Cash flow statement form 4, what kind of report is this, who submits it? We offer you a sample of filling out Form 4 of the financial statements for 2014. How to fill out report form 4? The cash flow statement relevant when filling out the financial statements for 2014 can be found below. This form was approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n (as amended on December 4, 2012).
In the usual sense, financial statements represent information about losses, profits, and show the state of the enterprise at a certain point in time (as a rule, this concerns the end of the reporting period).
Form 4 is prepared by commercial organizations. Only companies involved in lending, insurance and budgetary organizations are excluded from this list. The financial statements of these organizations have their own differences and are governed by separate accounting rules.
Based on the cash flow report form, then Form 4 must be submitted to the tax office with the signature of the head of the enterprise and the chief accountant. And, accordingly, they bear responsibility for the provision, failure to provide, or untimely provision of reports.
Enterprises considered small businesses may not submit the described reports. The financial statements of small businesses can be downloaded here (balance sheet and income statement).
Reports are submitted no later than 3 months after the end of the period. Delivery occurs once a year.
As a general rule, if the time allotted for submitting reports ends on a weekend or holiday, the submission time is extended until the first working day following them.
For violation of reporting rules, an accountant or the head of an enterprise is punished with a fine.
Along with Form 4, you also need to submit a completed balance sheet (Form 1), which can be downloaded in this article, and a statement of financial results (Form 2, former profit and loss statement), Form 2 can be downloaded here. It is also necessary to fill out a statement of changes in capital (Form 3). and a completed sample of Form 3 can be found here.
What is Form 4 financial statements
Concept and purpose
A sample of the “Cash Flow” form is provided in accordance with Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. The form must be filled out according to the results of the current year, it must be submitted in the general package of accounting reports.
What is Form 4 of financial statements, see this video:
Regulatory regulation
Filling out the form in accordance with the standards prescribed in Article 66n allows you not only to submit it on time, but also to avoid mistakes and, accordingly, fines. The main regulatory document that regulates and standardizes the rules for preparing Form 4 of financial statements is Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 66n “On Forms of Financial Statements.”
This order is intended to determine the standards for the data that must be present in the report of Form 4. The order of the Ministry is quite often amenable to changes and adjustments, many of the subtleties of the law on accounting forms become more accurate and perfect.
Also, the order of the Ministry of Finance determines the forms of accounting statements that must be submitted by objects and subjects of entrepreneurial activity (including a balance sheet, reports on financial results, capital, intended use of funds and an explanatory note to them). The list of documents and deadlines for submission are also determined by the clauses of the legislative act. The details, codes, and columns that must be displayed on the form are all determined by statute.
Who rents and where?
Form 4 of financial statements must be completed by all legal entities. The exceptions are:
- small and micro enterprises;
- insurance companies, as well as credit organizations;
- budgetary enterprises.
All enterprises that are not on this list are required to regularly submit Form 4 and thereby provide the state with an accurate report on all financial transactions.
Form 4 of the financial statements should be filled out in 2 copies. The first must be signed by the director of the enterprise (this copy is submitted to the Federal Tax Service and the Statistical Service).
It should be remembered that when submitting the form to the federal tax service, you should use the branch in which the company is registered. The document is similarly submitted to the statistical service at the place of registration.
Form 4 must be submitted no later than March 31 of the following year. For example, a report for 2021 must be submitted by March 31, 2021.
Who will have to submit a cash flow statement (CFT)
As mentioned above, the DDS report form is included in the annual financial statements. However, a number of taxpayers have the right not to submit this form. Such advantages are available to persons who have the right to submit simplified reporting (Part 4, Article 6 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ of December 6, 2011).
If persons exempt from submitting a DDS report decide that information about cash flows needs to be disclosed and shown to the Federal Tax Service, they should fill out this report.
Fill out and send reports to the Federal Tax Service on time and without errors with Kontur.Extern. 3 months of service are free for you!
Try it
How to fill out a report
The accounting regulations, which were drawn up back in 2011, fully describe all the principles and rules according to which Form 4 of the financial statements must be filled out.
- It should be remembered that all negative indicators (the meaning of numbers is negative) that are included in the report must be reflected in parentheses and without the minus sign.
- If indicators must be deducted to recalculate taxes, then the same should be done with them.
The units of measurement used in the Form 1 report are thousands or millions of rubles. Thus, if the indicator is 130 thousand rubles, then you do not need to write 130,000 in the column, you should write just 130, and in the name of the column it should be noted that all numbers are given with the dimension “thousand”. R".
