 175 | -8,37 |
| 28 | Inorganic chemical products; compounds, inorganic or organic, of precious metals, rare earth metals, radioactive elements or isotopes | 233 308 521 | 1,66 | 190 231 207 | 22,64 |
| 29 | Organic chemical compounds | 90 756 077 | 0,65 | 93 610 543 | -3,05 |
| 30 | Pharmaceutical products | 139 060 224 | 0,99 | 125 684 215 | 10,64 |
| 31 | Fertilizers | 98 252 216 | 0,70 | 68 840 092 | 42,73 |
| 32 | Tanning or dyeing extracts; tannins and their derivatives; dyes, pigments and other coloring substances; paints and varnishes; putties and other mastics; printing paint, ink, ink | 91 858 169 | 0,65 | 91 463 121 | 0,43 |
| 33 | Essential oils and resinoids; perfume, cosmetic or toilet preparations | 154 089 059 | 1,10 | 139 250 409 | 10,66 |
| 34 | Soaps, organic surfactants, detergents, lubricants, artificial and prepared waxes, scouring or polishing compounds, candles and similar articles, modeling pastes, plasticine, “dental wax” and dental compositions based on plaster | 152 717 388 | 1,09 | 203 106 092 | -24,81 |
| 35 | Protein substances; modified starches; adhesives; enzymes | 17 087 192 | 0,12 | 15 609 581 | 9,47 |
| 36 | Explosives; pyrotechnic products; matches; pyrophoric alloys; some flammable substances | 32 187 894 | 0,23 | 32 759 983 | -1,75 |
| 37 | Photo and film products | 4 519 880 | 0,03 | 3 043 704 | 48,50 |
| 38 | Other chemical products | 176 734 068 | 1,26 | 165 593 599 | 6,73 |
| 39 | Plastics and products made from them | 618 293 054 | 4,40 | 608 742 834 | 1,57 |
| 40 | Rubber, rubber and products made from them | 290 101 204 | 2,06 | 255 567 162 | 13,51 |
| 41 | Unprocessed hides (except natural fur) and tanned leather | 2 334 573 | 0,02 | 3 268 206 | -28,57 |
| 42 | Leather products; saddlery and harness; travel accessories, handbags and similar products; products made from animal intestines (except silkworm fibroin fiber) | 14 297 288 | 0,10 | 10 453 109 | 36,78 |
| 43 | Natural and artificial fur; products made from it | 1 973 836 | 0,01 | 3 177 618 | -37,88 |
| 44 | Wood and products made from it; charcoal | 318 612 495 | 2,27 | 302 030 482 | 5,49 |
| 45 | Cork and products made from it | 339 185 | 0,00 | 293 955 | 15,39 |
| 46 | Products made of straw, alfa or other weaving materials; basketry and wickerwork | 225 175 | 0,00 | 175 139 | 28,57 |
| 47 | Pulp of wood or other fibrous cellulosic materials; regenerated paper or cardboard (waste paper and waste) | 4 403 105 | 0,03 | 6 485 333 | -32,11 |
| 48 | Paper and cardboard; products made from paper pulp, paper or cardboard | 291 384 734 | 2,07 | 281 441 835 | 3,53 |
| 49 | Printed books, newspapers, reproductions and other products of the printing industry; manuscripts, typescripts and plans | 34 656 228 | 0,25 | 26 590 611 | 30,33 |
| 50 | Silk | 2 778 | 0,00 | 19 405 | -85,68 |
| 51 | Wool, fine or coarse animal hair; yarn and fabric, horsehair | 956 418 | 0,01 | 1 417 454 | -32,53 |
| 52 | Cotton | 8 224 265 | 0,06 | 8 982 515 | -8,44 |
| 53 | Other vegetable textile fibers; paper yarn and fabrics made from paper yarn | 540 636 | 0,00 | 676 639 | -20,10 |
| 54 | Chemical threads; flat and similar yarns of chemical textile materials | 7 239 615 | 0,05 | 5 206 354 | 39,05 |
| 55 | Chemical fibers | 11 471 695 | 0,08 | 11 541 862 | -0,61 |
| 56 | Cotton wool, felt or felt and non-woven materials; special yarn; twine, ropes, ropes and cables and products made from them | 39 883 731 | 0,28 | 34 589 716 | 15,31 |
| 57 | Carpets and other textile floor coverings | 3 761 411 | 0,03 | 4 469 409 | -15,84 |
