Selling goods
Sales of goods are reflected in the debit of account 90 of the sub-account “Cost” (90.02.1) and the Credit of account 41, the sub-accounts of which are determined by the type of trade (wholesale/retail, etc.):
- Revenue from the sale of goods is reflected in the Credit account 90 subaccount “Revenue” in correspondence with account 62.01.
Sales of goods can be carried out through an intermediary. Then it is necessary to make entries Debit 45 Credit 41 “Goods in warehouses”. As inventory items are sold, business entries are made to the debit of account 90 “Cost” and the credit of account 45. When exporting goods, the same entries are made.
In the main taxation system, it is necessary to pay VAT on sales. The tax is reflected by posting Debit 90.03 VAT Credit 68.02.
In retail trade, goods are sold at selling price. The markup is made on account 42. When selling at the end of the month, you need to make reversing entries:
- Debit 90 “Cost” Credit 42.
Sale of finished products or change of ownership
Finished products are considered to be products that represent the final result of the production cycle, are fully processed, completed, have passed the necessary tests, meet standards or technical parameters, have been shipped to customers or delivered to a warehouse.
Sales of finished products can be carried out:
- Based on the conclusion of a supply agreement.
- Through our own sales divisions (shops, kiosks).
The date of transfer of ownership of manufactured products is the date of their transfer to the buyer. When transferring finished products, accompanying documentation is drawn up - invoices and delivery notes, acceptance certificates, which confirm the change of ownership.
Postings for the sale of goods in wholesale trade
Payment for goods can usually be made by prepayment or upon shipment of the goods.
By prepayment
Example:
The organization, after receiving an advance payment from the buyer, shipped goods in the amount of 99,500 rubles. (VAT RUB 15,178).
Postings:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 62.02 | Received money for the goods from the buyer | 99 500 | Bank statement | |
| 76.AB | 68.02 | Issuing an invoice for advance payment | 15 178 | Ref. invoice |
| 62.01 | 90.01.1 | Revenue from the sale of finished products or goods is taken into account | 99 500 | Packing list |
| 90.03 | 68.02 | VAT is charged on sales | 15 178 | Packing list |
| 90.02.1 | 41.01 | Sold goods written off | 64 000 | Packing list |
| 62.02 | 62.01 | Advance credited | 99 500 | Packing list |
| An invoice for sales has been issued | 99 500 | Invoice | ||
| 68.02 | 76.AB | Deduction of advance VAT | 15178 | Invoice |
By shipment
Example:
The organization shipped goods worth RUB 32,000 to the buyer. (VAT 4881 rub.). Payment was received after delivery.
Postings:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 62.01 | 90.01.1 | Revenue from sales of goods is reflected | 32 000 | Packing list |
| 90.03 | 68.02 | VAT is charged on sales | 4881 | Packing list |
| 90.02.1 | 41.01 | Sold goods written off | 385 | Packing list |
| An invoice for sales has been issued | 32 000 | Invoice | ||
| 62.01 | Payment received from buyer | 32 000 | Bank statement |
Account 90: features of sales accounting
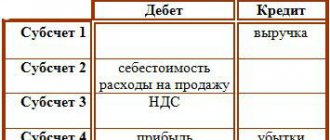
This accounting account generates all the information on sales carried out by the company, and since the sale of goods is a multi-stage process and is split into income and expenses, several functional sub-accounts are opened for it:
- 90/1 “Revenue”;
- 90/2 “Cost of sales”;
- 90/3 “VAT”;
- 90/4 “Excise duties”;
- 90/9 “Profit/loss from sales”.
Depending on the industry and specifics of production, other sub-accounts may be opened. The account works like this: data on cost accounting subaccounts (90/1, 90/2, 90/3, etc.) are accumulated incrementally throughout the month. At the end of it, the credit turnover (90/1) is compared with the total value of the debit turnover (90/2, 90/3, etc.) and a total is displayed, reflected in the account. 90/9. Profit from sales is recorded by posting D/t 90/9 K/t 99.
