The state seeks to support small and medium-sized businesses. Such support is most often expressed in the form of subsidies - gratuitous payments from the budget or special fund as equity financing of business costs. If the conditions are met and the subsidy is allocated, it is necessary not only to distribute and spend it correctly, but also to adequately reflect it in the accounting documentation.
Let's talk about how to account for the funds received as part of the subsidy and calculate taxes on them.
What are the rules for providing subsidies to small and medium-sized businesses ?
Receiving subsidies due to coronavirus in accounting
Accounting methodologists argue about how to correctly account for receiving a subsidy. Experts are unanimous in one thing: receiving a subsidy is a specific fact of economic life, therefore the accounts used daily in accounting are not suitable for reflecting it. What is suitable?
Account 86 “Targeted financing”
The logic is this: account 86 is intended to reflect information on the movement of funds received from other sources, including the budget, and intended to finance targeted activities. The purpose of the subsidies is partial compensation of salary costs in the period April-May 2021. Therefore, the receipt of funds must be reflected in credit 86 of account, in the context of the corresponding subaccount.
Account 98 “Deferred income”
The arguments in favor of using this account are as follows: according to the Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n), credit 98 of the account should reflect the amounts of budget funds allocated to a commercial company to finance expenses. Please note that in the same Instructions there is a recommendation that account 98 on the loan corresponds to account 86.
Thus, from a formal point of view, the following block of transactions when receiving a subsidy would be ideal:
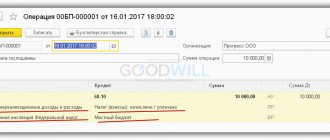
- Dt 86 Kt 98 – reflects the right to receive a subsidy (accrual);
- Dt 51 Kt 86 – the subsidy is credited to the bank account (receipt).
The question remains about the need for unnecessary running of the same amount across accounts. After all, to simplify the records, count 98 can simply be excluded. Then the subsidy is reflected as follows:
Dt 51 – Kt 86
Further, the compensated expenses incurred can be written off through the debit of account 86 .
Accounting
For accounting purposes, government assistance is divided into funds related to financing:
- capital expenditures for the acquisition (creation) of non-current assets (for example, fixed assets);
- current expenses.
In the first case, the provision of state assistance may be accompanied by additional conditions, such as:
- restricting the acquisition of certain types of assets;
- specific location of the acquired assets;
- established time frames for the acquisition and ownership of assets.
Financing of current expenses includes all other types of government assistance other than the acquisition (creation) of non-current assets. At the same time, for accounting purposes, funds (economic benefits) received within the framework of:
- state regulation of prices and tariffs;
- application of appropriate rules of profit taxation (for example, provision of tax benefits, deferment or installment plans for the payment of taxes and fees, investment tax credits);
- received budget investments (in particular, state participation in the formation of the authorized capital of an organization, for example, unitary).
State assistance can be provided to an organization in the form of:
- Money;
- other property (for example, fixed assets, materials).
This is stated in paragraphs 3 and 4 of PBU 13/2000.
Situation: how to determine in accounting the value of property (for example, fixed assets, materials) provided to an organization as a property within the framework of government assistance?
Property received on a reimbursable basis should be recorded at the cost specified in the contract. Accept the property received free of charge for accounting at market value.
If an organization receives property on a reimbursable basis (that is, on preferential terms, for example, as part of property support for small and medium-sized businesses), then, as a general rule, its value will be indicated in the contract for the provision of state assistance. Register the property at this value (clause 7 of PBU 6/01, clause 5 of PBU 5/01).
If property is provided free of charge, then to determine its value, use the rules established in paragraph 6 of PBU 13/2000. It states that the value of the property received (excluding cash) is determined based on the price at which, in comparable circumstances, the entity would normally charge the same or similar assets.
Thus, if an organization receives property free of charge, it has the right to use the general procedure provided for determining the value of assets received free of charge (clause 10.3 of PBU 9/99). For more information about this, see How to reflect the receipt of materials in accounting.