The cash flow statement is described in detail in this video:
Compound
Form 4 of the financial statements contains the following information regarding the movement of finances:
- Current activity;
- investment activities;
- financial activities.
Each variety is divided into the following sections:
- financial flows from current operations;
- financial flows from investment activities;
- financial operations.
Cash flows should be understood as all payments of the enterprise, as well as financial receipts. Receipts of property that has material value (material equivalent) are also taken into account as cash flow.
It should be remembered that there are income that do not significantly affect the total amount of funds. These do not need to be taken into account in Form 4. It is very important for an accountant to be able to separate “important” indicators from “unimportant” ones.
Stitches
In order to describe in detail the principles of filling, we will indicate what should be contained in each specific line.
- Line "4310". Total receipts are displayed here. The value of this line can be obtained by summing 4311-4319.
- Line "4311". The amount of all loans that the company received from banks should be indicated here. The amount is indicated without interest.
- Line "4312" and "4313". Here you should write the contribution that was made by the owner of the enterprise.
- Line "4320". The total payment amount is indicated here. The essence of line 4320 is the sum “4321” - “4329”.
- Line "4321". This displays the total number of all loans that the company managed to repay.
- Line "4322". This displays the amount of dividends that the company paid to the founders of the company.
- Line "4300". This line requires you to indicate the balance of financial flows from operations. Subtracting the line “4320” from “4310”, we get “4300”.
- Line "4400". The balance of the entire financial flow is taken into account here. The content of the line is the sum of “4100”+”4200″+”4300″.
- Line "4450". In this line you must indicate the balance of money at the beginning of the next reporting year. This value must also be written in the explanations to Form 4 of the financial statements.
- Line "4500". The balance of all finance and material equivalents at the end of the year is indicated here. This indicator is easily calculated: “line 4400” + “line 4450” + “line 4490”.
- Line "4490". The difference that arises when recalculating the financial flow and the balance of funds is displayed here. If there are more negative numbers than positive ones, then the contents of the line “4490” should be written in parentheses.
General rules
The following rules for submitting financial statements are legally approved:
- The reporting period for which documentation must be submitted is one year. Form 4 should be submitted to the Federal Tax Service no later than three months after the end of the reporting period.
- If the time allotted for submitting reporting documents ends with a holiday or weekend, then this time is extended until the next working day.
- For violation of the rules established by law, the director and chief accountant of the enterprise are punished with a fine.
Form 4 is the name of only one of the documents. In addition to this, the following are also available:
- Form 1 (completed balance sheet);
- Form 2 (financial performance statement, formerly known as the profit and loss statement);
- Form 3 (statement of changes in capital).
How to find out the form code using OKUD
In order to use codes correctly in your work, you need to know all their designations. And the statistics agency will help with this. When the business activity of any company or individual entrepreneur begins, codes are assigned by default. They also include OKUD codes.
If the employee knows the organization’s TIN, then you can use the following methods:
- Compose a request and send it to the statistics agency. It must be geographically tied to the enterprise for which the request is being made.
- Use the help of intermediaries. There are special law firms that can find out all the codes on their own for a small fee.
- Go to the State Statistics website ( www.gks.ru ) and find all the data you are interested in on your own.
The first two methods require a lot of time. If you use online resources, you can easily get information much faster.
Financial results reports
General report on income and expenses
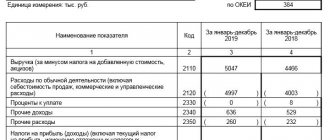
This is perhaps the leader among management reports in terms of frequency of use. Many financiers produce a standard report on income and expenses, most often in Excel.
Its approximate form is presented in Table 1.
Table 1 . Sample form of income and expense report (fragment)
| Items of income and expenses | January | February | March |
| INCOME | |||
| Revenue from operating activities | |||
| Other income | |||
| EXPENSES | |||
| Production cost | |||
| Raw materials | |||
| Payroll | |||
| Social contributions | |||
| other expenses | |||
| Depreciation | |||
| GROSS PROFIT | |||
| % | |||
| Selling expenses | |||
| Payroll | |||
| Social contributions | |||
| other expenses | |||
| Depreciation | |||
| Administrative expenses | |||
| Payroll | |||
| Social contributions | |||
| other expenses | |||
| Depreciation | |||
| EBITDA | |||
| % | |||
| EBIT | |||
| % | |||
| other expenses | |||
| Percentage to be paid | |||
| Taxes | |||
| Net profit | |||
| % |
From useful additional information on it, I can add that it can be generated not only manually in Excel, but also directly from 1C, using the analysts of the “Items of Income and Expenses” program and the “Financial Result and Controlling” panel. You just need to set up a directory of income and expense items, organize the entry of primary information in accordance with this directory, and as a result you will receive an always up-to-date, automated report without additional effort on counting and collating data.