According to the account 90 analytical accounting is carried out, which can be organized in many areas necessary for the company to effectively manage - by product range, types of services, regional divisions, etc.
Retail sales of goods
Example:
For the day, trading revenue in the store amounted to 12,335 rubles. Accounting is kept at sales prices, the organization is on the UTII taxation system, and the outlet is automated. The money was deposited at the company's cash desk on the same day.
Postings:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 50.01 | 90.01.2 | Receipt of proceeds from the sale of goods | 9000 | Cashier's report |
| 90.02.2 | 41.11 | Write-off of goods sold at sales price | 9000 | Cashier's report |
| Proceeds deposited at the cash register | 9000 | Receipt cash order | ||
| 90.02.2 | 42.01 | Calculation of markup on goods sold | -3700 | Help - calculation of markup write-off |
Accounting in the presence of special contract conditions
The right of ownership may remain with the seller even after the actual transfer of the product to the buyer until the occurrence of certain circumstances provided for by the relevant agreement of the parties to the transaction (Article 491 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In such situations, there is a discrepancy between the periods of product shipment and recognition of receipt of funds.
Therefore, if there is a special moment in the transaction (change in ownership), VAT will be charged at the time of shipment without taking into account the fact of receipt of payment. Revenue will be recognized only after receipt of additional payment from the buyer (Article 39, 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Deferment of VAT obligations from the time of shipment of the product until the receipt of payment for it is not permitted.
Due to the time difference between the date of shipment and the date of payment, the reflection of VAT on the sales invoice (Dt) to the tax settlement accounts (Kt) is incorrect. As an option, you can use an account for settlements with debtors and creditors:
- Debit account 76 / Credit account 68 – upon shipment.
- After the change of owner and recognition of payment (revenue) – Credit account. 76 / Debit account. 90 (sales).
But in this option, there is the formation (Dt account 76) of fictitious receivables. It would be more correct to use account 97 for VAT accounting for expenses expected in future periods.
If there is a special point in the agreement between the parties to the transaction regarding the change of the holder of ownership of the product, the shipped goods (from accounts 41 (goods) or 43 (finished products)) cannot immediately be taken into account in the debit of the sales account (90). Until the owner changes, the product is listed on account 45, intended for accounting for shipped products. Accounting is carried out not at the sales price, but at the cost used for accounting on the account. 41(43).
Postings for sales or provision of services
When selling services, the same accounts are involved, only instead of 41 accounts there are 20 accounts, which collect all the costs that make up the cost.
Example:
The organization performed services in the amount of 217,325 rubles. The cost of the service was 50,000 rubles.
Postings for the provision of services:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 62.01 | 90.01.1 | Revenue received from the sale of services | 217 325 | Certificate of completion |
| 62.01 | Receipt of payment to the bank account | 217 325 | Bank statement | |
| 90 | Cost of services provided | 50 000 | Accounting information |
Basic rules for creating transactions when selling products
The procedure for generating transactions for the sale of finished products depends on two circumstances:
- The first operation was shipping;
- The first transaction was payment.
The first option entails the occurrence of receivables from the manufacturer, since the moment of payment for the product occurs later than its actual shipment.
The second option demonstrates the occurrence of accounts payable on the part of the manufacturer, since the shipment is carried out much later than the payment made.
Please note that the procedure for writing off finished products depends on the chosen method:
- at actual cost;
- at planned (standard) cost.
How the implementation is adjusted
If the terms of the contract for the supply of industrial and industrial components have been changed or the accounting department has discovered a previously made error, then the accounting of sales operations can be changed in accordance with the legally established regulations. The parties can send the accompanying documentation necessary for the adjustment by e-mail (mail), and then hand over the original documents in person.
Postings for adjusting the implementation downward:
- reversal Dt 62 Kt 90.1 - decrease in revenue;
- reversal Dt 90.3 Kt 68 - deduction for the amount of the required difference;
- reversal Dt 20 Kt 60 - reduction of the buyer’s debt;
- reversal Dt 19 Kt 60 - VAT on the amount of the difference;
- Dt 19 Kt 68 - restoration of value added tax.
