The concept of capital investments is directly related in accounting to the concept of fixed assets. Capital investments are nothing more than the costs of acquisition, manufacturing, reconstruction or expansion, design, and other similar costs associated with the operating system. In other words, we can say that fixed assets in accounting are the result of capital investments in them. The general concept of capital investments is contained in Federal Law-39 of 02/25/99, in Art. 1. Accounting for capital investments, however, has features depending on their nature. Tax accounting for such investments also requires a serious approach.
Question: How to reflect in the tenant's accounting capital investments (in the form of inseparable improvements) in a leased fixed asset (fixed asset) (movable property), made with the consent of the lessor, if, under the terms of the lease agreement, the costs of inseparable improvements are not reimbursed by the lessor? View answer
Types of capital investments
Capital investments in an enterprise include:
- Buildings and constructions;
- Inventory that is necessary in the process of activity;
- Machine tools and equipment that are used to carry out activities at the enterprise;
- Cars, thanks to which transportation is carried out at the enterprise.
The main difference between capital investments and other expense items is that their use remains unchanged for one year or more. If investments are used for less than one year, then they cannot be classified as capital and cannot be recorded using this accounting entry. If financial expenses are made for the modernization or restoration of buildings or equipment, then such financial transactions can also be considered capital.
Liability balance
Balance sheet liability is a part of the balance sheet that reflects in monetary terms the organization’s own and borrowed sources of formation of property (table).
Balance sheet liability (abbreviated)
In Section III of the balance sheet “Capital and Reserves”, independent items reflect the own sources of property formation: authorized capital, additional capital, reserve capital. The same section shows the retained earnings of the enterprise from previous years and the reporting year. Independent items represent uncovered losses.
The articles of Section IV of the balance sheet “Long-term liabilities” characterize debt to banks for loans and borrowings received from other organizations for a period of more than one year.
Section V of the balance sheet “Short-term liabilities” combines several groups of short-term debt: borrowed funds, accounts payable, reserves for future expenses, deferred income.
Features of some types of capital investments
Let's look at the features in table form:
| Type of capital investment | Feature Description |
| Construction | This type includes not only newly erected buildings, but also those that will be used in the production process, as well as the real estate that is planned to be expanded. Capital investments also include costs that are associated with the restoration of damaged buildings, regardless of the amount of costs. Construction costs are divided into production and non-production: production are those premises that are associated with the production process; non-production facilities – office premises and public utility facilities. |
| Equipment | If equipment is purchased, then when accounting for the capital investment, it is necessary to clearly identify the acquired property. Equipment that requires installation is classified as requiring installation. This category includes technological or other equipment, the installation of which is carried out at a permanent place of operation. Equipment that does not require installation includes standing machines, cars and other equipment that moves. |
| Intangible assets | This category includes licenses, trademarks or permission to extract natural resources acquired on a paid basis. |
Capex structure
Based on the provisions of Federal Law-39, capital investments can be considered as a process of reproduction of fixed assets, accompanied by costs that are subject to accounting. To build an effective accounting system with all the variety of investments of this type, their correct grouping is important, on the basis of which analytical accounting of capital investments is built.
Question: The LLC transferred real estate (warehouse) as a contribution under a simple partnership agreement. For property tax purposes, who takes into account capital investments in the form of inseparable improvements to real estate made at the expense of the partnership: a simple partnership or LLC? View answer
It is advisable to build a classification taking into account the following characteristics:
- method of reproduction (construction, reconstruction, expansion, re-equipment, maintaining the operation of existing facilities, etc.);
- technology of costs (for construction, for the purchase of equipment, survey costs, investments in leased property, etc.);
- production and non-production nature of investments (depending on where the object is used).
In addition, capital investments are divided by sector of the economy (business), method of producing costs (in-house or by a third-party organization), readiness of the facility for use (whether it is completed or not completed by construction, reconstruction).