Reports on cost structure
This group of reports is already more interesting, since, having a wide product portfolio, the financier and top manager must understand what happens at the stage of formation of the cost of each product produced, for which products the margin is higher, for which it is lower and why.
To do this, the minimum that must be observed when entering primary documentation is dividing it into products, and when setting up closure, distributing common cost items (rent, depreciation, wages, etc.) in proportion to the selected distribution base. In general, management accounting will not bring anything new to bookkeeping. The mechanism for forming the cost per unit of production is carried out in a similar way; the whole question is in the detailing of the unit of production. For example, if an enterprise produces toys, then one toy is already a unit of production and accounting is kept for it. But if an enterprise operates under contract agreements, then records must be kept for each of the contracts and additional agreements, and, for example, not for one contract as a whole. Then you can easily track the cost and analyze the marginality of the products produced.
The form of the cost report can be any convenient for a specific industry, for example, such as in Table 2.
Table 2 . Cost report form (fragment)
| Items of income and expenses | Product 1 | Product 2 | Product 3 |
| INCOME | |||
| Revenue from operating activities | |||
| EXPENSES | |||
| Raw materials | |||
| Raw materials 1 | |||
| Raw materials 2 | |||
| Raw materials 3 | |||
| Raw materials 4 | |||
| Payroll | |||
| Cover part | |||
| Premium part | |||
| Social contributions | |||
| Rent | |||
| other expenses | |||
| … | |||
| … | |||
| … | |||
| Depreciation | |||
| GROSS PROFIT | |||
| % |
Just like a report on income and expenses, reports on the cost structure can be generated from 1C. The easiest to set up is the “Gross Profit” report, a standard report in many 1C software solutions. By detailing it by expense item, you will receive an effective cost analysis tool, which also allows you to “fall through” into the depths of expenses, detailing them down to the Registrar Document.
Reports on individual expense sections
Such reports are used less frequently, so we will pay less attention to them. However, many use one of them, the payroll report, only based on the distribution of employees among regulated departments: production, sales, accounting, and so on.
It is much more interesting and informative to look at the payroll report based on management units (or CFD), especially comparing it with revenue for a particular CFD, for example, such as in Table 3.
Table 3 . Payroll report for the Central Federal District
| Items of income and expenses | Cover part | Premium part | Social contributions | FOR REFERENCE Revenue |
| CFO PROJECT 1 | XXXX | XXXX | XXXX | XXXX |
| Cover part | ||||
| Premium part | ||||
| Social contributions | ||||
| CFO PROJECT 2 | XXXX | XXXX | XXXX | XXXX |
| Cover part | ||||
| Premium part | ||||
| Social contributions | ||||
| CFO PROJECT 3 | XXXX | XXXX | XXXX | XXXX |
| Cover part | ||||
| Premium part | ||||
| Social contributions | ||||
| TOTAL PRODUCTION | XXXX | XXXX | XXXX | XXXX |
| Cover part | ||||
| Premium part | ||||
| Social contributions |
Budget of income and expenses
The Budget of Income and Expenses is responsible for planning in most enterprises. It is usually approved for a year, but can be compiled for other periods of time. The form of the budget of income and expenses corresponds to the report on income and expenses with two goals: firstly, there is no need to re-enter items of income and expenses, and secondly, it is convenient that plan-fact analysis can be done automatically, pulling the fact up to the previously entered plan . Budgeting is not a standard 1C function, but today many solutions have been implemented to help automate this process.
An approximate form of plan-actual analysis for the budget is presented in Table 4.
Table 4 . Budget plan-fact analysis form
| Items of income and expenses | January plan | January fact | Abs deviations | Deviations rel. |
| INCOME | ||||
| Revenue from operating activities | ||||
| Other income | ||||
| EXPENSES | ||||
| Production cost | ||||
| Raw materials | ||||
| Payroll | ||||
| Social contributions | ||||
| other expenses | ||||
| Depreciation | ||||
| GROSS PROFIT | ||||
| % | ||||
| Selling expenses | ||||
| Payroll | ||||
| Social contributions | ||||
| other expenses | ||||
| Depreciation | ||||
| Administrative expenses | ||||
| Payroll | ||||
| Social contributions | ||||
| other expenses | ||||
| Depreciation | ||||
| EBITDA | ||||
| % | ||||
| EBIT | ||||
| % | ||||
| other expenses | ||||
| Percentage to be paid | ||||
| Taxes | ||||
| Net profit | ||||
| % |
However, a once agreed upon budget is no longer relevant after a month, since the business environment is constantly changing, new contracts with customers, new suppliers and other inputs appear. Therefore, in addition to the budget for income and expenses, it is customary to maintain a Rolling forecast, which updates planned information when new actual data appears. Its form is no different from the budget - but the semantic load is different. The budget can be defended in front of the owners and tried to be fulfilled, and the rolling forecast shows what the result of the enterprise strives for in the reporting period.