| 58 | Special fabrics; tufted textile materials; lace; tapestries; Decoration Materials; embroidery | 4 191 187 | 0,03 | 2 863 974 | 46,34 |
| 59 | Textile materials, impregnated, coated or laminated; textile products for technical purposes | 17 341 080 | 0,12 | 15 580 286 | 11,30 |
| 60 | Knitted or crocheted fabrics | 1 528 674 | 0,01 | 1 426 499 | 7,16 |
| 61 | Articles of clothing and clothing accessories, knitted or crocheted | 83 152 855 | 0,59 | 66 682 193 | 24,70 |
| 62 | Items of clothing and clothing accessories, except knitted or hand-knitted items | 92 126 510 | 0,66 | 81 664 474 | 12,81 |
| 63 | Other finished textile products; sets; used clothing and textiles; rags | 30 982 322 | 0,22 | 27 605 153 | 12,23 |
| 64 | Shoes, gaiters and similar articles; their details | 100 781 146 | 0,72 | 86 806 579 | 16,10 |
| 65 | Hats and their parts | 7 117 487 | 0,05 | 6 080 012 | 17,06 |
| 66 | Umbrellas, sun umbrellas, walking sticks, seat sticks, whips, riding crops and parts thereof | 539 593 | 0,00 | 581 175 | -7,15 |
| 67 | Processed feathers and down and articles made of feathers or down; artificial flowers; human hair products | 217 787 | 0,00 | 210 769 | 3,33 |
| 68 | Articles made of stone, plaster, cement, asbestos, mica or similar materials | 113 623 170 | 0,81 | 101 926 086 | 11,48 |
| 69 | Ceramic products | 144 014 363 | 1,02 | 133 206 723 | 8,11 |
| 70 | Glass and products made from it | 103 236 980 | 0,73 | 98 847 777 | 4,44 |
| 71 | Natural or cultured pearls, precious or semi-precious stones, precious metals, metals clad with precious metals, and products made from them; bijouterie; coins | 292 625 955 | 2,08 | 32 833 911 | 791,23 |
| 72 | Black metals | 1 026 386 995 | 7,30 | 981 594 333 | 4,56 |
| 73 | Ferrous metal products | 904 124 920 | 6,43 | 763 938 358 | 18,35 |
| 74 | Copper and products made from it | 40 818 725 | 0,29 | 29 451 546 | 38,60 |
| 75 | Nickel and products made from it | 2 285 335 | 0,02 | 2 150 605 | 6,26 |
| 76 | Aluminum and products made from it | 208 515 791 | 1,48 | 192 523 162 | 8,31 |
| 78 | Lead and products made from it | 1 517 155 | 0,01 | 1 926 431 | -21,25 |
| 79 | Zinc and products made from it | 4 863 559 | 0,03 | 2 146 027 | 126,63 |
| 80 | Tin and products made from it | 3 523 591 | 0,03 | 3 652 747 | -3,54 |
| 81 | Other base metals; metal ceramics; products made from them | 2 127 868 | 0,02 | 2 878 855 | -26,09 |
| 82 | Tools, utensils, cutlery, spoons and forks made of base metals; their parts are made of base metals | 48 000 687 | 0,34 | 50 433 850 | -4,82 |
| 83 | Other products made of base metals | 53 392 516 | 0,38 | 49 636 806 | 7,57 |
| 84 | Nuclear reactors, boilers, equipment and mechanical devices; their parts | 1 303 196 707 | 9,27 | 1 162 608 659 | 12,09 |
| 85 | Electrical machines and equipment, their parts; sound recording and reproducing equipment, equipment for recording and reproducing television images and sound, their parts and accessories | 816 506 374 | 5,81 | 815 879 602 | 0,08 |
| 86 | Railway locomotives or tram motor cars, rolling stock and parts thereof; track equipment and devices for railways or tramways and parts thereof; mechanical (including electromechanical) signaling equipment of all types | 335 281 042 | 2,39 | 324 179 210 | 3,42 |
| 87 | Ground transport vehicles, except railway or tram rolling stock, and their parts and accessories | 914 692 778 | 6,51 | 829 528 106 | 10,27 |
| 89 | Vessels, boats and floating structures | 3 343 881 | 0,02 | 1 578 894 | 111,79 |
| 90 | Optical, photographic, cinematographic, measuring, control, precision, medical or surgical instruments and apparatus; their parts and accessories | 168 969 812 | 1,20 | 136 848 433 | 23,47 |
