The balance sheet, since it is the main type of accounting reporting, carries a meaning dedicated to the financial condition of the business entity. At the same time, a beginner may find its structure incomprehensible and confusing, because in addition to complex page numbering, one also has to deal with the concept of codes, which sometimes becomes a whole problem. This article is devoted to decoding the lines of the balance sheet.
The balance sheet (form according to OKUD 0710001) can be found here.
A simplified form of the Balance sheet is available at the Link.
Financial reporting forms
There are 4 forms of financial (accounting) reporting :
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
- Balance sheet (it groups the assets and liabilities of the organization).
- Financial results report (the report presents data on the organization's income).
- Report on changes in capital (the report provides information on the movement of authorized, reserve and additional capital).
- Cash Flow Statement (the report displays information about cash flows).
The most used in the practice of financial analysis are the first two forms: Balance Sheet and Statement of Financial Results
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
Let's get acquainted with the balance sheet items for 2017–2018: their codes and explanations
Everyone who has ever held a balance sheet in their hands, much less drawn it up, paid attention to the “Code” column.
Thanks to this column, statistical authorities are able to systematize the information contained in the balance sheets of all companies. Therefore, it is necessary to indicate codes in the balance sheet only when this report is submitted to state statistics bodies and other executive authorities (Article 18 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, clause 5 of the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n). If the balance is not annual and is needed only by owners or other users, it is not necessary to indicate the codes. In the balance sheet, line codes from 2014 must correspond to the codes specified in Appendix 4 to Order No. 66n. At the same time, outdated codes from the expired order No. 67n with the same name, dated July 22, 2003, are no longer applied.
It is not difficult to distinguish previously used codes from modern ones - by the number of digits: modern codes are 4-digit (for example, lines 1230, 1170 of the balance sheet), while outdated ones contained only 3 digits (for example, 700, 140).
For information on what the form of the current balance sheet with line codes looks like, read the article “Filling out Form 1 of the balance sheet (sample).”
Where can I find financial reporting forms for business?
By law, all enterprises that issue shares must disclose their information (in accordance with the requirements of paragraph 1.7. “Regulations on the disclosure of information by issuers of equity securities”, approved by Order of the Federal Service for Financial Markets of the Russian Federation dated October 4, 2011 No. 11-46 /pz-n). All financial statements of joint stock companies can now be viewed.
Public reporting means that it is publicly available to all users. For example, on enterprise websites you can see the “Information Disclosure” section and there, as a rule, there is a “Shareholders and Investors” tab. It will contain the financial results of the year or financial reports by quarter.
The figure below, on the website of JSC Tupolev, shows the financial statements of the enterprise for 2013. There are 4 forms of financial reporting. An audit report is a fact of verification by an independent body of financial statements. There's no point in watching it for us. We also don’t really need explanations for the balance sheet to carry out financial analysis.
Forms of financial (accounting) statements of JSC Tupolev on the company website
Balance sheet: line 1150
In the balance sheet form approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n, line 1150 is called “Fixed assets.”
As the name suggests, line 1150 as of the reporting date reflects the amount of the organization’s fixed assets. But here it is necessary to take into account several features.
Firstly, line 1150 does not take into account all fixed assets, but only those reflected in account 01 “Fixed assets” (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). Let us recall that fixed assets that are intended exclusively for provision by an organization for a fee for temporary possession or use for the purpose of generating income are accounted for in account 03 “Income-generating investments in material assets” (clause 5 of PBU 6/01, Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). And they are reflected in the balance sheet on line 1160 “Profitable investments in material assets” (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n).
Secondly, fixed assets in the balance sheet, like all other indicators, are reflected in a net valuation (clause 35 of PBU 4/99). In relation to fixed assets, this means that they are shown on line 1150 at their residual value.
As for accounting accounts, to fill out line 1150 you need to subtract from the debit balance of account 01 the credit balance of account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” for the same reporting date. Naturally, depreciation needs to be deducted only that which relates to fixed assets accounted for in account 01. After all, for profitable investments in material assets accounted for in account 03, depreciation is also accrued for account 02. And since the debit balance of account 03 is not included in line 1150 , then the depreciation related to them should also be excluded from the balance of account 02.
We talked about deciphering all the lines of the balance sheet in this material. You can see an example of filling out a balance sheet using conventional digital data.
Who needs business financial reporting forms? Types of financial statements
Let's take a look: who needs data from the financial reporting forms of an enterprise? As a rule, these are investors and shareholders . They use a company's financial statements to assess the return on investment of their investments. The table below presents all users of the enterprise's financial statements.
| Financial Statement User | Purpose of financial statement analysis |
| Investors and shareholders | Assessing the profitability of your investment in the enterprise |
| FTS (Federal Tax Service) | Assessment of an enterprise for its taxability |
| Counterparties | Assessing the partner’s financial condition |
| Banks | Enterprise assessment for issuing a loan |
| Arbitration court | To assess the fact of bankruptcy of an enterprise |
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
Old and new balance: similarities and differences
The procedure for filling out payment orders in the new year will remain the same; changes affected budget classification codes. Officials added new BCCs:
- Income tax. A new BCC has been introduced for income received from bonds issued by Russian organizations during the period 01/01/2017–12/31/2021 (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 06/09/2017 No. 87n).