It is advisable to do all reports on income and expenses with a monthly period. More often it makes no sense because the financial period is not closed, less often there is no way to influence the situation promptly.
Balance reports
Managerial balance
Its structure may differ from the regulated balance, or it may correspond to it. The purpose of the management balance sheet is to provide a breakdown of the items sufficient to analyze the current situation based on the numbers.
Working capital reports
This is a large group of reports related to current assets. All of them are divided into reports reflecting accounts receivable (more often represented by a report on debt terms), work in progress (represented by a report on orders), inventories of raw materials and finished products (report on balances of raw materials in the warehouse, report on balances of goods in the warehouse).
The overall goal of reporting current assets (working capital) is to maintain the level of current assets at the lowest possible level.
Consider, for example, the Aging debtors report. You will find its form in Table 5. The report helps you understand which part of the receivables is within the payment terms and which is already overdue, and take timely actions to collect the debt. Debt by debt maturity is also one of the standard reports that can be generated in 1C without setting up anything (the “Sales” panel). It is better to use it weekly.
Table 5 . Accounts receivable report by debt maturity (fragment)
| Customer | Debt amount | Not expired | Overdue | from 1 to 10 days |
| Customer 1 | ||||
| Customer 2 | ||||
| Customer 3 | ||||
| Customer 4 | ||||
| Customer 5 | ||||
| Customer 6 | ||||
| Customer 7 | ||||
| Customer 8 | ||||
| Customer 9 | ||||
| Customer 10 | ||||
| … |
A work in progress report may look different depending on the industry in which the business operates. The main idea of generating this report is to reduce work in progress that is stuck at one or another stage of production by finding out where and why it is stuck. Tables 6 and 7 have 2 report forms. Both the possibility of formation in 1C and weekly use are applicable to it.
Table 6 . Report form for work in progress for customer orders (fragment)
| Buyer's order | Balance at start | Received | Written off | Remaining at the end |
| Customer order 1 | ||||
| Raw materials | ||||
| Contractor services | ||||
| Payroll | ||||
| other expenses | ||||
| Customer order 2 | ||||
| Raw materials | ||||
| Contractor services | ||||
| Payroll | ||||
| other expenses | ||||
| Customer order 3 | ||||
| Raw materials | ||||
| Contractor services | ||||
| Payroll | ||||
| other expenses | ||||
| Customer order 4 | ||||
| Raw materials | ||||
| Contractor services | ||||
| Payroll | ||||
| other expenses | ||||
| Buyer order 5 | ||||
| Raw materials | ||||
| Contractor services | ||||
| Payroll | ||||
| other expenses | ||||
| … |
Table 7 . Work in progress report (fragment)
| Balance at start | Total received | |||
| Arrival of goods and materials from the warehouse | Arrival of goods and materials from other workshops | Other income | ||
| Workshop 1 | ||||
| Inventory 1 | ||||
| PC | ||||
| rub | ||||
| Inventory 2 | ||||
| PC | ||||
| rub | ||||
| … | ||||
| Workshop 2 | ||||
| Workshop 3 | ||||
| … | ||||
Indispensable from the point of view of managing the operating cycle of an enterprise are a report on raw materials inventories and a report on GP inventories. This report is managed by the purchasing department and the sales department, respectively, and is used on a continuous basis. For a financial manager, reports have their value when it is necessary to calculate the turnover of current assets or asset items.
The report form is presented in Table 8. The report is 100% identical to the balance sheet for accounts 10, 43 and 41 with the only difference being that it shows the minimum balance for each inventory item. You can set up automatic control of minimum balances in many 1C configurations in the “Purchases” panel. Thus, if the balance of raw materials or finished products in the warehouse decreases below the specified level, a signal will be issued to the manager and an order will be generated for the supplier.
Table 8 . Inventory report
| Raw materials | Balance at start | Total received | Total written off | Remaining at the end | Minimum balance |
| Inventory 1 | |||||
| PC | |||||
| rub | |||||
| Inventory 2 | |||||
| PC | |||||
| rub | |||||
| … |
Reports on non-current assets
They are used by capital-intensive industries or enterprises with a large share of intangible assets that are not taken into account in RAS. In their form they are indistinguishable from the statement of fixed assets, so we will not present them in the article.