| 91 | Watches of all types and their parts | 5 123 783 | 0,04 | 4 445 838 | 15,25 |
| 92 | Musical instruments; their parts and accessories | 2 737 195 | 0,02 | 1 539 951 | 77,75 |
| 94 | Furniture; bedding, mattresses, mattress bases, cushions and similar stuffed furnishings; lamps and lighting fixtures not elsewhere specified or included; illuminated signs, illuminated name or address plates and similar products; prefabricated building structures | 201 604 959 | 1,43 | 167 066 051 | 20,67 |
| 95 | Toys, games and sports equipment; their parts and accessories | 77 117 714 | 0,55 | 70 103 846 | 10,00 |
| 96 | Various finished products | 92 614 344 | 0,66 | 110 426 038 | -16,13 |
| 97 | Artworks, collectibles and antiques | 53 718 | 0,00 | 10 123 | 430,65 |
| SS | Secret code | 169 423 895 | 1,21 | 200 231 867 | -15,39 |
Rules for importing products
It is allowed to import food, juices and waters, jewelry, personal belongings, items and things needed at home. The number of such objects should be such as to satisfy the individual needs of a person.
The list of mandatory declaration at the customs of Kazakhstan includes the following goods:
- It is allowed to import weapons (of any kind), explosives, ammunition, drugs, poisons and poisonous preparations, medicines, and pharmaceutical products from the Russian side, provided that all necessary documents are available.
- Imported goods also include substances that are included in the group of radiation and psychotropic substances.
- Goods subject to excise taxes.
- High frequency devices.
- Jewelry and metals.
- Goods for doing business in Kazakhstan.
Customs rules for individuals
When importing from the Russian Federation to Kazakhstan, goods that are included in the duty list are also subject to import.
At the border with Kazakhstan, first of all, a customs declaration is filled out, and then VAT is paid. Thus, if you have the financial means, you should not throw anything out of the bag, you just need to be prepared for the fact that you will have to pay a fee.
Food products imported from Russia include any vegetables, fruits, tea and coffee, the amount of which exceeds 10 kilograms per person. It could also be salmon/sturgeon caviar.
You cannot import things in large quantities, but you are allowed to transport more than 2 items of each type of clothing or shoes. These can be things of the same size and style.
Import procedure from Russia:
The Russian Federation and the Republic of Kazakhstan have been members of a single Customs Union since 2010. Therefore, passing through customs inspection is extremely quick and simple. However, any option for delivering cargo, be it land or air transport, requires the preparation of a package of documents.
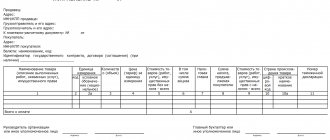
At least 3 weeks before sending the cargo, it is necessary to prepare 2 groups of papers: transport and accompanying. And also conclude a supply agreement, which must indicate all the nuances of the transaction.
It is important that the cargo is accompanied by a waybill or waybill with a waybill, an invoice and a CMR (consists of a shipping specification, an invoice specification, a certificate of quality of goods, veterinary and quarantine certificates).
Video and audio equipment
You can carry for an additional fee cameras, tape recorders, video and audio players, computers, household and office equipment, electrical items - kettles, hair dryers, curling irons. The list of imported items may be reduced under the influence of certain circumstances, sanctions or fines.