Question: How to reflect in the accounting of an organization engaged in freight transportation, capital investments in a fixed asset (fixed asset) (car) associated with its modernization? In order to improve the technical and operational qualities of the vehicle, the contracting organization (car repair shop) carried out work to install new equipment that would increase the vehicle's carrying capacity, improve its handling and traction properties. View answer
If capital investments are made in purchasing an OS, their cost is determined immediately. It is equal to the cost of purchasing the object. If capital investments are made during the process (for example, construction), until the end of the capital investments are considered unfinished, the value of the asset may increase by the value of the costs incurred.
Let us recall that the asset in which investments are made must be used in production for at least 1 year (PBU 6/01). Only in this case, investments are recognized as capital and are not taken into account in the company’s current expenses. They are collected in a separate BU account and then form the initial cost of the OS.
Question: When can expenses in the form of capital investments incurred during the validity of the preliminary lease agreement be taken into account for income tax purposes: before the conclusion of the main agreement or after (clause 1 of Article 256, clause 1 of Article 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)? View answer
Accounting for capital investments
In accounting, capital investments are taken into account separately from current production costs. This is stated in paragraph 6 of Article 8 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 N 129-FZ “On Accounting”.
In order to reflect information about the costs of objects that will later be accepted in accounting as fixed assets and intangible assets, account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” is used. This account reflects the expenses that the buyer actually paid, and then they will amount to the initial cost of fixed assets or intangible assets.
Sub-accounts are opened to account 08 to account for the relevant costs:
- “Purchase of land”;
- “Purchase of natural resources”;
- “Construction of fixed assets”;
- “Acquisition of fixed assets”;
- “Acquisition of intangible assets.”
According to clause 8 of PBU 6/01, the initial cost of purchased fixed assets is formed by the total costs of their acquisition, creation and construction (less VAT and other refundable taxes). In this case, accounting is carried out object by object.
The accounting entry in this case looks like this:
Dt 08 Kt 60.
How to form the initial cost of fixed assets, the enterprise independently forms the rules, this is discussed in paragraph 26 of the guidelines for accounting of fixed assets (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n). According to the rules, the initial cost of an asset is the actual cost of producing it.
Important!!! The procedure for accounting and forming capital costs for the production of fixed assets must correspond to the procedure that is determined for accounting for the costs of the corresponding types of products produced by the company.
For independently created assets, accounting entries will look like this:
Dt 08 Kt 10, 02, 07, 10, 23, 26, 60, 69, 70, 71, 76…
Assets that are created independently include equipment that requires installation or is simply impossible to operate without prior installation. Such assets are reflected in account “07”. And the wiring will be as follows:
Dt 07 Kt 15, 23, 60, 71, 75, 76, 79, 86, 91.
If the property is transferred for installation, then the equipment will be transferred from account 07 to account 08. And the postings will look like this:
Dt 08 Kt 07.
The process of creating a new object can take a very long time. This is due, in particular, to the phased method of accepting work, the long-term implementation of trial operation, which is carried out until the planned design parameters are achieved, and many other specific objective factors that take place in construction.
This entire process may require large capital expenditures, in which case the company will simply be forced to apply for borrowed funds. Consequently, interest on the payment of borrowed funds will increase the book value of capital investments in assets:
Dt 07, 08 Kt 66, 67.
IMPORTANT! This rule applies only to those interests that were accrued before the asset was accepted for accounting. After this event, interest is charged to operating expenses (clause 11 of PBU 10/99).
After all capital costs for the facility are fully collected on account “08”, it is considered ready for operation, and its cost is transferred to account “01”:
Dt 01 Kt 08.
Results
Reflection of unfinished capital investments in the balance sheet is carried out on line 1150, if the balance on the account is significant. 08 - on a separate line. Before drawing up annual reports, an enterprise is obliged to ensure the reliability of accounting data, for which an inventory is carried out, as well as an internal (and in cases established by law - external) audit of assets and liabilities.
When carrying out accounting, inexperienced workers may have some difficulties in determining the category of financial investments. Often such difficulties arise when posting capital investments, which must be reflected in the financial statements according to all the rules. To understand the definitions, you need to find out what is a capital investment in accounting.