When reflecting state aid (except for budget loans) in accounting, three groups of transactions arise:
- receipt of government assistance;
- use of government assistance;
- return of state aid.
Budget loans granted to organizations should be reflected in accounting in the manner prescribed for accounting for borrowed funds (clause 16 of PBU 13/2000). An exception to this rule is the case when an organization receives such loans on a non-repayable basis. Then reflect the receipt of funds in accounting in accordance with the general procedure provided for state assistance (clause 17 of PBU 13/2000).
Reflection of other forms of government assistance in accounting depends on what property the organization receives and under what conditions. So, for example, if, as part of property support from the state, an organization receives equipment, then the procedure for reflecting its receipt in accounting will correspond to the procedure provided for fixed assets acquired through state assistance.
The organization must disclose information about funds received from the budget in its financial statements (balance sheet). The procedure for disclosing such information is prescribed in section IV of PBU 13/2000. Commercial organizations must reflect data on the nature of the use of targeted funds in the Report on the targeted use of funds and Explanations to the Balance Sheet and the Statement of Financial Results. For more information about the composition of financial statements, see What documents to submit as part of financial statements.
Spending subsidy funds in accounting
When reflecting the expenditure of government subsidies, it should be taken into account that in most cases the amount received will not fully . Part of the funds will be paid for through subsidies, and part at our own expense. This must be reflected in the wiring.
Let's look at the situation using examples:
EXAMPLE 1
The company uses the funds received to pay salaries. The amount of the subsidy received for 10 employees is 121,300 rubles, the accrued salary is 300,000 rubles.
When preparing accounting records you need to consider:
To simplify the example, we will assume that the company is exempt from paying insurance premiums for the period of payment of this salary.
The postings will be like this:
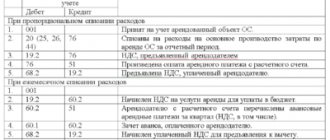
- Dt 44 Kt 70 300 000;
- Dt 70 Kt 68 39 000 – personal income tax withheld;
- Dt 70 Kt 51 – 121,300 – part of the salary was paid through a subsidy;
- Dt 70 Kt 51 – 139,700 – part of the salary was paid from own funds;
- Dt 86 Kt 44 – 121 300 reflects the use of the subsidy.
EXAMPLE 2
The company uses the subsidy to pay off part of the rental costs. Rent amount per paid month – 120,000 rubles. (including VAT – 20,000 rubles). The amount of subsidy received for 5 employees is 60,650 rubles.
When spending the subsidy on something other than a salary, certain conditions must also be met:
In accounting, the payment of part of the rent at the expense of the subsidy should be reflected as follows:
- Dt 26 Kt 60 – 100,000 – rent accrued;
- Dt 19 Kt 60 – 20,000 – input VAT on rent;
- Dt 60 Kt 51 – 60 650 – part of the rent was paid through a subsidy;
- Dt 60 Kt 51 – 39,350 – the balance of the rent was paid from our own funds;
- Dt 86 Kt 26 – 60 650 – reflects the use of the subsidy;
- Dt 68 Kt 19 – 20,000 – input VAT is accepted for deduction.
State aid
State assistance can be provided in the form of:
- subsidies;
- budget loans;
- other forms of government assistance. For example, this is property support for small and medium-sized businesses. When the state provides organizations with property (equipment, materials) on a reimbursable, gratuitous basis or on preferential terms (Part 1 of Article 18 of the Law of July 24, 2007 No. 209-FZ).
Situation: does the property (including funds) that the organization received as part of targeted programs from state extra-budgetary funds qualify as state aid?
Yes, it does.
Funds from state extra-budgetary funds are an integral part of the budget system of the Russian Federation (Article 10 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, funds received to finance targeted activities from an extra-budgetary fund (for example, from the Employment Fund) are classified as state aid. This position is also confirmed by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letter dated January 3, 2002 No. 04-02-05/1/223.