It has a huge impact on the fact that imported goods, including cars or animal meat, have compliance with the requirements of the Customs Union and national ones, i.e. Kazakh. An import ban may be imposed in the event of the spread of infections, diseases, or microbes.
Products costing from 501 euros and above
a smartphone for 550 euros through Amazon , then he will have to pay a fee of about 22,155 tenge:
(550 - 200) x 15%.
If 550 euros = 232,100 tenge (at an exchange rate of 1 euro = 422 tenge), and 200 euros = 84,400 tenge, then:
232 100 — 84 400 = 147 700;
147,700 x 15% = 22,155.
That is, the smartphone, including customs clearance, will cost almost 50 euros more. This may influence the customer’s decision not to purchase goods in this price range through foreign online platforms.
For comparison: in 2021, the duty-free threshold was up to 500 euros. If the order exceeded this amount, you had to pay 30% of the excess amount. That is:
(550 - 500) x 30%.
If we compare at the current exchange rate, where 550 euros = 232,100 tenge, and 500 euros = 211,000 tenge, then:
232 100 — 211 00 = 21 100;
21,100 x 30% = 6 330.
The customs duty on the same smartphone worth 550 euros last year was only 6,300 tenge instead of the current 22,155 tenge. That is, more expensive.
List of prohibited goods
While there is a huge list of permitted items that a person can take with him to Kazakhstan, there is also a rather impressive list of prohibitions on products.
In particular, it is prohibited to import psychotropic drugs or drugs, medicines with narcotic substances, weapons of mass destruction, as well as materials that can help create them, into the republic through customs.
The following types of goods are also strictly prohibited:
- Materials – printed or artistic, which are intended to promote war, racism, xenophobia, violence, undermining the foundations of the state, a call for uprising or revolutionary action.
- Prohibited pornographic materials.
- Soil, soil or plants in it.
- Microbes, viruses, infections that can cause diseases, pandemics and epidemics.
- Insects, mites, fungi, damaged plants and trees.
- Products under quarantine supervision and imported from Russia or other countries to Kazakhstan.
Products costing from 1,000 euros
If we take, for example, a laptop worth 1,500 euros the state duty for it is now approximately 82,290 tenge:
(1,500 - 200) x 15%.
If 1,500 euros = 633,000 tenge, and 200 euros = 84,400 tenge, then:
633 000 — 84 400 = 548 600;
548,600 x 15% = 82,290.
However, in 2021, with a 30% duty, the excess amount would be equal to 126,600 tenge:
(1,500 - 500) x 30%.
If at the current exchange rate 1,500 euros = 633,000 tenge, and 500 euros = 211,000 tenge, then:
633 000 — 211 000 = 422 000;
422,000 x 30 = 126,600.
Judging by the figures, the new duty threshold in this price range has become more profitable for Kazakhstanis than it was in 2021.
Rules for the export of currency and goods from Kazakhstan
It is prohibited to export more than 10 thousand US dollars or national currency in the same monetary equivalent from Kazakhstan. Such requirements are also established for Kazakhs who travel to Russia. In this case, you need to contact the customs office so that they can issue a certificate of the legal origin of the currency.
Also, the following groups of goods cannot be exported from Kazakhstan:
- military equipment and weapons;
- equipment;
- ammunition;
- weapons of mass destruction;
- objects of art and antiquities, historical and artistic artifacts that are protected by the government;
- rare minerals, jewelry;
- rare animals and plants;
- saiga horns;
- drugs and psychotropic drugs;
- canceled securities and shares;
- anti-Islamic literature, photos and videos;
- materials that discredit the work of state authorities and the government of Kazakhstan.
This list can be expanded if the government decides to prohibit the presence of certain items, food and things on the territory of the republic.
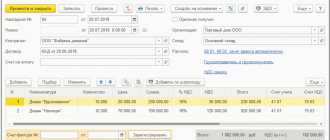
Features of including import EAEU-VAT in deductions
EAEU-VAT can be included in deductions that reduce the regular tax accrued for payment on sales in the Russian Federation. However, to carry out this operation, it will not be enough to comply with the usual set of requirements contained in Art. 171 (clause 2) and art. 172 (clause 1) of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- the goods are reflected in accounting;
- its further purpose is to use it in transactions subject to VAT;
- tax has been paid.