List of entries in accounting for capital investment
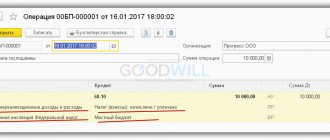
Let's look at the wiring as an example. So:
The company purchased warehouse space in March 2021 under a purchase and sale agreement, the cost of which was 1,184,000 rubles (including 18% VAT - 180,000 rubles). To purchase this premises, the company took out a loan from the bank in the amount of 500,000 rubles at 15% per annum for a period of one month. A month later, the company returned the borrowed funds to the bank and paid the required interest for using the loan. Interest amounted to 6,250 rubles.
In April 2021, the company incurred costs for registering ownership of the purchased warehouse space in the amount of 8,000 rubles. And in April the premises were put into operation.
Consequently, the following entries were made in accounting:
| Wiring name | Amount in rubles | Debit | Credit |
| March 2017 | |||
| Reflection of the cost of warehouse premises as part of capital investments | 1 000 000 | 08 | 60 |
| VAT charged to the buyer | 180 000 | 19 | 60 |
| Received borrowed funds from the bank | 500 000 | 51 | 66 |
| Cost of warehouse space | 1 180 000 | 60 | 51 |
| April 2017 | |||
| Payment for state registration of ownership of warehouse premises | 8000 | 76 | 51 |
| Inclusion in actual costs for the acquisition of fixed assets | 8000 | 09 | 76 |
| Interest debt | 6250 | 08 | 66 |
| Return of borrowed funds to the bank | 500 000 | 66 | 51 |
| Transfer of accrued interest to the bank for using the loan | 6250 | 66 | 51 |
| Warehouse put into operation | 1 041 250 | 01 | 08 |
How data on unfinished construction is generated for balance
Initially, all costs for the acquisition and construction of fixed assets are accumulated in the account. 08 “Investments in non-current assets”. Its four subaccounts allow you to group costs:
- for the acquisition of land (subaccount 1);
- environmental management facilities (subaccount 2);
- for the construction of fixed assets (subaccount 3);
- for the acquisition of fixed assets (subaccount 4);
On subaccount 3 counts 08 accumulate data on the costs of OS construction. Debit account 08 at the end of the period shows the amount of construction in progress, since even completed fixed assets that have not been put into operation are considered unfinished. With commissioning, the cost of fixed assets is transferred from the account. 08 on account 01 "Fixed assets".
Account debit data 01 and 08 are entered into the balance sheet in line 1150. If the amounts of capital investments are significant, then a separate line is created in the balance sheet to reflect them (clause PBU 4/99).
You can learn more about accounting for investments reflected in account 08 in the article “Rules for keeping records of investments in non-current assets.”
Capex Cost Accounting
The accounting procedure for certain types of costs has been clarified.
| WHAT IS SPECIFIED | EXPLANATION |
| The amount of actual costs includes the amount of the estimated liability incurred during capital investments, including for future dismantling, disposal of property and environmental restoration | Previously, the inclusion of such costs in capital investments was not provided for |
| The amount of capital investments is reduced by the estimated cost of products received during their implementation, secondary raw materials, and other material assets that the organization intends to sell or otherwise use | Previously, the requirement was not formulated. The estimated value of such assets, as well as material assets remaining unused when making capital investments, is determined based on their fair value, net realizable value, and the cost of similar assets. It cannot be higher than the amount of costs from which the cost is subtracted; |
| The cost of capital investments does not include costs incurred due to improper organization of the capital investment process (excessive consumption of raw materials, materials, energy, labor, losses from downtime, defects, violations of labor and technological discipline) | Previously, they were subject to inclusion, as a rule, in capital investments |
Tax accounting
The initial cost of assets formed through capital investments does not include VAT and other refundable taxes of a similar nature.