We will also omit the three remaining types of reports:
- statement of financial assets and liabilities due to the narrow applicability and wide variation of reporting forms,
- report on other obligations due to its similarity with the report on debt terms,
- budget on balance due to the similarity of the form of the budget to the form of the management balance sheet and the similarity of the process of formation and plan-fact analysis of the budget of income and expenses.
Detailed list of indicators
| OKUD 0200000 | 2 | Unified system of organizational and administrative documentation |
| OKUD 0211000 | 0 | Documentation on the creation of an organization or enterprise |
| OKUD 0212000 | 4 | Documentation on the reorganization of an organization or enterprise |
| OKUD 0213000 | 8 | Documentation on liquidation of an organization or enterprise |
| OKUD 0214000 | 1 | Documentation on the privatization of state and municipal organizations and enterprises |
| OKUD 0251000 | 1 | Documentation on administrative activities of an organization, enterprise |
| OKUD 0252000 | 5 | Documentation on organizational and normative regulation of the activities of an organization or enterprise |
| OKUD 0253000 | 9 | Documentation on operational information regulation of the activities of an organization or enterprise |
| OKUD 0281000 | 0 | Hiring documentation |
| OKUD 0281000 | 3 | Documentation for transfer to another job |
| OKUD 0283000 | 7 | Documentation for dismissal from work |
| OKUD 0284000 | 0 | Vacation registration documentation |
| OKUD 0285000 | 4 | Documentation for registration of incentives |
| OKUD 0286000 | 8 | Documentation for filing disciplinary sanctions |
| OKUD 0300000 | 1 | Unified system of primary accounting documentation |
| OKUD 0400000 | 8 | Unified system of banking documentation |
| OKUD 0500000 | 9 | Unified system of accounting, financial, accounting and reporting documentation of the public sector of management |
| OKUD 0600000 | 1 | Unified system of reporting and statistical documentation |
| OKUD 0700000 | Unified system of reporting and accounting documentation for enterprises | |
| OKUD 0800000 | 5 | Unified labor documentation system |
| OKUD 0900000 | 7 | Unified system of documents for the pension fund of the Russian Federation |
| OKUD 1000000 | 1 | Unified system of foreign trade documentation |
| OKUD 403203 | 7 | Information on identifying incidents related to violation of information security requirements when making money transfers |
Examples of the OKUD form
- Code "0200000" . This code has 13 more subclasses. They regulate information, regulatory and other activities of enterprises. Using these codes in the documents, you can understand what information is contained: the liquidation of the enterprise, the process of privatization, or reorganization. In addition, these OKUD codes help classify document flow associated with hiring, dismissal of people, transfers, calculation of bonuses, and vacation registration.
- If an employee sees the code “0300000” , then it means that we are talking about systematizing primary information. It has 11 subclasses. And they relate more to the accounting department of the enterprise: payroll, labor control, cash reporting, control of material and technical base, inventory, report on repair work.
- When using the code “0400000” we can say that the documentation belongs to the banking sector. He has 8 more codes.
- The code “0500000” is all budget documents.
- Codes with the numbers “0600000” control all reports and statistical documents.
- Business entities use the code "0700000" .
- When classifying labor relations, the code “0800000” .
- Document flow on pension securities is regulated by codes “0900000” .
- Foreign trade activities are codes “1000000” . She has 7 more additional codes. Their task is to regulate documents on foreign trade transactions.
General characteristics of management reporting
The purpose of management reports is different from accounting reports. Accounting (regulated) - primarily serve the interests of external users of information:
- maternal campaigns
- potential investors,
- Federal Tax Service,
- state and non-state services and funds,
- analysts and market researchers.
Internal users: top management, management board or owner are not interested in regulated reporting, since it is compiled late, without proper detail and does not reflect the conclusions that the owner should draw for himself after reading it.
Management reports serve the purposes of internal users - they always contain up-to-date information on the necessary areas of accounting and in the necessary detail.
Characteristics of management reports:
- Informative – they contain all the information necessary for analysis and management decisions.
- Conciseness - they contain only useful information presented in the most concise form.
- Timeliness – the report reflects the current situation and/or a forecast of the development of the situation for several financial periods in advance.
- Detailability - each interesting figure in the report can be disclosed in clear, informative and concise analytics.
- Relevance - the amount of effort spent on generating a management report should be less than the effect of creating this report.