Nuances of tax accounting for subsidies
As can be seen from the examples given, tax requirements to exclude subsidies from expenses that reduce the tax base for the OSN and simplified tax system are regulated by the correct preparation of accounting entries.
In Example 1 this is: Dt 86 Kt 44 – 121,300.
In Example 2: Dt 86 Kt 26 – 60,650.
In both cases, the use of the subsidy reflected in accounting reduces what will then be used to calculate the tax base for profit or the income-expenditure simplified tax system.
When received, the subsidy itself is not included in the taxable base:
- for legal entities on OSN (subclause 60, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- for individual entrepreneurs and organizations on the simplified tax system (subclause 1, clause 1, article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- for individual entrepreneurs on OSN (subclause 82 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Therefore, when transferring budget funds to the account, no entries need .
Target purpose of subsidies
A subsidy is a government subsidy. It is designed to help a legal entity or individual entrepreneur solve one of the financial issues:
- cover part of the business expenses;
- reimburse part of past losses;
- compensate for part of the lost profits.
The state provides subsidies in 2 main ways:
- Pricing regulation - with this money, the authorities help entrepreneurs somewhat compensate for the costs that have increased due to the rise in prices of raw materials, fuel, energy, etc.
- Socio-economic programs - in order to promote economic growth and development, the state subsidizes production and enterprises that are significant from a social point of view.
REFERENCE! State-owned enterprises, as well as commercial and non-profit organizations can count on subsidies from the state.
Depending on the purpose, the subsidy is reflected in accounting records in different ways: it is recorded in accounting and reflected in the tax base. In any case, they are required to be taken into account if two conditions are simultaneously met:
- funds allocated by the budget;
- the organization adheres to the requirements put forward by the state for subsidies.
Reflection in accounting of receipt of subsidies by a commercial organization for reimbursement or financing of expenses depends on the method of their recognition adopted in the accounting policy of the organization: - as the organization becomes confident in receiving these funds; - as budget funds are actually received. How is the receipt of subsidies for reimbursement or financing of expenses reflected? View answer
Accounting for subsidies under the simplified tax system
Among individual entrepreneurs, the simplified tax regime is most popular. The simplified tax system allows you to significantly reduce the tax burden and simplify the filing procedure and volume of reporting. The simplified tax regime gives the entrepreneur the opportunity to control all his payments independently. Subsidies can be taken into account under the simplified tax system if amounts already spent are taken into account. This is stated in Chapter 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Subsidies are also taxed on the basis of Article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However there are exceptions:
- when assistance is provided to a small/medium business, the amount received is recorded in profit and taken into account in proportion to the costs incurred from it. When accounting for money, it makes no difference which taxation method is used under the simplified tax system - “income” or “income minus expenses”;
- the subsidy is given to promote employment. Money is allocated to the unemployed to start their own business and create new workers. Accounting is carried out in the same way as in the previous version. Only the subsidy is taken into account in the first case in two, and in the second in three tax periods.
Employment assistance is given to a start-up entrepreneur who was previously unemployed. The organization cannot receive it. If a person has lost his job and decided to start a business, the state will support him by providing targeted financial assistance for business development.
Wage subsidy - amount and conditions
The procedure for providing subsidies from the federal budget to SMEs affected by coronavirus was approved by Government Decree No. 576 dated April 24, 2020. The amount of the subsidy is tied to:
- the federal minimum wage as of January 1, 2021 (RUB 12,130);
- the number of employees recorded in the SZV-M report for March 2020.
For individual entrepreneurs with employees, one more unit (the individual entrepreneur itself) is added to the number of employees for March. Affected individual entrepreneurs without employees will receive a subsidy equal to one minimum wage (RUB 12,130).
The money can be spent on paying wages for April and May 2021, as well as on other production needs.
When can a preferential rate be applied?
Let us recall that income from the sale of agricultural products is subject to a profit tax rate of 0 percent (clause 1.3 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).