- Excise taxes. New budget classification codes for electronic cigarettes, heating tobacco and nicotine-containing liquids have been added (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 06/06/2017 No. 84n).
- Resort fee. New KBK for paying resort fees to the budget. Now the payment should be transferred using 000 1 1500 140 (“Fees for the use of resort infrastructure (resort fee)”), where the first three digits (zeros) are the revenue administrator. The administrator of the resort fee has not yet been determined.
Read more about the new accounting standards in the article “New Accounting Standards: Changes in 2018.”
- Changes in accounting policies (standards, adjustments to the chart of accounts and tax legislation).
We talked about what needs to be reflected in the accounting policies for 2021 in the article “Accounting policies: how to draw up according to new requirements.”
- The reporting procedure has been updated.
When preparing financial statements, organizations no longer have to reflect changes in accounting policies for future periods. Such standards are established in clause 14 of Order No. 69n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2017.
- The simplified form of accounting is retained.
Some organizations have the right to maintain simplified accounting. This right continues in 2021. Read more in the article “Submitting reporting using a simplified scheme.”
Previously, the line code consisted of three digits. At the moment, only those codes that are specified in a special appendix to Order 66 of the Ministry of Finance are being considered. This is app #4 which sets up four digit codes for use.
The encoding of the old form differs from the new one only in that the list of these lines changes, their encoding turns into a four-digit indicator, and the detail of the information provided in the balance sheet changes slightly. The row assignments remain the same.
Transformation of the old form of financial reporting into a new one (after 2011)
After 2011, new forms of financial reporting appeared. It is often necessary to convert old forms of financial (accounting) reporting to new ones. Below is a table of translation (Forms No. 1 and Forms No. 2 into the new forms “Balance Sheet” and “Financial Results”). The old lines (designated by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n) are matched with new lines (designated by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 67n).
| Indicator name | Old codes (before 2011) | New codes (after 2011) |
| Intangible assets | 110 | 1110 |
| Fixed assets | 120 | 1130 |
| Construction in progress | 130 | |
| Profitable investments in material assets | 135 | 1140 |
| Long-term financial investments | 140 | 1150 |
| Deferred tax assets | 145 | 1160 |
| Other noncurrent assets | 150 | 1170 |
| FIXED ASSETS | 190 | 1100 |
| Reserves | 210 | 1210 |
| VAT on purchased assets | 220 | 1220 |
| Accounts receivable (more than a year) | 230 | |
| buyers and customers | 231 | |
| Accounts receivable (less than a year) | 240 | 1230 |
| buyers and customers | 241 | |
| Short-term financial investments | 250 | 1240 |
| Cash | 260 | 1250 |
| Other current assets | 270 | 1260 |
| CURRENT ASSETS | 290 | 1200 |
| ASSETS total | 300 | 1600 |
| Authorized capital | 410 | 1310 |
| Extra capital | 420 | 1350+1340 |
| Reserve capital | 430 | 1360 |
| reserves formed in accordance with legislation | 431 | |
| reserves formed in accordance with the establishment. documents | 432 | |
| Retained earnings (uncovered loss) | 470 | 1370 |
| CAPITAL AND RESERVES | 490 | 1300 |
| Loans and credits (long-term) | 510 | 1410 |
| Other long-term liabilities | 520 | 1450 |
| LONG TERM DUTIES | 590 | 1400 |
| Loans and credits (short-term) | 610 | 1510 |
| Accounts payable | 620 | 1520 |
| debt to the government off-budget funds | 625 | |
| Debt to participants (founders) for payment of income | 630 | |
| revenue of the future periods | 640 | 1530 |
| Reserves for upcoming expenses and payments | 650 | 1540+1430 |
| Other current liabilities | 660 | 1550 |
| SHORT-TERM LIABILITIES | 690 | 1500 |
| LIABILITIES total | 700 | 1700 |
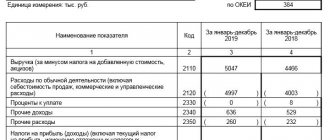
| Sales proceeds (excluding VAT, excise taxes...) | 010 | 2110 |
| Cost of goods, products, works, services sold | 020 | 2120 |
| Gross profit | 029 | 2100 |
| Business expenses | 030 | 2210 |
| Administrative expenses | 040 | 2220 |
| Profit (loss) from sale | 050 | 2200 |
| Interest receivable | 060 | 2320 |
| Percentage to be paid | 070 | 2330 |
| Income from participation in other organizations | 080 | 2310 |
| Other income | 090 | 2340 |
| Other operating expenses | 100 | 2350 |
| Profit (loss) before tax | 140 | 2300 |
| Current income tax | 150 | 2410 |
| Net profit | 190 | 2400 |
Updated format strings and codes
It should be noted that the asset has a specialized format based on the liquidity factor of the property that the organization has. The least liquid of it will be located at the very top of the column, since it is this property that remains almost unchanged from the beginning of the organization until its liquidation.
The asset lines in the new balance sheet are: 1100, 1150-1260, 1600.
A liability tends to reflect where the company gets money for its operation. And also what part of these funds is the property of the company, and what part is borrowed and requires repayment. This part of the balance sheet plays an important role, since when compared with the asset, one can accurately say whether the company has the funds to successfully continue its activities, or whether the time will soon come to “wind up shop.”
The lines reflecting the passive part of the balance are: 1300, 1360-70, 1410-20, 1500-1550, 1700.