Expenses attributed to depreciable property are not included in the calculation of income tax (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 270-5), including the gratuitous transfer of capital investments (ibid., clause 16). Similarly, if there is an unfinished construction project that is subject to liquidation, the costs of this project are not taken into account in the income tax base (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 265).
When selling capital investments in the form of property (this should clearly follow from the sales agreement), its value is taken into account in the tax base. NU rules are set out in Art. 268 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The cost of fixed assets is written off according to the rules of Art. 258, 259, 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Including amounts in capex
FSBU 26/2020 changed the procedure for determining the amounts included in the cost of capital investments.
| WHAT CHANGED | EXPLANATION |
| When making capital investments on the terms of deferred (installment) payment for a period exceeding 12 months or a shorter period established by the organization, the capital investments include the amount of money that would have been paid by the organization in the absence of the specified deferment (installment plan) | Previously – amounts actually paid to the supplier under the contract |
| When making capital investments under contracts that provide for the fulfillment of obligations (payment) in whole or in part by non-monetary means, the actual costs (in terms of payment by non-monetary means) are considered to be the fair value of the transferred property, property rights, works, services | Previously – the value of the assets transferred or subject to transfer. Fair value is determined in the manner prescribed by IFRS 13 “Fair value measurement” (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated December 28, 2015 No. 217n). |
| The actual costs of property that an organization receives free of charge are considered to be the fair value of this property | Previously - based on the current market value as of the date of acceptance for accounting |
How to draw up a balance sheet - 2021 for the Federal Tax Service: rules and techniques
The first type of audit allows you to assess what documents are available at the construction site and whether they comply with technical requirements and standards. This type of audit is carried out by technical specialists. Together with them, at this stage, workers of economic services assess the correctness of the application of estimated prices and the cost of equipment included in the estimates. To fill out line 1140, from the debit balance of account 08 subaccount “Tangible exploration assets,” subtract the credit balance of account 02 subaccount “Depreciation and impairment of tangible exploration assets.”
Analytical accounting of equipment for installation at developer organizations is carried out by storage locations of equipment and its individual names (types, brands, etc.).
The variety of capital investments requires their correct grouping. Let's look at some grouping characteristics used in planning and accounting.
The composition of equipment, tools and inventory includes equipment that requires installation and equipment, tools, inventory that does not require installation.
Instruction of the State Tax Service of Russia dated August 10, 1995 N 37 “On the procedure for calculating and paying income tax for enterprises and organizations to the budget” (with subsequent amendments and additions).
Today, enterprises and other organizations (with the exception of credit institutions) use the new accounting system. balance, approved The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, in particular, by Order No. 66n dated July 2, 2010. It is called form No. 1, and according to OKUD 0710001. The composition of long-term liabilities can be fairly accurately traced along the balance sheet lines. Section No. IV is intended for them, which is called “Long-term obligations”.
A commercial organization has the right, no more than once a year (at the beginning of the reporting year), to revaluate fixed assets at replacement cost by indexation or direct recalculation at documented market prices with the attribution of any resulting differences to the organization’s additional capital.
Simplified methods of accounting for capital investments
Organizations that, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, have the right to use simplified accounting methods, can determine actual costs when recognizing capital investments:
- excluding certain types of costs (subclauses “b” - “z” of paragraph 10 of FSBU 26/2020), incl. the amount of the estimated liability for future dismantling, disposal of this facility and restoration of the environment, as well as the costs incurred in connection with the use of workers’ labor. Costs not taken into account are recognized as expenses of the period in which they were incurred;
- in the amount of amounts paid and/or payable by the organization to the supplier (seller, contractor) when making capital investments without taking into account all discounts, deductions, bonuses, benefits provided to the organization, regardless of the form of their provision, as well as without discounting in case of deferment (installment plan) ) payment for a period exceeding 12 months;
- in the amount of the book value of the transferred assets - when making capital investments under agreements that provide for payment in kind.
In addition, these entities may elect not to test capital investments for impairment. That is, evaluate them at their book value as of the reporting date and disclose information about them in the financial statements to a limited extent.