Methods of revenue recognition in accounting
There are two methods for recording revenue in accounting:
- Accrual method - is a generally accepted method, revenue is recorded as shipment;
- Cash method - revenue with this method is taken into account when payment is received.
The accrual method is used by all organizations to account for all revenue, with the exception of revenue under contracts with a special right to transfer ownership.
By the way, small businesses are given the right to choose; they can use both the accrual method and the cash method. This possibility is provided for in clause 20 of the Standard Accounting Recommendations. But when using the cash accrual method, the following requirement must be taken into account: expenses are recognized only after the debt is repaid.
The chosen method of revenue recognition is necessarily recorded in the accounting policies of the organization. The cash method is more convenient to use only for those small businesses that do not have many business transactions. Since, under the cash method, a company recognizes expenses only after they have been paid, then with a large number of such expenses, it is very difficult to track which of them are reflected in accounting and which are not yet.
When the cash method is used, costs that are related to the sale of products should be reflected in account 20 “Main production”.
Return of shipped products
The purchaser, who discovers upon acceptance of receipt a discrepancy between the shipped products and the terms of the agreement, draws up a report on the identified discrepancies, issues a written claim to the seller, and an invoice with a return note. The second copy of the document is recorded by the consumer in the sales book, the seller enters the received invoice into the purchase book as the right to a tax deduction is formed (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-07-15/29, 03/07/2007).
If the return of the defective material occurred in one tax period, the seller makes adjustments to sales (account 90); if the return occurred in the next calendar year, then the cost of the returned object is included in the accounts of non-operating costs as a loss of the past period, which was determined in the reporting period. year (count 91):
- Debit account 91 / Credit account 62 (loss of the past period discovered in the reporting period);
- Debit account 43 / Credit account 91 (restoration of the cost of returned goods, previously written off);
- Debit account 68 / Credit account. 91 (profit of previous years calculated in the reporting year in the amount of VAT paid).
Defects identified before the end of production are accounted for in the main production: Debit account. 28 (manufacturing defect) / Credit account. 20, and defects detected upon completion of production - in finished products: Debit account. 28 / Credit account 43.
For your information! When returning goods, the seller has the right to deduct the VAT amount (Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). A deduction is allowed no later than 12 months from the date of return and in full after reflecting adjustment entries for the return (rejection) of the product.
The amount of VAT sent by the seller to the budget upon sale is deducted for the period in which there are adjustment entries due to returns. In this case, when sending a replacement to the buyer, the seller issues an invoice to him.
If the defect returned in the next tax period, then the profit tax base is subject to recalculation for the period when the goods were sold, or the costs of the cost of the returned product can be attributed to expenses in the form of damage from the defect (Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; letter from the Ministry of Finance RF No. 03-03-05/47, 04/29/2008).
If a defective product can be used in production, perform the following operations:
Therefore, damage from defects will be reduced by the price of a spoiled product suitable for use.
Accounting for services from the customer
Services are expenses of the customer enterprise and are most often included in expense accounts 20 (23, 25, 26, 44).
Let's continue the example
The accountant of Assorti LLC will make the following entries in the accounting:
- Dt 60 Kt 51 - 38,335 rub. - paid for advertising.
- Dt 44 Kt 60 — 32,487.29 rub. — advertising costs are taken into account.
- Dt 19 Kt 60 — 5,847.71 rub. — input VAT is taken into account.
However, some services may increase the cost of purchased goods or fixed assets (clause 6 of PBU 5/01, clause 8 of PBU /01), for example, transport or information services. In this case, they are reflected as follows:
- Dt 08 (10, 41) Kt 60 - the cost of fixed assets (inventory, goods and materials) has been increased by the amount of transport or other services to be included in the price.
For the procedure for forming the cost of fixed assets and inventory items, see the articles:
- “Fixed assets in accounting (nuances)”;
- «What entries reflect transportation costs?.
Do you want to know what risks a customer may have when concluding a contract for paid services? Sign up for a free trial access to the ConsultantPlus system and proceed to the Guide to Contractual Work.