Additionally, you must have the following accepted by the tax authority (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2015 No. 03-07-13/1/38180):
- import application;
- declaration in the form KND 1151088.
When preparing regular VAT reporting for a quarter in which all these conditions are met, the amount of EAEU-VAT to be deducted is reflected in line 160 of section 3 of the quarterly declaration, drawn up in the KND form 1151001.
Despite the obligation to pay import tax and report on it, deductions under the EAEU-VAT will not be available to special regime residents and persons exempt from paying tax under Art. 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, since they do not charge VAT on sales made in Russia.
Customs changes 2020-2021
Over the past few years, the government of the country has been reducing duties on the import of goods, which is associated with accession to the WTO and the EAEU. Low tariffs are set for fish and meat, dairy and pharmaceutical products, agricultural goods, machinery, and equipment. Entrepreneurs who import must pay the rates established in the Customs Union. As a result, goods that are purchased at low tariffs end up in Russia.
What changes have occurred in the Russian customs code by 2021, watch the video.
What reporting must be submitted to the importer?
When importing goods from the territory of the EAEU, the importer is required to provide two forms of tax reporting (Article 456 of the Tax Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan):
- f.328.00 (application);
- f.320.00 (declaration).
Attention! As early as 02/03/2020, Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 39 of 01/20/2020 was published, according to which form 320.00 was excluded starting from 01/01/2020 from the list of forms that the importer is required to submit. However, the corresponding changes have not been made to Article 456 of the Tax Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan (as of September 1, 2020). A draft law introducing corresponding amendments to the Tax Code has already been developed, but has not yet been approved at the moment. In this connection, entrepreneurs, according to the principle of priority, should be guided by the norms of the Tax Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan, which means they should provide a declaration until its cancellation is enshrined in Art. 456 Tax Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The reporting deadline is the 20th of the following month. The delivery procedure is as follows:
- provide form 328.00;
- receive a Notice of Acceptance;
- enter in Form 320.00 the registration number of the Application specified in the Notification of Acceptance;
- provide form 320.00
In addition to tax, for imports from the EAEU it is also necessary to submit statistical reporting in Form 1-TS. The deadline for submission is similar to tax reporting forms - before the 20th day after the reporting month. The 1-TS report is filled out in tenge, regardless of the currency in which the contract is concluded.
The form is submitted by legal entities, individual entrepreneurs, as well as individuals importing from the EAEU member states.
Important! From 02/17/2020, new forms are applied (including the new form 1-TS), approved by Order of the Ministry of Economy No. 9 of 01/24/2020.
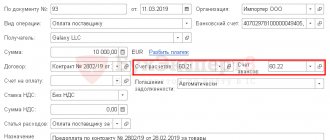
We are preparing a contract
We start with preparing a foreign trade contract. First of all, you need to decide on the currency of the contract. Many enterprises prefer to receive funds in Russian rubles, which is much simpler. But there are also contracts in euros or US dollars.
In addition, the contract should provide for deadlines for the return of documents, such as: CMR (International Consignment Note), application for the import of goods and payment of indirect tax. We are given 180 calendar days to collect the package. This means that the period for submitting documents should not exceed this period.
So, the contract is signed by both parties, specifications are drawn up and delivery and payment terms are determined.
If the contract amount is more than $50,000, then it is necessary to open a transaction passport. To do this, we make copies of the above documents, certify them by authorized persons (the first and second signatures on the bank card of sample signatures) and stamp them, and take the documents to the bank. The transaction passport must be opened before payment or sale of goods is made. Otherwise, you face a fine of 40,000 to 50,000 rubles. (Part 6 of Article 15.25 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
If the contract amount is less than $50,000, then there is no need to open a transaction passport.
Next, I will consider the situation with the issued transaction passport. Now those who do not need to obtain a passport may think: “Well, why do we need this?” Don't worry, there is a lot of useful information for you too.